This chicken adobo recipe is the kind of dinner that feels like it’s doing you a favor: rich, tangy, and deeply savory, yet built from pantry staples and one dependable method. Even when the day has been long, you can still end up with tender chicken in a glossy adobo sauce that tastes like it took far more effort than it did.
What makes Filipino chicken adobo so beloved is the balance. Vinegar keeps everything bright. Soy sauce brings depth and color. Garlic turns sweet and mellow as it simmers, while bay leaves and peppercorns give that unmistakable “adobo” perfume. Then, right at the end, the sauce is reduced until it clings—so each bite carries the full flavor instead of leaving it behind in the pot.
Just as importantly, once you learn the rhythm of this chicken adobo recipe—sear, simmer, reduce—you can adjust it without stress. You can make it saucier or drier, sweeter or sharper, with potato for a one-pot feel, or with coconut milk for a creamy finish. For now, though, we’ll start with a classic chicken adobo recipe that’s clear, measured, and reliable, with enough detail that you’ll cook it confidently the first time.
Also Read: Sweetened Condensed Milk Fudge: 10 Easy Recipes
Chicken Adobo Recipe Ingredients and Measurements (Adobo Sangkap)
A traditional adobo recipe can look slightly different from home to home, yet the core stays recognizable. Think of these ingredients as the backbone of an adobong manok recipe that tastes right whether you’re cooking for yourself or feeding a table.

Chicken adobo recipe ingredients list (for classic adobong manok)
Chicken
- 1.2 to 1.5 kg chicken, preferably bone-in thighs and drumsticks (skin-on optional)
For browning
- 1 tbsp neutral oil (canola, sunflower, rice bran)
For the adobo braise
- 10–12 cloves garlic, smashed (keep them chunky, not minced)
- 3 bay leaves
- 1 to 1½ tsp whole black peppercorns (or ¾ tsp coarsely cracked pepper)
- ½ cup (120 ml) soy sauce
- ⅓ cup (80 ml) vinegar (cane vinegar is classic; white vinegar works; coconut vinegar is lovely)
- ¾ to 1 cup (180–240 ml) water
Optional, depending on the style
- 1–2 tsp brown sugar (for sweet chicken adobo)
- 1 small onion, sliced (softens the sauce and adds gentle sweetness)
- 1 tbsp oyster sauce (extra depth; use carefully because it adds salt)
- 1-inch knob ginger (luya), sliced (clean warmth)
- 1–2 small chilies, whole (warmth without turning the whole pot fiery)
If you ever find yourself wondering why your soy sauce tastes saltier than expected—or why one bottle makes the sauce darker and another stays lighter—this MasalaMonk guide makes the basics easy to understand: Soy Sauce Saga: Are You Drizzling, Dipping, and Cooking Right?.
Choosing the chicken for this chicken adobo recipe
Bone-in thighs and drumsticks are the most forgiving cut for Filipino style adobo. They stay juicy, they tolerate simmering without drying out, and they contribute richness to the sauce as they cook. In contrast, chicken breast can work, though it needs gentler timing and a slightly different finish so it stays tender.

Wings are another great option if you love sticky, glossy adobo. Because they’re smaller, they cook faster, and they glaze beautifully when you reduce the sauce into an adobong manok na tuyo style finish.
Vinegar and soy sauce: how the balance actually works
Vinegar is the brightness. Soy sauce is the depth. Water is the buffer that prevents the dish from feeling aggressively salty or sharply sour before reduction brings everything together.
Cane vinegar is often used in classic Filipino chicken adobo because it’s bright yet not harsh. White vinegar works too—especially if you like a crisp tang—although you may want to start with the lower end of the water range (or add vinegar gradually near the end) so the sharpness doesn’t dominate early.

Coconut vinegar, if you have it, can taste softer and rounder. As a result, it pairs especially well when you plan to add coconut milk later.
Also Read: Sourdough Recipe: 10 Easy Bread Bakes (Loaves, Rolls & Bagels)
Chicken Adobo Recipe Step by Step (Procedure in Cooking Adobo)
This is the chicken adobo recipe step by step method you can follow without guessing. You’ll build flavor with browning, tenderness with simmering, and that glossy finish with reduction.
Step 1: Prep the chicken so it browns instead of steaming
Pat the chicken dry with paper towels. That small step changes everything: moisture on the surface turns into steam, and steam prevents browning. Meanwhile, check the pieces. If you’re working with large leg quarters, separate them into thighs and drumsticks so they cook evenly.

At this point, avoid salting heavily. Since soy sauce already brings salt, you’ll get a better final balance by waiting until the sauce has reduced before deciding if it needs anything.
Step 2: Optional short marinade (adobo marinade recipe, simplified)
Some cooks marinate, others skip it completely. For a practical middle path, you can do a short marinade that builds flavor without turning dinner into a project.

In a bowl, combine:
- 2 tbsp soy sauce
- 1 tbsp vinegar
- 3–4 smashed garlic cloves
Toss the chicken and let it sit for 15–30 minutes while you prepare everything else. Even so, if you skip this step, the dish still works—because the braise does the real seasoning.
Step 3: Brown the chicken (build the base, not the final color)
Heat 1 tablespoon oil in a wide, heavy pan over medium-high heat. Once the oil shimmers, place chicken pieces in a single layer. Don’t crowd the pan; otherwise, the chicken releases moisture and steams.

Let the chicken sit for a few minutes without moving it. When it’s ready, it will release easily and show golden patches. Turn and brown the other side briefly, then transfer to a plate.
You are not trying to cook it through here. Instead, you’re creating a flavor foundation that will melt into the adobo sauce later.
Step 4: Bloom the garlic, then add bay and peppercorn
Lower heat to medium. Add smashed garlic (and onion, if using). Stir for 30–60 seconds until fragrant.

Keep it gentle. Garlic should smell sweet and aromatic, not bitter. If it starts to brown too quickly, lower the heat and add a splash of water to calm the pan.
Next, add bay leaves and peppercorns. At this stage, the kitchen smell shifts into something instantly recognizable: warm bay, peppery lift, and garlic at the center.
Step 5: Build the braise (soy + vinegar + water)
Pour in the water first and scrape up the browned bits. Those little stuck-on pieces are concentrated flavor; they belong in the sauce, not on the pan.

Then add soy sauce and vinegar. Bring the pot to a lively simmer.
A classic habit in many kitchens is to let the vinegar simmer briefly before stirring aggressively. In practice, giving it 1–2 minutes at a simmer helps soften that raw sharpness so the final sauce tastes integrated rather than harsh.
Step 6: Simmer chicken adobo until tender
Return the chicken (and any juices on the plate) to the pot. Once it returns to a simmer, reduce heat to low, cover, and cook gently.

Use these times as a guide:
- Bone-in thighs and drumsticks: 25–35 minutes
- Wings: 18–25 minutes
- Chicken breast pieces: 12–18 minutes, then remove early

If you’re using chicken breast, don’t try to “force” tenderness by cooking longer. Instead, pull it when it’s just done, then finish reducing the sauce separately and return the chicken briefly to glaze.
If you prefer certainty, chicken is considered safely cooked at 165°F / 74°C. (Food Safety and Inspection Service)
Step 7: Reduce the sauce into glossy adobo sauce (classic or “tuyo”)
Once the chicken is tender, remove the lid. Raise heat to medium and simmer uncovered.
At first the liquid looks thin, almost broth-like. However, as it reduces, it becomes shiny and sauce-like. Turn the chicken once or twice so it glazes evenly, and stir occasionally so nothing sticks.

- For a classic saucy finish, reduce 8–12 minutes until the sauce coats the back of a spoon.
- For adobong manok na tuyo (drier finish), reduce longer—12–18 minutes—until the sauce clings tightly and looks lacquered.

If you want sweet chicken adobo, stir in 1–2 teaspoons brown sugar during the final few minutes of reduction. Added late, it melts into the sauce and tastes rounded; added early, it can taste flat.
Step 8: Rest before serving (it really helps)
Turn off the heat and rest the chicken in the pan for about 5 minutes. During that pause, the sauce settles into its final texture, and the chicken reabsorbs juices.

Serve hot with rice and spoon the sauce over everything.
If you want rice that behaves perfectly under a bold sauce—fluffy, not gummy—this MasalaMonk guide makes the timings easy whether you’re using stovetop, a rice cooker, or Instant Pot: How to Cook Perfect Rice (Stovetop, Cooker, Instant Pot).
Also Read: Kahlua Drinks: 10 Easy Cocktail Recipes (Milk, Vodka, Coffee)
Chicken Adobo Recipe Flavor Balance (So It Tastes “Right” Every Time)
Even a perfect method can land slightly differently depending on vinegar strength, soy sauce saltiness, chicken size, and how hard you reduce the sauce. Fortunately, this chicken adobo recipe is easy to steer back on track—especially if you make adjustments at the right moment.

If the adobo tastes too sour
Before changing ingredients, reduce the sauce a little longer. Often the dish tastes overly sharp simply because there’s still too much water in the pot.
If, after reduction, it still tastes too tangy, you have a few gentle options:
- Add a small pinch of brown sugar and simmer 1–2 minutes.
- Add a splash of water, then simmer uncovered again to re-balance.
- Add a spoonful of chicken fat (skin-on pieces help naturally) to soften the edges.
The goal isn’t to erase vinegar. Rather, it’s to make the tang feel woven into the sauce.
If the adobo tastes too salty
Saltiness is usually a concentration issue. Add a splash of water, simmer uncovered, and taste again. That may feel backward at first, yet it works because you’re diluting salt while still keeping flavor from the aromatics and reduction.
Next time, use a slightly less salty soy sauce, or start with a bit less soy and add it gradually near the end. If you want to understand what kind of soy sauce you’re working with, the quick breakdown in Soy Sauce Saga can save you a lot of guesswork later.
If the sauce feels thin
Keep reducing. That’s the simplest fix, and it’s usually the correct one. Meanwhile, make sure your pan is wide enough that evaporation can happen at a steady pace.
If you want an even clingier finish, you can:
- Remove the chicken when tender
- Reduce the sauce more aggressively for a few minutes
- Return the chicken to glaze
That approach gives you maximum shine without overcooking the meat.
If the garlic tastes bitter
Bitterness usually comes from garlic browning too hard early on. Next time, lower heat after browning chicken, stir garlic briefly, then add liquid sooner so it doesn’t scorch.
Still, if you’re already mid-cook and the garlic tastes sharp, reduction and resting often mellow it. In addition, serving with rice and something creamy on the side can soften that perception.
If the chicken feels tough
Toughness can happen if the simmer is too hard (boiling can tighten protein), or if the chicken pieces are particularly mature. If you’re using native chicken, longer gentle simmering helps, and thighs/drumsticks are far more forgiving than breast.
Instead of turning the heat up, keep it at a lazy simmer and extend the cooking time. Once the chicken is tender, proceed with the reduction as usual so the sauce still turns glossy.
Also Read: 10 Vegan Chocolate Cake Recipes (Easy, Moist, & Dairy-Free)
Chicken Adobo Recipe Serving Ideas (What to Eat With Adobo)
Rice is the classic partner because it absorbs adobo sauce like it was built for it. That said, the dish becomes even more satisfying when you add contrast: something crisp, something creamy, or something spicy on the side.

The rice that makes adobo feel complete
For everyday bowls, plain white rice is perfect. For a weekend feel, you can cook jasmine or basmati and let the aroma do extra work. Either way, if you want clean, fluffy grains—especially if you’re cooking rice alongside the simmer—MasalaMonk’s rice guide keeps it simple across methods: How to Cook Perfect Rice.
A creamy side that loves tangy sauce
A potato salad might not be the first thing you think of, yet it works surprisingly well. The creaminess softens the vinegar edge, while the tang makes the potatoes taste brighter.
If you want options beyond one “standard” bowl, this guide gives you several directions: Potato Salad Recipe: Classic, Russian, German, Vegan & More.
Heat on the side, not in the whole pot
One of the nicest ways to serve adobo is letting everyone control their own heat. A bright, vinegar-based chili sauce makes each bite feel sharper and more alive without changing the entire pot.
If you enjoy exploring different chili styles—from thin hot pepper vinegar to chipotle-based sauces—this MasalaMonk guide is a fun rabbit hole: Pepper Sauce Recipe | Ultimate Guide: 30+ Hot & Chili Sauces.
Also Read: Cold Brew Espresso Martini: How to Make It (Step-by-Step Recipe)
Chicken Adobo Recipe Variations (Same Method, Different Mood)
Once you’ve cooked the classic once, variations become easy because the core doesn’t change. You still brown, braise, and reduce. After that, one ingredient or one timing shift can take the dish somewhere new.

Chicken adobo recipe: adobong manok na tuyo (dry-style)
If you love sticky chicken, this is the finish to aim for. Follow the classic method, then reduce longer until the sauce clings tightly and looks lacquered.
For an even more dramatic glaze, remove the chicken when it’s tender, reduce the sauce harder for a few minutes, then return the chicken and toss until it shines.
Chicken adobo recipe with potato (one-pot comfort)
Potatoes make the pot feel heartier and more generous, and they soak up sauce like sponges.
Add 2 medium potatoes, peeled and cut into chunks, right after you return chicken to simmer. Then simmer covered as usual until chicken is tender and potatoes are cooked through. Finally, reduce the sauce uncovered and let the potatoes glaze slightly at the edges.
Sweet chicken adobo (subtle, not sugary)
Sweet adobo chicken is best when it’s restrained. You’re aiming to round out the tang, not turn the dish into a sticky dessert.

Add 1–2 teaspoons brown sugar during the final reduction. That timing matters because it melts cleanly into the glossy sauce and tastes integrated.
Chicken adobo with pineapple (bright sweet-sour)
Pineapple brings a playful sweetness and a tropical edge that pairs beautifully with garlic and soy.
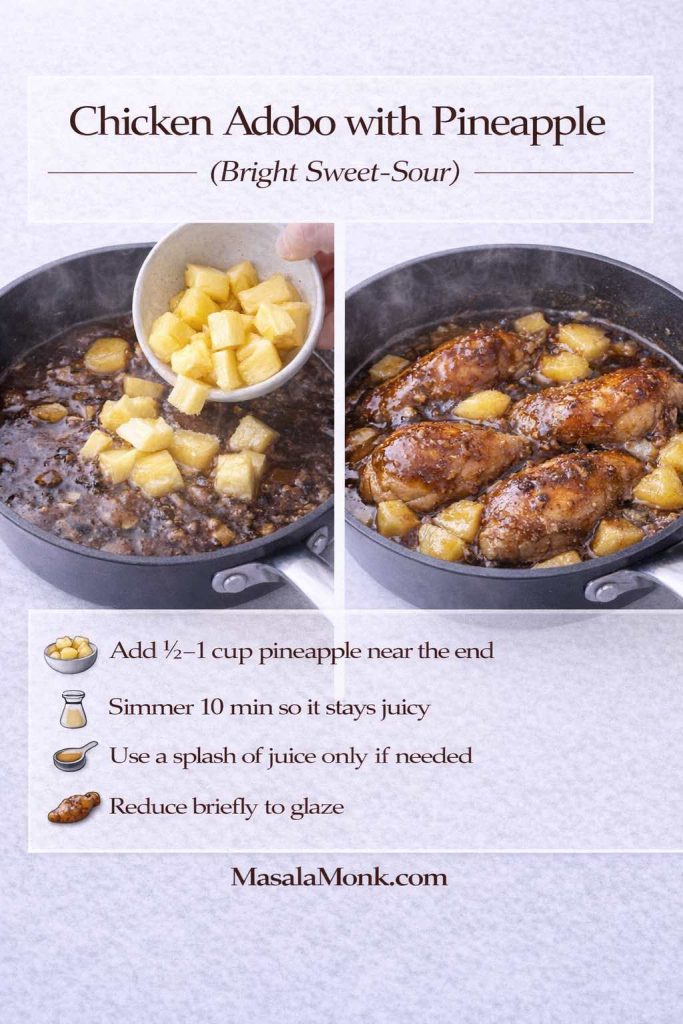
Add ½ to 1 cup pineapple chunks during the last 10 minutes of simmering, then reduce as usual. If you use canned pineapple, a small splash of juice can help, though too much can push the sauce toward syrupy, so go lightly.
Chicken adobo with oyster sauce (deeper umami)
This is a modern variation rather than a classic, yet it can be delicious when you want extra savory depth.

Stir in 1 tablespoon oyster sauce after adding soy, vinegar, and water. Because oyster sauce adds salt, consider starting with a little less soy sauce, then adjust near the end.
Adobo with luya (ginger)
Ginger makes the sauce feel cleaner and warmer without shouting “ginger.” It’s especially comforting on a cool day.

Add a 1-inch knob of sliced ginger with the garlic, then proceed as usual.
Adobong puti (white adobo)
White adobo skips soy sauce and leans into vinegar, garlic, bay, and pepper. It tastes brighter, sharper, and a bit more minimalist.

To adapt this chicken adobo recipe into adobong puti:
- Omit soy sauce
- Add salt gradually (start with 1 to 1½ teaspoons)
- Keep water closer to the higher end at first
- Reduce near the end for body
Because soy sauce isn’t there to deepen the sauce, reduction becomes even more important.
Chicken adobo sa gata (coconut milk adobo)
Coconut milk turns the dish creamy and luxurious while still keeping the adobo backbone.

Cook the chicken until tender using the classic steps. Then, once you remove the lid and begin reducing, stir in ¾ cup coconut milk. Simmer gently for 5–8 minutes. Avoid a hard boil because coconut milk can split if pushed.
If you ever want to make coconut milk yourself, this step-by-step guide is straightforward: How to Make Coconut Milk at Home.
Also Read: Peanut Butter Fudge: Recipes & Guide (8 Methods + Easy Variations)
Chicken Adobo Recipe Storage and Reheating (So Leftovers Stay Great)
One of the best things about chicken adobo is that it often tastes even better the next day. The sauce settles, the garlic mellows, and the whole pot feels more cohesive.
Still, leftovers deserve a little care.

Cool promptly and refrigerate within two hours
Food-safety guidance commonly emphasizes the “danger zone” and the two-hour window for refrigeration, especially for cooked meats. (Food Safety and Inspection Service)
A practical way to cool faster is to transfer adobo into shallower containers rather than leaving a deep pot on the counter. The sauce cools more quickly, and you’re not waiting on a dense mass of food to drop in temperature. (Food Safety and Inspection Service)
How long cooked chicken keeps
USDA guidance recommends using cooked chicken within three to four days when refrigerated (40°F / 4°C or lower). (Ask USDA)
If you want longer storage, freezing is an option. For best texture, freeze in portions with enough sauce to protect the meat from drying out when reheated.
Reheating chicken adobo the right way
Reheat until steaming hot, and if you like certainty, bring it back to 165°F / 74°C. (Food Safety and Inspection Service)
For texture, stovetop reheating is the gentlest:
- Add a small splash of water
- Warm over medium-low until hot
- Then simmer uncovered briefly so the sauce becomes glossy again
That last step matters because the sauce thickens in the fridge. A quick uncovered simmer wakes it up and restores its shine.
Also Read: Manhattan Cocktail Recipe (Classic + 6 Variations)
Make-Ahead and Next-Day Ideas (So One Pot Feeds You Well)
If you like cooking once and eating twice, this chicken adobo recipe is a natural fit. In fact, adobo is one of those dishes that doesn’t mind being made ahead; it often rewards you for it.
The simplest make-ahead plan
Cook the adobo fully, including the reduction. Cool and refrigerate. The next day, reheat gently and add a splash of water only if the sauce feels too thick. Then simmer uncovered briefly to re-gloss.

Crispy skin option (without changing the sauce)
If you used skin-on chicken and you miss that crispness after simmering, there’s an easy workaround:
- Remove cooked chicken pieces from the sauce
- Pat dry lightly
- Crisp under a broiler or in a hot pan for a minute or two
- Then spoon reduced sauce over the top
This way, you get crisp edges and glossy sauce together, rather than choosing one over the other.

Leftovers that feel like a new meal
Sometimes the best “variation” is simply serving the same pot differently.
- Adobo rice bowl: Chop leftover chicken, warm with a spoonful of sauce, pile over rice, and add fresh cucumber or herbs for contrast.
- Shredded adobo chicken: Pull meat from the bone, toss with sauce, and use it as a savory filling.

If you’re already in a chicken-for-the-week mindset, these internal recipes can keep things varied without leaving the comfort zone:
- Cheesy Chicken Broccoli Rice – Full Recipe and 4 Easy Ways
- Chicken Salad Sandwich Recipe: Classic + 10 Easy Variations
And if you end up with extra rice, turning it into something crisp and snacky the next day is a satisfying upgrade: How to Turn Leftover Rice into Gourmet Arancini Balls.
Also Read: Rob Roy Drink Recipe: Classic Scotch Cocktail (Perfect + Dry + Sweet Variations)
A Few Trusted References for Classic Filipino Chicken Adobo (If You Like Comparing Styles)
Every family has a “best adobo” version, and that’s part of the charm. Still, if you enjoy seeing how other well-tested recipes handle ratios and method choices, these are strong baselines:
- Chicken Adobo (Filipino-Style Braised Chicken) — Serious Eats.
- Filipino Chicken Adobo — The Kitchn.
- Filipino Chicken Adobo Recipe — Panlasang Pinoy.
For food-safety references on temperatures and cooling guidance:
- USDA FSIS Safe Minimum Internal Temperature Chart.
- USDA FSIS “Danger Zone” (40°F–140°F).
- Ask USDA: How long can you keep cooked chicken?.
Also Read: Sandwich for Breakfast: Breakfast Sandwich Recipe + 10 Variations
Closing: why this chicken adobo recipe keeps earning its place
A good chicken adobo recipe doesn’t need theatrics. It needs the right balance, a patient simmer, and a final reduction that turns the pot into something glossy and irresistible. Once you’ve cooked it this way, you’ll start to see how adaptable it is: classic and saucy one night, dry-style and sticky the next, then creamy coconut adobo when you want comfort.
Most of all, it stays true to what makes adobong manok special—bold flavor from simple ingredients, built with a method you can repeat whenever you want dinner to feel like it went exactly right.
Also Read: Classic Rum Punch + 9 Recipes (Pitcher & Party-Friendly)
FAQs
1) What is the best chicken adobo recipe for beginners?
If you’re new to adobo, start with a classic chicken adobo recipe using bone-in thighs and drumsticks. Because those cuts stay juicy during simmering, you get tender meat and a flavorful adobo sauce without needing perfect timing. In addition, the method is forgiving: sear for depth, simmer for tenderness, then reduce for a glossy finish.
2) What are the chicken adobo ingredients in a classic adobong manok?
A traditional ingredient list for adobong manok usually includes chicken, garlic, soy sauce, vinegar, bay leaves, and whole peppercorns. Meanwhile, water helps balance the sauce while it simmers. Optionally, you can add onion for softness or a small amount of sugar for a sweeter chicken adobo.
3) What is the vinegar and soy sauce ratio for Filipino chicken adobo?
A common starting point is more soy sauce than vinegar, often around 1/2 cup soy sauce to 1/3 cup vinegar, plus water to mellow the mixture early on. However, the ideal ratio depends on your vinegar strength and soy sauce saltiness. As a result, it’s smart to reduce the sauce at the end, then adjust only if needed.
4) Is marinating required for an authentic adobo recipe?
Not necessarily. Many authentic adobo recipes skip a long marinade and rely on simmering to season the chicken thoroughly. Still, a short 15–30 minute rest in soy, vinegar, and garlic can deepen flavor. Either way, the final sauce reduction is what makes the dish taste cohesive.
5) How do you cook chicken adobo step by step without overcooking it?
First, brown the chicken lightly for deeper flavor. Next, simmer gently until the meat is tender. Finally, reduce the sauce uncovered until it turns glossy and coats the chicken. For chicken breast, shorten the simmer time and finish the reduction after pulling the breast pieces, then return them briefly to glaze.
6) What is the correct procedure in cooking adobo if my sauce tastes too sour?
Before changing anything, let the sauce reduce longer; often, extra liquid makes vinegar seem louder than it really is. If it still tastes sharp afterward, add a splash of water and simmer again, or stir in a tiny amount of sugar to round the edges. Moreover, serving with rice naturally softens the tang.
7) How can I make low sodium adobo without losing flavor?
Use a low-sodium soy sauce, then build flavor with garlic, bay leaves, peppercorns, and a proper reduction. Additionally, browning the chicken first adds depth, so you won’t rely only on saltiness for taste. If needed, finish with a small squeeze of citrus or a pinch of sugar for balance rather than extra soy.
8) How long should you simmer chicken adobo for tender results?
For bone-in thighs and drumsticks, simmering often takes about 25–35 minutes at a gentle bubble. Meanwhile, wings can finish sooner, and chicken breast needs less time to avoid drying out. Instead of boiling hard, keep the heat low so the meat stays juicy and the sauce stays smooth.
9) Why is my chicken adobo tough even after simmering?
Usually, the heat is too high or the cut needs more time at a gentle simmer. Toughness can also happen with older or leaner chicken. Therefore, lower the heat, cover, and extend the simmer until a knife slides in easily. After that, reduce the sauce only once the chicken is tender.
10) How do you make adobong manok na tuyo (dry-style chicken adobo)?
Cook the chicken adobo recipe as usual, then reduce the sauce longer until it clings tightly and looks lacquered. For an even drier finish, remove the chicken when tender, reduce the sauce more aggressively, and return the chicken to coat. Consequently, you get a sticky glaze rather than a pool of sauce.
11) How do I make sweet chicken adobo without making it sugary?
Add only a small amount of sugar—often 1–2 teaspoons—during the final reduction so it melts into the sauce instead of tasting separate. Alternatively, a few pineapple chunks near the end can add sweetness with a brighter flavor. Either way, the goal is to round the tang, not overpower it.
12) Can I cook chicken adobo with potato in the same pot?
Yes. Add peeled potato chunks after returning the chicken to the braise, then simmer until both are tender. As the potatoes cook, they also slightly thicken the sauce. Later, reduce the liquid uncovered so the potatoes and chicken get coated in glossy adobo sauce.
13) What is adobo sa gata, and when do you add coconut milk?
Adobo sa gata is a creamy version of Filipino adobo made by adding coconut milk near the end. After the chicken is tender, stir in coconut milk and simmer gently for a few minutes. Importantly, avoid a hard boil, because coconut milk can split if cooked too aggressively.
14) What is adobong puti, and how is it different from classic adobo?
Adobong puti (white adobo) usually skips soy sauce, relying on vinegar, garlic, bay leaves, and peppercorns instead. Because it’s brighter and more vinegar-forward, careful simmering and reduction matter even more. As a result, it tastes clean, sharp, and aromatic—yet still unmistakably adobo.
15) What are the most common mistakes in a classic chicken adobo recipe?
Common issues include skipping browning (which can make the sauce taste flatter), boiling too hard (which can toughen the chicken), and reducing too early (before the chicken is tender). Also, adding too much vinegar or soy without tasting after reduction can throw off balance. Instead, simmer gently, reduce at the end, then adjust in small steps.
16) How do I know chicken adobo is fully cooked?
The chicken should be tender and the juices should run clear. Additionally, the safest check is temperature: the thickest part should reach 74°C / 165°F. Once that’s done, you can focus on reducing the sauce for texture and flavor.
17) Can I make chicken adobo ahead of time?
Definitely. In fact, chicken adobo often tastes better the next day because the flavors settle and the sauce thickens slightly. Reheat gently with a splash of water if the sauce is too thick, then simmer uncovered briefly to bring back the glossy finish.
18) How do you store and reheat leftover chicken adobo?
Cool leftovers promptly, then store in an airtight container in the fridge. When reheating, warm gently on the stovetop so the sauce doesn’t scorch. Finally, simmer uncovered for a minute or two to restore the glossy adobo sauce texture.
19) What is the best cut for Filipino chicken breast adobo?
If you prefer breast, use larger pieces and shorten the simmer time. Then finish reducing the sauce separately and return the breast briefly to coat. Consequently, you keep the chicken tender while still getting the full flavor of the sauce.
20) What does “adobo” mean in Filipino cooking?
In Filipino cooking, “adobo” generally refers to the method: braising in vinegar and salt (often soy sauce), along with garlic, bay leaves, and peppercorns. Because it’s both flavorful and practical, the technique has become one of the most iconic Filipino dishes—especially chicken adobo and pork adobo.