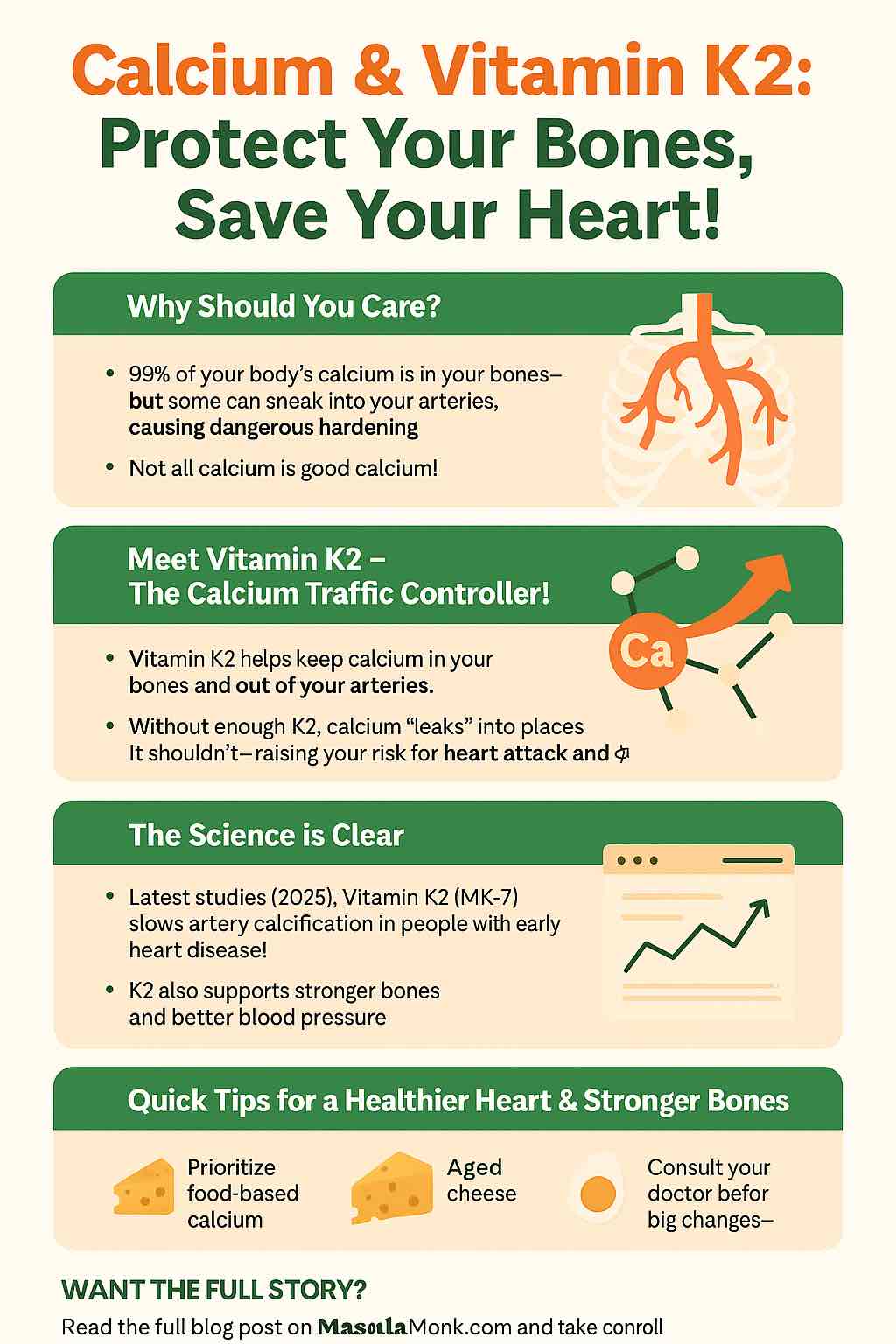
Why Talk About Vitamin D₃ + K₂?
Vitamin D deficiency is almost an epidemic in India today — with over 70–80% of urban adults showing insufficient levels. Here are 14 common signs of Vitamin D deficiency you may already be familiar with: fatigue, muscle pain, brittle bones, frequent colds, and even low mood.
But there’s a twist many people miss: Vitamin D alone is not enough. Without Vitamin K₂, the calcium that Vitamin D helps absorb may get deposited in arteries instead of bones — leading to calcification and stiffness. That’s where the D₃ + K₂ synergy steps in. Together, they don’t just absorb calcium, they direct it to the right places. Here’s a deep dive into the connection between calcium, Vitamin K₂, and vascular calcification.
Meet Body Reserve Plant-Based Vitamin D₃ + K₂ MK-7 🌿
This supplement positions itself differently from others on the market. Instead of relying on lanolin (sheep’s wool) or synthetic Vitamin D, Body Reserve’s Vitamin D₃ + K₂ uses plant-based lichen-derived Vitamin D₃ and chickpea-derived MK-7 Vitamin K₂.
👉 Why this matters:
- It’s vegan-friendly and cruelty-free.
- MK-7 (the superior form of K₂) stays active in the body longer, giving more consistent support.
- It avoids unnecessary additives, fillers, or allergens.
This makes it an excellent option for those who care not just about health outcomes but also about clean-label, plant-based nutrition.
This Product features in Top-Rated Vitamin D Supplements Available on Amazon India
What’s Inside the Bottle?
- 🌞 Vitamin D₃ (Plant-based, from lichen) → boosts calcium absorption, supports immunity, uplifts energy.
- 🥬 Vitamin K₂ (MK-7, from chickpeas) → ensures calcium goes to bones and teeth, not arteries.
- 🚫 No synthetic fillers → clean, minimal formula that is easier on the stomach.
Compare this to Pure Nutrition’s Natural Treasures blend, which leans on ayurvedic positioning, or Osoaa’s triple-action blend with B₁₂. Body Reserve’s Vitamin D₃ + K₂ keeps things lean and purely plant-powered.
Who Needs This Supplement Most?
- Vegans & Vegetarians 🥦 → Since natural D₃ is usually animal-derived, this is one of the few clean vegan options.
- People with bone health concerns 🦴 → Osteoporosis risk, frequent fractures, or joint issues.
- Cardio-conscious adults ❤️ → Preventing calcium buildup in arteries is critical for long-term heart health.
- Urban lifestyles 🌆 → Limited sun exposure due to work-from-home, pollution, or sunscreen use.
- Elderly population 👵 → Absorption of Vitamin D naturally reduces with age.
If you’re still unsure, revisit our earlier primer on food sources of Vitamin D to understand why supplementation is often unavoidable.
How Does It Compare With Other Brands?
Let’s put Body Reserve’s Vitamin D₃ + K₂ side by side with the other supplements we’ve reviewed in this series:
- Vlado’s Himalayan Organics → Budget-friendly, mass market appeal.
- Tata 1mg → Trustworthy, pharma-quality, good for first-time buyers.
- Pure Nutrition → Strong natural health positioning with an ayurvedic touch.
- Osoaa → A more comprehensive blend (D₃, K₂, B₁₂) aimed at active lifestyles.
- Body Reserve → The cleanest, most vegan-friendly option, though with a slightly higher price tag.
What Are People Saying on Amazon?
From browsing verified buyer reviews:
- 🌟 Many praise it for being gentle on the stomach compared to other capsules.
- 🌟 Vegans love the fact that it’s non-lanolin sourced.
- 🌟 Some users report improved energy and reduced joint stiffness after regular use.
- ⚠️ A few mention the price point feels high for the number of capsules compared to Tata or Osoaa.
How to Get the Most Out of Body Reserve Vitamin D₃ + K₂
Supplements work best when combined with lifestyle tweaks:
- Pair with calcium-rich foods (like dairy, ragi, or fortified plant milk).
- Add healthy fats (like nuts, olive oil, or fish oils) since Vitamin D is fat-soluble.
- Make time for morning sunlight exposure — even 15 minutes helps.
- Avoid excessive junk food or soda, which can weaken bone density.
Final Thoughts
Body Reserve Plant-Based Vitamin D₃ + K₂ MK-7 is an excellent choice for those who want a clean, vegan, and effective solution to two of the most common deficiencies today. It stands apart with its plant-based sourcing, which isn’t just about being vegan — it’s about being sustainable, gentle, and future-forward.
If you’re building your supplement stack, consider:
- Vitamin D for immunity and skin health,
- Fish Oils for Omega-3 balance, and
- Osoaa or Pure Nutrition alternatives if you want more complex blends.
- Top-Rated Vitamin D Supplements Available on Amazon India
But if you want to keep things simple, plant-powered, and targeted at bone + heart health — Body Reserve’s Vitamin D₃ + K₂ is hard to beat.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why should Vitamin D₃ always be paired with Vitamin K₂?
Vitamin D₃ helps absorb calcium, but without K₂, that calcium may end up in arteries instead of bones. K₂ directs calcium into bones and teeth, improving bone density while protecting cardiovascular health.
2. Is Body Reserve Vitamin D₃ + K₂ vegan?
Yes. Unlike many Vitamin D supplements derived from lanolin (sheep’s wool), this one uses lichen-derived D₃ and chickpea-derived MK-7, making it 100% plant-based and vegan-friendly.
3. How is this different from Tata 1mg or Vlado’s Himalayan Organics?
- Tata 1mg → Pharma-trust, affordable, but not plant-based.
- Vlado’s Himalayan Organics → Budget option, mass-market appeal.
- Body Reserve → Higher price but premium, vegan-friendly formula with clean sourcing.
4. Who should avoid this supplement?
People on blood-thinning medications (like Warfarin) should consult a doctor before taking Vitamin K₂, as it can interfere with clotting.
5. How long does it take to see results?
Bone density changes take months, but many users report improved energy, mood, and reduced joint stiffness within 4–6 weeks of consistent use.
6. Can children take this supplement?
This formulation is intended for adults. For children, pediatric Vitamin D drops or chewables are more suitable.
7. Does it help with immunity?
Yes. Vitamin D₃ plays a key role in regulating immune responses, lowering infection risks, and supporting overall wellness.
8. How should it be consumed?
Take 1 capsule daily with a meal containing healthy fats for maximum absorption.
9. Can it be combined with fish oil supplements?
Absolutely. Fish oils provide Omega-3s, which further support bone and cardiovascular health, making them a great stack with Vitamin D₃ + K₂.
10. Where can this product be purchased?
The most reliable source is Amazon India’s official listing, which ensures authenticity and timely delivery.