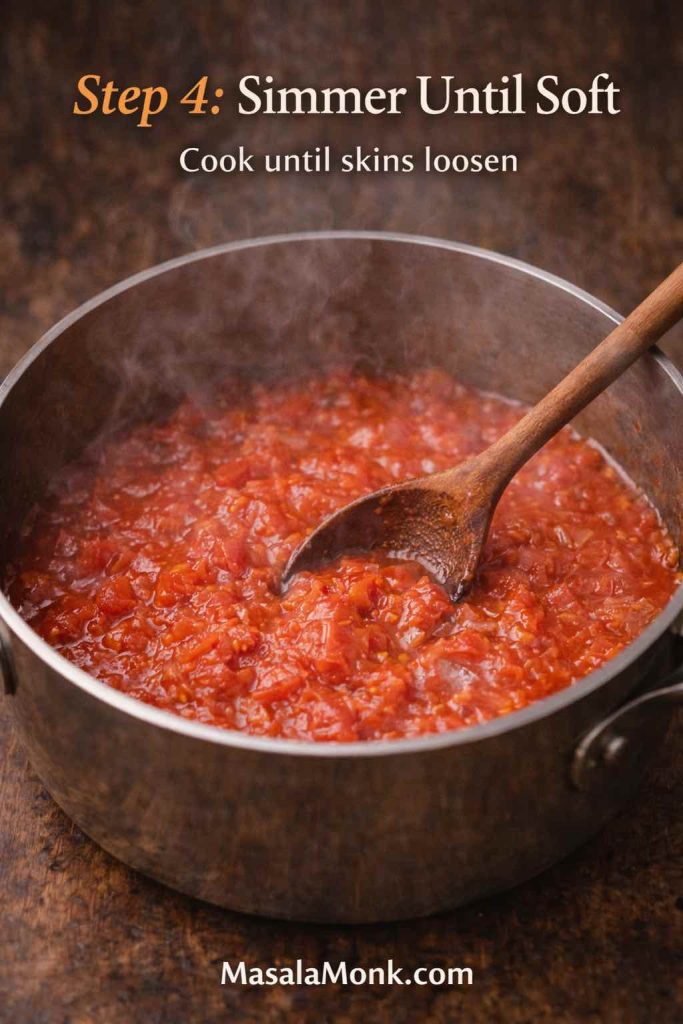
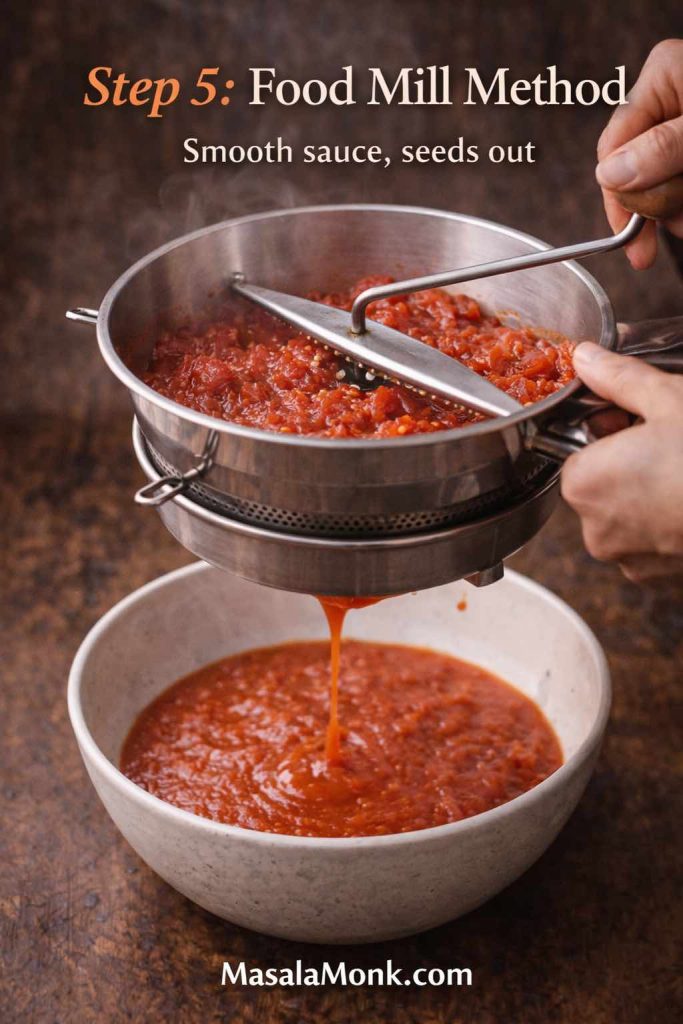
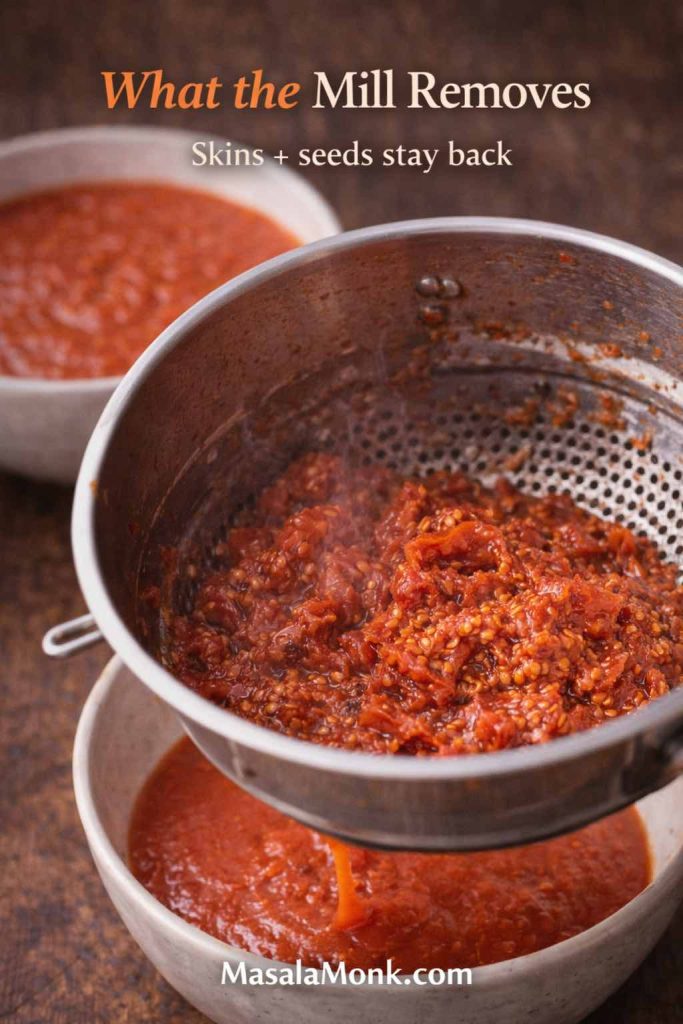
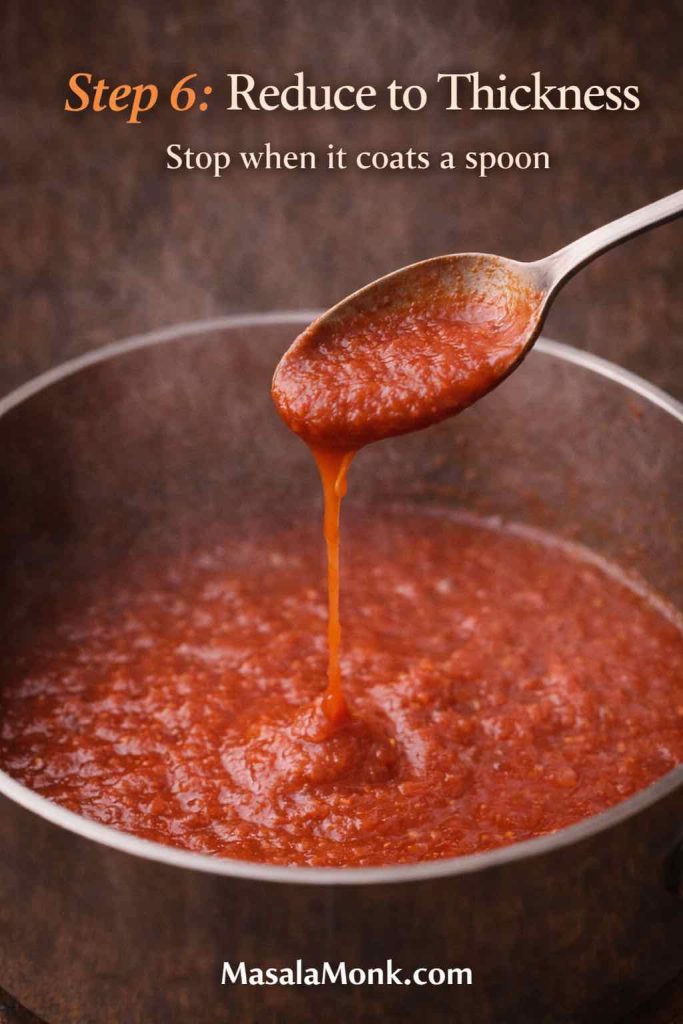
If you’re figuring out how to cook tortellini so it stays tender, bouncy, and intact—without turning mushy or splitting open—you’re about to make tortellini nights much easier. Cooking tortellini is mostly about a few small, repeatable moves: salted water, a controlled simmer, early tasting, and a quick finish in sauce or broth. Once those habits click, you can cook tortellini confidently whether it’s fresh tortellini from the fridge, frozen tortellini from the freezer, or dried tortellini from the pantry.
Because tortellini is stuffed pasta, it brings its own richness and seasoning. As a result, dinner doesn’t need a complicated plan. On one night, cheese tortellini can become pesto tortellini with chicken and tomatoes. On another, spinach and ricotta tortellini can turn into a bright, simple pomodoro bowl. Meanwhile, meat tortellini in broth can feel soothing in the best way. And when you want something snacky, you can air fry tortellini until crisp and dip it into marinara.
This is a practical, reader-first guide to how to cook tortellini in the formats you actually buy, followed by dinner frameworks you can reuse without boredom—one pot tortellini, slow cooker tortellini, creamy tortellini pasta, tortellini pomodoro, bolognese tortellini, tortellini in brodo, and tortellini prosciutto e panna.
Tortellini basics that make everything else easier
Tortellini is a small, ring-shaped stuffed pasta with deep roots in Bologna and the surrounding region. Traditionally, tortellini in brodo—tortellini served in broth—is one of the most iconic ways to eat it. If you’re curious about the cultural side, the Dotta Confraternita del Tortellino shares the tradition around the “registered” tortellino filling on their site. You don’t need that history to cook well; still, it explains why tortellini is designed to taste complete with simple treatment.
In everyday cooking, tortellini’s superpower is this: the filling is already seasoned, and the pasta shape catches sauce naturally. Therefore, you can keep your sauce straightforward and still end up with a bowl that feels finished.
Tortellini vs ravioli: why shape changes how you cook and serve
Ravioli is larger and often more delicate, so it’s commonly served with sauce spooned over the top. Tortellini is smaller, which makes it easy to toss in sauce and easy to serve in soups. If you enjoy stuffed pasta in general, you might like MasalaMonk’s playful take on variation and filling ideas in this ravioli piece. It’s a nice reminder that stuffed pasta can be flexible and fun.
Also Read: Manhattan Cocktail Recipe (Classic + 6 Variations)
How to cook tortellini every time: the universal method
Before you choose pesto or cream or broth, lock in the basics. This is how to cook tortellini successfully no matter what the filling is—cheese tortellini, spinach tortellini, meat tortellini, mushroom tortellini, or pumpkin tortellini.
- Use a roomy pot and plenty of water
Stuffed pasta needs space. When the pot is crowded, tortellini sticks and cooks unevenly. More water also helps the temperature recover quickly after you add the pasta. - Salt the water generously
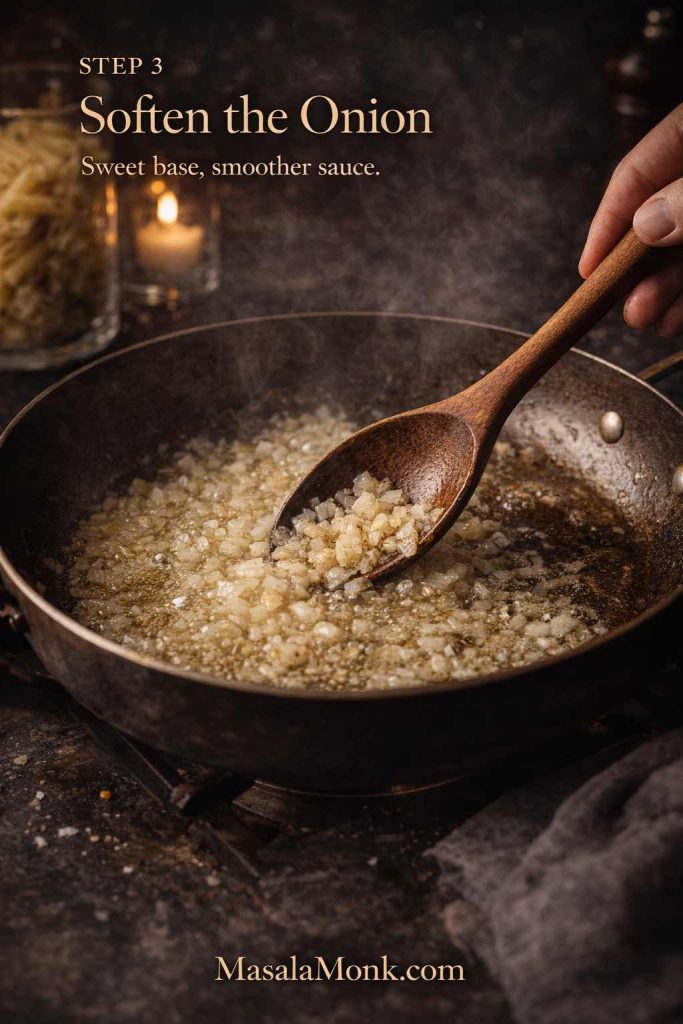
This matters more than people expect. Tortellini is thick and filled, so the outer pasta can taste bland if the water isn’t seasoned. With salted water, even simple sauces taste better. - Choose a lively simmer over a violent boil
A roaring, chaotic boil can knock tortellini around and encourage splitting. Instead, keep the water bubbling actively but not aggressively—especially for fresh tortellini and refrigerated tortellini. - Stir early, then back off
Stir gently right after adding tortellini so it doesn’t stick to itself or to the pot. After that, let it cook. Too much stirring can tear delicate pasta. - Reserve pasta water—every time
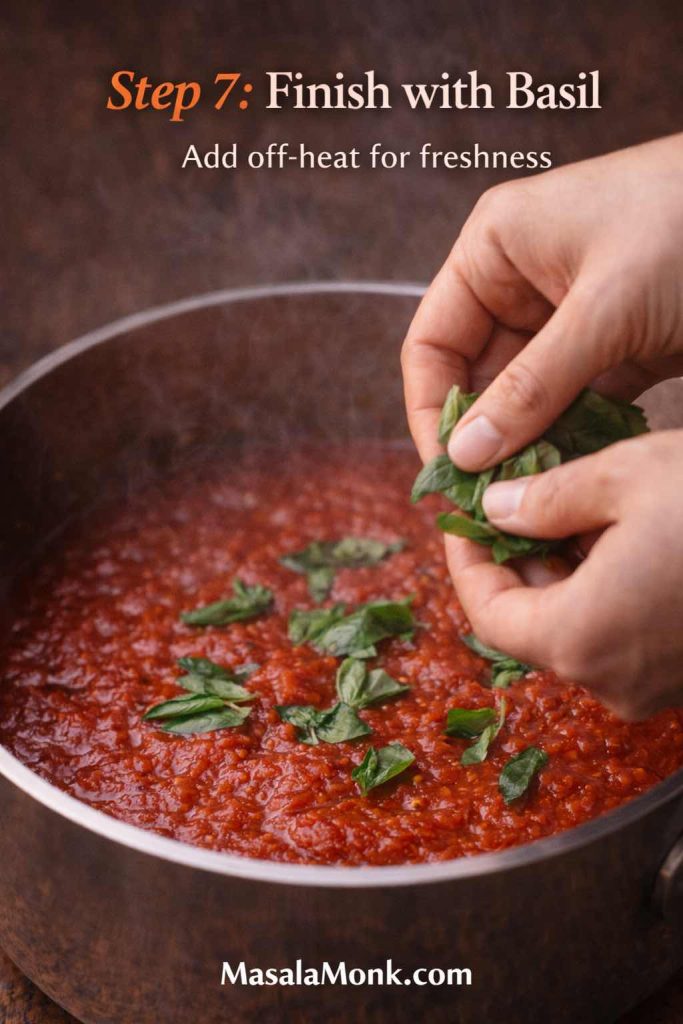
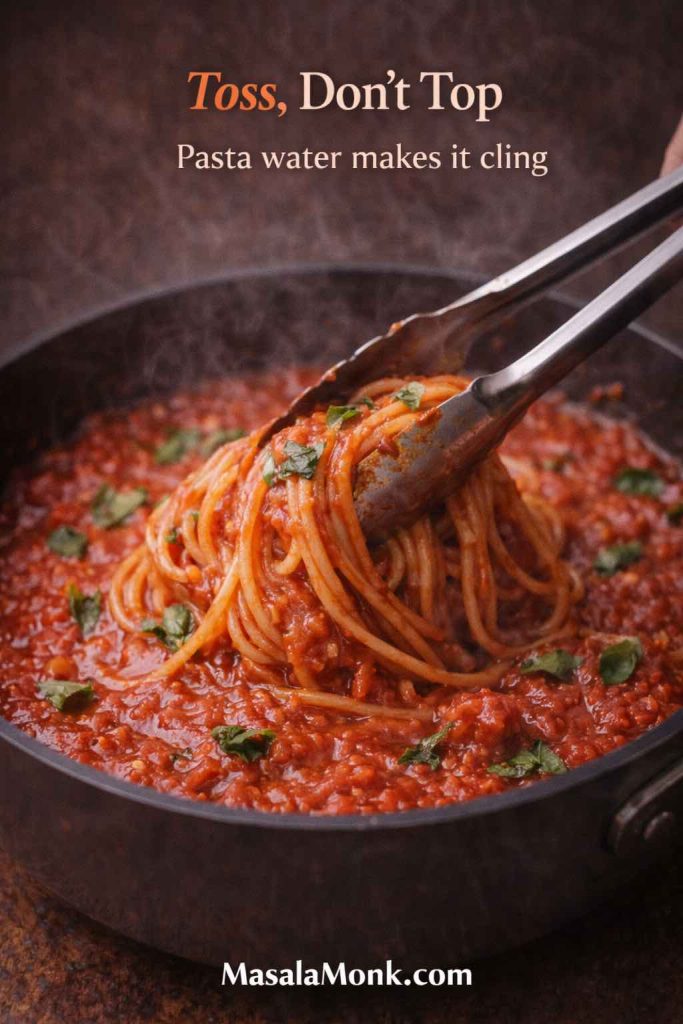
Before draining, scoop out a mug of cooking water. That starchy water helps sauces cling and emulsify. Consequently, pesto turns glossy instead of oily, cream sauces loosen without thinning, and tomato sauces coat instead of sliding. - Finish in sauce or broth for 30–60 seconds
Instead of draining and pouring sauce over the top, toss cooked tortellini in a warm pan of sauce for a minute. This short finish is a major part of how to cook tortellini so it tastes cohesive rather than assembled.
You’ll see these steps repeated throughout the recipes below because they’re the foundation.

Also Read: Green Chutney Recipe (Coriander–Mint / Cilantro Chutney)
Tortellini you’ll see most often: fillings and formats
Knowing what you bought makes “what should I do with it?” instantly easier.
Common fillings and what they naturally like
- Cheese tortellini is the weeknight workhorse. It might be labeled three cheese tortellini, 3 cheese tortellini, four cheese tortellini, 4 cheese tortellini, five cheese tortellini, or 5 cheese tortellini. It also shows up as tortellini formaggi or tortellini formaggio. Because it’s rich, it pairs beautifully with pesto, tomato sauce, or broth. It also works in a cream sauce, especially with pepper.
- Spinach tortellini often appears as spinach and ricotta tortellini, ricotta spinach tortellini, or tortellini ricotta spinaci. It’s excellent with lighter sauces: butter and garlic, bright tomato, or a gentle cream finish.
- Meat tortellini can be labeled meat filled tortellini, meat stuffed tortellini, beef tortellini, or veal tortellini. It shines in broth and also works in ragù when the sauce is balanced.
- Specialty fillings like mushroom tortellini, porcini tortellini, gorgonzola tortellini, pumpkin tortellini, lobster tortellini, and truffle tortellini (tortellini tartufo) usually taste best with a restrained sauce so the filling remains the star.

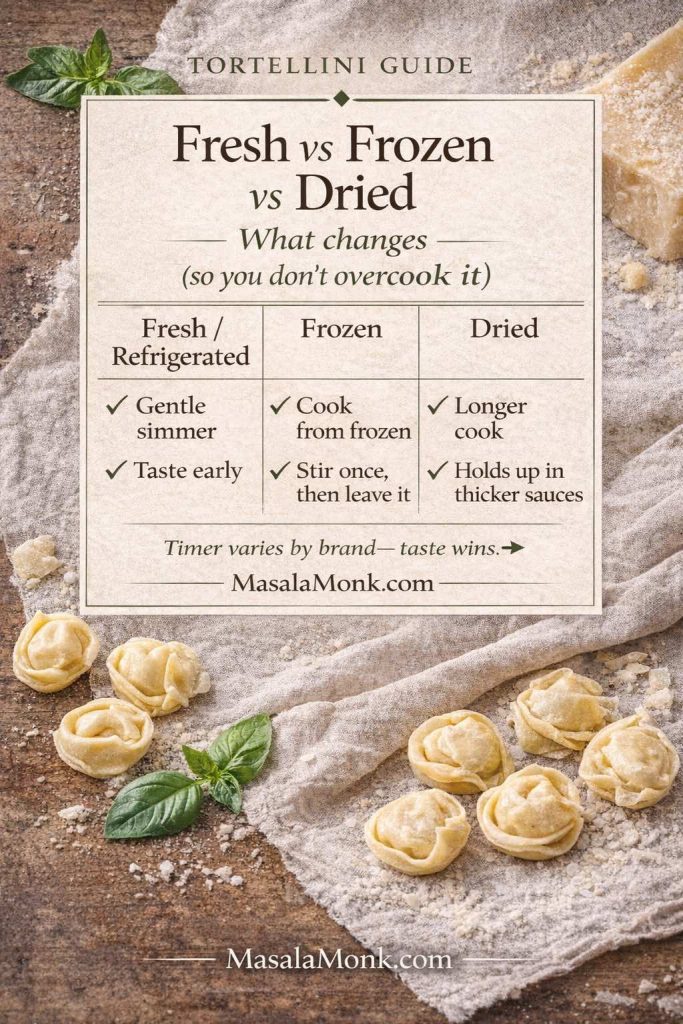
Formats: fresh, refrigerated, frozen, dried
- Fresh tortellini / refrigerated tortellini cooks quickly and needs gentle heat.
- Frozen tortellini cooks straight from frozen and benefits from careful tasting.
- Dried tortellini takes longer and holds up well in thicker sauces.
Once you identify the format, how to cook tortellini becomes far more predictable.
Also Read: Best Vermouth for a Negroni Cocktail Drink Recipe
How to cook fresh tortellini and refrigerated tortellini
Fresh and refrigerated tortellini cook fast, so the goal is to hit tender-and-bouncy rather than soft-and-saggy.
Bring salted water to a gentle boil. Then reduce slightly to a lively simmer. Add tortellini and stir gently once or twice. Start checking early and keep tasting.
A lot of refrigerated “fresh style” tortellini lines cook in just a few minutes. For an example of clear brand timing, Giovanni Rana shares cooking guidance on this product page. If you’re cooking rana tortellini, rana cheese tortellini, or a similar refrigerated pack, that’s a helpful reference point.
How to tell it’s done:
The pasta should feel tender but still springy, and the filling should be hot through the center. If the pasta feels floppy or waterlogged, it’s gone too far.

What to do immediately after draining:
Fresh tortellini keeps cooking from residual heat. Therefore, have your sauce ready before you drain. Toss it in warm sauce right away and loosen with pasta water until glossy. This is a crucial detail in how to cook tortellini well, and it’s also the easiest improvement to make.
Also Read: Sandwich for Breakfast: Breakfast Sandwich Recipe + 10 Variations
How to cook frozen tortellini so it doesn’t split
Frozen tortellini is convenient, but it’s easiest to ruin by treating it roughly.
Don’t thaw it first. Instead, cook it straight from frozen in salted water. Stir gently at the beginning to prevent sticking. Then let it cook and start tasting early. Since frozen tortellini thickness varies by brand and style, tasting beats guessing.

If you’re using a refrigerated line that’s meant to be cooked from frozen with a simple adjustment, follow the package guidance. Giovanni Rana notes a cook-from-frozen timing approach on the same instruction page.
Once tender, drain carefully and finish gently in sauce. A soft toss matters because hot tortellini is delicate; consequently, aggressive stirring can cause splits right at the end.
That “gentle finish” is central to how to cook tortellini from frozen with consistent results.
Also Read: Rob Roy Drink Recipe: Classic Scotch Cocktail (Perfect + Dry + Sweet Variations)
How to cook dried tortellini and keep it tender
Dried tortellini behaves more like pantry pasta. It needs longer cooking and tolerates a stronger boil, yet it still benefits from tasting near the end.
Bring salted water to a boil. Add tortellini and stir gently. Maintain a steady boil until the pasta is fully tender and the filling is hot through the center.
If you want a reference point for timing expectations, Barilla provides context on this tortellini recipe page. It’s especially useful if you’re cooking barilla tortellini or another shelf-stable tortellini.
After draining, finish the tortellini in sauce for a minute with pasta water. Because dried tortellini is sturdy, it’s excellent for marinara tortellini, bolognese tortellini, and baked pasta dinners.
Also Read: Strawberry Smoothie Recipes (12 Easy Blends + Bowls & Protein Shakes)
How to cook tortellini in broth and tortellini in brodo
Broth is one of the most satisfying ways to serve stuffed pasta. It’s light, soothing, and surprisingly elegant. Better still, broth allows the filling to shine rather than competing with it.
Warm good broth gently. Add aromatics if you like—garlic, onion, pepper, herbs, or a Parmesan rind. Then add tortellini and cook until tender. Finish with Parmesan and pepper.

Tortellini in broth with greens and herbs
To make it feel more complete, add greens near the end. Spinach is easiest because it wilts quickly. Kale works too, although it benefits from a little more time. Finish with herbs and a squeeze of lemon if you want extra lift.
Meat tortellini in broth is especially satisfying. However, cheese tortellini in broth can be wonderful too, particularly when you want comfort without heaviness.
Tortellini in brodo: the classic style
Tortellini in brodo is a traditional presentation associated with Bologna. For a cultural reference and overview, Bologna Welcome shares an explanation on this page. At home, keep it simple: good broth, gently cooked tortellini, Parmesan, and pepper. That restraint is what makes it special.
If you’re learning how to cook tortellini for soups, remember this: add the tortellini near the end and keep the simmer gentle so the pasta stays intact.
Also Read: Paper Plane Cocktail Recipe + Best Amaro Substitutes & Tips
Pesto tortellini: bright dinners in minutes
Pesto tortellini is fast, vibrant, and forgiving. It’s especially good with cheese tortellini because the basil and garlic cut the richness. Spinach tortellini works too, although a lighter coating tends to taste better.
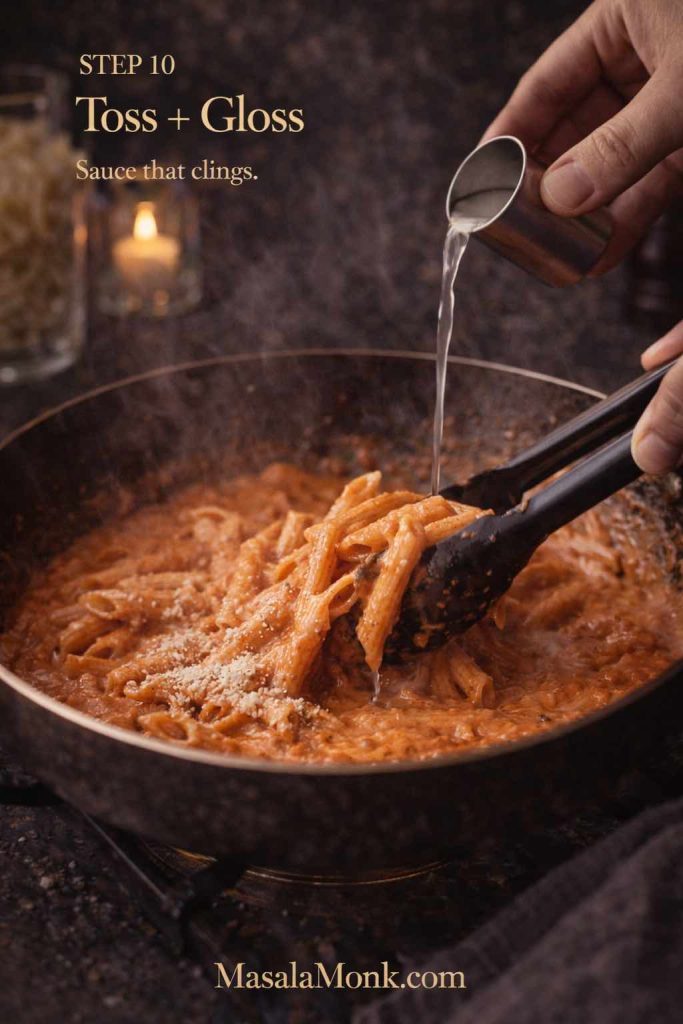
Cook tortellini, drain, and reserve pasta water. Warm pesto gently in a pan without boiling it. Toss in tortellini and add pasta water a spoonful at a time until the sauce becomes glossy and clings.

For pesto inspiration and variations, these MasalaMonk posts fit naturally, and you might want to have a look:
Chicken pesto tortellini with tomatoes
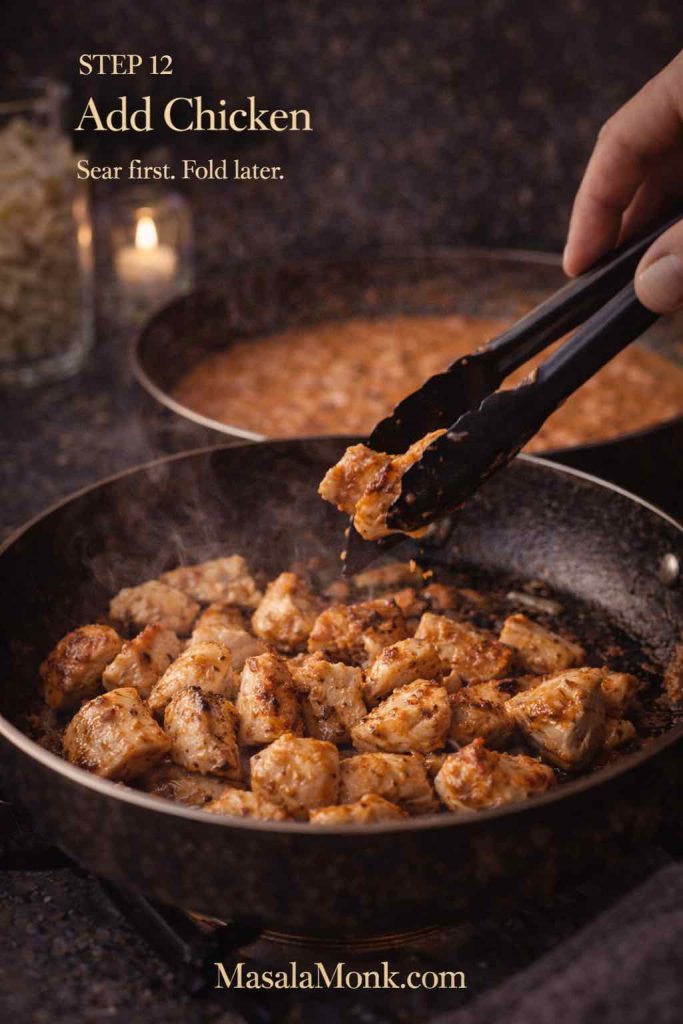
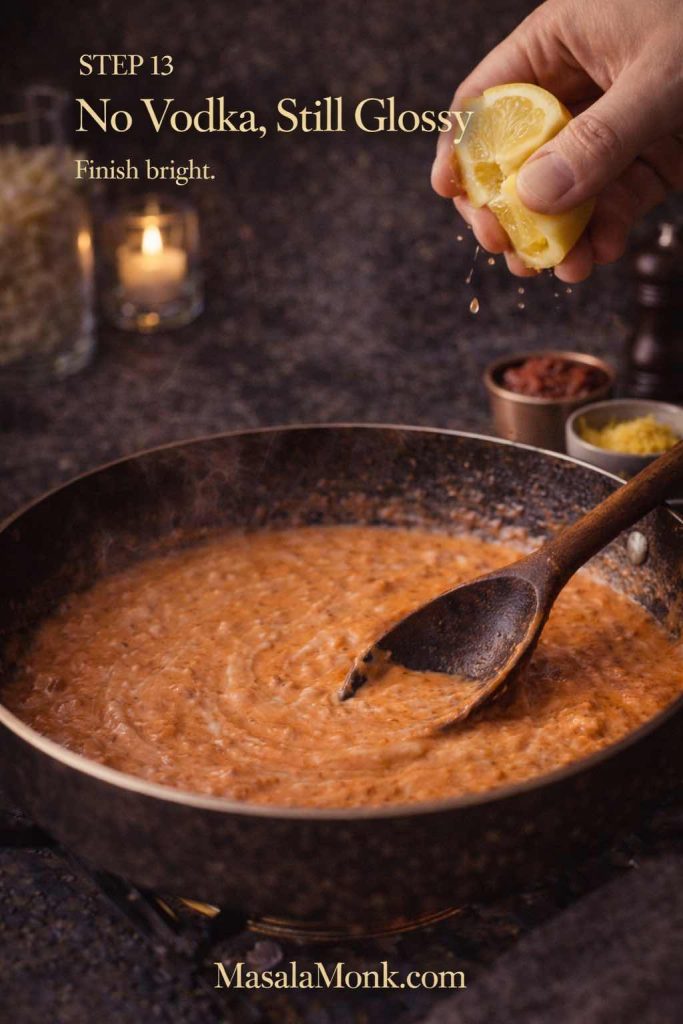
To make chicken pesto tortellini, add shredded chicken at the end and toss briefly. Then add cherry tomatoes or roasted peppers for sweetness. Finish with pepper and a squeeze of lemon. As a result, the bowl stays bright rather than heavy.
Pesto and tortellini with vegetables
For a lighter dinner, add vegetables. Broccoli, peas, asparagus, and zucchini all work. Add sturdy vegetables earlier and leafy greens later. Meanwhile, keep the pesto coating light and glossy.
This is a simple way to practice how to cook tortellini while also making it feel fresh and varied.
Also Read: 7 Pizza Sauce Recipes | Marinara, White Garlic, Alfredo, Buffalo, BBQ, Vodka & Ranch
Creamy tortellini pasta that tastes rich but not heavy
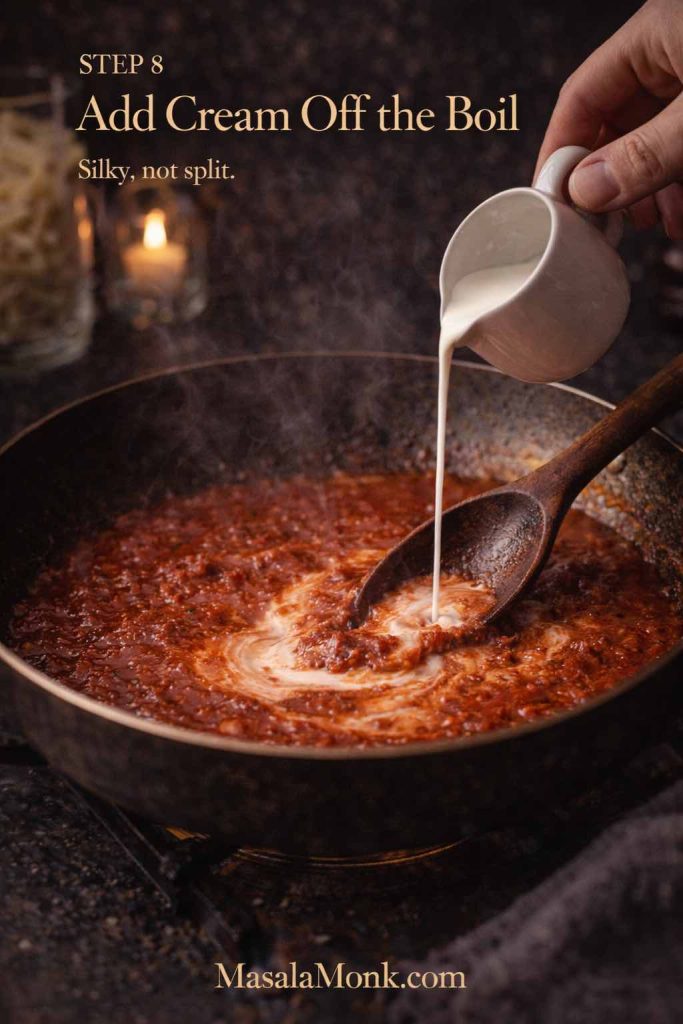
Creamy tortellini is comfort food. Still, it doesn’t have to feel overly heavy. The trick is using pasta water to create a silky sauce rather than a thick one.
Start with butter and garlic in a pan. Add cream and warm gently. Then add tortellini and toss. Finally, loosen with pasta water until glossy. Finish with Parmesan and pepper.
For creamy pasta technique and variations, these MasalaMonk resources are excellent companions:

Cream cheese tortellini for weeknights
Cream cheese tortellini is a fast shortcut that still tastes luxurious. Warm a splash of broth or milk, whisk in cream cheese, and then loosen with pasta water. Add garlic, pepper, and Parmesan. Toss in tortellini and finish with spinach.
Because spinach adds freshness, the bowl feels balanced. Moreover, it turns “creamy” into “creamy but not too much.”
Creamy chicken tortellini and creamy sausage tortellini
To make creamy chicken tortellini, stir shredded chicken in at the end and finish with lemon zest or herbs. For creamy sausage tortellini, brown sausage first, then build the cream sauce around it. Add spinach near the end for color and contrast.
When you’re building these bowls, you’re practicing how to cook tortellini and how to finish it properly—two skills that make the whole category easier.
Also Read: Oat Pancakes Recipe (Healthy Oatmeal Pancakes)
Tortellini pomodoro and marinara tortellini for classic comfort
Tomato sauce is one of the easiest ways to balance rich fillings. Tortellini pomodoro tastes bright and simple, while marinara tortellini leans more cozy and savory.
Warm tomato sauce in a pan. Cook tortellini. Add it to the sauce and toss gently. Use pasta water to help the sauce cling. Finish with Parmesan and a drizzle of olive oil.
If you like making sauce from scratch, MasalaMonk has a helpful guide to tomato sauce from fresh tomatoes. If you want multiple sauce styles for different moods, this roundup is useful: sauce variations including marinara and vodka.
How to cook tortellini and mushrooms in tomato sauce
Sauté mushrooms until browned. Add them to the sauce. Then toss in tortellini and finish with Parmesan and pepper. This works especially well with mushroom tortellini, but it upgrades plain cheese tortellini too.
Tortellini and spinach in tomato sauce
Add spinach at the end so it stays green. Meanwhile, keep the sauce bright with a little basil or oregano.
In both cases, the key is the finish: that quick toss is still how to cook tortellini so it tastes unified.
Also Read: Double Chocolate Chip Cookies – Easy Recipe with 7 Variations
Bolognese tortellini, ground beef tortellini, and sausage tortellini
Ragù-style sauces pair beautifully with tortellini, particularly meat tortellini and cheese tortellini. However, because tortellini filling is already rich, the sauce should be savory and balanced rather than greasy.
For a solid ragù foundation, MasalaMonk’s bolognese sauce recipe is a great internal reference.
How to cook ground beef and tortellini: weeknight ragù energy
Brown ground beef with onion and garlic. Add tomato sauce and herbs. Simmer briefly. Cook tortellini separately, then toss it into the sauce for a minute with a splash of pasta water. Finish with Parmesan.
Italian sausage and tortellini: deeper flavor, same method
Brown sausage first. Add onion and garlic. Add sauce and a splash of broth. Toss in cooked tortellini and finish with spinach and Parmesan. Consequently, sausage and tortellini tastes hearty without feeling clumsy.
Tortelloni bolognese note
If you’re using tortelloni (larger stuffed pasta), keep the stirring gentle and taste early. Tortelloni can be slightly more delicate when hot, so finishing carefully matters even more.
In every case, you’re applying the same idea: cook tortellini gently, then finish it briefly in sauce. That’s how to cook tortellini so it stays intact and tastes cohesive.
Also Read: 10 High Calorie Protein Shakes & Smoothie Recipes for Healthy Weight Gain
How to cook one pot tortellini that doesn’t feel like a shortcut
One pot tortellini is popular because it saves dishes, but it can also taste genuinely good when the sauce and pasta finish together.
Start by sautéing onion and garlic in olive oil. Add broth and sauce. Bring to a gentle simmer. Add tortellini and cook until tender. Finish with Parmesan and herbs.

If you like the general one-pot structure, MasalaMonk’s one-pot chicken bacon ranch pasta shows the comfort-forward approach in a way that’s easy to adapt.
One pot tortellini and sausage
Brown sausage first to build flavor. Then add onion and garlic, pour in marinara and broth, and add tortellini. Finish with spinach and Parmesan.
One pot chicken and tortellini
Build a lighter base with broth and a spoonful of tomato sauce. Add tortellini, then stir in shredded chicken near the end. Finish with basil and pepper. Alternatively, swap the tomato base for pesto and you’ve got chicken tortellini with pesto in a one-pot lane.
One pot tortellini and vegetables
Add broccoli, peas, asparagus, or zucchini. Add sturdy vegetables earlier and greens later. Meanwhile, keep the sauce simple so the bowl stays clean.
These dinners reinforce how to cook tortellini while also keeping the routine interesting.
Also Read: Healthy Pumpkin Spice Latte (Low Cal, Real Pumpkin)
Slow cooker tortellini and crock pot chicken tortellini that stays tender
Slow cooker tortellini can be excellent, yet timing matters. Tortellini cooks quickly, so it should go in near the end. Add it too early and it turns soft. Therefore, build the base first, then add tortellini late.

For a useful internal reference on slow cooker soup structure, MasalaMonk’s crock pot lasagna soup is a strong companion.
How to cook chicken tortellini crock pot style (brothy or creamy)
Add chicken, broth, aromatics, and vegetables to the slow cooker. Cook until the chicken is tender, then shred it. Add tortellini during the final stretch. Finish with spinach and Parmesan.
For a creamy version, stir in cream cheese or a splash of cream right before serving. This approach naturally covers chicken tortellini crock pot, chicken tortellini in crock pot, chicken tortellini slow cooker, and crockpot chicken and tortellini without forcing anything.
How to cook slow cooker tortellini with sausage
Brown sausage if you can; it adds depth. If you’re short on time, it still works, although the flavor is milder. Add sauce and broth, let the base cook, then add tortellini near the end. Finish with Parmesan and pepper.
Again, the principle holds: timing is the heart of how to cook tortellini in slow cooker meals.
Also Read: Mayo Recipe: 15+ Homemade Mayonnaise Variations
How to cook instant Pot tortellini with better control
Stuffed pasta can overcook under pressure, so a controlled simmer often works better than a long pressure cook.
Use sauté mode to cook onion and garlic. Add broth and sauce. Bring to a simmer. Add tortellini and cook until tender, tasting early. Finish with Parmesan and herbs.
It’s simple, yet it’s reliable. In other words, it’s a practical way to apply how to cook tortellini when you want speed without guesswork.
Also Read: Instant Pot Lentil Recipes for Effortless Weight Loss and Quick Meals
Air fry tortellini: crunchy snacks and easy appetizers
Air fried tortellini is crunchy, salty, and perfect for dipping. It’s also a great way to make a simple package feel like a fun event.
Cook tortellini first. Drain thoroughly and pat dry. Toss lightly with oil and seasoning. Air fry until crisp, shaking occasionally for even browning.

For a tested external reference, The Kitchn shares a method and review on air-fried cheese tortellini.
Air fryers vary, so technique matters. If you run into uneven browning or sogginess, MasalaMonk’s air fryer mistakes guide helps you troubleshoot quickly.
For another crisp snack companion, MasalaMonk’s air fried chilli garlic potato bites is a fun pairing idea for parties.
Serve air fry tortellini with marinara, pesto, or a creamy dip. If you want “fried tortellini” vibes without deep frying, this method hits that craving.
Also Read: French Toast Sticks (Air Fryer + Oven Recipe) — Crispy Outside, Custardy Inside
Tortellini prosciutto e panna: How to cook the creamy classic
Tortellini prosciutto e panna is one of those dishes that tastes like you ordered it, even though it comes together quickly. You get a silky cream sauce, savory prosciutto, tender pasta, and a peppery finish.
For a traditional reference, La Cucina Italiana shares a classic approach on tortellini panna e prosciutto.
To make it at home, cook tortellini gently and reserve pasta water. Warm butter in a pan, sizzle chopped prosciutto briefly, then add cream. Toss in tortellini and loosen with pasta water until glossy. Finish with black pepper and Parmesan.
If you enjoy understanding how different Parmesan styles affect flavor, MasalaMonk’s Parmesan guide is a great companion.
This dish is also a reminder that how to cook tortellini for cream sauces is mostly about the finish: gentle toss, glossy coating, and serving promptly.
Also Read: Peanut Butter Cookies (Classic Recipe & 3 Variations)
Store-bought tortellini: Rana, Barilla, Buitoni, and what really matters
Store-bought tortellini can taste excellent. The secret isn’t magic—it’s matching format to method and finishing properly.
- For refrigerated rana tortellini or giovanni rana tortellini, keep the simmer gentle and taste early. If you want a concrete reference for timing, check Giovanni Rana’s instructions.
- For pantry-style products such as barilla tortellini (where available), longer boiling and sturdier sauces work well. Timing expectations are reflected on Barilla’s recipe page.
- For buitoni tortellini, the same logic applies: salted water, gentle simmer, early tasting, and a brief finish in sauce.
If you like browsing for variation ideas, these external sources are useful for inspiration:
- Epicurious: ways to turn tortellini into dinner
- Bon Appétit: tortellini ideas
The big takeaway is simple: brands vary, but how to cook tortellini successfully is consistent—gentle cooking and a smart finish.
Also Read: Moscow Mule Recipe (Vodka Mule): The Master Formula + 9 Variations
Dietary versions: vegan tortellini, vegetarian tortellini, gf tortellini, eggless, non-dairy
Tortellini can fit many diets if you choose the right product and pair it with the right sauce.
- Vegan tortellini / non dairy tortellini: finish in tomato sauce, broth, or dairy-free pesto. For pesto flexibility, MasalaMonk’s pesto hub is a helpful starting point.
- Vegetarian tortellini: cheese tortellini and spinach and ricotta tortellini work beautifully in pesto, tomato, and light cream lanes.
- GF tortellini: keep the simmer gentle and stir carefully, since gluten-free pastas can be more delicate.
- Eggless tortellini: treat it like delicate fresh pasta and avoid aggressive boiling.
If you occasionally enjoy pasta alternatives, MasalaMonk has thoughtful reads on lentil pasta and keto-friendly pasta alternatives.
No matter the diet, the method stays the same. In other words, how to cook tortellini still comes down to gentle heat, tasting early, and finishing properly.
Also Read: Blueberry Pancakes (6 Recipes) + Homemade Pancake Mix
Troubleshooting: quick fixes when tortellini misbehaves
Even when you’ve learned how to cook tortellini, a few common problems can pop up. Fortunately, most fixes are simple.

Tortellini sticks together
Use a larger pot and more water. Stir gently right after adding it. If it clumps anyway, don’t force it aggressively; often it loosens as it cooks.
Tortellini splits or leaks filling
Lower the boil to a lively simmer. Stir less. Drain gently. If it’s frozen, don’t thaw first.
Tortellini turns mushy
It likely overcooked or sat too long in hot sauce. Next time, taste earlier and serve soon after finishing.
Sauce is thin or slides off
Use reserved pasta water and toss longer. The starch helps emulsify. As a result, the sauce clings instead of slipping.
Also Read: Baked Jalapeño Poppers (Oven) — Time, Temp & Bacon Tips
Leftovers: storing and reheating without ruining the texture
Tortellini is best fresh, yet leftovers can still be enjoyable when reheated gently.

For safety guidance, these references are reliable:
- USDA: leftovers and food safety
- FoodSafety.gov: cold storage chart
For texture, reheat slowly and add a splash of liquid:
- For creamy tortellini pasta, add a little milk or water and warm gently.
- For tomato-based tortellini, add a spoonful of water and stir.
- For tortellini in broth, warm slowly without boiling hard.
This approach preserves the “just cooked” feel as much as possible.
Also Read: Classic Deviled Eggs (Easy) + 8 Flavorful Variations
What to serve with tortellini so dinner feels complete
A good side dish doesn’t need to be complicated. It just needs to complement the bowl.
Garlic bread is a classic with marinara tortellini and bolognese tortellini. If you want a homemade option, MasalaMonk’s garlic bread loaf recipe fits naturally.

If you’re building a more social meal—especially with tortellini prosciutto e panna—a small board works beautifully. MasalaMonk’s charcuterie board guide can help you set that up with confidence.
For quick seasoning support in soups and sauces, an herb blend can help. MasalaMonk’s Italian seasoning mix is a simple pantry staple.
If you want baked-pasta comfort on another night, MasalaMonk’s baked ziti recipes can offer inspiration, while their béchamel sauce guide and cottage cheese lasagna are excellent for creamy, layered comfort.
A simple dinner “template” that makes tortellini nights effortless
When you’re holding a pack of tortellini and don’t want to overthink, use this quick template:
- Pick the format: fresh/refrigerated, frozen, or dried.
- Pick the lane: pesto, creamy, tomato, broth, or ragù.
- Pick one add-in: chicken, sausage, mushrooms, or greens.
- Pick a finish: Parmesan, pepper, lemon, or herbs.
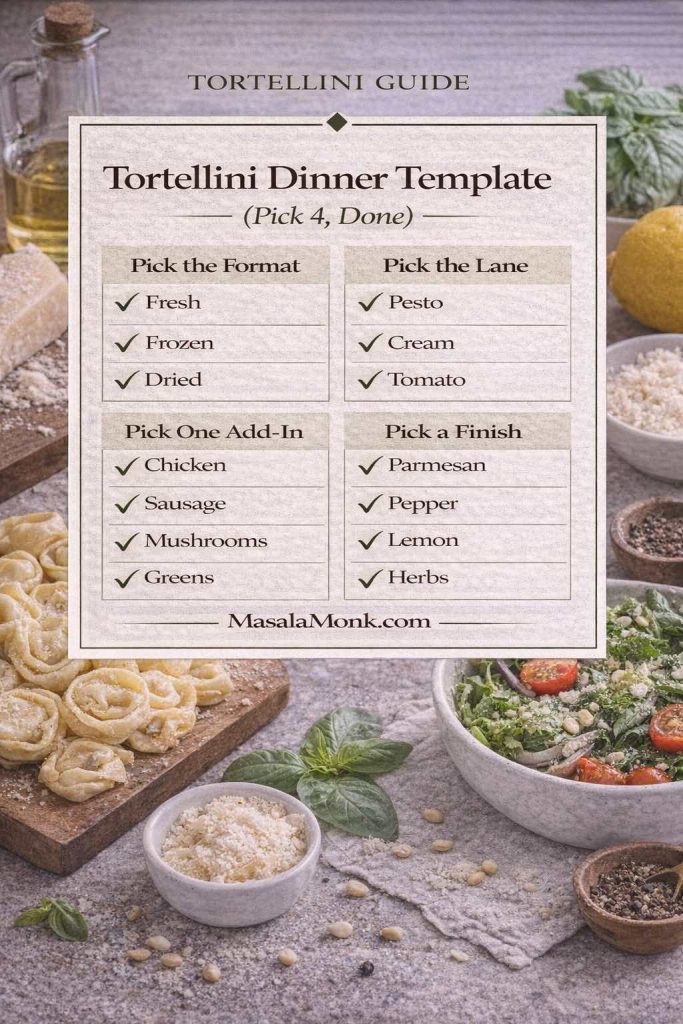
That’s it. With those four choices, you’ll never feel stuck—and you’ll naturally practice how to cook tortellini in ways that keep getting easier.
Also Read: Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas Recipe (Easy One-Pan Oven Fajitas)
The bottom line on how to cook tortellini
The best way to master how to cook tortellini isn’t memorizing an exact number of minutes. It’s repeating the same handful of habits until they become automatic: salt the water, keep the simmer controlled, taste early, reserve pasta water, and finish in sauce or broth.
From there, tortellini becomes endlessly flexible. Pesto tortellini can become a bright chicken dinner. Creamy tortellini pasta can become a cozy bowl with spinach. Tortellini pomodoro can become a reliable classic. Tortellini in brodo can become your comforting reset meal. One pot tortellini can become your low-dishes routine. Slow cooker tortellini can become your hands-off plan. Air fry tortellini can become your crunchy appetizer.
Once you have the rhythm, you won’t just know how to cook tortellini—you’ll know how to turn it into dinner, almost any way you want, whenever you need it.
Also Read: How to Make Churros (Authentic + Easy Recipe)
FAQs about How to Cook Tortellini
1) How long does it take to cook tortellini?
Most tortellini cooks quickly, yet the exact time depends on whether it’s fresh tortellini, refrigerated tortellini, frozen tortellini, or dried tortellini. In practice, the best approach is to taste early and keep checking until the pasta is tender and the filling is hot through the center. If you’re learning how to cook tortellini consistently, tasting is more dependable than relying on one fixed number.
2) How do I know when tortellini is done cooking?
Tortellini is done when the pasta feels tender but still springy and the filling tastes fully warmed. Also, the pieces usually look slightly plumper. If the pasta feels firm at the edges, it needs a bit more time. Conversely, if it feels floppy or waterlogged, it likely cooked too long.
3) Should tortellini float when it’s finished?
Often, tortellini will float as it nears doneness, although floating alone isn’t a guarantee. Instead, treat floating as a sign to start tasting. That way, you’ll learn how to cook tortellini to the exact texture you like.
4) Do I cook frozen tortellini without thawing?
Yes—cook frozen tortellini straight from frozen. Thawing can weaken the pasta and increase the chance of splitting. Rather than thawing, add the frozen tortellini to salted water at a controlled boil and taste early as it cooks.
5) Why does my tortellini break or leak filling?
Tortellini may split if the boil is too aggressive, if it’s stirred roughly, or if it’s overcooked. For better results, keep the water at a lively simmer, stir gently only at the start, and drain carefully. In addition, finishing tortellini in sauce with a light toss helps prevent tearing.
6) What’s the best way to cook cheese tortellini?
Cheese tortellini tastes best when the water is salted and the pasta is finished briefly in sauce. After draining, toss it in marinara, pesto, or a light cream sauce with a splash of pasta water to help the sauce cling. If you’re focusing on how to cook tortellini for weeknights, cheese-filled tortellini is the easiest place to start.
7) How do I cook spinach and ricotta tortellini without making it soggy?
For spinach and ricotta tortellini (also called ricotta spinach tortellini or tortellini ricotta spinaci), use a gentle simmer and start tasting early. Then, avoid letting it sit in a colander. Instead, transfer it straight into a warm sauce so it stays tender yet not mushy.
8) Can I cook tortellini in broth?
Absolutely. Tortellini in broth is a classic way to serve stuffed pasta. Warm the broth gently, then cook tortellini at a mild simmer until tender. Afterwards, add herbs or spinach near the end for a fresher bowl.
9) What is tortellini in brodo?
Tortellini in brodo is tortellini served in broth, traditionally associated with Bologna. Even at home, it’s straightforward: a flavorful broth, tender tortellini, and a simple finish like Parmesan and pepper.
10) How do I make pesto tortellini without it turning oily?
To keep pesto tortellini glossy, warm the pesto gently instead of boiling it. Then, add a splash of reserved pasta water while tossing. As a result, the sauce emulsifies and coats the tortellini evenly.
11) What’s the easiest creamy tortellini pasta for beginners?
A simple creamy tortellini pasta often starts with butter, garlic, and cream, finished with pasta water for a silky texture. Alternatively, cream cheese tortellini is even simpler: melt cream cheese with a little milk or broth, then loosen with pasta water before tossing in tortellini.
12) Can I make one pot tortellini?
Yes—one pot tortellini is a practical dinner. Simmer your sauce with broth, then add tortellini and cook until tender. Finally, finish with Parmesan or herbs. This method works particularly well for cheese tortellini pasta and tortellini with veggies.
13) Can I make tortellini in a slow cooker or crock pot?
Yes, though timing matters. For slow cooker tortellini or crock pot tortellini, build the soup or sauce base first and add tortellini near the end so it doesn’t overcook. The same idea applies to chicken tortellini crock pot and chicken tortellini slow cooker recipes.
14) How do I make chicken tortellini in a crock pot without mushy pasta?
Cook the chicken and broth base first, shred the chicken, then add tortellini during the last part of cooking. That way, the tortellini stays tender. Likewise, add spinach at the end so it remains bright.
15) Can I cook tortellini in an Instant Pot?
Yes, although it’s easy to overcook stuffed pasta under pressure. For better control, use sauté mode to build flavor, then simmer tortellini gently until tender. This approach fits how to cook tortellini when you want speed without guesswork.
16) How do I make air fryer tortellini?
To make air fry tortellini (or air fried tortellini), cook tortellini first, drain well, pat dry, then toss lightly with oil and seasoning. Next, air fry until crisp, shaking occasionally for even browning. Serve with marinara, pesto, or a creamy dip.
17) What’s the difference between tortellini and tortelloni?
Tortelloni is larger than tortellini and often has a softer, more delicate feel. Because of its size, it may need a bit more time to heat through. Still, the same principles for how to cook tortellini apply: gentle simmer, early tasting, and a careful finish in sauce.
18) How do I cook store-bought tortellini like Rana tortellini or Buitoni tortellini?
For rana tortellini, giovanni rana tortellini, and buitoni tortellini, follow the package timing as a baseline, then taste to confirm doneness. Usually, refrigerated styles cook quickly, whereas dried versions take longer. In all cases, finishing in sauce with pasta water improves texture and flavor.
19) How do I keep tortellini from sticking together?
Use plenty of water, stir gently right after adding tortellini, and avoid overcrowding the pot. Additionally, don’t drain and let it sit too long; transferring into sauce promptly helps keep pieces separate.
20) Can I reheat tortellini without it turning mushy?
Yes. Reheat gently with a splash of liquid—water for tomato sauces, milk or broth for creamy sauces, and extra broth for soups. Then warm slowly rather than boiling hard. This method helps preserve texture when you’re practicing how to cook tortellini for leftovers, too.
21) Can tortellini be vegetarian or vegan?
Yes. Vegetarian tortellini often includes cheese or spinach and ricotta. Vegan tortellini and non dairy tortellini are also available depending on brand and store. Even so, the cooking method stays similar: gentle simmer, early tasting, and a careful finish.
22) Is there gluten-free tortellini?
Yes—gf tortellini exists, although it can be more delicate than wheat-based pasta. Therefore, keep the simmer controlled, stir minimally, and taste early so it doesn’t overcook.
23) Can I make tortellini with sausage or ground beef?
Definitely. Sausage tortellini works well in tomato sauce, creamy sauces, or one-pot dinners. Similarly, ground beef tortellini pairs nicely with a bolognese-style sauce. For best texture, cook tortellini separately and toss it in the sauce briefly right before serving.
24) What are the best sauces for tortellini?
The best sauces depend on the filling. Cheese tortellini suits pesto, marinara, pomodoro, and cream sauces. Spinach and ricotta tortellini often shines with lighter tomato or butter-garlic sauces. Meat tortellini is excellent in broth and also works in ragù. When in doubt, keep the sauce balanced and let the filling lead.
25) Why does my tortellini taste bland even when the sauce is good?
Usually, the cooking water wasn’t salted enough, or the tortellini wasn’t finished in sauce. Salted water seasons the pasta itself, while a short toss in sauce helps the flavors stick. Together, those steps are the simplest upgrade in how to cook tortellini so it tastes fully seasoned.