Ravioli has range. It can be quiet and cozy—just a few pasta pillows with a simple butter sauce—or it can feel like a restaurant plate with glossy sauce, a finishing drizzle, and that little moment where everyone at the table pauses after the first bite. The funny part is, you don’t need a culinary degree to make a ravioli recipe feel special. You need a plan: the right cooking method for the ravioli you have (fresh, frozen, or refrigerated), a sauce that actually clings, and a finishing move that makes the whole thing taste intentional.
This post is built for all of it. If you’re making ravioli from scratch, you’ll find a solid ravioli dough recipe and sealing tips that help prevent blowouts. If you’re leaning on store bought ravioli (which is honestly a smart move half the time), you’ll still get “best ravioli” results at home—because sauce choice and finishing technique matter more than people admit. Along the way, we’ll take the Italian classic and give it an Indian accent in the most natural way: nutty brown ghee instead of sage brown butter, malai-style mushroom cream sauce, curry leaf tempering over butter-garlic cream, and a tomato-cream sauce that feels unmistakably makhani without turning your ravioli into curry.
If you like this crossover energy, you’ll also enjoy our other Italian comfort-food remixes like Alfredo pasta reinvented with Indian-inspired twists and pesto pasta with delightful Indian twists. They’re built with the same mindset: keep the structure people love, then nudge the flavor in a new direction.
Even so, before we jump into fillings and sauces, it helps to start with one calming idea: ravioli doesn’t need perfection. Instead, it needs gentleness, timing, and a little confidence. Once you have those three, everything else becomes play.
Ravioli, but smarter: fresh vs frozen vs refrigerated
Any ravioli recipe can go wrong in predictable ways. Fresh ravioli tears because it’s delicate and overhandled. Frozen ravioli goes watery because it’s boiled too hard, then dumped onto a plate while the sauce waits somewhere else. Refrigerated ravioli turns bland because it’s treated like a generic pasta instead of a filled pasta that needs gentleness.

So let’s lock in the base.
If you ever want a deep, reassuring read on handmade ravioli technique—rolling thickness, shaping, sealing, all the little details that keep your ravioli from leaking—King Arthur’s guide is genuinely helpful: How to make ravioli at home. If you’re the kind of person who likes to understand why pasta behaves the way it does, Serious Eats has a classic step-by-step approach to fresh egg pasta: Fresh egg pasta technique.
How to cook fresh ravioli without bursting
Fresh ravioli cooks fast. That’s the entire point. Use a wide pot, salted water, and a gentle simmer. You want movement, not chaos. A rolling boil can smack ravioli into itself until seams pop.

A reliable rhythm looks like this:
- Bring water to a boil, then reduce to a lively simmer.
- Drop ravioli in gently.
- Stir once with a soft hand to prevent sticking.
- When ravioli floats, give it another 30–60 seconds.
- Lift out with a slotted spoon, not a colander.
The biggest upgrade: sauce goes into the pan first. Not on the plate. Not in a separate bowl. A thin layer of sauce in a skillet, ravioli lands into it, and then you spoon sauce over the top while it bubbles for a few seconds. That tiny finishing step helps the sauce cling and protects the ravioli from being torn apart by enthusiastic tossing.
Also, if you’re cooking very delicate handmade ravioli, consider cooking in batches. That way, the pot stays steady, the water temperature doesn’t crash, and you’re not stirring through a crowd of pasta pillows that want to be treated like glass.
How to cook frozen ravioli so it stays tender
Frozen ravioli wants steadiness. It can handle a bit more time, yet it hates being boiled aggressively. Keep the water at a steady simmer.
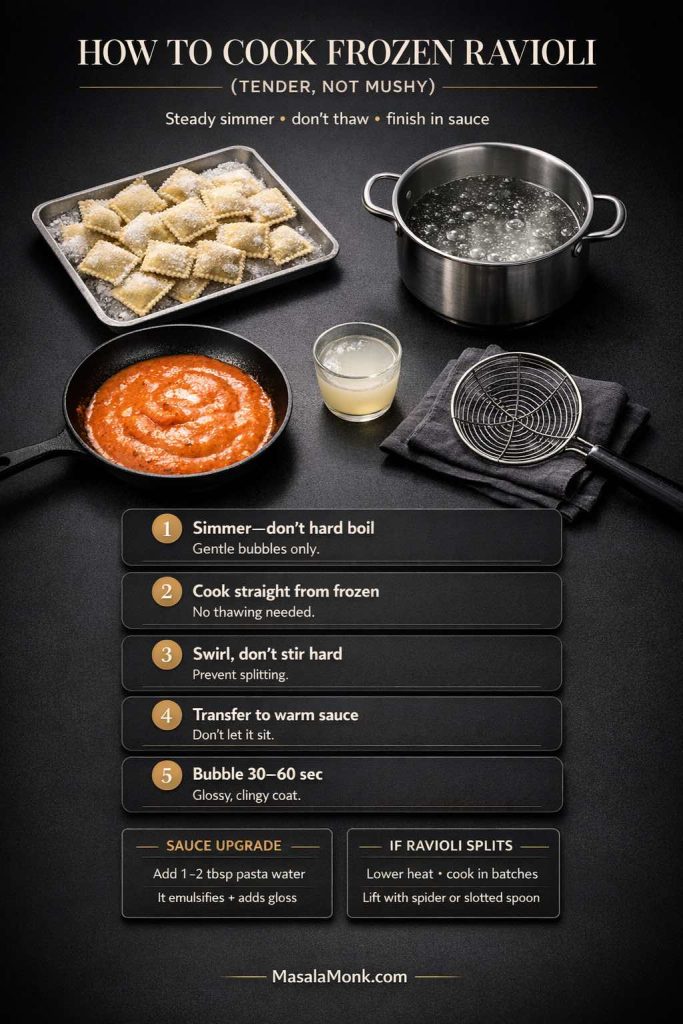
The next move is what separates “fine” from “wow”: transfer the cooked ravioli directly into a skillet of warm sauce and let it bubble together for 30–60 seconds. That little bit of pasta water that comes along for the ride is not a problem; it’s an emulsifier. It turns “pasta sauce for ravioli” into a glossy coat instead of a puddle.
If you’re trying to make a “best frozen ravioli” moment at home, don’t judge the ravioli alone. Judge the sauce-to-ravioli relationship. Most frozen ravioli becomes excellent when the sauce is thick enough to cling and you finish it in the pan.
Meanwhile, if your frozen ravioli tends to split, lower the heat slightly and avoid stirring with a spoon that has sharp edges. A gentle swirl of the pot is often enough; afterwards, use a slotted spoon to lift, not pour.
How to cook refrigerated ravioli (the weeknight hero)
Refrigerated ravioli is the sweet spot for most people. It’s faster than frozen and sturdier than handmade. Treat it like fresh ravioli with slightly more forgiveness.
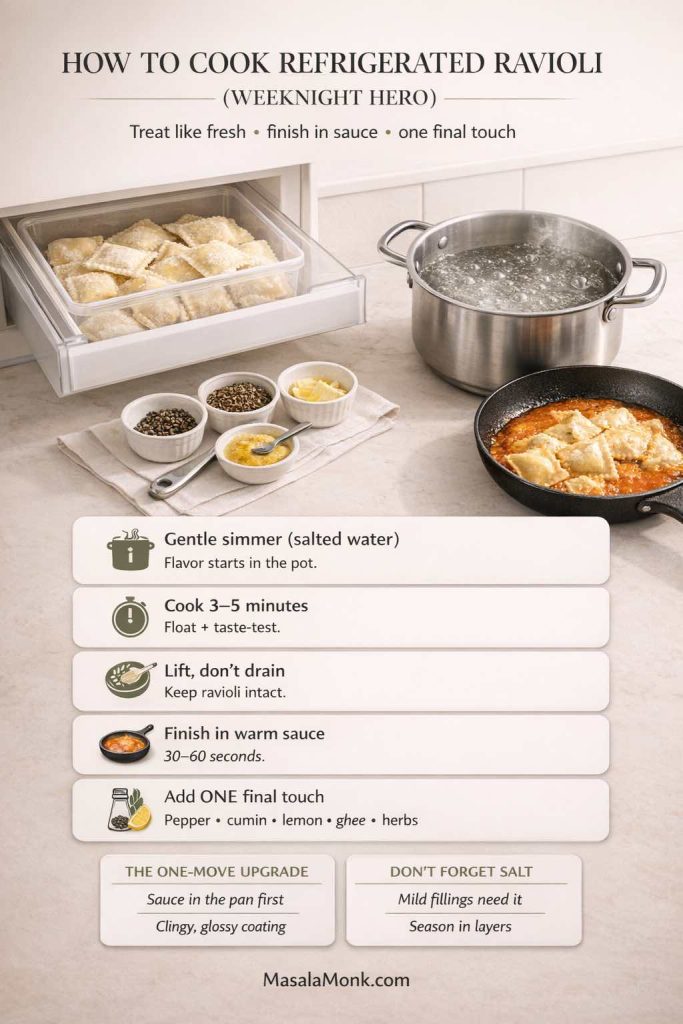
Here’s the trick that keeps refrigerated ravioli from tasting like “just a packet”: finish it in sauce and add one finishing element—cracked pepper, toasted cumin, a splash of lemon, a drizzle of spiced ghee, a handful of herbs. One move. Not ten.
When you do that, “store bought ravioli” stops being a compromise and starts being a strategy.
At the same time, don’t forget salt. A mild filling needs a properly salted cooking liquid, and a sauce needs seasoning in layers. If you salt only at the end, the ravioli can taste oddly flat even when the sauce looks perfect.
Also Read: Fish and Chips Reimagined: 5 Indian Twists (Recipe + Method)
The foundation: a ravioli dough recipe (plus wrappers and shortcuts)
Some nights call for the full project: flour on the counter, dough resting under a bowl, the whole experience. On other nights, you want ravioli for dinner without turning your kitchen into a workshop. Both are valid. The goal here is to give you options that still feel like real ravioli, whether you’re mixing dough or using ravioli wrappers.

Classic egg ravioli dough (by hand or mixer)
If you’ve been using a stand mixer or rolling by hand, the principles stay the same: hydration, kneading, resting, rolling thin, and sealing with care.
Ingredients
- 300 g flour (all-purpose works; 00 flour is lovely if you have it)
- 3 large eggs
- 1 egg yolk (for elasticity and richer color)
- 1/2 tsp fine salt
- 1 tsp olive oil (optional, helps handling)
- 1–2 tbsp water only if needed

Method
- Make a mound of flour, create a well, add eggs, yolk, salt, and oil.
- Whisk inside the well, slowly pulling flour inward until a shaggy dough forms.
- Knead 8–10 minutes until smooth and elastic.
- Wrap and rest 30–60 minutes.
That rest is not optional. It lets the flour hydrate and relaxes gluten so rolling is easier. After resting, roll thin—thinner than you think—and use minimal filling so the ravioli seals without strain.
If you want a technique-first explanation with visuals and rolling guidance, King Arthur’s ravioli resource is worth keeping bookmarked: How to make ravioli at home.
A quick rolling note: if you roll too thick, the ravioli tastes heavy and the seams don’t seal as cleanly. Conversely, if you roll too thin, it can tear. The sweet spot is thin enough to see a faint shadow of your hand through it, yet strong enough to lift without stretching.
Eggless ravioli dough (still legit recipe)
If you want eggless ravioli, aim for a dough that’s pliable and not too dry.

Ingredients
- 300 g all-purpose flour
- 1/2 tsp salt
- 2 tbsp olive oil
- ~140–160 ml warm water (add gradually)
Knead until smooth, rest 45–60 minutes, and roll thin. Eggless dough can be slightly less elastic, so seal carefully and avoid overstuffing.
Ravioli wrappers, wonton sheets, and “tonight” shortcuts
Wrapper shortcuts can deliver a surprisingly good ravioli dinner, especially when the filling is thick and the sauce is clingy.

If you’re using wonton sheets as ravioli wrappers:
- Keep filling thick, not wet.
- Seal with a thin smear of water, press out air, and crimp firmly.
- Simmer gently—don’t boil hard.
- Finish in sauce quickly; don’t let wrappers sit too long in water.
This approach won’t mimic handmade pasta perfectly, but it can deliver a surprisingly good ravioli dinner with far less effort. More importantly, it opens the door to creative fillings and sauces—exactly what we’re about to do.
To make wrappers feel more “pasta-like,” you can also brush them lightly with egg wash before sealing. It strengthens the seam and adds a richer bite. In addition, try cooking them at a gentler simmer and finishing them in sauce immediately; that finishing step does a lot of heavy lifting.
Also Read: Dirty Martini Recipe (Classic, Extra Dirty, No Vermouth, Spicy, Blue Cheese, Tequila + Batched)
Twist 1: Butternut squash ravioli with brown ghee + curry leaves
Butternut squash ravioli has a built-in personality: sweet, mellow, slightly nutty. That’s why the classic pairing is brown butter sage. People love the toasted butter aroma against the sweetness of squash, and it’s a combination that shows up constantly in “butternut squash ravioli with brown butter sage” conversations.

The Indian move is not to reinvent the wheel. It’s to keep the wheel, change the spokes.
Instead of sage, we lean on curry leaves. Instead of brown butter, we use brown ghee. You keep the nutty aroma, yet the finish is unmistakably different—warm, fragrant, and just a little more exciting.
Brown ghee “sage-butter” sauce recipe for squash ravioli
This works beautifully for butternut squash ravioli, pumpkin ravioli, and squash stuffed ravioli recipes. It also turns frozen butternut squash ravioli into something that feels handmade.

Ingredients
- 3 tbsp ghee
- 10–15 curry leaves (fresh is best; dried works in a pinch)
- 1/2 tsp toasted cumin seeds or a pinch of ground cumin
- Black pepper
- Optional: pinch of nutmeg
- Optional: lemon zest + a squeeze of lemon
Method
- Warm ghee in a small pan until it starts to smell toasted and deepens slightly in color.
- Add curry leaves. They’ll crackle and perfume the ghee.
- Stir in cumin and black pepper.
- Add nutmeg if you want a warmer, slightly sweet background note.
- Toss cooked ravioli in the sauce and finish with lemon zest if the ravioli is very sweet.
Why it works: squash wants something nutty and aromatic. Brown butter gives nutty; curry leaf gives aromatic. Brown ghee gives both without needing sage at all.
If you want to link this section into your broader “Indian twist pasta” universe, it plays nicely with creamy pasta reinventions like our Indian-inspired Alfredo twists because they share the same silky, comfort-forward DNA.
A gentle pumpkin ravioli recipe variation
If you’re working with pumpkin ravioli—fresh or frozen—consider adding a whisper of Kashmiri chili for warmth and color. Not heat. Warmth. Pumpkin likes spice that feels cozy rather than aggressive.
At the end, sprinkle roasted pistachios if you want a subtle Indian dessert vibe without turning dinner sweet. The pistachio crunch also helps if the ravioli is very soft.
Ravioli filling recipe: roasted butternut squash + cumin-paneer (or vegan option)
If you want to make the squash ravioli from scratch—dough, filling, the whole thing—this filling is structured to be thick enough to seal well and rich enough to taste like something you’d order.

Ingredients
- 2 cups roasted butternut squash (roast cubes until caramelized, then mash)
- 1/2 cup paneer, finely crumbled (optional but excellent)
- 1 tbsp ghee
- 1/2 tsp cumin seeds
- 1/2 tsp ground coriander
- 1/4 tsp black pepper
- 1/4 tsp nutmeg (optional, but gorgeous with squash)
- 1/2 tsp salt (adjust)
- 1 tbsp finely chopped toasted nuts (optional)
- 1–2 tsp lemon juice (optional, for brightness)
Method
- Roast squash until edges caramelize, then mash until smooth.
- Heat ghee, add cumin seeds, let them sizzle briefly.
- Stir in mashed squash and spices, cook 2–3 minutes to evaporate excess moisture.
- Fold in paneer off heat so it stays creamy.
- Let cool completely before filling ravioli.
Vegan swap: use cashew cream or coconut cream in place of paneer, or fold in a thick mashed white bean for body. The goal is a filling that is creamy yet not wet.
Assembly tip: keep filling small—about 1 to 1½ teaspoons per ravioli for standard sizes. More filling feels generous, but it puts stress on the seam and raises the chances of leaking.
As an alternative, you can also try a goats cheese ravioli style vibe by blending a small amount of tangy cheese into the squash; it’s not traditional Indian, yet it pairs beautifully with curry leaf brown ghee and tastes elegant.
Also Read: Keto Hot Chocolate Recipe (Sugar-Free Hot Cocoa) + Best Homemade Mix
Twist 2: Mushroom ravioli with creamy “mushroom malai” sauce recipe
Mushroom ravioli lives in that earthy, savory zone where cream sauces make sense. That’s why people gravitate toward creamy mushroom sauce for ravioli, and why mushroom ravioli recipe ideas often feel restaurant-y even when they’re simple.

The Indian twist here is subtle. We’re not trying to make it spicy. We’re trying to make it deeper. Malai-style sauces tend to be creamy, aromatic, and gently spiced. In other words, they’re a natural match for a mushroom ravioli recipe.
Creamy mushroom sauce recipe for ravioli
This sauce works with mushroom stuffed ravioli, cheese ravioli, spinach ravioli, and even store bought ravioli that leans earthy.
Ingredients
- 2 tbsp butter or ghee
- 250–300 g mushrooms, sliced
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1/2 tsp black pepper (more if you love peppery sauces)
- Pinch of cumin (or a few cumin seeds toasted first)
- 1/2 cup cream (or cashew cream for a plant based ravioli dinner)
- 1/4 tsp kasuri methi, crushed between your palms
- Salt
- A splash of pasta water

Method
- Sauté mushrooms in butter/ghee until they release water and start browning.
- Add garlic and pepper; cook until fragrant.
- Add a splash of pasta water to create a glossy base.
- Stir in cream; simmer until thick enough to coat a spoon.
- Finish with kasuri methi and adjust salt.
The kasuri methi is the quiet hero. It doesn’t scream “Indian.” It murmurs it. That’s exactly what you want: a familiar creamy mushroom ravioli sauce that tastes new without tasting confused.
Truffle ravioli vibes without overdoing it
Truffle ravioli and ravioli truffle sauce often lead people into heavy-handed flavors. If you want that truffle-ish feeling without the intensity, stick to the elements that make truffle exciting: earthiness and richness.
Here are gentle ways to get there:
- Brown mushrooms harder for deeper savoriness.
- Use more black pepper than you normally would.
- Finish with a small gloss of butter/ghee and a sprinkle of parmesan.
You’ll still hit that “truffle ravioli” mood, especially with mushroom ravioli, yet it won’t dominate the plate.
As a pairing, coffee-forward cocktails tend to sit beautifully after rich mushroom ravioli dinners. If you want a fun blog post that fits naturally, our espresso martini variations are an easy “dessert drink” moment—especially when the meal has that creamy, earthy finish.
Ravioli filling recipe: mushroom masala + ricotta (or vegan “cream”)
If you’re making mushroom ravioli from scratch, this filling leans into deep mushroom flavor while staying thick enough to seal cleanly.

Ingredients
- 350–400 g mushrooms, finely chopped (a mix is best, but even one type works)
- 1 tbsp ghee or butter
- 1 small onion, finely chopped
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1/2 tsp cumin seeds
- 1/2 tsp ground coriander
- 1/2 tsp black pepper
- 1/4 tsp chili flakes (optional)
- 1/2 tsp salt (adjust)
- 1/2 cup ricotta (or thick hung curd; ricotta is classic)
- 2 tbsp grated parmesan (optional, but helps structure)
- 1 tbsp chopped herbs (parsley or cilantro—either works)
- 1 tsp lemon zest (optional)
Method
- Heat ghee, toast cumin seeds briefly.
- Add onion, cook until translucent, then add garlic.
- Add mushrooms and cook until moisture evaporates and the mixture browns.
- Stir in spices and salt, cook another minute.
- Cool completely.
- Fold in ricotta and parmesan; mix until thick and scoopable.
Vegan option: use thick cashew cream + a spoon of nutritional yeast + a small amount of mashed tofu for body. The key is still the same: thick filling, no watery seep.
This filling also works beautifully in “ravioli di portobello” style dinners and feels naturally aligned with creamy mushroom sauce for ravioli, mushroom ravioli pasta sauce, and those cozy “best fresh ravioli” nights when you want something earthy.
Also Read: 10 Low Carb Chia Pudding Recipes for Weight Loss (Keto, High-Protein, Dairy-Free)
Twist 3: Lobster ravioli sauce—butter garlic cream with a curry leaf recipe
Seafood ravioli has a particular kind of appeal. Its a recipe that feels fancy, it cooks fast, and it’s exactly the sort of thing people buy when they want a “treat” without doing too much. That’s why lobster ravioli shows up so often—along with the real question behind it: what’s the best sauce for a lobster ravioli recipe?

Butter sauce for lobster ravioli is the classic. Butter garlic sauce for lobster ravioli is the louder classic. Add cream to the recipe and suddenly the whole plate feels “restaurant.” We’ll keep that structure, then add one finishing move that makes it feel Indian-inspired without hijacking the seafood.
Butter garlic cream sauce for lobster ravioli
This is your easy lobster ravioli sauce recipe that still tastes luxurious.
Ingredients
- 2 tbsp butter (or ghee)
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1/2 cup cream
- Lemon zest + a squeeze of lemon
- Black pepper
- A splash of pasta water
Method
- Melt butter, sauté garlic gently (don’t brown it aggressively).
- Stir in cream and a splash of pasta water.
- Simmer until slightly thick and glossy.
- Finish with lemon and pepper.
That’s your base. Now the twist.

The Indian finish: curry leaf + Kashmiri chili tempering
In a separate small pan:
- Warm 1 tsp ghee.
- Add a handful of curry leaves (they crackle instantly).
- Add a pinch of Kashmiri chili.
Drizzle this over your finished sauce right before serving.
Suddenly, your creamy lobster ravioli sauce has aroma. It has lift. It has that “what did you do?” effect.
If you’re cooking lobster filled ravioli or crab ravioli, a quick seafood-handling reference is always reassuring—especially if you’re storing leftovers. FoodSafety.gov has clear guidance on handling fish and shellfish: Safe selection and handling of fish & shellfish. For a straightforward storage reference, USDA’s answer on fish storage timing is useful: How long can you store fish?.
A quick note on “butter garlic ravioli sauce” balance
It’s easy for butter-garlic sauces to taste flat if there’s no brightness. Lemon is the simplest fix. So is zest. So is black pepper. Even a tiny splash of pasta water can help the sauce cling instead of separating.
When you get this right, it becomes the kind of sauce you’ll use not only for a seafood ravioli recipe but for cheese raviolis, spinach cheese ravioli, and even basic meat ravioli frozen dinners you want to upgrade.
Filling recipe: homemade lobster (or crab) ravioli that won’t leak
Homemade lobster ravioli sounds like a flex, yet the recipe of ravioli filling itself can be straightforward if you treat it like a seafood mousse-light: rich, cohesive, and not watery.

Ingredients
- 250 g cooked lobster meat (or crabmeat), finely chopped
- 2 tbsp butter
- 1 small shallot (or very finely chopped onion), sautéed until soft
- 1 clove garlic, minced (optional)
- 1/4 cup ricotta (or cream cheese for a firmer set)
- 2 tbsp grated parmesan (optional)
- 1 tbsp chopped chives or cilantro
- Zest of 1/2 lemon
- Black pepper
- Salt to taste
Method
- Sauté shallot in butter until soft; add garlic briefly if using.
- Cool slightly, then combine with chopped lobster/crab.
- Stir in ricotta and parmesan until the mixture holds together.
- Add herbs, lemon zest, pepper, and salt.
- Chill 20–30 minutes so it firms up before filling.
Why this works: ricotta (or cream cheese) keeps the filling creamy while preventing free liquid from seeping into dough. That matters, because wet filling is the quickest path to ravioli blowouts.
This filling pairs beautifully with the butter sauce for lobster ravioli, but it also holds its own under a tomato-cream sauce if you prefer that lane.
Also Read: Garlic & Paprika Cabbage Rolls (Keto-Friendly Recipes) – 5 Bold Savory Twists
Twist 4: Creamy tomato sauce for lobster ravioli—makhani recipe without going off-road
Tomato-cream sauce is the other major lobster lane. You see it in creamy lobster ravioli sauce ideas, lobster ravioli pasta sauce recipe discussions, and every “best pasta sauce for lobster ravioli” type conversation. The base makes sense: tomatoes bring acidity, cream brings richness, and together they create a sauce that tastes indulgent while still feeling balanced.

The Indian-inspired move here is makhani-adjacent: tomato, butter, cream (or cashew cream), and a finishing note that hints at that familiar restaurant flavor.
Tomato-cream sauce recipe that clings to ravioli
The key is structure. In this recipe, thin tomato sauce slides right off ravioli. A sauce that’s been reduced and enriched clings.
Ingredients
- 2 tbsp butter or ghee
- 2 cloves garlic
- 2 tbsp tomato paste
- 1/2 cup crushed tomatoes or passata
- 1/2 cup cream (or cashew cream)
- Pinch of kasuri methi
- Pinch of garam masala (optional, keep it light)
- Salt, pepper
- Pasta water

Method
- Heat butter/ghee, sauté garlic.
- Add tomato paste and cook it for a minute until it darkens slightly.
- Add crushed tomatoes; simmer until thicker than you think it needs to be.
- Add cream/cashew cream and a splash of pasta water to emulsify.
- Finish with kasuri methi and a tiny pinch of garam masala if you want that makhani whisper.
This sauce works for lobster ravioli, crab ravioli, shrimp ravioli (if you ever go there), and surprisingly well for cheese ravioli too. It’s also a beautiful answer to “best ravioli sauce recipe” because it does the two things ravioli needs most: cling and contrast.
Make it feel “restaurant” without making it heavy
If your tomato-cream sauce tastes too rich, it doesn’t need less cream. It needs more balance:
- lemon zest
- black pepper
- a hint of heat
- or simply more reduction before adding cream
Once it tastes lively, it suddenly feels expensive.
For readers who like a broader context on fats and cooking choices—especially when you’re choosing between butter, ghee, cream, and oils—Harvard Health has a straightforward overview of cooking oil choices: Expand your healthy cooking oil choices. You don’t need to turn dinner into a lecture; it’s just a handy perspective if you like understanding how fats fit into a bigger picture.
Filling recipe: keema ravioli (the “short rib / beef” comfort lane, Indian-style)
This is where ravioli becomes deeply satisfying. Keema-style filling gives you that rich, meaty ravioli experience that sits in the same comfort zone as beef ravioli, meat ravioli, and even those hearty “short rib ravioli” dinners—just with Indian warmth.

Ingredients
- 300 g ground meat (lamb, beef, or chicken)
- 1 tbsp ghee or oil
- 1 small onion, very finely chopped
- 1 tsp ginger-garlic paste (or minced ginger + garlic)
- 1/2 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1/2 tsp garam masala
- 1/2 tsp Kashmiri chili (optional)
- 1/2 tsp salt (adjust)
- 2 tbsp tomato paste (or finely chopped tomato cooked down)
- 2 tbsp peas (optional, classic keema touch)
- 1 tbsp chopped cilantro
- 1 tbsp breadcrumbs or finely grated parmesan (optional binder)
Method
- Heat ghee, toast cumin seeds.
- Add onion, cook until golden.
- Add ginger-garlic, cook until fragrant.
- Add meat, break it up, cook until browned.
- Stir in spices, salt, and tomato paste; cook until the mixture looks dry and cohesive.
- Add peas if using; cook briefly.
- Cool completely; fold in cilantro and a binder if needed.
Important: keema filling must be dry enough to seal. If it looks wet, keep cooking it down. If it feels crumbly, add a spoon of ricotta or a tiny splash of cream to bind. You’re looking for something that scoops neatly and holds shape.
Keema ravioli loves either sauce lane:
- butter-garlic cream with curry leaf tempering for a luxurious feel, or
- tomato-cream makhani style for a comforting, “Sunday dinner” vibe.
Also Read: Eggless Yorkshire Pudding (No Milk) Recipe
Twist 5: Toasted ravioli—air fryer or oven, plus chutney-style dips
Toasted ravioli is the snack version of ravioli, and it’s genuinely addictive. It also happens to be a way to make frozen ravioli exciting, which is why toasted versions spread fast at parties and on game nights.

The Indian-inspired recipe is playful: toasted ravioli becomes a crispy appetizer with dips that feel like they belong at a party. Instead of marinara-only energy, you give it chutney energy.
Toasted ravioli recipe (air fryer)
This works with cheese ravioli, meat ravioli, mushroom ravioli, and even mini ravioli if you find them.
Method
- Lightly coat ravioli in oil. If you want extra crunch, dip in beaten egg and coat in breadcrumbs.
- Air fry until crisp and golden, flipping once.
Timing varies by ravioli size and fryer power, so the best rule is visual: you want deep golden edges and a firm bite. If you hear a light crisp crackle when you tap one, you’re in business.
Oven baked toasted ravioli (less fuss, still crisp)
Bake on a rack if possible. A rack keeps air moving so you don’t get soggy bottoms. If you’re doing a tray-only method, flip halfway.

Deep-fried ravioli from frozen
If you want the classic fried raviolis feel, deep frying is fast:
- keep oil hot enough to crisp quickly
- don’t crowd the pot
- drain on a rack, not paper towels (paper towels can trap steam)
If you’re serving a platter of toasted ravioli at a party, it’s smart to follow basic food safety timing so things don’t sit out too long. USDA’s food safety basics keep it clear and practical: Steps to keep food safe.
Dips that make it Indian-inspired without trying too hard
Here’s the fun part. You don’t need ten dips. You need two or three that cover different moods.
- For creamy, cooling balance: South Indian coconut chutney is an easy win with toasted ravioli, especially cheese and spinach ravioli bites.
- For deeper heat and a punchy snack vibe: Kara chutney gives the platter a bold, savory backbone.
- If you want something that leans spicy and garlicky, Thecha chutney turns toasted ravioli into a genuinely addictive snack.
If this section is your favorite—and it often becomes the favorite—pair it with something bright and citrusy for a complete appetizer moment. A Lemon Drop Martini fits beautifully when the dips are spicy and the bites are crisp.
Ravioli filling recipe: palak-paneer-inspired filling (the most natural crossover)
Palak paneer is already a creamy, garlicky, comforting dish. Fold it into ravioli and it feels like it was meant to happen.

Ingredients
- 250 g spinach (fresh or frozen)
- 1 tbsp ghee
- 1/2 tsp cumin seeds
- 2 cloves garlic, minced
- 1 small green chili (optional, adjust)
- 200 g paneer, crumbled finely
- 2 tbsp cream (optional, helps bind)
- 1/2 tsp salt (adjust)
- Black pepper
- Optional: pinch of kasuri methi
Method
- Blanch spinach quickly, squeeze out moisture, then chop finely or blend.
- Heat ghee, toast cumin seeds, add garlic and chili.
- Add spinach and cook until thick and not watery.
- Mix in paneer, cream, salt, pepper, and kasuri methi.
- Cool completely before filling ravioli.
Why it seals well: the spinach is cooked down, the paneer is crumbly and absorbent, and the mixture becomes thick. That thickness matters, especially if you’re using thinner pasta dough or wrapper shortcuts.
This filling is also a brilliant candidate for baked ravioli casseroles because it stays creamy under heat without becoming runny.
Also Read: Crock Pot Chicken Breast Recipes: 10 Easy Slow Cooker Dinners (Juicy Every Time)
Ravioli variations that keep the flavor: keto, low carb, vegan, gluten-free
A good ravioli night shouldn’t be limited by dietary needs. The trick is to respect structure: ravioli is wrapper + filling + sauce. If one element changes (keto wrapper, gluten-free wrapper, vegan filling), the other two can compensate.
Keto ravioli (cheese-wrap recipe)
Keto ravioli is one of those ideas that sounds fake until you try it. It works because melted cheese becomes pliable, then crisps into a satisfying wrapper.

How it goes
- Use thin mozzarella slices as “sheets.”
- Warm until pliable.
- Add a thick filling, fold, and seal.
- Crisp lightly in a pan or bake briefly.
For fillings, Indian flavors shine because they bring intensity without relying on carbs:
- palak-style spiced spinach
- paneer-style seasoned cheese
- keema-style spiced meat
Since keto also tends to overlap with drink choices, a natural companion for this section is our keto mocktails roundup. If you want something cozy instead, keto hot chocolate turns dinner into a full vibe.
Low carb ravioli that still feels like comfort food
Low carb ravioli doesn’t have to mean joyless. If you’re not doing cheese-wrap ravioli, another approach is to focus on sauces and fillings and keep portions satisfying:
- choose a richer sauce (butter-garlic cream, mushroom malai, tomato-cream)
- add protein and vegetables on the side
- serve fewer ravioli, but make each bite count
Vegan ravioli (plant based filling ideas)
For a vegan ravioli recipe, the best fillings are thick and bold:
- lentil filling (dal-style, reduced until thick)
- spiced mushroom-onion filling
- coconut vegetable filling with mustard seeds and curry leaves
Pair vegan ravioli with coconut chutney or a coconut-forward sauce, and you’ll never feel like something is missing.
Gluten-free ravioli without frustration
Gluten-free ravioli can be done, yet it’s easiest when you use a tested method or a wrapper shortcut. If you’re doing gluten free ravioli dough, the big keys are hydration and gentle handling. If you’re using gluten-free wrappers or wonton-style sheets, keep the filling thick and seal carefully.
Even when the wrapper changes, sealing technique stays the same. King Arthur’s ravioli guide remains useful for the mechanics of sealing and shaping: How to make ravioli at home.
Recipe for Filling: vegan lentil “dal” filling (surprisingly perfect for ravioli)
This is one of the most satisfying plant based ravioli options because it’s naturally thick and flavorful.
Ingredients
- 1 cup red lentils
- 2 1/2 cups water
- 1 tbsp oil
- 1/2 tsp cumin seeds
- 1 small onion, finely chopped
- 1 tsp ginger-garlic paste
- 1 tsp ground coriander
- 1/2 tsp turmeric
- 1/2 tsp salt (adjust)
- Lemon juice
- Chopped cilantro

Method
- Cook lentils until soft; then cook down until thick.
- In a separate pan, temper cumin in oil, sauté onion until golden.
- Add ginger-garlic and spices, then stir into lentils.
- Cook another few minutes until the mixture is scoopable.
- Finish with lemon and cilantro, then cool.
Pair this filling with coconut-curry style sauce or a tomato-based sauce depending on mood. Either way, it feels hearty rather than “replacement.”
Also Read: Sourdough Starter Recipe: Make, Feed, Store & Fix Your Starter (Beginner Guide)
The sauce logic that makes ravioli feel “best” at home
People talk about “best ravioli sauce” like it’s one thing. In reality, it’s a match.
Ravioli is already stuffed, which means it doesn’t want a sauce that competes with its filling. It wants a sauce that either supports the filling or contrasts it gently. When you get that right, “ravioli and sauce” becomes something you crave, not just something you eat.

Cheese ravioli sauce ideas
Cheese ravioli tends to be mild and creamy, so it benefits from:
- tomato-cream sauce with a little brightness
- butter sauce with black pepper and lemon zest
- a thin drizzle of spiced ghee if you want an Indian hint without changing the whole dish
That said cheese raviolis also work surprisingly well as toasted ravioli because their filling stays stable and the crisp wrapper creates contrast.
Spinach and cheese ravioli (ricotta-style recipe)
Spinach ravioli wants:
- cream sauce that’s peppery and not too thick
- a light garlic butter sauce
- or a spinach-forward sauce that feels palak-inspired
If you’ve ever made ricotta spinach ravioli and wondered why it tasted flat, it was likely missing pepper, acid, or a finishing herb.
Mushroom ravioli
Mushroom ravioli loves cream sauces, but it also loves simplicity:
- mushroom malai cream sauce for richness
- butter sauce with pepper for something lighter
- tomato-cream if you want a contrasting tang
Seafood ravioli (lobster/crab)
Seafood ravioli loves:
- butter-garlic cream with curry leaf tadka
- tomato-cream makhani style if you want richer, “restaurant” feel
Squash ravioli (butternut/pumpkin)
Squash ravioli loves:
- brown ghee + curry leaves (nutty, aromatic)
- or a lighter butter sauce with lemon zest for balance
If you’re ever unsure, taste the filling first. If the filling is sweet, add brightness. Then if the filling is rich, add acid or pepper. And if the filling is mild, add aroma. That one small habit keeps the whole meal from feeling one-note.
Also Read: How to make No-Bake Banana Pudding: No Oven Required Recipe
Bringing it all together: a ravioli night that feels effortless
It’s easy to overcomplicate a ravioli recipe because it looks fancy. However, the real charm is that ravioli is forgiving when you treat it gently and finish it well.

Here’s a simple way to build a meal that feels complete:
- Pick your ravioli (cheese, mushroom, squash, seafood).
- Choose the sauce lane that matches it.
- Add one finishing move: curry leaf tempering, kasuri methi, lemon zest, pepper.
- Decide whether you want it plated like dinner or served like a snack.
If you’re doing the snack route, toasted ravioli with coconut chutney and kara chutney can be the entire evening’s personality. If you’re doing the cozy dinner route, mushroom ravioli with malai-style cream sauce and a quiet dessert-drink moment like an espresso martini can make the night feel surprisingly special without any extra work.
Still, sometimes the mood is “feed a crowd,” and that’s where baked and slow-cooker versions become genuinely useful. They keep the ravioli theme intact while shifting the labor from “hands-on cooking” to “set it and relax.”
Also Read: Chicken Adobo — Step-by-Step Recipe — Classic Filipino Adobong Manok
Baked ravioli casserole (the “million-dollar” comfort recipe)
A baked ravioli casserole is the ultimate shortcut-meets-comfort dish. It’s the same idea as a lasagna, but easier because ravioli becomes the “layer.” This style works especially well with frozen cheese ravioli, frozen meat ravioli, and refrigerated ravioli. It also adapts beautifully to Indian-inspired sauces—because baked pasta loves bold flavor.

A classic baked ravioli casserole (with Indian-leaning sauce options)
Ingredients
- 1 to 1.5 kg ravioli (frozen or refrigerated)
- 3–4 cups sauce (choose one below)
- 2 cups shredded mozzarella (or a mix of mozzarella + cheddar)
- 1/2 cup parmesan (optional)
- 1 tbsp butter or ghee (for greasing)
- Optional: sautéed mushrooms, spinach, or cooked keema as an extra layer
Sauce options
- Tomato-cream makhani-style sauce (from Twist 4): thick, glossy, clingy
- Mushroom malai sauce (from Twist 2): rich and earthy
- Simple marinara-style tomato sauce finished with curry leaf tempering (lighter, still special)

Method
- Heat oven to 190°C / 375°F.
- Grease a baking dish with butter/ghee.
- Add a thin layer of sauce.
- Layer ravioli in a single layer.
- Spoon sauce over, then add cheese.
- Repeat layers until you’re done, finishing with sauce and cheese.
- Cover with foil and bake 25–30 minutes.
- Uncover and bake another 10–15 minutes until bubbly and browned.
Why it works: ravioli already contains filling, so the casserole stays interesting even if you don’t add extra layers. Nevertheless, adding a thin layer of keema or sautéed mushrooms between ravioli layers can make it feel like a “million dollar” baked ravioli casserole without making it complicated.
Serving idea: finish with a drizzle of curry leaf ghee or a pinch of kasuri methi over the top right before serving. That last aromatic lift makes the whole casserole taste intentional.
Baked lobster ravioli (yes, you can)
If you’re baking lobster ravioli, choose a sauce that protects it:
- a gentle tomato-cream sauce
- or a butter-cream sauce with lemon
Avoid super-high heat for too long. Seafood filling can get rubbery if overbaked, so keep the bake time closer to “just until heated through and bubbly,” not “deeply browned for an hour.”
Also Read: Sweetened Condensed Milk Fudge: 10 Easy Recipes
Crock pot ravioli recipe (and slow cooker ravioli “lasagna”)
Slow cooker ravioli is one of those recipes that sounds suspicious until you try it. It’s essentially a crockpot lasagna with ravioli: layers of ravioli, sauce, cheese, and any extras you like. It’s perfect for busy days and surprisingly reliable for feeding people.

Crock pot ravioli (basic recipe)
Ingredients
- 1 kg frozen ravioli (cheese ravioli is the easiest starting point)
- 4 cups sauce (thicker is better)
- 2 cups shredded mozzarella
- 1/2 cup parmesan (optional)
- Optional add-ins: cooked keema, sautéed mushrooms, spinach, or roasted vegetables
Method
- Lightly grease the slow cooker.
- Spread a thin layer of sauce on the bottom.
- Add a layer of frozen ravioli.
- Add sauce, then cheese.
- Repeat layers.
- Cook on LOW for 3–4 hours or HIGH for 1.5–2.5 hours, depending on your slow cooker.
- Let it sit 10–15 minutes before serving so it sets.
Why thickness matters: a watery sauce can make slow cooker ravioli loose and soupy. A thicker sauce creates layers and keeps everything cohesive.

Indian-inspired slow cooker variations
- Makhani-style slow cooker ravioli: use tomato-cream sauce and add a light kasuri methi finish at the end.
- Keema ravioli “lasagna” in the crock pot: add cooked keema as a thin layer between ravioli.
- Palak-paneer ravioli slow cooker bake: layer spinach-paneer filling as an extra or use spinach-and-cheese ravioli plus a creamy sauce.
Because slow cookers hold heat for a long time, seafood ravioli is not the best candidate here. Stick to cheese, mushroom, beef/keema, spinach, or squash. Those fillings love gentle, extended heat.
Also Read: Sourdough Recipe: 10 Easy Bread Bakes (Loaves, Rolls & Bagels)
A final word on what makes these “Indian twists” actually work
A good twist doesn’t fight the original dish. It harmonizes with it. That’s why these five ideas hold together:
- Squash ravioli stays nutty and aromatic; it just moves from sage to curry leaf.
- Mushroom ravioli stays creamy and earthy; it just gets a malai-style finish.
- Lobster ravioli sauce stays butter-garlic and glossy; it just gets a tempering drizzle.
- Tomato-cream stays tomato-cream; it just leans makhani in the most subtle, respectful way.
- Toasted ravioli stays crisp and snacky; it just gets dips that feel exciting.
You can use these as a template for almost any ravioli dinner: choose your base, pick a sauce that clings, finish with one Indian accent, and let ravioli do what it does best—feel comforting and impressive at the same time.

And if you’re planning a full “ravioli night,” it’s easy to round it out without drifting away from the theme. For something bright and citrusy, a Lemon Drop Martini matches seafood and creamy sauces surprisingly well. Meanwhile, for a deeper after-dinner note, an espresso martini turns the end of the meal into a small event. Finally, if you’re keeping things low carb, keto mocktails or keto hot chocolate keep the cozy factor high without feeling like an afterthought.
Also Read: Kahlua Drinks: 10 Easy Cocktail Recipes (Milk, Vodka, Coffee)
FAQ
1) How do you cook ravioli so it doesn’t fall apart?
Start with gently simmering water instead of a hard boil, because aggressive bubbling can bang ravioli into itself and split the seams. Next, stir only once at the beginning to prevent sticking. After that, lift ravioli out with a slotted spoon rather than dumping it into a colander. Finally, finish it in warm sauce for 30–60 seconds so the ravioli stays coated and intact.
2) How long do you cook fresh ravioli?
In most cases, fresh ravioli takes about 2–4 minutes. Once it floats, let it go another 30–60 seconds, then lift it out. If the ravioli is large ravioli or extra thick, it may need a little longer. Either way, the goal is tender pasta with a filling that stays creamy, not overcooked.
3) How do you cook frozen ravioli without making it mushy?
Rather than thawing first, cook frozen ravioli straight from the freezer in gently simmering water for roughly 4–7 minutes, depending on size. Then, instead of letting it sit, move it directly into sauce and let it bubble briefly. That quick finish helps the sauce cling and prevents a watery, slippery bite.
4) How long does refrigerated ravioli take to cook?
Typically, ravioli refrigerated packs cook similarly to fresh ravioli—around 3–5 minutes in gently simmering water. Even so, the best move is to transfer it into sauce right away so it doesn’t taste plain. In addition, a final touch like black pepper, lemon zest, or a drizzle of spiced ghee can make refrigerated ravioli feel far more “fresh.”
5) What is the easiest way to make ravioli at home?
If you want the simplest route, use ravioli wrappers or ravioli wonton sheets, keep the filling thick, seal tightly, and simmer gently. Alternatively, if you want true homemade texture, make a basic ravioli dough, rest it well, roll it thin, and keep fillings modest so sealing is easy. Either way, the most important part is squeezing out air before sealing.
6) How do you seal ravioli so it doesn’t leak?
First, keep the edge of the dough clean—any filling on the rim will break the seal. Then, lightly moisten the border with water or egg wash, press out air pockets, and seal firmly. Afterward, crimp with a fork if you like. As a last step, let shaped ravioli rest a few minutes before cooking; that short pause can help the seal set.
7) What’s the best flour for ravioli dough?
Many people use all-purpose flour successfully, especially for weeknight ravioli. However, “00” flour creates a silkier texture if you prefer a softer bite. If you want a slightly firmer chew, blending a small portion of semolina with all-purpose can help. Ultimately, the key is proper kneading and resting, not chasing one perfect flour.
8) Can you make ravioli dough in a KitchenAid?
Yes—ravioli dough KitchenAid mixing works well. Use the paddle initially to combine, then switch to the dough hook for kneading until smooth. Still, you’ll likely need to finish with a short hand-knead to feel the texture. After that, wrap and rest the dough so rolling is easier and the dough doesn’t spring back.
9) What’s the best ravioli dough recipe texture supposed to feel like?
A good pasta dough should feel smooth, elastic, and only slightly tacky. If it’s crumbly, it needs more hydration. If it’s sticky, it needs a dusting of flour and more kneading. Meanwhile, resting is crucial; without rest, even a good dough can feel too tight and difficult to roll thin.
10) How thin should pasta dough be for ravioli?
Aim for thin enough that you can see a faint shadow of your hand through it, yet strong enough to lift without tearing. If it’s too thick, the ravioli tastes heavy and the seams feel bulky. On the other hand, if it’s paper-thin, it may tear around the filling. Therefore, thin-and-strong is the goal.
11) What’s the best sauce for ravioli?
The best sauce for ravioli depends on what’s inside the pasta. Cheese-filled ravioli usually tastes best with a bright tomato sauce, a simple butter sauce, or a light cream sauce that doesn’t overwhelm the filling. Mushroom ravioli pairs naturally with a creamy mushroom sauce because it amplifies the earthy flavor and keeps the bite rich and smooth. Butternut squash ravioli is happiest with a nutty butter-style sauce—often brown butter with sage—because it balances sweetness; however, a brown ghee finish with curry leaves gives the same toasted warmth with a different aroma. Lobster ravioli typically shines with a butter-garlic cream sauce or a tomato-cream sauce, since both support seafood without masking it; in either case, a touch of lemon and black pepper keeps the plate lively rather than heavy.
12) What’s a good sauce for cheese ravioli?
If you want classic comfort, use a simple ravioli sauce like marinara or tomato sauce. If you want richer flavor, choose a cream sauce for ravioli or a butter sauce for ravioli with garlic and pepper. Additionally, a small finishing touch—lemon zest, chili flakes, or herbs—can brighten cheese ravioli without overpowering it.
13) What sauce goes with spinach and ricotta ravioli?
Spinach and ricotta ravioli sauce options tend to work best when they’re not too heavy. A light cream sauce, a gentle garlic-butter sauce, or a tomato sauce with enough acidity to balance the creamy filling are all strong picks. Moreover, black pepper and a hint of lemon can make spinach ravioli taste more vivid.
14) What’s the best sauce for butternut squash ravioli?
Classic pairings include brown butter sage sauce for butternut squash ravioli, because nutty butter balances the sweetness. If you want something different, a butter sauce for butternut squash ravioli with citrus zest, toasted spices, or a curry-leaf ghee finish can be equally satisfying. Either way, avoid watery sauces—squash ravioli needs cling.
15) How do you make brown butter sage sauce for ravioli?
Melt butter, let it foam, then continue cooking until it smells nutty and turns golden-brown. Next, add sage leaves until crisp. Finally, season with salt. For squash ravioli, this sauce is especially popular; for other fillings, it still works whenever you want a rich, aromatic finish.
16) What’s the best lobster ravioli sauce?
Butter garlic sauce for lobster ravioli is a top choice because it supports the seafood without masking it. Alternatively, creamy lobster ravioli sauce with tomato and cream is another favorite when you want a richer, restaurant-style feel. In either case, lemon and black pepper keep lobster ravioli from tasting too heavy.
17) How do you make an easy lobster ravioli sauce at home?
Start with butter and gently sautéed garlic. Then add cream and a splash of pasta water to emulsify. Afterward, finish with lemon zest and pepper. If you want extra depth, add a small pinch of chili or herbs. This approach stays simple while still tasting special.
18) What’s the best cream sauce for lobster ravioli?
A good cream sauce for lobster ravioli should be silky, not thick like glue. Use butter, garlic, cream, and a bit of pasta water to help it cling. Then finish with lemon for brightness. If you want a slightly tangy version, blend in a small amount of reduced tomato paste to create a gentle “pink” sauce effect.
19) What’s the best sauce for mushroom ravioli?
Cream sauce for mushroom ravioli is the most common pairing because it amplifies the earthy flavor. A creamy mushroom sauce for ravioli made with sautéed mushrooms, garlic, pepper, and cream usually hits the sweet spot. Still, if you want something lighter, a butter-and-pepper sauce can also work well.
20) Can you bake ravioli instead of boiling it?
Yes—baked ravioli is a popular comfort option. Generally, you layer ravioli with sauce and cheese and bake until bubbly. Because the sauce does most of the cooking, ravioli can go into the dish frozen or refrigerated in many cases. After baking, let it rest briefly so it sets and slices neatly.
21) What is a “million dollar ravioli casserole” and how is it different?
A million dollar ravioli casserole is essentially baked ravioli layered with a rich sauce, plenty of cheese, and sometimes an added creamy layer for extra indulgence. Compared with basic baked ravioli, it’s richer, more “lasagna-like,” and designed to feed a crowd. For that reason, frozen cheese ravioli and frozen meat ravioli are common choices.
22) Can you make a crock pot ravioli recipe?
Yes—crock pot ravioli is a slow cooker version of ravioli lasagna. Typically, you layer sauce, frozen ravioli, and cheese, then cook until tender. Since slow cookers vary, the timing depends on your model; however, using a thicker sauce helps everything stay cohesive rather than soupy.
23) Is ravioli healthy?
Ravioli can fit into many eating styles depending on portion, filling, and sauce. Vegetable ravioli or ravioli with vegetables can feel lighter, while creamy sauces and extra cheese make it richer. If you want a healthier ravioli approach, use a lighter sauce, add vegetables, and keep portions satisfying rather than oversized.
24) What’s the easiest low carb ravioli option?
One of the simplest low carb ravioli approaches is using a cheese-wrap “shell” instead of pasta dough. That style also fits well for keto ravioli. Another option is focusing on a rich sauce and filling while serving a smaller portion alongside vegetables or salad.
25) Can you make gluten free ravioli at home?
Yes, although gluten free ravioli dough can be more delicate and requires careful handling. Many people use a tested gluten-free dough blend or a wrapper shortcut. In all cases, thick fillings, gentle simmering, and careful sealing make a big difference in whether gluten free ravioli holds together.
26) Can you make vegan ravioli that still tastes rich?
Absolutely. Vegan ravioli works best with fillings that are naturally creamy or thick—such as lentils, mushrooms, or coconut-based vegetables. Then, pair it with a sauce that clings, like a tomato-based sauce or a creamy plant-based sauce. As a result, the meal feels complete rather than “missing something.”
27) How do you toast ravioli from frozen?
Toasted ravioli frozen is usually made by coating ravioli lightly (oil or breading), then crisping it in an oven or air fryer until golden. For extra crunch, breadcrumb coating helps. Once it’s crisp, serve immediately so the exterior stays snappy.
28) How do you make toasted ravioli in an air fryer?
For toasted ravioli recipe air fryer style, coat ravioli lightly, place in a single layer, and air fry until crisp, flipping once. Since air fryers vary, check early; you want deep golden edges without drying out the filling.
29) Can you deep fry ravioli from frozen?
Yes—deep fried ravioli frozen is a classic appetizer style. Keep the oil hot enough to crisp quickly, fry in batches, and drain well. Afterwards, serve right away so the coating stays crisp rather than steaming.
30) What’s the best way to reheat ravioli?
For the best texture, reheat ravioli in sauce on the stove over gentle heat with a splash of water. Alternatively, for baked ravioli casseroles, reheat covered so it warms through without drying. Microwaving works in a pinch, yet it can make ravioli a bit softer, so sauce helps protect the texture.
31) How do you store cooked ravioli?
Cool cooked ravioli quickly, store in an airtight container, and keep it with a bit of sauce so it doesn’t stick. Then reheat gently in sauce. This method preserves texture better than storing ravioli completely dry.
32) What’s the best filling for homemade ravioli?
That depends on the mood. Cheese and spinach ravioli is classic. Mushroom stuffed ravioli feels rich and earthy. Squash filled ravioli is sweet and cozy. Meat ravioli recipe styles (beef, sausage, or keema) feel hearty. Ultimately, the best filling is one that’s thick enough to seal and flavorful enough that the ravioli stands on its own even before sauce.