When you think of the world’s most expensive wines, your mind might drift to the fabled vineyards of Bordeaux or Burgundy. But in recent decades, a handful of American wines—mostly from California’s Napa Valley—have joined the global elite, shattering auction records and creating a cult-like following. What makes these bottles so valuable, who is buying them, and what should you know if you want to experience a piece of American wine history? Let’s uncork the secrets behind the USA’s most sought-after wines.
1. The Icons: Meet America’s Most Expensive Wines
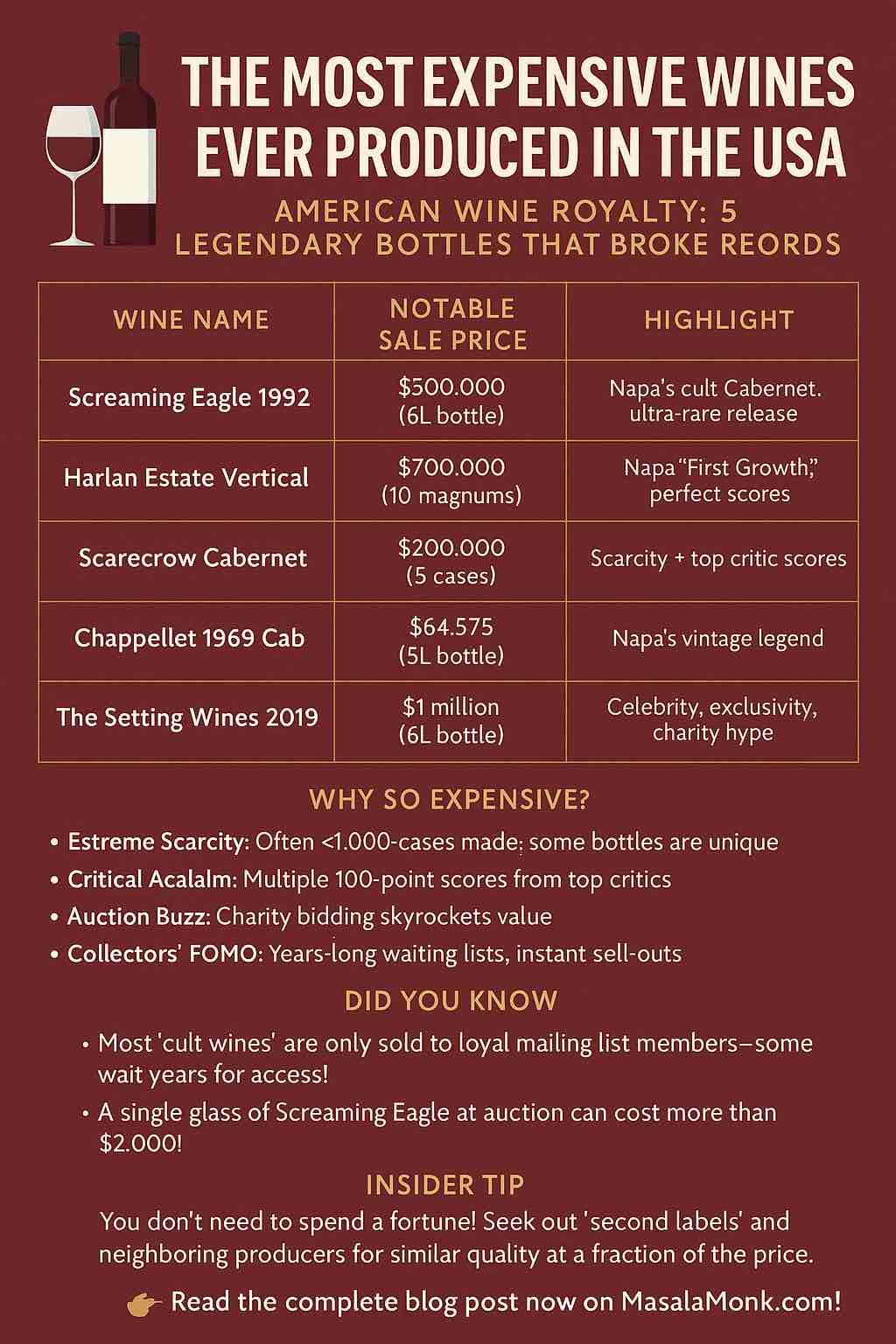
Here’s a breakdown of some of the most jaw-droppingly expensive wines produced in the United States, with real-world sales and auction records to back them up.
Screaming Eagle Cabernet Sauvignon (Napa Valley)
- Record Sale: A 6-liter (imperial) bottle of the 1992 vintage sold for $500,000 at the Napa Valley charity auction in 2000.
- Typical Price: Even today, a standard bottle fetches $3,000–$8,000, depending on the vintage and provenance.
- Why so valuable?: Micro-production (hundreds of cases per year), near-mythic status among collectors, and a mailing list harder to get on than the waitlist for the newest iPhone. Screaming Eagle is the blueprint for a “cult” Napa wine.
Harlan Estate Cabernet Sauvignon (Napa Valley)
- Record Sale: A vertical of 10 magnums sold for $700,000 at auction.
- Typical Price: $1,500–$2,500 per 750ml bottle.
- Why so valuable?: Consistently high critic scores, lush branding, and a reputation as the “First Growth” of California. Each release is instantly snapped up by collectors worldwide.
Scarecrow Cabernet Sauvignon (Rutherford, Napa Valley)
- Record Sale: Five cases (60 bottles) sold for $200,000 at Premiere Napa Valley Auction 2017 (that’s over $3,000 per bottle).
- Typical Price: $1,000–$2,000 per bottle.
- Why so valuable?: Scarcity (often less than 1,000 cases/year), direct-to-list allocation, and wines that critics describe as “powerful, but with finesse.”
Chappellet 1969 Cabernet Sauvignon (Pritchard Hill, Napa)
- Record Sale: One of only four 5-liter bottles ever made sold for $64,575 at Heritage Auctions in 2024. Two magnums fetched over $54,000 each, and a single 750ml bottle reached $17,220.
- Why so valuable?: Historical significance—an iconic early Napa Cabernet from a legendary vintage and producer. The older the better, when it comes to provenance and storytelling.
The Setting Wines Alexander Valley Cabernet Sauvignon 2019
- Record Sale: A 6-liter bottle sold for $1 million at charity auction in 2021, smashing previous records for modern California wines.
- Why so valuable?: Limited edition, celebrity association, charity hype, and a compelling narrative that connects the wine to pop culture.
2. What Makes These Wines So Expensive? The Secret Ingredients
Rarity & Scarcity:
Most of these producers release just a few hundred to a couple thousand cases a year. Some bottles are even more limited—just a handful of magnums or imperials, sometimes auctioned for charity, never to be seen again.
Critical Acclaim:
A high score (95–100 points) from critics like Robert Parker, Wine Spectator, or Jancis Robinson can instantly double the value of a wine. Some bottles earn legendary “100-point” scores year after year.
Exclusivity & Allocation:
Want to buy Screaming Eagle or Scarecrow at release price? Get in line. Most are sold only via ultra-exclusive mailing lists. Some lists take years to join, others close altogether. The result? Instant aftermarket markups.
Provenance & Storytelling:
The story behind a wine—an iconic vintage, a rare format, or a connection to a famous event (like the Judgment of Paris, or a celebrity endorsement)—boosts the price and desirability.
Charity Auction Hype:
Many record sales happen at charity auctions, where prestige and philanthropy collide and bidders go above and beyond to support a cause (and secure bragging rights).
3. Not Just for Billionaires: Practical Advice for Wine Lovers
You don’t need a black card or a mansion in Bel Air to enjoy some of the best that American wine has to offer. Here’s how you can get involved, no matter your budget or experience level:
Start with “Cult Adjacent” Wines
While Screaming Eagle may be out of reach, many neighboring wineries or off-vintages offer a taste of Napa magic for a fraction of the price. Seek out:
- Forman, Spottswoode, Corison, Mayacamas, Ridge, Dunn, and Stag’s Leap for ageworthy, classic Napa Cabernet.
- Paso Robles, Santa Barbara, and Oregon for up-and-coming producers with excellent price-to-quality ratios.
Explore Second Wines and Lesser Vintages
Some cult producers offer “second labels” made from younger vines or barrels not selected for the flagship wine. Examples: “The Maiden” from Harlan, “Leviathan” from Andy Erickson (former Screaming Eagle winemaker).
Attend Tastings and Join Collectors’ Groups
Wine shops, sommeliers, and local clubs often host events featuring rare bottles. These tastings are a great way to try legendary wines by the ounce (or glass), not the bottle.
Track Auction Markets
Websites like WineBid, Heritage Auctions, and Wine-Searcher let you follow prices, provenance, and sometimes even snag “sleepers” (wines that are undervalued).
Investing in Wine? Know the Risks
Fine wine can appreciate in value, but storage, provenance, and market trends all matter. If you plan to collect or invest, consider professional storage, insurance, and focus on blue-chip producers with consistent demand.
4. What Does a $5,000 Bottle Actually Taste Like?
Let’s get real: The world’s most expensive wines are about more than just taste. Yes, they’re expertly made, meticulously farmed, and cellared under perfect conditions. But what you’re really paying for is the experience—the history, the story, and the privilege of sharing something truly rare.
That said, legendary bottles like Screaming Eagle, Harlan Estate, or a perfectly preserved Chappellet 1969 can offer unforgettable moments:
- Aromas of blackcurrant, tobacco, graphite, violets, and exotic spices.
- Textures that are both silky and powerful.
- Flavors that evolve over hours in the glass—layer upon layer of fruit, earth, and savory depth.
- A finish that seems to last forever, lingering on the palate and in memory.
Most of all, you’re tasting history: a living snapshot of a place, time, and the vision of its creators.
5. Final Thoughts: Why Collect or Care About Expensive Wines?
Whether you dream of owning a legendary bottle or just want to know what all the fuss is about, America’s most expensive wines are more than status symbols—they’re a testament to what’s possible when land, artistry, and a bit of hype come together.
You don’t have to buy a $10,000 bottle to share in that spirit.
Exploring wine is about curiosity, community, and finding your own “wow” moments—whether that’s a Screaming Eagle Cabernet or a backyard BBQ Zin.
What’s the most memorable wine you’ve ever tried? Would you ever splurge for a bucket-list bottle, or do you have a favorite hidden gem? Share your story below! 🍇🍷👇
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most expensive wine ever produced in the United States?
The 1992 Screaming Eagle Cabernet Sauvignon holds the record, with a 6-liter bottle selling for $500,000 at a charity auction in 2000. However, more recent charity lots and ultra-limited releases (like The Setting Wines 6L at $1 million) have challenged this figure, but these prices are typically realized in unique charity auction settings.
2. Why are certain American wines so expensive?
Their high price is due to a combination of extreme rarity, critical acclaim, prestigious history, limited direct allocations (usually through exclusive mailing lists), and heightened demand among collectors. Charity auctions can further inflate prices due to competitive bidding and philanthropic motives.
3. Are these expensive wines actually better in taste than regular wines?
Not necessarily for every palate. While they are often world-class and exceptionally well-made, much of their value comes from rarity, collectibility, brand, and story. Many moderately priced wines can provide an outstanding tasting experience, especially to those new to fine wine.
4. Can regular consumers ever buy these cult wines at retail price?
Rarely. Most are allocated to long-standing mailing list members or high-profile collectors. Secondary market prices (auction or wine retailers) are usually much higher than release price. Some wine shops occasionally receive a bottle or two, but expect to pay a premium.
5. Is wine a good investment?
Fine wine can appreciate in value, but it’s not guaranteed. Top producers like Screaming Eagle, Harlan Estate, and Sine Qua Non have strong track records, but storage, provenance, and market timing are crucial. Beginners should research thoroughly or consult with experts before investing.
6. How should I store high-value wine?
High-value wines require proper cellaring: a consistent cool temperature (around 55°F/13°C), humidity around 70%, minimal vibration, and no direct light. Professional storage facilities are best for bottles valued in the thousands.
7. Can I ever taste these wines without buying a bottle?
Yes! Look for wine tasting events, charity dinners, or special tastings at top restaurants or wine clubs. Occasionally, “by the ounce” pours of rare bottles are offered, especially in major wine regions.
8. What is a “second wine” or “second label” and are they worth buying?
A second wine is made from the same producer but typically from younger vines or lots not selected for the flagship label. They are more affordable and can offer great value, giving you a taste of a top estate’s style at a lower price point.
9. What are some alternatives to Napa Valley for high-quality American wines?
Look to regions like Sonoma County, Santa Barbara, Paso Robles, and Oregon’s Willamette Valley for world-class wines at more accessible prices. Producers in these regions are gaining international acclaim.
10. How do I join a mailing list for these cult wineries?
Visit the winery’s official website and look for their “Mailing List” or “Allocation List.” Sign up as early as possible—many top lists are full and only accept new members when someone drops off. Some require years of waiting or minimum purchase commitments.














