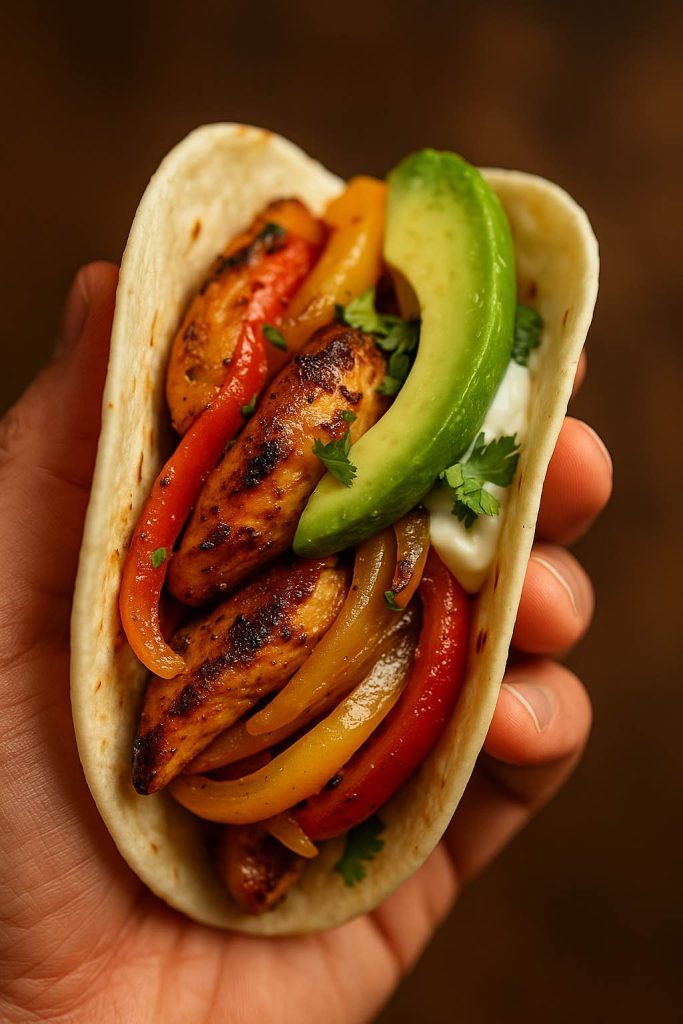
Sheet pan chicken fajitas are one of those meals that feel like a tiny miracle. You get juicy chicken, caramelised onions, and colourful peppers, all sizzling with smoky fajita spices, but instead of juggling three pans on the stove, everything happens together on one tray in the oven. It’s the kind of recipe that works on frantic weeknights, lazy Sundays, game days, and everything in between. This sheet pan chicken fajitas recipe is all about ease.
You toss strips of chicken and vegetables in a bold spice blend, spread them over a pan, and let the oven transform them into tender, slightly charred perfection. While your oven fajitas roast, you can warm tortillas, mix a simple sauce, or just sit down for a minute and breathe. By the time the timer rings, the kitchen smells like your favourite Tex-Mex spot, and you’ve got a full chicken fajita sheet pan dinner ready to slide onto the table.
Why Sheet Pan Fajitas Chicken Recipe Beats Skillet Fajitas
Traditional skillet fajitas chicken has its charms: a screaming-hot skillet for fajitas, that dramatic sizzle as the pan hits the table, the cloud of steam scented with lime and chili. Yet there’s a reason sheet pan fajitas have become such a staple in modern kitchens.

First, there’s the simplicity. With this easy sheet pan chicken fajitas method, you’re making a true one pan chicken fajita dinner. Instead of cooking in batches, then keeping everything warm, the meat and vegetables roast together. That means less hovering, fewer dishes, and more time to deal with everything else calling your name.
Second, the texture is fantastic. High oven heat encourages the peppers and onions to soften while still keeping a bit of bite, and the chicken picks up lovely browned edges. When you spread everything out properly on the tray, your baked chicken fajitas end up tasting like you fussed far more than you did.
Finally, this style is incredibly flexible. You can turn it into a chicken fajita tray bake for a crowd, scale down to chicken fajitas for one, make it extra spicy, keep it mild for kids, or adapt the marinade for pork, shrimp, or vegetables. Once you’ve learned the rhythm of cooking chicken fajitas in the oven, you’ll find yourself using the same technique for other dishes too.
Also Read: 10 Best Espresso Martini Recipe Variations (Bar-Tested)
Understanding Fajitas (and Why They Love the Oven)
Before diving into the nuts and bolts of this sheet pan chicken fajitas recipe, it helps to know what fajitas actually are. Traditionally, fajitas started as strips of grilled skirt steak served with onions and peppers in tortillas as part of Tex-Mex cooking, and the name itself comes from “faja,” meaning “strip” or “belt.” Over time, the concept expanded to include chicken fajitas, shrimp, and even all-vegetable versions, all built around that core idea of savoury strips tucked into warm tortillas.
Because fajitas are usually cooked hot and fast, transferring that method to the oven makes a lot of sense. When you cook fajitas in oven, you’re essentially recreating the high heat of the grill or stovetop, just with a different heat source. The key difference is that instead of shaking a pan throughout the cooking process, you let the oven do most of the work and just give your sheet pan fajita chicken a stir once or twice.
Stovetop chicken fajitas in a pan are still wonderful when you’re in the mood to stand and cook, but making fajitas in the oven is the move when life is hectic. You end up with the same satisfying flavours in a more forgiving, lower-effort format.
Also Read: Katsu Curry Rice (Japanese Recipe, with Chicken Cutlet)
Ingredients for Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas Recipe
You don’t need anything fancy for baking sheet fajitas—just everyday staples that work incredibly well together.

Chicken: breast or thigh
Start with about 700–900 g (1½–2 lb) of boneless, skinless chicken. Both options work:
- Chicken breasts give you leaner chicken breast fajitas oven style fajitas. They cook quickly and slice neatly, which is useful if you’re building bowls or meal-prep boxes.
- Chicken thighs stay juicy even if they roast a little longer, making them ideal for a slightly more forgiving chicken thigh fajitas oven version.
Slice the chicken into thin strips across the grain. Thin, even strips are crucial for chicken fajitas baked in oven because they cook at roughly the same time as the vegetables.

Peppers and onions
Next, grab your vegetables:
- 3 bell peppers (red, yellow, orange, or green)
- 1–2 medium onions
Bell peppers are naturally sweet and full of vitamin C and antioxidants, so they’re one of the reasons these healthy sheet pan chicken fajitas feel as nourishing as they do. Thin slices roast quickly and tuck perfectly into tortillas or bowls. Onions bring savoury depth and a touch of natural sweetness as they caramelise, turning the entire fajita sheet pan dinner into something rich and comforting.
Slice both peppers and onions into strips that mirror the size of your chicken pieces. Matching everything like this makes your one sheet chicken fajitas cook more evenly.

Oil, lime, and spice mix
For that signature fajita flavour, you’ll need:
- Neutral oil (or mild olive oil)
- Fresh lime juice
- Chili powder
- Ground cumin
- Paprika (regular or smoked)
- Garlic powder or minced garlic
- Dried oregano
- Salt and black pepper
- Optional cayenne for heat
This blend turns basic chicken and peppers into full-on fajita chicken sheet pan magic. As the tray roasts, the spices toast and cling to every piece, giving your sheet fajitas their unmistakable colour and aroma.

Tortillas and toppings
Once your chicken fajitas in the oven recipe comes out bubbling and browned, you’ll want a few extras to round things out:
- Flour or corn tortillas
- Grated cheese
- Sour cream or thick Greek yogurt
- Sliced jalapeños
- Fresh coriander
- Extra lime wedges
If you’d like a lighter, more refreshing topping, a bowl of cool Greek tzatziki sauce is a beautiful alternative to sour cream. It brings creaminess, garlic, cucumber, and herbs that play wonderfully with spicy chicken fajita oven tray flavours.
Choosing the Best Sheet Pan for Recipe of Chicken Fajitas
Because this recipe hangs on your pan, it’s worth a quick look at equipment. The same mixture of chicken and peppers behaves differently in a cast-iron chicken fajita pan, a light cookie sheet, and a heavy-duty baking tray.
Sheet pan vs skillet
If you’ve always made skillet fajitas chicken, shifting to the oven might feel like a big step. In reality, each method has its niche:
- A cast-iron skillet for fajitas is unbeatable when you want dramatic sizzle and dark char. You get those hot spots that bring extra browning, and it’s fun for smaller batches you want to serve right away.
- A sturdy sheet pan is better when you need 1 pan chicken fajitas for four people (or more) without hovering. You get more surface area, so your pan sheet chicken fajitas can spread out and roast instead of steaming.
For this recipe, a rimmed, heavy-duty baking sheet is ideal. It’s stable under high heat and holds onto some of that warmth, helping the edges crisp up.

Cookie sheet vs baking sheet
You can absolutely use a cookie sheet if that’s what you have; a lot of people make cookie sheet fajitas and cookie sheet chicken fajitas successfully. Just keep these points in mind:
- Thin pans may warp at high temperatures, which can cause the oil to pool and parts of your pan sheet fajitas to brown faster.
- Darker pans brown more aggressively, which can be great for extra char but requires closer watching at the end.
If you’re shopping with fajitas in mind, look for something marketed as a half-sheet pan or roasting tray. That’s essentially the best pan to cook fajitas in when you’re leaning into the baked fajitas style.
Also Read: Vegan French Toast: 6 Easy Recipes (Pan, Air Fryer, GF & High-Protein)
Step-by-Step: Making Chicken Fajitas in the Oven
Now that your ingredients and pan are ready, it’s time to make easy oven baked chicken fajitas from start to finish.

1. Preheat and prep the tray
Begin by preheating your oven to around 220°C (425°F). This high heat is what makes fajitas baked in oven taste similar to grilled versions. While the oven heats, line your pan with parchment or lightly brush it with oil.
Scatter your sliced peppers and onions across the tray. This base layer becomes the foundation of your sheet pan chicken and peppers, catching juices and seasonings as everything cooks.
Arrange the sliced chicken on top. You’re building your chicken sheet pan fajitas right on the tray, so there’s no need for extra bowls once you get the hang of it.

2. Mix and add the seasoning
Drizzle oil and lime juice over the chicken and vegetables. Sprinkle over your spice mix, making sure every strip has a little colour. Then, use your hands or tongs to toss everything together directly on the pan until the entire chicken fajita sheet pan recipe looks well coated.
At this point, the mixture already resembles a fajita tray bake: vibrant, glossy, and promising. Make sure nothing is piled too high; for the best sheet pan fajitas, you want most pieces in a single layer, or as close as you can get.

3. Roast until juicy and slightly charred
Slide the pan into the hot oven and roast for about 18–22 minutes:
- Stir once halfway through to make sure your pan fajita mix cooks evenly.
- Keep an eye on smaller pieces; they might brown a bit faster at the edges.
- If you’d like a darker finish, you can increase the heat slightly or use the broiler for the last few minutes for broiled chicken fajitas.
For safety, aim for an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) in the thickest pieces of chicken. A small instant-read thermometer takes the guesswork out of this part and guarantees fully cooked baked chicken fajitas every time.
When the chicken is opaque and tender and the vegetables have softened and picked up browned spots, your oven baked chicken fajita recipe is ready.
Also Read: Baked Jalapeño Poppers (Oven) — Time, Temp & Bacon Tips
Getting the Texture Just Right
Good chicken fajitas baked in oven are all about balance. You want soft onions, tender peppers, and juicy chicken, but you also want enough colour and char to bring depth.

Here are a few small tweaks that make a big difference:
- Spread the mixture out. Crowding the tray makes fajitas bake tray style dishes steam. If things are piled high, use two pans.
- Rotate the pan halfway through if your oven runs hot in certain spots. This simple step can turn a decent fajita sheet pan recipe into the best sheet pan fajitas your oven can produce.
- Stir gently. Flipping everything once in the middle helps both sides brown without shredding the chicken.
If you love the seared edges you get from cooking fajitas in a pan, you can always transfer a portion of the roasted fajita chicken sheet pan mix to a hot cast-iron chicken fajita pan for a minute or two before serving. It’s the best of both worlds: low-effort cooking plus that restaurant-style finish.
Also Read: Vodka with Lemon: Easy Cocktails, Martini Twist & DIY Infusion
Turning One Recipe into Many: Variations on Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas
A good sheet pan fajita chicken base opens up a lot of possibilities. Once you’ve mastered the classic version, you can start playing with different combinations.

Classic tray bake fajitas
You can lean harder into the chicken fajita tray bake idea by nestling lime wedges, whole garlic cloves, and even halved cherry tomatoes around the pan before roasting. As the tomatoes burst and the garlic softens, they create pockets of extra flavour that melt into the juices and coat the chicken.
For a slightly heartier fajita chicken tray bake, try adding:
- Drained black beans or chickpeas
- Frozen corn (no need to thaw)
- Diced sweet potato or small potato cubes for a more substantial baked fajitas recipe
These additions make your chicken fajita sheet pan meal feel more like a complete tray dinner that can be served as is, without many extra sides.

Extra-charred and broiled fajitas
If you lean towards the smoky, charred edges you get from grilling or pan fajita recipe styles, the broiler is your friend. Once the chicken is cooked through, slide the pan under the broiler for two to three minutes, watching closely. The vegetables will blister in places, and you’ll end up with something closer to restaurant-style oven fajitas.
Some cooks like to marinate the chicken first, inspired by recipes like sheet pan chicken fajitas from Serious Eats, then finish under the broiler for a deep, roasty flavour. Others love the simplicity of budget-friendly oven fajitas where you just toss everything and bake. Both approaches fit happily within this chicken fajita recipe sheet pan framework; feel free to adapt.

Sheet pan taco chicken and chicken tacos
Sometimes you’re craving tacos rather than classic fajitas. Luckily, the same sheet pan chicken fajitas mixture doubles as sheet pan taco chicken with almost no changes.
Once your easy sheet pan fajitas come out of the oven:
- Shred a portion of the chicken with two forks.
- Spoon the shredded pieces into small tortillas with extra cheese and salsa.
- Keep some of the sliced version for traditional fajitas.
You’ve just transformed easy baked chicken fajitas into both fajitas and tacos, using one tray and one round of cooking.

Small-batch fajitas for one or two
The beauty of this method is how easy it is to scale down. For chicken fajitas for one, just cut the amounts to a single chicken breast, one pepper, and half an onion. You’ll still spread everything out so it roasts properly, and you’ll still be rewarded with a personal-sized chicken fajita sheet pan dinner without leftovers, if that’s what you prefer.
On evenings when you want leftovers on purpose, doubling the recipe turns the same base into meal prep gold.
Also Read: Coconut Water Cocktails: 10 Easy, Refreshing Drinks
Serving Ideas: Toppings, Sides, and Full Fajita Nights
Once your best sheet pan chicken fajitas are out of the oven, you can serve them simply or turn them into an entire feast.
Classic fajita spread
Lay out warmed tortillas, your sheet pan chicken fajitas, and bowls of toppings:
- Grated cheese
- Sour cream or Greek yogurt
- Salsa or pico de gallo
- Avocado slices or guacamole
- Fresh coriander and lime wedges
If you’d like something a bit different from sour cream, spoon some Greek tzatziki sauce into a bowl and let people drizzle it over their baked chicken fajitas. The cool yogurt, cucumber, and herbs bring a wonderful contrast to the spicy, smoky chicken.

Party platters and game-day food
For gatherings, you can use your one pan fajita recipe as the centrepiece of a game-day spread. Arrange the tray bake fajitas on a board with bowls of tortilla chips, crunchy vegetables, and a few dips. A bubbling Buffalo chicken dip on the side adds creamy heat, while a selection of spinach dips brings extra richness.
If you want something on the side that everyone loves, a tray of crispy homemade French fries turns fajita night into a full-on comfort feast. You can even add a platter of lemon pepper chicken wings so guests can load their plates with wings, fries, and sheet pan chicken fajitas pioneer woman–style trays of sizzling chicken and peppers.
Bowls, salads, and low-carb options
On nights when you’re craving something lighter, skip the tortillas and build fajita bowls:
- Spoon your fajitas in oven chicken over shredded lettuce, rice, quinoa, or cauliflower rice.
- Add beans, corn, chopped tomatoes, and avocado.
- Finish with lime juice and a spoonful of yogurt or tzatziki.
If you’re exploring lower-carb eating, you might enjoy browsing plant-powered keto Mexican recipes for inspiration. You’ll find ideas there for vegetable-based fillings that pair nicely with this fajita oven recipe, especially when you’re using the same spices in creative ways.
Drinks that pair beautifully with this Recipe of Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas
Fajitas are festive by nature, so they love good drinks. For brunch-style spreads or weekend dinners with friends, a pitcher of Bloody Marys or colourful mimosas fits right in with fajitas, nachos, and dip.
If you’re more in the mood for something sweet after dinner, a slice of tres leches cake or another dessert brings everything to a gentle close after the warm spice of your fajita sheet pan chicken.
Leftovers, Meal Prep, and Next-Day Ideas
One of the nicest things about easy oven baked sheet pan chicken fajitas is how gracefully they turn into other meals.
Storing and reheating
Let leftovers cool slightly, then pack them in airtight containers. They’ll keep well in the fridge for three days or so. Reheat gently in a skillet, in the oven, or even in the microwave, though a quick blast in a pan or oven helps revive those tasty browned edges.
Because the vegetables hold up, easy baked chicken fajitas make excellent lunches. Tuck them into tortillas, spoon them over rice, or toss them through salads for quick meals that still feel satisfying.

Fresh ways to use leftovers from Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas Recipe
Leftover sheet pan fajita chicken doesn’t have to be eaten in exactly the same format. You can:
- Turn it into quesadillas by folding the chicken and peppers into tortillas with cheese and crisping them in a pan.
- Build burrito bowls or burritos with rice, beans, and whatever else you have around.
- Add it to omelettes or scrambled eggs for a fajita-style breakfast.
- Stir it through a simple pasta with a bit of cream or yogurt and extra lime juice for a fajita-inspired pasta night.
If you’re looking for more easy chicken ideas to keep in your weekly rotation, recipes like whole chicken in crock pot or cheesy chicken broccoli rice fit right alongside this easy chicken fajitas sheet pan method. They all deliver that same comforting feeling with minimal fuss.
Are Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas Healthy?
Because this sheet pan fajita recipe leans heavily on chicken and vegetables, it’s simple to tweak it towards your own idea of “healthy.”
Protein and vegetables
You’re getting a good dose of protein from the chicken, plus fibre and vitamins from peppers and onions. Bell peppers are rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, while onions contribute their own unique compounds and prebiotic fibre. When you serve this chicken fajita one pan meal with extra vegetables or a salad, you’re building a plate that’s both satisfying and colourful.

Choices that change the balance
The health profile of easy fajitas in the oven depends heavily on what you serve alongside them. Flour tortillas, cheese, sour cream, and chips will make it more indulgent; lettuce, salsa, yogurt, and beans keep it feeling a bit lighter.
You can also swap chicken for vegetables entirely. Jackfruit, mushrooms, and tempeh can all stand in for meat while keeping the spirit of sheet pan fajitas alive. For inspiration, you might enjoy jackfruit-based meal ideas or tempeh “beef” style fillings, both of which adapt beautifully to fajita spices.
If you’re curious about how onions fit into a low-carb or keto approach, you can also explore a gentle breakdown of onions and keto to see how they can still have a place in a mindful diet.
Comparing Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas Recipe to Stovetop Fajitas
It’s natural to wonder how chicken fajitas in oven recipe versions stack up against the classic pan fajita recipe cooked on the stove.
Stovetop fajitas
With cooking fajitas in a pan, you get:
- A bit more control over individual pieces as you stir and flip.
- Very quick cooking, which is great for small batches.
- That sizzle and sear you might associate with restaurant fajitas.
However, you also get more active time at the stove, and if you’re making a large batch of pan fajitas chicken, you may need to cook in rounds.

Oven fajitas
With fajitas baked in oven, you enjoy:
- A mostly hands-off experience: toss, spread, roast.
- The ability to cook a lot at once, ideal for families or leftovers.
- Easy cleanup, because you’ve truly made 1 pan fajitas.
There’s no wrong answer here. Many people use oven methods during the week for easy sheet pan fajitas and save skillet or grilled versions for weekends when they feel like cooking in a more leisurely way. You can even move between methods in the same meal: roast most of the fajita sheet pan bake in the oven, then finish a portion in a hot skillet if you’re craving that extra sear.
Also Read: Whiskey Sour Recipe: Classic Cocktail, Best Whiskey & Easy Twists
A Short Fajita Story to Serve with Dinner
When you bring a tray of sheet pan chicken fajitas to the table, you’re not just serving dinner; you’re offering a tiny piece of culinary history, adapted to modern life. Fajitas may have started as grilled strips of beef cooked over open flames and served to hungry ranch workers, but they’ve travelled a long way from those early days.
Now, they show up as restaurant sizzlers, street food, skillet suppers, and, increasingly, as fajitas in oven chicken dinners pulled from home ovens around the world. Recipes like classic grilled chicken fajitas keep the outdoor tradition alive, while damn delicious sheet pan fajitas and similar recipes prove that you can get big flavour from a humble baking tray.
Your own chicken fajita sheet pan pioneer woman moment might look like a pan pulled from the oven on a Wednesday night, kids spooning sheet pan fajita chicken into tortillas at the counter, someone mixing drinks in the corner, and everyone leaning over the table to build their perfect bite. It doesn’t have to be dramatic; it just has to taste good and feel welcoming.

Bringing It All Together
In the end, this sheet pan chicken fajitas recipe is really an invitation. It invites you to trade a little stovetop juggling for the convenience of easy oven baked fajitas, to let the oven carry more of the load while you use the extra time however you need.
Whether you’re serving classic baked chicken fajitas with warm tortillas, building low-carb bowls from a fajita oven tray, or turning leftovers into quesadillas and tacos, you’re working with a method that’s endlessly adaptable. One night you might pair your pan sheet fajitas with tzatziki and salads; another night you might bring out dips, fries, and wings and turn it into a party.
However you choose to plate them, these best sheet pan chicken fajitas are there to make dinner easier, a little brighter, and a lot more satisfying—one tray at a time.

FAQs about Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas Recipe
1. Can I use chicken breasts or thighs for sheet pan chicken fajitas?
You can use either, and both work beautifully in a sheet pan chicken fajitas recipe. Chicken breasts give leaner baked chicken fajitas, while thighs stay extra juicy and forgiving if they roast a little longer. As long as you slice them into similar strips, your chicken sheet pan fajitas will cook evenly.
2. How thick should I slice the chicken and vegetables?
Aim for strips about 1–1.5 cm thick so everything in your sheet pan fajitas roasts at roughly the same pace. Thin slices of chicken, peppers, and onions give you tender pieces with nicely browned edges. When the sizes match, your one sheet chicken fajitas are much less likely to end up with overcooked chicken and underdone veg.
3. What oven temperature works best for baking sheet fajitas?
A hot oven is ideal; most oven fajitas turn out best around 220°C / 425°F. That higher heat lets the sheet pan fajita chicken caramelise instead of steaming. Once the chicken is cooked through and the vegetables are lightly charred, your chicken fajitas baked in oven are ready to serve.
4. How long do sheet pan chicken fajitas usually take to cook?
For a typical oven baked chicken fajita recipe, the tray needs about 18–22 minutes, depending on your oven and how crowded the pan is. Stir once halfway so the chicken fajita in oven mix colours on all sides. When the chicken is opaque and the vegetables look glossy and tender, your baked fajitas are done.
5. How do I stop my sheet fajitas from going soggy?
Give everything room to breathe on the tray. If your chicken fajita sheet pan is piled too high, the juices collect and you get more steam than roast. Spreading the mixture into a shallow layer—or using two pans for pan sheet chicken fajitas—helps you get those tasty browned edges instead of soft, wet vegetables.
6. What’s the best pan for fajitas in the oven?
A sturdy rimmed baking sheet is usually the best pan for fajitas when you’re using this method. It’s big enough for easy sheet pan chicken fajitas and strong enough not to warp at high heat. You can still make cookie sheet fajitas, but a heavy tray tends to give more even browning.
7. Can I use a non-stick or glass dish for this sheet pan fajita recipe?
You can, although the results change slightly. Non-stick trays make clean-up easier but may brown sheet pan chicken fajitas a little less. Glass dishes hold heat differently, so your chicken fajita one pan dinner might need a few extra minutes; simply watch for colour and doneness rather than relying only on the clock.
8. Can I cook fajitas in the oven if I’m used to making them in a skillet?
Yes, you can easily move from skillet fajitas chicken to a chicken fajitas in the oven recipe. The ingredients stay almost the same; only the technique changes. Instead of tossing everything in a chicken fajita pan on the stove, you toss on a tray, roast, and stir once, letting the heat build flavour while you step away.
9. Are sheet pan chicken fajitas spicy?
They’re usually moderately spiced rather than extremely hot. Most sheet pan fajita recipes rely on chili powder, cumin, and paprika for warmth, then add cayenne or fresh chili for extra kick. If you like mild baked chicken fajitas, simply skip the hotter spices; if you love heat, sprinkle more over your pan fajita before roasting.
10. How can I adjust the heat level in my baked fajitas recipe?
You control the spice level with your seasoning. To keep easy oven baked chicken fajitas gentle, use mild chili powder and no cayenne. On the other hand, if you want fiery sheet pan fajitas, add extra cayenne, fresh jalapeños, or a hotter chili powder to the sheet pan fajita chicken mix before cooking.
11. Can I prepare the chicken fajitas ahead of time?
You can slice the chicken and vegetables and mix them with oil and spices a few hours ahead. Keep the chicken fajita sheet pan mixture covered in the fridge until you’re ready to bake. When it’s time for dinner, spread everything out and roast, turning marinated one pan chicken fajita components into a flavourful tray with very little effort.
12. Is it okay to use frozen vegetables for sheet pan fajitas?
Frozen peppers and onions can work in a pinch, though the texture will be softer. If you scatter them straight onto the tray for baking sheet fajitas, expect less char and more moisture. Fresh vegetables give crisper edges and brighter colour, but frozen still make decent oven fajitas when you’re short on time.
13. How do I keep the chicken from drying out?
Don’t overcook it and avoid very tiny pieces. Cutting even strips, using enough oil, and pulling the chicken fajita in oven tray out as soon as the meat is just done all help keep your chicken fajita pan recipe juicy. Thighs are especially forgiving in a chicken fajita tray bake because they stay tender even if they roast a bit longer.
14. Can I make sheet pan fajitas for one or two people?
Definitely. For chicken fajitas for one or a small household, simply reduce the quantities and use a smaller tray. You’ll still enjoy one sheet fajitas with the same flavour and texture, just in a more manageable size that doesn’t leave you with too many leftovers.
15. Do I need to line the pan when I make sheet pan chicken fajitas?
Lining the pan with parchment makes clean-up easier but isn’t compulsory. If you skip lining, lightly oil the surface so your chicken sheet pan fajitas don’t stick. Either way, the sheet pan chicken and peppers will still roast nicely and pick up plenty of flavour.
16. Can I cook these fajitas under the broiler instead of just baking?
Yes, the broiler can give you extra char. Many people bake the chicken fajita sheet pan dinner until almost done, then move it under the broiler for a couple of minutes for lightly blackened edges. This approach gives broiled chicken fajitas that look close to grilled ones, while still using a single pan.
17. Are baked chicken fajitas healthier than fried versions?
Baked chicken fajitas generally use less oil than deep-fried options, and they’re built around lean protein and vegetables. Because you’re roasting the chicken fajita oven tray rather than frying, the meal often feels lighter. The overall balance still depends on your tortillas, toppings, and portion sizes, but the base of baked chicken fajita recipe is a wholesome starting point.
18. Can I double the recipe for a crowd?
You can absolutely scale this sheet pan chicken fajitas recipe up. For a large group, divide the mixture between two trays so the pan sheet fajitas still roast instead of steaming. Rotate the pans halfway through, and you’ll end up with a big batch of best sheet pan chicken fajitas ready at the same time.
19. What other meats can I use for a sheet pan fajita tray bake?
Chicken is classic, yet the same method works with beef strips, pork, or even shrimp. If you use quicker-cooking proteins like prawns, add them later in the baking time so they don’t overcook. No matter which protein you choose, the basic pan fajita pattern—strips, spices, and high heat—stays the same.
20. Can I make a vegetarian version of sheet pan fajitas?
Yes, it’s simple to adapt this into a vegetable-only fajita sheet pan recipe. Swap the chicken for mushrooms, tofu, paneer, jackfruit, or a mix of hearty vegetables and keep the same seasoning and roasting method. The result still feels like easy sheet pan fajitas, just without the meat.
21. How should I reheat leftover sheet pan chicken fajitas?
Leftover baked chicken fajitas reheat well in a hot skillet or in the oven. Spread the chicken fajita tray bake mixture in a single layer and warm it just until hot, so the chicken doesn’t dry out. A quick reheat brings your pan sheet chicken fajitas back to life for tacos, bowls, or wraps the next day.
22. What’s the difference between sheet pan fajitas and baked chicken tacos?
Sheet pan fajitas focus on strips of chicken and vegetables that you stuff into tortillas right at the table. Baked chicken tacos usually have the filling tucked inside the shells before going into the oven. Nevertheless, the same sheet pan fajita chicken can be used for both; you just decide whether to assemble first or after roasting.
23. Can I make this recipe milder for kids?
Yes, you can easily keep easy sheet pan chicken fajitas gentle enough for younger eaters. Use mild chili powder, skip the cayenne, and maybe add a bit more paprika for colour. Then, if adults want extra heat, they can sprinkle chili or hot sauce over their own chicken fajita sheet pan meal.
24. Do I need special fajita seasoning packets for this recipe?
Packets are convenient, but they’re not required for an easy sheet pan fajita recipe. A simple mix of chili powder, cumin, paprika, garlic, salt, and pepper gives the same character. Once you’ve tasted your homemade seasoning on a chicken fajita in oven tray, you may not feel the need to buy packets again.
25. Can I use this method for a chicken fajita pan on the stovetop?
You can borrow the same spice mix and proportions when you’re cooking chicken fajitas in a pan. Simply sear the chicken and vegetables in a hot skillet for fajitas instead of on a tray. That way, you can enjoy both skillet fajitas chicken and easy oven baked chicken fajitas using one familiar flavour base.