
There’s a moment in low carb baking that feels almost universal: you pull something warm from the oven—maybe a tray of brownies, maybe a “simple keto bread,” maybe a batch of cookies—and the first bite tells you the truth. Keto flour can still deliver something genuinely delicious, yet the texture often feels different at first. Drier than you hoped. More fragile than you expected. Sometimes oddly eggy. Occasionally too dense, as if the batter never learned how to lift.
That moment isn’t failure. It’s feedback.
Regular flour is predictable because gluten does so much of the heavy lifting. Keto flour, on the other hand, asks you to be a little more intentional. Once you understand what each flour brings—bulk, tenderness, moisture, chew, browning—your results get calmer and more repeatable. In fact, you can go from “random experiments” to a pantry that reliably turns out low carb brownies, keto pancakes, keto pie crust, muffins, and even sandwich-style bread that doesn’t crumble into confetti.
So think of this as your reset: not a lecture, not a set of rules, but a cooking-minded guide to choosing a keto flour substitute that actually works.
Also Read: A Guide to Keto Diet for Beginners
Keto flour basics: why low carb baking plays by different rules
Traditional wheat flour is a whole system. When it meets liquid and mixing, gluten forms a stretchy network that traps air, holds moisture, and gives bread that familiar tear. Consequently, even a “just okay” recipe can still turn out fine because gluten forgives a lot.

Keto flour alternatives rarely have that safety net. Instead, low carb baking is built from smaller pieces that you assemble on purpose:
- A base for bulk and tenderness (almond flour, coconut flour, some wheat-based keto blends, or a low carb all purpose flour mix)
- A binder for structure (eggs, psyllium husk, flax, xanthan/guar)
- A moisture plan (fat, dairy, extra liquid, or a sweetener that helps retain softness)
- A lift plan (fresh baking powder, baking soda plus acid, or whipped egg whites)
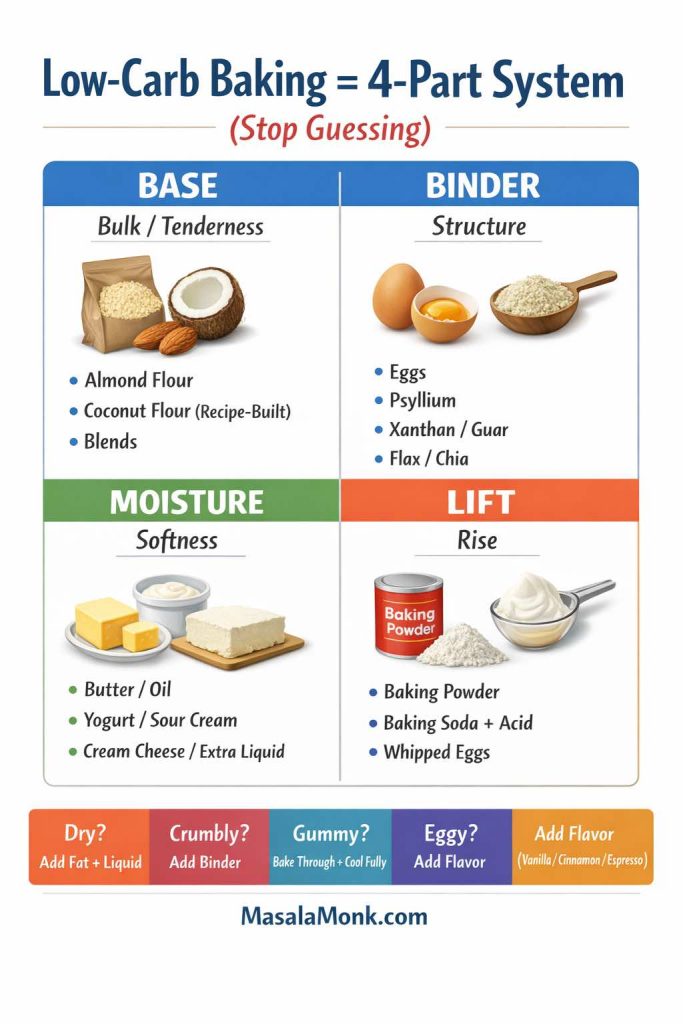
That’s why one “keto flour” doesn’t do everything. A flour that makes an incredible cookie can make a sad loaf. Similarly, a bread-focused mix can feel tough in brownies. Once you accept that each bake wants a slightly different toolkit, your kitchen gets easier.
Also Read: The Must-Have Condiment for Keto: Mustard – Flavorful, Low-Carb, and Versatile
Keto flour labels: how to read carbs on mixes, tortillas, and “net carb” claims
Low carb packaged products—especially tortillas, wraps, and baking mixes—often lean on “net carbs.” Net carbs can be a useful shorthand, but it isn’t a standardized number on the Nutrition Facts label. The label gives you total carbohydrate, and under that, it breaks down fiber and sugars; your “net” number is a calculation people do from the label.

The FDA explains how to interpret the Nutrition Facts label and why serving size matters, because every number on the label is tied to that serving size. That alone changes the story more than most people realize. See: How to understand and use the Nutrition Facts label.
Meanwhile, the American Diabetes Association notes that net carbs are commonly calculated by subtracting fiber and sugar alcohols from total carbohydrate; however, that calculation isn’t always accurate because different fibers and sugar alcohols can be partially absorbed and still affect blood glucose in some people. See: ADA: Get to know carbs.
If you’re counting carbs for any reason—keto goals, blood sugar management, or simple preference—this is the practical takeaway:
Use the label as the source of truth, then decide how you personally interpret it. Don’t let marketing language do the math for you.
For additional clarity, the FDA’s Interactive Nutrition Facts Label PDF on “Total Carbohydrate” breaks down what that line includes and how fiber fits into the definition: Interactive Nutrition Facts Label: Total Carbohydrate (PDF).
Also Read: How to make No-Bake Banana Pudding: No Oven Required Recipe
Best keto flour for baking: a quick chooser by what you’re making
Before you choose any low carb flour substitute, pick the result you want. Then you can choose the flour that behaves that way.

Brownies and bars: fudgy vs cakey
Brownies are where keto baking can feel either magical or tragic.
- If you want fudgy brownies, you typically want a flour that stays tender and doesn’t drink every drop of moisture. Almond flour often shines here.
- If you want a more cakey brownie, you’ll usually need more structure—either from a blend designed to mimic wheat flour, or from careful binder choices (and sometimes a touch of coconut flour).

If you’re using a keto brownies mix or low carb brownie mix, the best question isn’t “Is it good?” but “What kind of flour system is it?” Almond-based mixes and wheat-style keto blends can both work, yet they produce different textures.
Pancakes and waffles: the fastest way to learn your flour
Waffles & Pancakes are a low-risk training ground: quick feedback, easy to tweak, forgiving enough to repeat.

If you want a gentle on-ramp, start with a dependable keto approach like Keto Pancakes: almond flour, coconut flour, and cottage cheese methods.
Then, if you want a broader “this is how pancakes behave with different bases” baseline, Blueberry Pancakes (6 recipes + homemade pancake mix) gives you a useful reference point for batter rest, browning, and texture.
Pie crust and cookies: crisp vs tender
A keto pie crust needs to slice cleanly, so structure matters. On the cookie side, you may want crisp edges and a tender middle, or you may want chewy softness. Those are different jobs.
- Almond flour tends to give a tender, rich crumb.
- Coconut flour can firm and tighten texture, but it can also dry things out if you push it too far.
- Psyllium husk and certain fibers can help crusts hold together, although too much can make things gummy.
Bread and pizza: structure first, tenderness second
Bread is where low carb baking stops being “swap flour, hope for the best” and becomes “choose a system.” Keto bread usually needs binders, hydration control, and a flour blend that can hold gas.
For a reminder of how much structure matters in conventional bread, Sourdough Bread Recipes: 10 easy bread bakes (loaves, rolls & bagels) is a helpful example of how fermentation, hydration, and timing shape the crumb—even if you’re not baking sourdough on keto.
Also Read: Chicken Adobo — Step-by-Step Recipe — Classic Filipino Adobong Manok
Keto flour substitutes: the low carbohydrate flour list that actually earns its space
You’ll see endless “low carb flour” lists online. The problem is that many of them treat these flours as interchangeable. They aren’t.
Here’s the kitchen-reality version—what each keto flour does well, what it does poorly, and how to use it without wasting a weekend.

Almond flour: the most versatile keto friendly flour
Almond flour is popular for a reason: it’s forgiving. It browns nicely, tastes rich, and tends to produce tender baked goods without advanced technique.
Where it shines
- Cakes, muffins, pancakes, waffles
- Cookies (especially chewy styles)
- Brownies, bars, crumb toppings
- Coating and breading jobs (especially when you want a crisp outside)
Where it struggles
- Yeasted breads that need chew and lift
- Ultra-crisp pastry unless you blend for more structure

If you want a practical internal guide that frames almond flour in everyday cooking (including a diabetes/blood sugar perspective), Almond Flour and Diabetes: a low-carb swap for better blood sugar is a relevant read.
And if you want a straightforward “make it taste good fast” use case, Almond Flour Pancakes is an easy entry point for batter thickness, browning control, and fluffiness without turning it into a science project.
A note on almond flour vs almond meal
Almond meal is coarser, which can make bakes feel heavier or more rustic. Sometimes that’s exactly what you want. Other times, it’s the reason your cookie feels gritty. When in doubt, choose almond flour for baking and save almond meal for breading and hearty muffins.

Coconut flour: extremely absorbent, powerful in small doses
Coconut flour is one of the most misunderstood keto flour alternatives. People love it because it’s compact and can be very low net carb in small quantities. Then they treat it like all-purpose flour and wonder why everything turns to sand.
Coconut flour is high in fiber, which means it absorbs a lot of liquid during baking. Bob’s Red Mill emphasizes that you should follow coconut flour recipes closely and not make additional substitutions, because dough will often be much thicker than expected—and the absorbency changes everything. See: Bob’s Red Mill on coconut flour baking.
Iowa State University Extension notes that coconut flour shouldn’t be substituted 1:1 for wheat flour and can hold up to four times its weight in liquid, which helps explain why “just swap it” usually fails. See: Coconut flour (Iowa State Extension PDF).

Where coconut flour shines
- “Cake-like” quick breads when the recipe is designed for it
- Muffins that need a firmer set
- Blends, where a small amount adds structure
Where coconut flour struggles
- Anything you want chewy unless you pair it with the right binders
- Free-form cookies (it can over-tighten and dry)
If you love coconut flour, treat it like a concentrated ingredient. Use it with intention, not as a general-purpose low carb flour replacement.
Lupin flour: protein-forward structure with a distinct personality
Lupin flour can be a useful keto flour substitute because it brings protein and structure. It can also bring a flavor that some people notice more than others, especially in lightly flavored bakes.
Where lupin flour shines
- Chocolate bakes (the flavor hides well)
- Savory bakes and crackers
- Blends designed for more structure
Where lupin flour struggles
- Delicate cakes unless blended thoughtfully
- Light, buttery cookies where you want clean sweetness
Oat fiber, bamboo fiber, and other fiber flours: bulk without traditional starch
If you’ve seen “0 carb flour,” “zero net carb flour,” or “carb free flour substitute,” it’s often tied to fiber-heavy ingredients. These can be helpful, particularly in bread and pizza systems where you want bulk and structure without starch. Still, they can also turn baked goods dry if you overdo them.
Fiber choices vary widely, and not all “added fiber” behaves the same. If you want a grounded, label-oriented reminder that fiber type matters, it’s useful to keep the ADA’s note about net carb calculations in mind: ADA: net carbs aren’t always fully accurate.
Where fiber flours shine
- Bread and pizza systems when paired with binders and hydration
- Thick batters (mug cakes, pancakes) where you can control moisture
Where fiber flours struggle
- Cookies and cakes when they’re used as the primary “flour”
- Anything where you want a soft, bouncy crumb without gumminess
Psyllium husk: the binder that makes keto bread behave like bread
Psyllium isn’t “flour” in the classic sense, yet in keto baking it functions like architecture. It can provide elasticity, moisture retention, and a more bread-like chew, especially when paired with eggs and the right hydration.

The trick is balance. Too little and your loaf crumbles. Too much and the texture can turn dense or slightly gummy. When it’s right, though, it’s one of the main reasons keto bread can slice.
Flax meal and chia: binding, moisture, and a rustic crumb
Flax and chia add structure and moisture control. They also add flavor, so they’re often better in spiced bakes, nutty muffins, and hearty breads than in a delicate vanilla cake.

“Pork rind flour” and seed crumbs: the crunch category
Sometimes you don’t need flour at all—you need texture. For breading, coating, and crisp topping jobs, pork rind crumbs and crushed seeds can do what flour would do, without pretending to be something else.
That’s how you keep keto cooking satisfying: by choosing the tool that matches the task.
Also Read: Keto Mocktails: 10 Low-Carb Recipes for Guilt-Free Happy Hour Indulgence
Keto all purpose flour: what it can do, and what it can’t
A keto all purpose flour sounds like a dream: one bag, every bake, no guesswork. In practice, it depends on what that “all purpose” blend is made to mimic.
Some blends aim to behave like wheat flour in a one-to-one swap. Others aim for a gluten-free style. Some focus on fiber bulk. Each approach can work. The only problem is expecting a cookie blend to behave like a bread blend.

Store-bought wheat-style keto blends (the “1:1” promise)
A well-known example is King Arthur’s Keto Wheat Flour, described as a 1:1 swap for recipes calling for all-purpose flour, with a traditional wheat taste and low net carbs per serving. See: King Arthur Keto Wheat Flour.
That kind of flour can be appealing if you want wheat-like structure for bread, rolls, or yeasted bakes, and you’re not aiming for gluten-free baking.
DIY low carb flour mix: why it’s often better
Even if you love a store blend, it’s worth having a simple DIY approach, because your baking goals change. Some days you want brownies that stay fudgy. Other days you want a pizza crust that can be picked up. Those are different recipes, so it helps to have different “default blends.”

A practical way to think about DIY blends is:
- Tender blend for cakes, muffins, and brownies: almond flour-forward, minimal fiber
- Structure blend for bread and pizza: includes psyllium and/or fiber components, with careful hydration
- Nut-free blend when needed: coconut flour plus binders, used in recipes designed around its absorbency
Once you label your jars that way—tender, structure, nut-free—you stop expecting one bag to do everything. Then your baking suddenly feels easier.
Also Read: Creamy Cauliflower Soup—Keto-Friendly, Ultra-Comforting (Vegan Option)
Keto baking mixes and keto flour blends: what changes in the bake
Keto baking products have expanded quickly. There are keto baking mixes for brownies, pancakes, biscuits, cakes, and even “shake and bake” style coatings. You’ll also see brand-specific products such as Atkins bake mixes, Carbquik baking mix, Lakanto baking mix, and specialty companies offering cookies and brownie mixes.

These products can be helpful, especially when you want consistency or when you’re new to low carb baking. Still, mixes vary hugely in results, so it helps to evaluate them using a simple lens:
- What’s the primary flour system?
Almond flour-based mixes tend to be tender. Coconut flour-based mixes tend to firm quickly. Wheat-style keto blends tend to mimic flour-like structure. - What’s providing structure?
If the mix relies on added fiber and gums, it may need extra resting time for hydration. If it relies heavily on egg, it may risk an eggy finish unless flavor is boosted. - What’s the sweetener profile?
Sweetener choice affects aftertaste, browning, moisture, and how soft the bake stays after cooling. - How is “serving size” defined?
The FDA’s label guidance is useful here because serving sizes can make products look more “carb friendly” than they feel in real life. See: FDA Nutrition Facts Label basics.
If you’ve tried a few mixes and felt disappointed, it’s often not because keto baking is doomed. Instead, it’s because the mix wasn’t designed for the texture you wanted.
Also Read: Green Tea for Weight Loss: The No-Hype, Done-For-You Guide
Keto flour for brownies: how to get that rich, not-dry finish
Brownies are the emotional center of keto baking. They’re what people want to feel “normal” again. The good news is that brownies are also one of the easiest places to win—provided you choose the right flour approach.

Pick your brownie style first
A “best keto brownies” goal can mean three different things:
- Fudgy and dense (almost truffle-like)
- Soft and cakey (more like a snack cake)
- Chewy with crisp edges (classic pan brownie energy)
Each style wants a different flour strategy.
The fudgy path: almond flour plus moisture control
Almond flour tends to be your friend here because it stays tender. To keep brownies from drying out, focus on:
- Enough fat (butter, coconut oil, or a neutral oil)
- A sweetener that doesn’t turn the crumb dusty
- Not overbaking—pull them when the center is set but still soft
If you like learning by contrast, it can help to taste a conventional brownie and pay attention to what flour contributes: structure, yes, but also how it holds moisture in place. Keto brownies replicate that by balancing almond flour with eggs and fat, then keeping bake time gentle.
The “clean slice” path: tiny amounts of coconut flour or fiber support
If your almond flour brownies feel too soft or fall apart, you can add a small amount of coconut flour or a touch of fiber/binder support. This is where restraint matters. Coconut flour is powerful; too much turns brownies dry. Used lightly, it tightens the structure and helps slices hold.
Mixes: how to make a keto brownie mix taste homemade
A low carb brownie mix can be excellent, although it often benefits from a few simple upgrades:
- Add a pinch of salt if it tastes flat
- Add vanilla or espresso powder for depth
- Add extra fat if the mix bakes up dry
- Rest the batter briefly if it includes fiber-heavy ingredients
In other words, treat the mix like a base. You’re still the baker.
Keto flour for pie crust: the butter + structure balance
Pie crust is the place where people chase unicorns: “no carb pie crust,” “sugar free low carb pie crust,” “keto pie crust that tastes like bakery pastry.” You can get close, but only if you accept what makes classic crust work.
Classic crust is about fat layers, controlled hydration, and just enough structure to hold a slice.
Keto crusts often use almond flour because it tastes good and handles butter well. However, almond flour crust can be fragile, particularly when warm. That fragility is not a flaw; it’s a clue that you need a bit more structure.

A reliable keto pie crust strategy
- Almond flour for tenderness and richness
- Butter for flavor and flake-like feel
- A small structure helper for sliceability (egg, psyllium, or a small amount of coconut flour, depending on your preferred texture)
- Salt, always—otherwise the crust tastes like “health food,” even when it isn’t
Crisp vs tender crust: choose your finish
If you want a crisp, cookie-like crust, you can lean more toward almond flour plus sweetener and bake it like a shortbread base. On the other hand, if you want a more pastry-like crust, you’ll usually prefer a less sweet, more structured approach that can be rolled or pressed without cracking.
This is also where your sweetener choice matters. Some sweeteners keep crusts softer; others crisp more readily. Either can be good—it just depends on what you’re making.
Also Read: Navigating Beans on the Keto Diet: Which Varieties Are Suitable?
Keto flour for muffins, banana bread, and “quick breads” that stay moist
Muffins and banana bread are deceptively tricky on keto because the classic versions rely on sugar and starch for moisture retention. When you remove both, you need a new plan.
The win here is simple: build moisture on purpose, then choose a flour that supports it.

Almond flour muffins: soft, rich, forgiving
Almond flour muffins tend to stay tender, especially if they include yogurt, sour cream, or a bit of cream cheese. They also reheat well, which matters more than you’d think. Warmed muffins taste fresher; chilled muffins can taste drier than they are.
Coconut flour muffins: light, structured, but easy to dry out
Coconut flour muffins can be excellent when the recipe is designed for them, because they can set into a neat crumb and feel pleasantly cakey. The danger is treating coconut flour as a 1:1 substitute. As Bob’s Red Mill notes, coconut flour absorbs a lot of liquid and requires careful recipe adherence; it also often calls for more eggs to compensate. See: Bob’s Red Mill coconut flour baking guidance.
Banana bread on keto: pick your “banana” strategy
“Keto banana bread” usually means one of two things:
- A banana-flavored bread with extracts/spices (banana without the carbs)
- A low-carb “banana-ish” bread that uses a small amount of banana, portioned carefully
Either can work. The point is to decide what you mean by “banana bread” first: aroma and comfort, or literal banana content.
A non-keto but useful comparison: why “no refined flour” baking still teaches you something
Even when you’re staying keto, it can be useful to look at how other styles of baking build sweetness and moisture without relying on refined ingredients. For example, Easy and healthy cookies (no sugar, no butter, no refined flour) uses a whole-food approach to sweetness and softness—different macros, yes, but still a reminder that texture is often created by technique and ingredient roles, not just flour.
Also Read: 5 Keto-Friendly Salami Dishes That Promote Weight Loss
Keto pancakes and low carb pancakes: how to avoid the eggy, rubbery trap
Pancakes are where people either fall in love with keto baking or swear it off forever. The main complaint is usually the same: “Why does this taste like an omelet pretending to be breakfast?”
That eggy taste happens when the batter is built mainly from eggs and dairy without enough flour-like bulk and flavor support.
A strong approach is to choose a base that actually behaves like a flour system, then cook with gentler heat so the pancake sets without overbrowning. Both Keto Pancakes and Almond Flour Pancakes lean into practical texture cues like resting batter, controlling browning, and choosing the right thickness.
Why almond flour pancakes brown faster
Almond flour has fat and fine particles that brown quickly. That’s why a medium-low heat approach often gives better results: slower setting inside, less overbrowning outside. The almond flour pancakes guide calls this out directly as a common issue and solution.

Why coconut flour pancakes need a different mindset
Coconut flour pancakes can be excellent, yet they often want more resting time because hydration changes the batter dramatically. If you cook too soon, the batter can feel grainy or tight. If you rest, it smooths out and sets more evenly.
A quick way to keep pancakes interesting without turning them into dessert
One of the most practical ways to stick with low carb baking is to keep flavors rotating. Berries, citrus zest, cinnamon, and vanilla all pull attention away from “this is a substitute” and toward “this is breakfast.”
If you want a general pancake playground (keto or not), Blueberry Pancakes (6 variations) is useful for mix upgrades and batter handling tips.
Also Read: Katsu Curry Rice (Japanese Recipe, with Chicken Cutlet)
Keto flour for bread: how to build lift, chew, and clean slices
Bread is the most emotionally loaded category in keto baking, and understandably so. Bread isn’t just food; it’s a format—sandwiches, toast, grilled cheese, wraps, “something you can hold.”
To make bread without traditional flour, you need a structure plan.

The three bread jobs your flour must do
A good bread flour system—keto or not—must do these things:
- Trap gas so the loaf rises
- Hold moisture so it doesn’t crumble
- Set into a sliceable crumb when cooled
Gluten does all three in wheat bread. Keto bread recreates them through binders and careful hydration.
That’s why a conventional bread roadmap like Sourdough Bread Recipes: 10 easy bakes is still useful as a learning lens: it reinforces that bread texture is shaped by hydration, timing, and structure—not just ingredients.
The “crumbly loaf” fix: binders and patience
If your keto loaf crumbles, it’s usually one of these:
- Not enough binder support (psyllium/flax/eggs)
- Too dry (coconut flour pushed too far, or fiber flours without enough hydration)
- Overbaked (keto breads dry out quickly)
- Sliced too early (cooling sets the crumb)
Cooling is underrated. Even wheat bread slices better once it’s fully cooled. Keto bread often needs that time even more.
Wheat-style keto flour blends for bread and yeasted bakes
If you’re using a wheat-style keto blend like King Arthur Keto Wheat Flour, the promise is that you can swap 1:1 for all-purpose flour while keeping a more traditional wheat taste and texture.
That may be attractive if you’re aiming for a more classic bread feel and gluten-free isn’t your goal. Even then, treat it like any flour: test once, adjust once, then keep notes. Bread rewards repetition.
Also Read: Beyond Chicken: 5 Tofu-Tastic Keto-Friendly Dinner Meal Prep Ideas, Chicken-Free and Protein-Rich
Keto pizza flour and crusts: crisp edges, tender center, sturdy slice
Pizza is another category where “best keto flour” depends entirely on the style you want.

- If you want a thin, crisp crust, you’ll likely choose a structure-heavy approach (often with binders and a bake-hot strategy).
- If you want a soft, foldable slice, you’ll usually lean into a more bread-like system with moisture and chew.
In either case, the same principle applies: choose your crust identity first. Otherwise, you’ll keep judging a “crisp cracker crust” as if it was a Neapolitan base, and nothing will feel right.
Also Read: Carbs in Cheese: Keto Diet Perspective
Keto flour tortillas and low carb flour tortillas: how to make the section genuinely useful
Tortillas and wraps are where “low carb” becomes everyday. A tortilla can be breakfast, lunch, dinner, and a quick snack format—so it makes sense to include a real section that isn’t just a brand list.
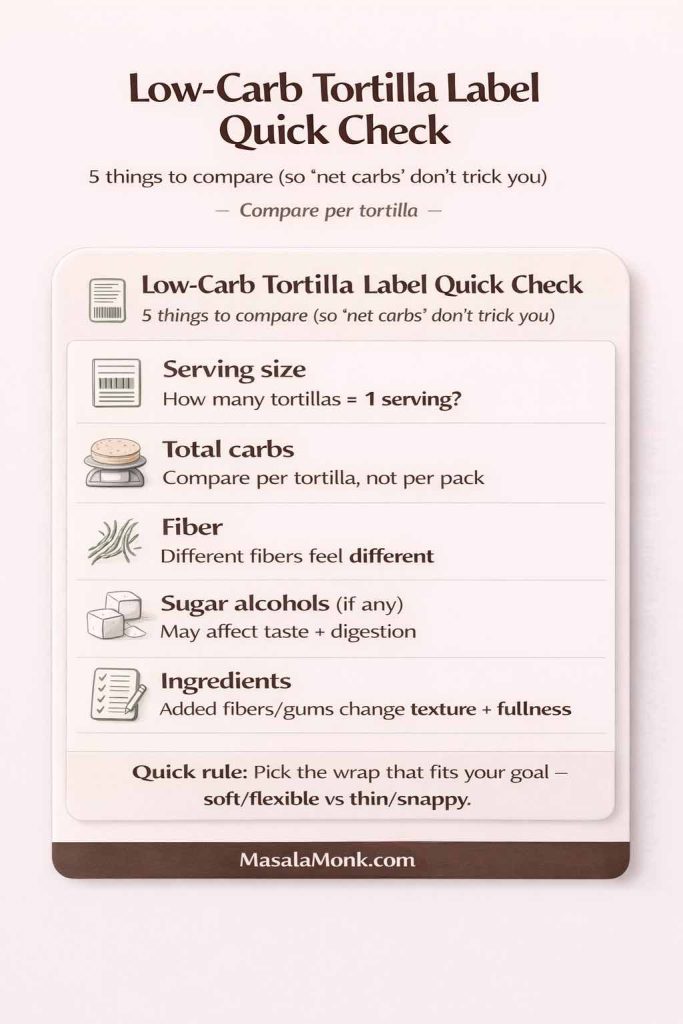
Store-bought low carb wraps: what actually matters
If you’re using packaged low carb tortillas, focus on:
- Serving size (and how many you actually eat)
- Total carbohydrate and fiber (then decide how you interpret net carbs)
- Sugar alcohols, if present
- Ingredient list, especially added fibers
The FDA’s label guidance is the clearest reference point for serving size and how numbers are presented: How to understand and use the Nutrition Facts label.
Additionally, the ADA notes that net carb math can be imperfect because fiber and sugar alcohol absorption varies: ADA: Get to know carbs.
In practical terms, that means one “mission carb balance tortilla” style product may feel different from another depending on fiber type and serving size, even when the front label looks similar.
Make tortillas useful even when you don’t want to rely on packaged wraps
The easiest way to keep this part of the guide valuable is to offer wrap-format meal ideas that work whether you use low carb tortillas, lettuce wraps, or bowls.
For example, Sheet Pan Chicken Fajitas is a perfect “build-your-own” filling that adapts to any wrap format.
In other words, even if your tortilla choice changes week to week, the meal stays consistent.
Also Read: Keto Indulgence: Decadent Cheesecake Fat Bombs with Irresistible Spice Variations!
Keto baking sweeteners: how to choose a keto sugar substitute for baking without ruining texture
Flour gets most of the attention, yet sweetener can make or break low carb baking. Sweeteners affect:
- Moisture retention (soft brownies vs dry brownies)
- Browning (some brown faster)
- Crispness (cookies that snap vs cookies that bend)
- Aftertaste and flavor clarity

Stevia blends, erythritol blends, and “baking” sweeteners
If you’ve used a sweetener that left your cookies gritty or your brownies dry, you’re not imagining it. Some sweeteners recrystallize as they cool, which can change mouthfeel.
For a general reference on what Truvia is and how it compares, What is Truvia sweetener? offers a clear overview of common formulations and comparisons.
If you’re choosing between stevia and aspartame in a broader sugar-free context, Stevia vs Aspartame provides a readable comparison and notes key considerations (including PKU cautions for aspartame).
Allulose: why bakers like it
Allulose is often discussed as a sugar-like option because it can behave more like sugar in recipes. Cleveland Clinic explains what allulose is and why people use it as a sugar substitute, including for diets that aim to reduce sugar intake. See: Cleveland Clinic: What is allulose?.
Oregon State University Extension also describes allulose as about 70% as sweet as sugar with far fewer calories and notes it’s relatively new on the market with limited research on long-term health effects: OSU Extension: Sweeteners (allulose section).
From a baking standpoint, the practical note is this: allulose can brown faster and keep things softer, which is great in some recipes and requires slight temperature awareness in others.
Also Read: Mozzarella: A Keto-Friendly Cheese Powerhouse for Your Low-Carb Journey
Keto baking powder, lift, and why “resting batter” matters more with low carb flour
Keto baking often leans on baking powder because it creates lift in batters that don’t have gluten. Two simple habits improve results dramatically:
- Use fresh baking powder. Old leavening gives flat, dense results, and you’ll blame your flour when it wasn’t the flour.
- Let fiber-heavy batters rest. Resting allows hydration to stabilize thickness, which improves rise and prevents a grainy finish.

This rest-and-hydrate approach shows up in practical pancake guidance too—both in keto pancake methods and in broader pancake mix handling tips.
Also Read: Are Lentils Keto-Friendly?
Putting it into a kitchen rhythm: a simple way to stop guessing
Once you’ve read enough about keto flour, the real win is building a routine you can repeat. Here’s a calm, practical way to get there:

Step 1: Choose two “anchor bakes” you’ll repeat until they’re easy
Pick:
- One fast bake (pancakes, mug cake, or simple cookies)
- One slow bake (bread, pizza crust, or pie crust)
For pancakes, use Keto Pancakes and/or Almond Flour Pancakes as your baseline so you’re not reinventing the wheel every time.
Step 2: Build a “tender jar” and a “structure jar”
- Tender jar: almond flour-forward, minimal fiber
- Structure jar: includes psyllium and/or fiber support, tuned for bread/pizza
Even if you still buy a keto baking mix now and then, these jars give you control when you want it.
Step 3: Keep flavor boosters ready
Low carb baking tastes better when flavor is intentional. Cinnamon, vanilla, espresso powder, citrus zest, and a pinch of salt are not optional extras—they’re how you make the bake taste complete.
Also Read: Keto Vegan Indulgences: 5 Dessert Recipes with Hemp Seeds, Walnuts, and Ginger
A broader, useful perspective: flour choices that aren’t strictly keto, but teach you technique
A strong guide doesn’t pretend only one eating style exists. It gives you perspective.
If you bake for a household where not everyone eats keto all the time, it’s helpful to understand how other flour systems behave—because it sharpens your intuition. Oat-based pancakes, for example, teach you about batter hydration and tenderness in a way that directly carries over to almond and coconut flour batters. See: Oat Pancakes Recipe (healthy oatmeal pancakes + variations).

Likewise, a classic wheat-flour pancake recipe highlights how gluten and starch create a certain bounce, which is exactly what you’re rebuilding in keto baking through different tools. See: Fluffy Buttermilk Pancakes.
And if you want the “whole-food sweetness” approach (different macros, but helpful technique), Easy and healthy cookies (no refined flour) is a reminder that texture often comes from method and moisture strategy, not just flour choice.
Also Read: Celery: The Keto Superfood You Didn’t Know About! Boosting Nutrition, Flavor, and Versatility
The quiet truth about “no carb flour,” “0 carb flour,” and “carb free flour”
It’s tempting to chase a mythical flour with zero carbs that behaves like wheat. In practice, “no carb flour” language usually points to fiber-heavy ingredients or specialized blends. Those can be useful, particularly in bread and pizza systems, yet they can also create digestive discomfort for some people, and they don’t behave like wheat flour in every recipe.

This is where label literacy matters again. Total carbohydrate and fiber are defined on the label, and what counts as “fiber” can vary by type. The FDA’s Interactive Nutrition Facts Label on total carbohydrate is a grounded reference point for what that line means: Interactive Nutrition Facts Label: Total Carbohydrate (PDF).
Meanwhile, the ADA’s note about net carb calculations explains why subtracting fiber and sugar alcohols isn’t always perfectly accurate across products: ADA: Get to know carbs.
So rather than chasing a slogan, chase results: a flour system that tastes good, bakes well, and fits your preferences.
Also Read: is Aspartame Keto Friendly? Aspartame and Ketosis
A simple “starter kit” pantry for keto baking that actually covers real life
If you want a keto pantry that makes you feel capable on a random Tuesday, not just inspired on a Sunday, aim for a kit that supports multiple outcomes.

Base flours
- Almond flour (fine, for baking)
- Coconut flour (for recipes designed around it; small doses in blends)
Binders and structure
- Psyllium husk
- Flax meal (optional, but useful)
- Xanthan or guar gum (optional, in tiny amounts)
Moisture and flavor
- Butter or coconut oil
- Vanilla
- Cinnamon
- Unsweetened cocoa
- Salt (always)
Lift
- Fresh baking powder
Flexible add-ons
- Sugar-free chocolate options for baking (choose based on your sweetener preference)
- Nuts, seeds, and shredded coconut for texture
When you have that kit, the question “What can I bake?” becomes practical. You’re no longer waiting for a specialized product to arrive. You can make pancakes, brownies, and a basic crust without drama.
Also Read: How to Keto – 5 Ways Butter Chicken can be Made Keto-Friendly

Closing: keto flour gets easier when you stop asking it to be one thing
Keto baking feels hard when you keep asking one flour to behave like every flour. It becomes surprisingly approachable when you treat keto flour as a set of tools:
- Almond flour for tenderness and comfort
- Coconut flour for structure, used carefully
- Psyllium and binders for bread-like results
- Thoughtful sweeteners for moisture and flavor
- Good label reading habits so products don’t confuse you
Start with one bake you’ll repeat—pancakes are perfect for that—and let the results teach you what your flour wants. From there, move into brownies, crusts, and bread with a calmer hand. If you want a strong baseline for that first step, Keto Pancakes and Almond Flour Pancakes are both reliable starting points.
And when you’re choosing packaged foods or mixes, keep the label grounding close. The FDA’s Nutrition Facts label guide and the ADA’s net carb explanation we have linked earlier in this ost – are two references worth returning to whenever something feels “too good to be true.”
Also Read: Pepperoni: The Keto-Friendly Pizza Topping You Love

FAQs
1) Is keto flour the same as low carb flour?
Not always. “Keto flour” usually implies a flour or blend that can fit stricter carb targets, while “low carb flour” can include options that are lower than wheat flour yet still too high for many keto plans. Because labels and serving sizes vary, it helps to treat them as overlapping categories rather than identical ones.
2) Can you eat flour on keto?
Yes—if it’s a keto-friendly flour substitute. Instead of regular wheat flour, many people use almond flour, coconut flour, or a keto all purpose flour blend. Even so, the best choice depends on what you’re baking and how you count carbs.
3) What flour has the least carbs?
There isn’t one universal winner. Some fiber-forward “carb free flour” style products can be extremely low net carb per serving, whereas almond flour and coconut flour are low-carb staples with more predictable baking behavior. Rather than chasing a single “0 carb flour,” aim for the option that gives you the best texture for the bake you’re making.
4) Is there a true zero carb flour?
In practical kitchen terms, “zero carb flour” is usually shorthand for fiber-heavy ingredients or specialty blends that calculate very low net carbs per serving. However, those ingredients may behave differently than regular flour, so results can range from excellent to oddly dry if the recipe isn’t designed for them.
5) What is the best keto flour for baking overall?
If you want one starting point, almond flour is often the easiest because it’s forgiving and produces tender cakes, cookies, muffins, and pancakes. That said, coconut flour can be fantastic when used correctly, while blends can outperform both for bread-like structure.
6) What’s the best keto flour substitute for all-purpose flour?
A keto all purpose flour blend is usually the closest substitute, especially if it’s designed for 1:1 swapping. Still, “closest” depends on the recipe: brownies want tenderness, whereas bread wants structure, so a single substitute won’t be perfect in every bake.
7) Almond flour vs coconut flour: which is better for keto baking?
Almond flour tends to be richer and more tender, so it shines in brownies, cookies, muffins, and pancakes. Coconut flour, on the other hand, is much more absorbent, which means it can create a lighter, cake-like crumb when the liquid and eggs are adjusted properly.
8) Why does coconut flour make recipes dry?
Because coconut flour absorbs a lot of moisture. Consequently, recipes that use coconut flour usually need more eggs, more liquid, and often a short resting time so the batter can hydrate fully before baking.
9) Can I swap coconut flour for almond flour 1:1?
Usually not. Coconut flour is far more absorbent, so a direct swap often leads to a stiff batter and a dry final bake. Instead, use coconut flour recipes as written, or use it in small amounts to help firm up a blend.
10) Why does my keto bread crumble?
Most often, it’s a structure issue. Either the loaf needs more binder support (like psyllium or flax), more moisture, or a gentler bake. Additionally, slicing too soon can make the crumb fall apart, so cooling fully can help a lot.
11) What is keto bread and pastry flour used for?
Keto bread and pastry flour blends are typically designed to mimic flour-like structure in doughs and batters. As a result, they’re often used for sandwich-style loaves, rolls, pizza crust, and bakes where you want a more “traditional” bite.
12) What’s the best keto flour for bread?
Bread usually benefits from a blend that prioritizes structure, not just tenderness. For that reason, many bakers use a keto flour mix that includes binders such as psyllium, plus a base flour that supports a sliceable crumb.
13) What is a low carb flour mix?
A low carb flour mix is a blended “system” meant to behave more predictably than a single flour. Typically, it combines a base flour (for bulk), a binder (for structure), and sometimes fiber ingredients (for texture and lower net carbs).
14) What’s the best keto flour for brownies?
For fudgy brownies, almond flour is often the easiest path because it stays tender and rich. If you prefer a more cake-like brownie, a more structured keto flour blend—or a tiny amount of coconut flour used carefully—can help the bars set neatly.
15) Are keto brownies mix products worth it?
They can be, especially if you want convenience. Even so, mixes vary in texture depending on whether they’re almond-based, coconut-based, or built from a more flour-like blend. Therefore, it’s smart to pick a mix that matches your preferred brownie style.
16) What’s the difference between low carb brownie and keto brownie?
Often, it’s about how strict the carb target is and how the product is labeled. In practice, both can be made with similar ingredients, yet serving size and sweetener choice can change the final numbers dramatically.
17) What’s the best flour for keto pie crust?
Almond flour is the classic choice for a tender, buttery crust. However, if you want cleaner slices and less crumbling, a small amount of binder or a carefully measured blend can make the crust sturdier without making it tough.
18) Can you make a sugar free low carb pie crust?
Yes. Many low carb pie crusts use almond flour plus butter, then rely on a keto baking sweetener only if you want a sweeter, cookie-like base. Otherwise, you can keep it savory and let the filling provide sweetness.
19) Is there a no carb pie crust?
Some “no carb” claims refer to fiber-heavy crust approaches or very small serving-size calculations. Even if a crust is extremely low net carb, it still needs a solid texture plan; otherwise, it can turn either brittle or gummy.
20) What’s the best keto sugar substitute for baking?
It depends on the bake. Some sweeteners create crisp cookies but drier cakes, while others keep brownies softer yet brown faster. Accordingly, it helps to match your sweetener to your goal—crisp, chewy, cakey, or fudgy.
21) Why do keto cookies sometimes turn out gritty?
That grit usually comes from a sweetener that recrystallizes as the cookies cool. If that happens, try a different sweetener blend, adjust baking time slightly, or use recipes designed for that sweetener’s behavior.
22) What are keto baking chips and do they melt like chocolate?
Keto baking chips vary based on sweetener and fat composition. Some melt smoothly, while others soften but hold their shape more. If you want gooey pockets, choose chips known for melting well; if you want defined chips, pick a variety that stays intact.
23) Can I use keto baking chocolate in brownies and frosting?
Yes, although the sweetness level and texture can vary. For brownies, it can deepen flavor without adding extra sweetness. For frosting, it helps to balance with enough fat so the finish stays smooth rather than stiff.
24) What is carbquik and how is it used?
Carbquik is a low carb baking mix often used for biscuit-style doughs and quick bakes. Since mixes differ by formula, results can range from fluffy to dense depending on liquid ratios and baking time.
25) Where can I buy keto bread mixes or low carb bread mixes?
Keto bread mix and low carb bread mixes are commonly sold online and at larger grocery retailers. Still, before buying, compare serving sizes and ingredients to make sure the mix matches your preferences for taste, texture, and carbs.
26) Are keto baked goods from an online keto bakery always low carb?
Not automatically. “Keto bakery online” offerings vary in ingredients and portion sizes, so it’s worth checking how they calculate carbs, what sweeteners they use, and how large each serving is.
27) Are low carb flour tortillas keto friendly?
Sometimes, yes—depending on serving size, fiber content, and how you count net carbs. Because wraps can be easy to overeat, it helps to decide in advance whether you’re having one tortilla, two, or building a bowl instead.
28) What are Mission Carb Balance tortillas and how many carbs do they have?
Mission Carb Balance tortillas are marketed as reduced net-carb tortillas, yet the exact carbs depend on the variety and serving size. Therefore, check the label for the specific package you’re buying rather than assuming all versions match.
29) Are “no carb tortillas” or “zero net carb wraps” too good to be true?
They can be very low net carb on paper; however, fiber type and portion size still matter. If you feel better with a conservative approach, treat them as an occasional convenience rather than an unlimited staple.
30) Can I make keto flour tortillas at home?
Yes. Homemade versions often use almond flour, coconut flour, or binder-based doughs that roll and cook like tortillas. The main advantage is control: you can tune thickness, softness, and flavor to your liking.
31) What can I use instead of flour for keto bread crumbs?
Almond flour, almond meal, crushed seeds, and pork rind crumbs are popular substitutes. Depending on the dish, each can deliver crispness, although seed-based crumbs add a nuttier flavor.
32) What’s the best low carb flour substitute for thickening sauces?
Instead of wheat flour, many people use small amounts of xanthan gum, psyllium, or even a reduced cream-based approach. The key is to add slowly, because a little goes a long way and can thicken quickly.
33) Is lupin flour keto friendly?
Often, yes, and it can add helpful structure because it’s protein-forward. Still, taste varies by person, so it’s usually best to try it first in chocolate bakes or blended recipes.
34) What is bamboo flour keto baking used for?
Bamboo fiber-style ingredients are typically used to add bulk and help reduce net carbs in certain blends. Since they can be drying, they usually work best when paired with enough moisture and binders.
35) Is there a keto alternative to wheat flour for chapati or roti?
Many people try low carb atta blends or nut-and-fiber based doughs. Results vary, though, because chapati texture depends heavily on gluten. A more realistic goal is a soft flatbread that satisfies the role of roti, even if it isn’t identical.
36) Why does keto cake sometimes sink in the middle?
This can happen when batter is under-structured, over-leavened, or baked at too high a temperature. Additionally, opening the oven early can cause a fragile keto cake to collapse before it sets.
37) How do I store keto baked goods so they don’t dry out?
Because low carb bakes can lose moisture quickly, store them tightly wrapped. Also, many keto breads and muffins taste better after a brief rewarm, since heat softens fats and improves texture.
38) What’s the best way to start keto baking if I’m new?
Begin with a simple bake that teaches you how the flour behaves—pancakes or brownies are ideal. Then, once you understand your preferred base flour and sweetener, move into pie crust and bread with more confidence.
39) Can keto baking be nut-free?
Yes. Coconut flour is the most common nut-free keto flour option, and some blends avoid nuts entirely. Even so, nut-free keto baking often requires more careful moisture and binder balance to avoid dryness.
40) What’s the “ultimate guide to keto baking” mindset?
Think in systems, not swaps. Choose the flour and binder that fit the bake, control moisture on purpose, and treat texture as feedback. Over time, keto baking becomes less experimental and far more reliable.
































