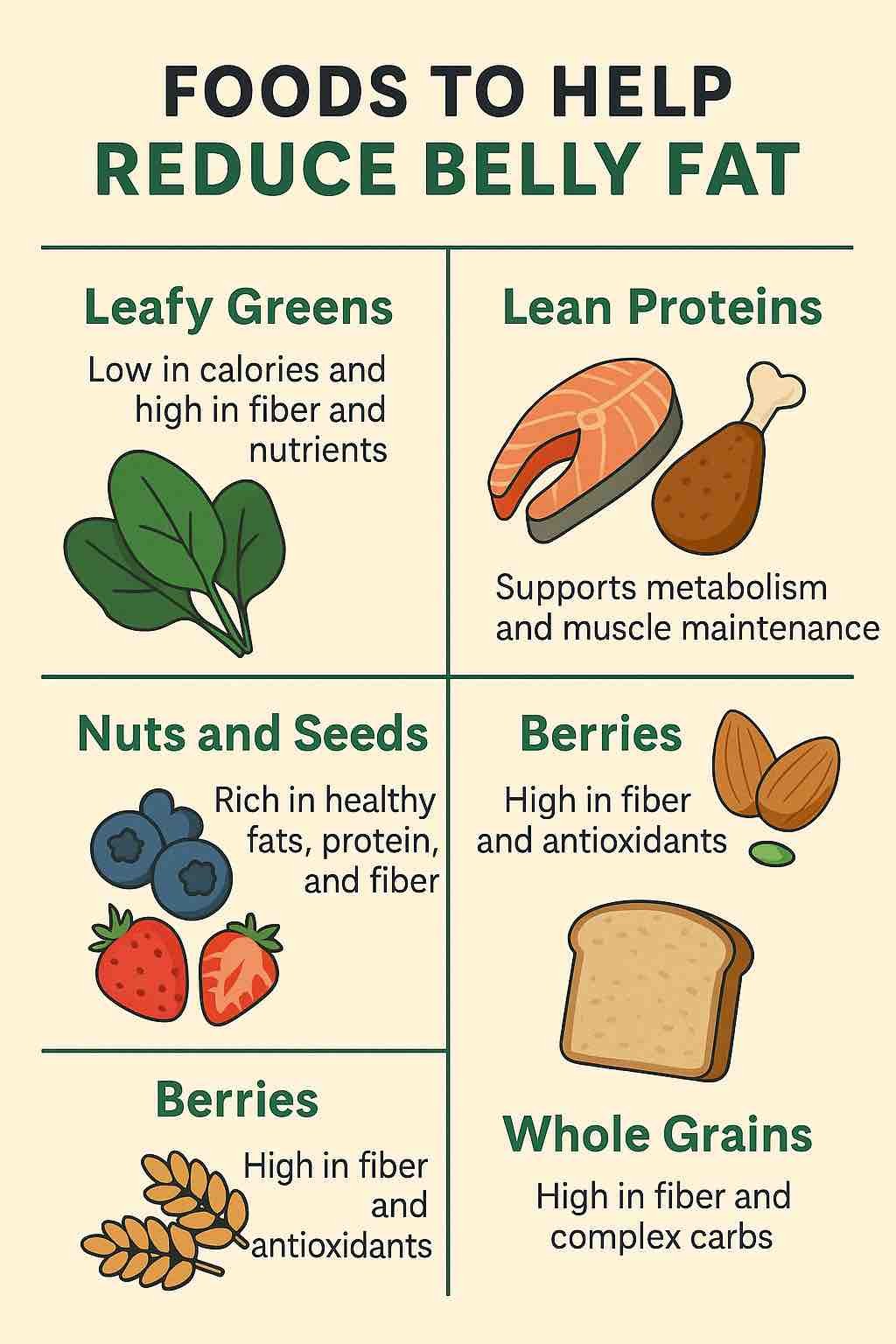
While there’s no single food that can magically reduce belly fat on its own, incorporating certain foods into your diet can help support weight loss and healthier body composition. Here are five foods that can be part of a healthy diet for reducing belly fat:
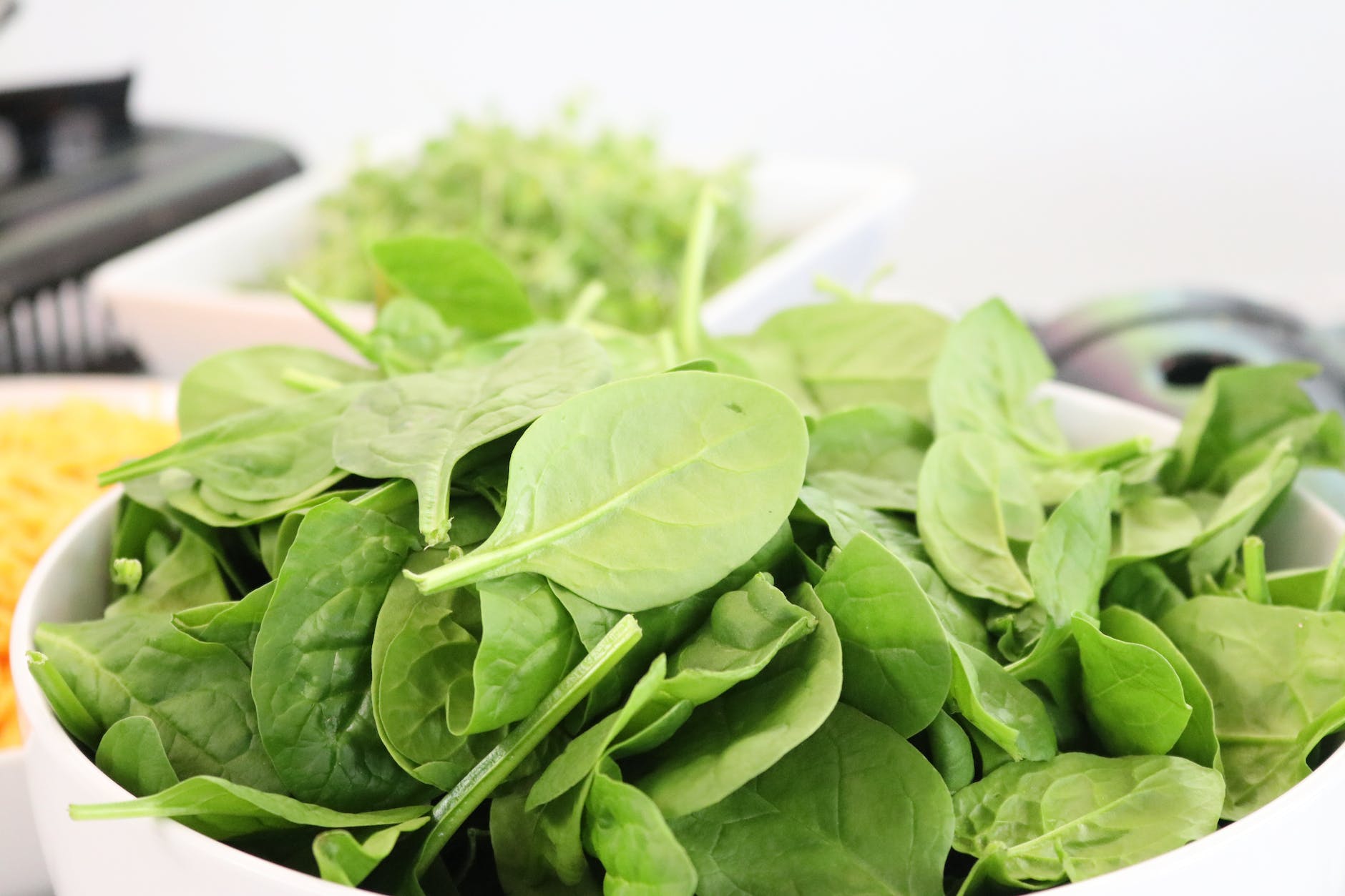
- Leafy greens: Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and collard greens are low in calories and high in fiber, which can help keep you feeling full for longer and reduce overall calorie intake. They’re also rich in nutrients like vitamins A and C, which support healthy metabolism and immune function.
- Lean proteins: Protein is important for building and maintaining muscle, which can help increase metabolism and reduce overall body fat. Good sources of lean protein include chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, and legumes like lentils and chickpeas.
- Nuts and seeds: Nuts and seeds are high in healthy fats, protein, and fiber, which can help keep you feeling full and support healthy digestion. They’re also rich in micronutrients like vitamin E, which has been shown to support healthy skin and reduce inflammation.
- Berries: Berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are low in calories and high in fiber and antioxidants, which can help reduce inflammation and support a healthy metabolism. They’re also a great source of natural sweetness without the added sugar found in many processed foods.
- Whole grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are high in fiber and complex carbohydrates, which can help keep you feeling full and support healthy digestion. They’re also rich in micronutrients like magnesium, which is important for healthy metabolism and nerve function.
Remember, while these foods can be part of a healthy diet for reducing belly fat, it’s important to also focus on overall calorie intake and physical activity to support weight loss and healthier body composition.
Leafy greens
Leafy greens are a powerhouse of nutrients that can have a significant impact on our health and well-being. Research has shown that incorporating leafy greens into our diet can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. But it’s not just about the science – the benefits of eating leafy greens can also be emotional.
For many of us, food is a source of comfort and pleasure, and eating leafy greens can help boost our mood and overall sense of well-being. Studies have found that eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, including leafy greens, can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety. This is because leafy greens are high in folate, a B-vitamin that plays a key role in the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood.
Eating leafy greens can also help us feel more connected to the earth and our environment. Growing our own vegetables or visiting local farms and farmers markets to purchase fresh produce can help us feel a sense of community and connection to the natural world. And when we eat leafy greens, we’re not just nourishing our own bodies – we’re also supporting sustainable agriculture and helping to reduce our impact on the planet.
🥬 Leafy Greens
Physical Benefits:
- Low in calories, high in fiber — promotes satiety and weight management.
- Rich in vitamins A, C, and folate — supports metabolism, immune function, and neurotransmitter production.
Emotional & Psychological Benefits:
- Associated with reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Helps people feel grounded and connected to the environment, especially when sourced locally or homegrown.
Lean proteins
Incorporating lean protein sources like chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, and legumes into our diets can be a powerful way to support both physical and emotional well-being. Research has shown that protein intake is associated with improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
A study published in the American Journal of Psychiatry found that individuals who consumed a higher proportion of plant-based protein sources had a lower risk of developing depressive symptoms over time. Similarly, a review of 27 studies found that dietary interventions that increased protein intake led to improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
In addition to these emotional benefits, consuming lean protein sources can also support weight loss and a healthier body composition. As I mentioned earlier, protein is important for building and maintaining muscle mass, which can increase metabolism and help reduce overall body fat. This can lead to improved self-esteem and confidence, which can further contribute to emotional well-being.
Incorporating lean protein sources like chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, and legumes into our diets can have a positive impact not only on our physical health but also on our emotional well-being. By providing the building blocks for muscle mass and supporting healthy mood and emotional balance, these foods can help us feel our best both inside and out.
🍗 Lean Proteins
Physical Benefits:
- Supports muscle mass, boosting metabolism and reducing fat.
- Plant-based proteins linked to lower risk of depression.
Emotional & Psychological Benefits:
- Protein intake correlates with better mood regulation.
- Muscle maintenance may boost confidence and self-esteem.
Nuts and seeds
Nuts and seeds are not only delicious and convenient, but they’re also incredibly good for you. They’re packed with nutrients like healthy fats, protein, and fiber, which can help keep you feeling full and satisfied, and promote healthy digestion.
Research has shown that consuming nuts and seeds regularly can have a number of health benefits. For example, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that people who ate nuts at least twice a week had a lower risk of heart disease and all-cause mortality compared to those who rarely ate nuts.
In addition, nuts and seeds have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases like cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. One study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that consuming a mixture of nuts and seeds was associated with lower levels of inflammation in the body.
Furthermore, nuts and seeds are rich in vitamin E, which is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage. In fact, research has shown that consuming nuts and seeds regularly can help improve skin health and reduce the signs of aging.
So, incorporating nuts and seeds into your diet is not only good for your physical health, but it can also have emotional benefits as well. Knowing that you’re fueling your body with nutritious, whole foods can boost your mood and give you a sense of empowerment and control over your health.
Overall, nuts and seeds are a delicious and convenient way to support your overall health and well-being. So, the next time you’re looking for a snack, reach for a handful of nuts or seeds and know that you’re doing something good for your body and mind.
🌰 Nuts and Seeds
Physical Benefits:
- Nutrient-dense (healthy fats, protein, fiber).
- Lower risk of heart disease, reduced inflammation, improved skin via vitamin E.
Emotional & Psychological Benefits:
- Snacking on nutrient-rich foods reinforces positive self-care.
- Empowerment through healthy choices.
Berries
Berries, particularly blueberries, have been extensively studied for their potential health benefits, and the results are truly remarkable. In fact, the research on berries is so compelling that it’s hard not to get emotional about the potential impact these little fruits can have on our health.
Numerous studies have shown that the antioxidants in blueberries can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, which are both linked to a variety of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. These same antioxidants also help improve brain function and may even help protect against age-related cognitive decline and dementia.
But that’s not all. Blueberries have also been shown to have a positive impact on weight management, particularly in reducing belly fat. One study found that overweight and obese individuals who consumed a daily smoothie containing blueberries experienced a significant reduction in belly fat compared to a control group. This is likely due to the high fiber content of blueberries, which can help keep you feeling full and reduce overall calorie intake.
Furthermore, blueberries have been shown to have a positive impact on mood and emotional well-being. One study found that consuming blueberries for just three weeks resulted in improved mood and increased levels of optimism, compared to a control group.
So not only do blueberries taste great and make a delicious addition to your diet, but the research suggests they may also have a profound impact on your health and well-being. Incorporating a variety of berries into your diet, including blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, can be a simple and delicious way to support your overall health and reduce belly fat.
🫐 Berries
Physical Benefits:
- Antioxidants reduce inflammation, oxidative stress, and belly fat.
- Support brain health and may slow cognitive decline.
Emotional & Psychological Benefits:
- Improved mood and optimism shown in short-term interventions.
- Natural sweetness offers emotional comfort without processed sugar.
Whole grains
Research has shown that incorporating whole grains into your diet can have a significant impact on reducing belly fat and improving overall health. In fact, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that consuming whole grains was associated with a 10% reduction in belly fat over a 5-year period. This is because whole grains are high in fiber and complex carbohydrates, which can help keep you feeling full and satisfied, and can also support healthy digestion.
But beyond just the physical benefits, there’s also an emotional connection to eating whole grains. Many people find that incorporating whole grains into their diet can help them feel more energized, focused, and even happier. This is because whole grains contain nutrients like magnesium, which is important for healthy nerve function and mood regulation.
Eating whole grains can also be a way to connect with your cultural heritage or family traditions. For example, many cultures have traditional dishes that incorporate whole grains like quinoa, barley, or millet. Eating these foods can help you feel a sense of connection to your roots and the people who came before you.
Adding whole grains into your diet can be a powerful way to support your physical and emotional health. So why not try swapping out your white bread or pasta for whole grain versions, or experimenting with new whole grain recipes? Your belly (and your soul) will thank you.
🌾 Whole Grains
Physical Benefits:
- High fiber content reduces belly fat and supports digestion.
- Nutrients like magnesium aid in metabolism and nerve function.
Emotional & Psychological Benefits:
- Magnesium supports emotional balance and calmness.
- Cultural and familial connections through traditional grain-based meals.
Final Summary:
Together, these foods support a holistic model of wellness—they nourish the body while also uplifting emotional and psychological health. Importantly, they work best as part of an overall balanced diet and healthy lifestyle (including exercise and mindful eating).
FAQs
- Can these foods target belly fat specifically?
No food can target belly fat directly, but these nutrient-dense foods support weight loss and reduce overall body fat, which includes abdominal fat. - How often should I eat these foods to see results?
Incorporate them into your meals daily as part of a balanced diet and pair with regular physical activity for the best results. - Do I need to avoid carbs entirely to lose belly fat?
No—complex carbs like those in whole grains provide fiber and energy, supporting digestion and preventing overeating. - Are all nuts and seeds good for weight loss?
Yes, in moderation. Choose raw or dry-roasted varieties without added sugars or oils to maximize health benefits. - Can berries replace sugary desserts?
Absolutely. Berries offer natural sweetness with fewer calories, plus antioxidants and fiber that support digestion and metabolism. - Is it better to eat leafy greens raw or cooked?
Both are beneficial. Raw greens preserve vitamin C, while cooking can increase absorption of nutrients like iron and calcium. - What’s the best lean protein for vegetarians?
Legumes (like lentils and chickpeas), tofu, tempeh, and quinoa are excellent high-protein, plant-based options. - How do whole grains help reduce belly fat?
Their fiber content keeps you full longer, stabilizes blood sugar, and promotes healthy gut bacteria—all linked to lower abdominal fat. - Will eating more of these foods alone lead to weight loss?
Not necessarily. You also need to maintain a calorie deficit and stay active. These foods simply make it easier and healthier. - Can I mix these foods together in meals?
Yes! Salads with leafy greens, nuts, lean protein, and whole grains or breakfast bowls with berries and seeds are great combos.













