There are some foods that feel bigger than the sum of their ingredients. Falafel is one of them. At a glance, a falafel recipe seems humble enough: chickpeas, herbs, onion, garlic, spices, and a little patience. Yet when everything comes together properly, the result is far more memorable than that short ingredient list suggests. A really good falafel has a crisp, deeply golden shell, a tender green center, and the kind of savoury, herb-packed character that makes one bite lead to another before you have even reached for the sauce.
That contrast is exactly why a proper falafel recipe deserves more than a quick set of instructions. It helps to understand what falafel is, why some versions turn light while others become heavy, why soaked dried chickpeas behave differently from canned chickpeas, and how the cooking method changes the final texture. Once those pieces fall into place, making falafel at home becomes less mysterious and much more rewarding.
Why a homemade falafel recipe can feel intimidating at first
For many home cooks, falafel falls into that frustrating category of dishes they happily order but hesitate to make themselves. One person worries about dealing with hot oil, while another is put off by the fear of a dense or crumbly result. Quite often, the concern is that the mixture will turn bland, fall apart in the pan, or end up pasty rather than light. There is also the lingering question of method: does an authentic falafel recipe really need deep frying, or can air fryer falafel and baked falafel still be crisp, satisfying, and fully worth making?
Then again, the hesitation does not only come from technique. Plenty of people also wonder whether a chickpea falafel recipe made with canned chickpeas can ever be as good as one made with soaked dried chickpeas. Others are unsure about the herbs, the spices, or the right sauce to serve alongside the final plate. Once all those questions pile up, a dish that sounds simple in theory can start feeling strangely complicated in practice.

What this falafel recipe guide covers
This guide brings all of that together in one place. It begins with the classic foundations, moves through the ingredient choices that matter most, explains how to make falafel from scratch, and then walks through fried, air fryer, and baked options with the kind of detail that helps in a real kitchen. Along the way, it also makes room for serving ideas, falafel sauces, pita and wrap combinations, bowl variations, canned chickpea options, make-ahead advice, and the troubleshooting that turns a frustrating first attempt into a dependable homemade meal.
Falafel is widely understood as a Middle Eastern dish made from chickpeas, fava beans, or both, shaped and cooked until crisp, and often served with pita, salad, and tahini. It is also often linked to Egypt in origin discussions, although it now belongs to a much broader and richly shared regional story. If you enjoy food history, both Britannica’s overview of falafel and its notes on daily life and cuisine in Egypt give helpful background without getting in the way of dinner.
Why falafel becomes a repeat recipe
Still, what matters most here is what happens on the plate. Whether you want an easy falafel recipe for a weekday lunch, a more traditional homemade falafel for a weekend spread, a healthy falafel option for meal prep, or a crisp falafel wrap with sauce and salad, the fundamentals remain the same. Start with the right base. Build in enough herbs and seasoning. Respect the texture. Choose the cooking method that suits the meal in front of you.
Once you do that, falafel stops feeling like a specialty and starts feeling like one of the smartest things you can cook with chickpeas.
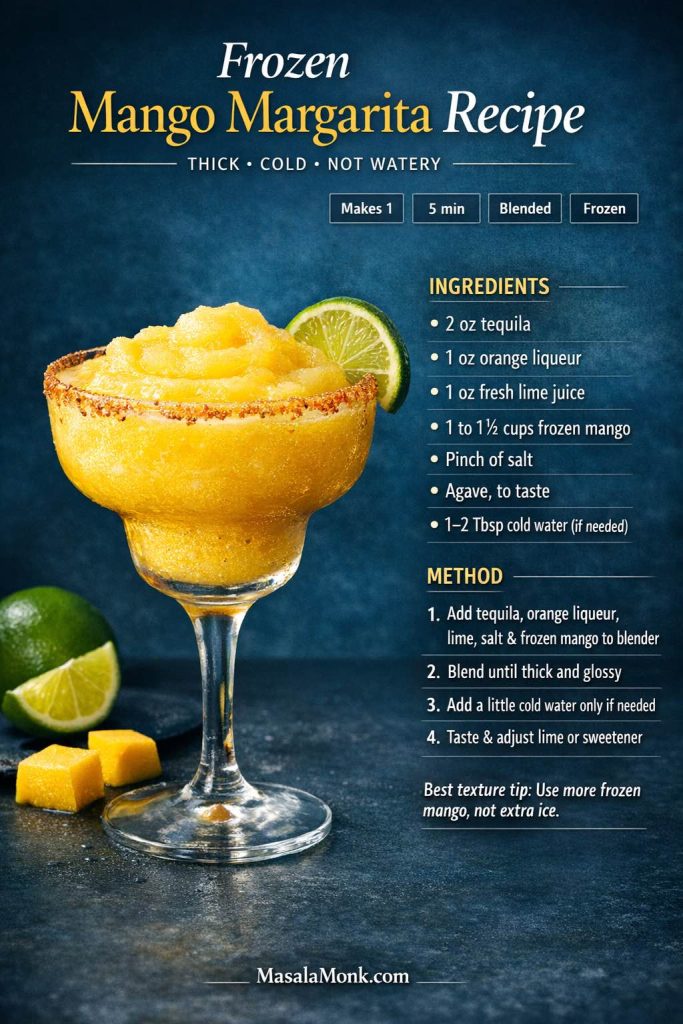
Also Read: Mango Margarita Recipe (Frozen or On the Rocks)
What Is Falafel and What Makes a Good Falafel Recipe
Falafel is often described in a sentence or two, but it becomes much easier to appreciate once you think of it not as a single rigid recipe but as a family of preparations built around legumes, herbs, aromatics, and spice. The basic idea is straightforward: chickpeas or fava beans are combined with onion, garlic, parsley, cilantro, cumin, coriander, salt, and sometimes other seasonings, then shaped into balls or patties and cooked until crisp outside and tender inside.

What makes a good falafel recipe so satisfying
Still, that basic definition does not fully explain why falafel has such lasting appeal. At its best, it is earthy without feeling heavy, fragrant without becoming overpowering, and substantial without tipping into stodgy territory. Just as importantly, it slips easily into different kinds of meals. One day it becomes lunch tucked into pita, while on another it lands in a grain bowl, joins a mezze-style spread, or turns into a quick snack with tahini sauce on the side. Depending on how you serve it, falafel can feel firmly traditional or pleasantly flexible.
A good falafel recipe is also built around contrast. The shell should be crisp rather than oily. The center should be tender and herb-flecked rather than pasty. The chickpeas should still feel like chickpeas, yet the mixture should be processed enough to hold together with confidence. In other words, the pleasure of falafel comes not from one single element but from the way texture, aroma, seasoning, and serving all work together.
Chickpeas, fava beans, and authentic falafel variation
Because falafel has spread so widely across kitchens, restaurants, and home tables, there is more than one accepted version. Some cooks build an authentic falafel recipe around chickpeas. Others lean toward fava beans. Some make small balls. Others prefer patties. Some stay very close to a classic seasoning profile, while others add chillies, sesame seeds, or regional twists. What ties these approaches together is the pursuit of that unmistakable texture: crisp shell, soft center, lively flavour.
That broader view matters because people often search for falafel as though there is only one correct version. In reality, there is a core identity, but there is also room for regional nuance. A chickpea falafel recipe may be the most familiar style in many kitchens, whereas a broad bean falafel recipe may feel more connected to Egyptian tradition. Both belong to the wider falafel story.
Why homemade falafel can surprise you
That is also why homemade falafel can be such a surprise if your main reference point is dry takeaway falafel. When it is fresh and properly seasoned, it tastes greener, brighter, warmer, and more alive. The herbs are more pronounced. The crust is more delicate. The interior has more nuance. In other words, a good homemade falafel recipe does not simply recreate something familiar. It can completely change how you think about the dish.
Also Read: Sourdough Pizza Dough Recipe (Crispy Crust & Easy Pizza Base)
Falafel Recipe Ingredients: What Falafel Is Made Of
At its heart, falafel relies on a handful of ingredients that each play a distinct role. The list is not long, yet the balance is everything.

The best chickpeas for a falafel recipe
Chickpeas are the base most people have in mind when they picture falafel. They bring body, earthy flavour, and enough structure to create the right interior once processed properly. For a traditional falafel recipe, dried chickpeas are soaked and used raw rather than boiled first. That step matters more than it may seem, because their firmness affects both texture and how the mixture holds together.
A chickpea falafel recipe made this way usually has the most satisfying interior. The chickpeas stay structured, the mixture remains textured, and the final falafel cooks into something crisp outside and tender inside. By contrast, softer cooked chickpeas move much more quickly toward a paste.
The aromatics
Onion and garlic build the savoury backbone. Without them, the mixture can taste flat and timid. They also contribute a little moisture, which is helpful in moderation and troublesome in excess. That is one reason why the exact balance of onion, garlic, and herbs matters so much.
Too much onion can loosen the mixture more than you expect, especially if the onion is watery. Too little garlic, meanwhile, can leave the final falafel feeling mild rather than warmly savoury. The aim is not sharpness for its own sake, but depth.
The herbs that lift a homemade falafel recipe
Parsley and cilantro are not decorative extras. They are central to the flavour and appearance of falafel. They create that fresh, green interior that sets a truly good falafel apart from a beige, dense one. If you have ever bitten into a falafel that felt oddly dull, the herb ratio was often part of the problem.
Parsley brings clean freshness, while cilantro adds brightness and a slightly sharper herbal note. If you prefer less cilantro, it is usually better to replace it with more parsley than to reduce the herbs overall. Otherwise, the mixture can lose the lively quality that makes falafel feel fresh rather than heavy.
The spices behind an authentic falafel recipe
Cumin and coriander are the classic pair. Cumin adds warmth and depth, while coriander lifts the flavour and keeps the mixture from leaning too heavily into earthiness alone. Black pepper appears often. So does a little chilli in some kitchens. Beyond that, there is room for modest variation, though it is usually wiser to perfect the fundamentals before adding too many extra notes.
The salt
Salt is not a background player here. Since falafel contains chickpeas, herbs, onion, and garlic, it needs enough seasoning to prevent all that wholesome goodness from becoming merely worthy. One of the most common issues with a homemade falafel recipe is not texture but blandness, and that often begins with under-seasoning the raw mixture.
The optional helpers
Some recipes include chickpea flour, a little plain flour, or baking powder. These are not always necessary, especially when the mixture is well balanced and the chickpeas have been handled correctly. Still, they can be useful in specific contexts, particularly for baked falafel, air fryer falafel, or mixtures that feel slightly too loose after processing.
For a gluten free falafel recipe, chickpea flour is especially useful because it helps bind without changing the character of the mixture too much. Baking powder, on the other hand, is best seen as a small supporting detail rather than the secret to success.
Also Read: Balti Paneer Gravy (Restaurant-Style, Creamy + Bold Recipe)
What Makes This Homemade Falafel Recipe So Good for Texture and Flavor
The difference between average falafel and memorable falafel is rarely about extravagance. More often, it comes down to texture, balance, and timing.
A strong falafel recipe should deliver contrast at every stage. The first bite should meet a crisp exterior rather than a soft, oily shell. The interior should feel tender and almost fluffy, yet still have enough texture to remind you it came from soaked chickpeas and herbs, not from a smooth purée. The seasoning should taste warm and rounded rather than harsh or flat. The herbs should be present enough to brighten each bite without turning the whole mixture grassy.

This is exactly where rushed methods tend to disappoint. Over-process the chickpeas and the mixture quickly turns pasty instead of textured. Treat canned chickpeas the same way as soaked dried chickpeas and the finished falafel often comes out denser than you hoped. Skimp on the herbs and the center loses the freshness that makes falafel so distinctive. Meanwhile, if the oil temperature is off, the exterior may brown too fast or soak up more oil than it should.
Writers who focus closely on texture, such as Serious Eats, and cooks who emphasize practical home technique, such as The Mediterranean Dish, return to these same points again and again for good reason. They are not small details. They are the difference between falafel you politely finish and falafel you start planning to make again before the meal is over.
Also Read: Mojito Recipe (Classic) + Ratios, Pitcher, Mocktail & Easy Variations
Ingredients for This Homemade Falafel Recipe
Here is a balanced ingredient list for a classic chickpea falafel that works beautifully as a base recipe.
Ingredients
- 1 1/2 cups dried chickpeas
- 1 small onion, roughly chopped
- 4 to 6 garlic cloves
- 1 packed cup parsley leaves and tender stems
- 1/2 to 1 cup cilantro leaves and tender stems
- 2 teaspoons ground cumin
- 1 teaspoon ground coriander
- 1/2 to 1 teaspoon black pepper
- 1 1/2 to 2 teaspoons salt
- 1 to 2 tablespoons chickpea flour, only if needed
- 1 teaspoon baking powder, optional
- neutral oil for frying, or a little oil for brushing in air fryer and baked methods

A few ingredient notes
For a greener and fresher falafel, add a little more parsley to the mixture. Anyone who does not love cilantro can scale it back and replace that volume with extra parsley rather than leaving the herbs unbalanced. A touch of chilli can also be introduced for heat, although the classic flavour profile leans far more on cumin and coriander than on spice alone.
For a gluten free falafel recipe, chickpea flour is the simplest binder when needed. Since chickpeas themselves are naturally gluten free, the key is simply to avoid unnecessary additions that introduce gluten.
This is also naturally very close to a vegan falafel recipe. The mixture itself relies on chickpeas, herbs, aromatics, and spices, so the falafel can easily remain vegan as long as the sauces and sides you choose do the same.
Also Read: Paloma Recipe: 12 Paloma Cocktail Drinks
Dried Chickpeas vs Canned Chickpeas for a Falafel Recipe
This question sits at the center of nearly every serious falafel conversation, and rightly so. The choice between dried chickpeas and canned chickpeas changes the texture, the handling, and often the final method.

Why dried chickpeas make the best falafel recipe
For a traditional or authentic falafel recipe, dried chickpeas are soaked in water until they swell, then drained and processed raw. They have enough firmness to create a mixture that stays textured rather than turning creamy. They also behave better in hot oil because they are not already fully cooked and softened.
That is why many respected falafel recipes insist on dried chickpeas and warn against canned chickpeas for the classic version. Both The Mediterranean Dish and Serious Eats make this point clearly, and once you have seen the difference in the food processor, it becomes obvious.
Can canned chickpeas work in a falafel recipe?
Yes, canned chickpea falafel can work. It simply behaves differently. Canned chickpeas are already cooked and much softer, so they are more likely to become mushy when processed. That can make it harder to form balls that stay light inside. The resulting falafel may still taste good, but it usually has a denser, less open texture.
When to use canned chickpeas anyway
There are moments when convenience matters more than orthodoxy. If you need an easy falafel recipe on a weekday and did not soak dried chickpeas ahead of time, canned chickpeas can still get dinner on the table. In that case, it helps to pulse very carefully, dry the chickpeas thoroughly, use a modest amount of binder if needed, and lean toward flatter patties for baking or air frying.
The honest difference
If you are chasing the best falafel recipe you can make at home, dried chickpeas are worth it. If you are chasing speed and flexibility, canned chickpeas remain an option. The key is knowing that these are not interchangeable choices with identical results. They are two related but different paths.
Also Read: Air Fryer Donuts Recipe (2 Ways): Glazed Homemade Donuts + Biscuit Donuts
How to Soak Dried Chickpeas for the Best Falafel Recipe
Soaking chickpeas is easy, though it does require a little foresight.
Place the dried chickpeas in a large bowl and cover them generously with cold water. They need far more room than you might expect because they expand as they absorb liquid. Leave them overnight, or for roughly 18 to 24 hours if your kitchen is cool and your timing allows. Then drain them well.

What you are looking for is this: the chickpeas should be larger and hydrated, but still firm. They should not resemble boiled chickpeas, and they definitely should not be soft enough to mash between your fingers with almost no effort. That firmer state is what helps create the right falafel texture later.
Once drained, it helps to let them sit in a colander for a few minutes so extra moisture can run off. Too much lingering water can loosen the mixture more than necessary.
Also Read: Tapas Recipe With a Twist: 5 Indian-Inspired Small Plates
Chickpea Falafel Recipe vs Broad Bean Falafel
Although chickpea falafel is the version many readers will be searching for, it is worth noting that falafel is not limited to chickpeas alone. In some traditions, especially those tied more closely to Egypt, falafel may be made with fava beans or broad beans instead. That version can taste slightly different and may have a softer, more delicate character depending on the recipe.

For that reason, when people search for an Egyptian falafel recipe or a broad bean falafel recipe, they are often looking for a related but not identical dish. Chickpea falafel tends to be the most familiar version in many home kitchens, and it is also the easiest one to build a broad guide around. Even so, knowing that fava bean falafel exists adds useful context. It reminds us that falafel has regional breadth and a longer story than one single formula can capture.
Also Read: Air Fryer Salmon Recipe (Time, Temp, and Tips for Perfect Fillets)
How to Make Falafel from Scratch: Step-by-Step Falafel Recipe
Making falafel at home becomes much less intimidating once you see that the steps are logical and manageable.

Step 1: Prepare the ingredients
Drain the soaked chickpeas. Roughly chop the onion if it is large. Peel the garlic. Wash and dry the herbs. Gather the spices and salt. This is not a fussy recipe, but having everything ready makes it easier to stop processing at the right moment rather than scrambling for ingredients while the food processor is running.

Step 2: Process the mixture
Add the chickpeas, onion, garlic, parsley, cilantro, cumin, coriander, salt, and pepper to a food processor. Pulse in short bursts. Scrape down the bowl as needed. The goal is a coarse, even mixture that holds together when pressed but still shows texture.

Step 3: Check the texture
Take a small amount of the mixture in your palm and press it gently. A mixture that holds together under light pressure is usually in good shape. On the other hand, if it crumbles straight away, it needs a little more pulsing. Should it feel wetter than expected, add a small spoonful of chickpea flour and pulse again briefly until the texture looks more cooperative.

Step 4: Rest the mixture
Cover and chill the processed mixture for at least 30 minutes. This resting time helps in two ways. First, it firms the mixture and makes shaping easier. Second, it gives the flavors a moment to settle together.

Step 5: Shape the falafel
Use your hands, a spoon, or a falafel scoop if you have one. Small balls are traditional and beautiful when fried. Slightly flattened patties are particularly useful for baked falafel and air fryer falafel, since they brown more evenly and are easier to turn.

Step 6: Cook by your chosen method
From here, you can fry, air fry, or bake. Each route has its own appeal, and none of them are difficult once the mixture is right.

Also Read: Masterclass in Chai: How to Make the Perfect Masala Chai (Recipe)
Fried Falafel Recipe: How to Make Crispy Falafel
For many cooks, fried falafel remains the benchmark. There is a reason for that. Hot oil creates a crust that is difficult for any other method to match. The shell becomes deeply crisp, the center stays tender, and the whole thing tastes unmistakably falafel in the way many people first fell in love with it.
How to fry falafel
Fill a deep pan or pot with enough neutral oil to allow the falafel to cook without touching the bottom too aggressively. Heat the oil until it is hot but not smoking. If the oil is too cool, the falafel may absorb excess oil and feel greasy. If it is too hot, the exterior will brown too quickly.
Lower a few pieces in at a time. Avoid crowding the pan, since that can drop the temperature and make the batch less crisp. Let them cook until evenly golden brown, then remove and drain on paper towels or a wire rack.

What fried falafel should look like
The outside should be dark golden and crisp, not pale. The inside should be cooked through but still moist and green-flecked. If you split one open and it looks smooth or pasty, the mixture was likely processed too far or the chickpeas were not ideal for the method.
Why people keep coming back to fried falafel
Because it is hard to beat. Fried falafel offers the strongest crust and the clearest contrast between crisp exterior and tender middle. For a weekend lunch, a dinner spread, or any time you want the most classic version, it remains the method that most fully expresses what falafel can be.
Also Read: Crock Pot Pork Chops and Sauerkraut (No Dry Chops Recipe)
Air Fryer Falafel Recipe
Air fryer falafel occupies a very useful place in a modern kitchen. It gives you a lighter option, avoids a pot of oil, and still creates browning and texture when done well. It is not identical to fried falafel, but it can be genuinely satisfying rather than a compromise made with resignation.
Why air fryer falafel works
The circulating heat of the air fryer encourages the exterior to dry and color while keeping the inside relatively tender. A light brushing or spraying of oil helps enormously here. Without a little exterior fat, the surface can dry before it crisps.

How to shape air fryer falafel
Slightly flattened patties often work best because they expose more surface area and cook more evenly. Small balls can also work, although they may need turning and a little more attention.
How to cook falafel in an air fryer without drying it out
Preheat the air fryer if your model allows it. Arrange the falafel in a single layer with space between each piece. Cook until the surface is browned and the falafel feels set, turning once if needed. Since every air fryer behaves a little differently, it helps to watch the first batch closely rather than trusting one exact minute count.
How to keep air fryer falafel from drying out
There are several ways. Use enough herbs so the interior stays lively. Do not over-process the mixture. Do not make the patties too small. Lightly oil the exterior. Most importantly, stop cooking as soon as they are crisp rather than pushing for a darker shade at the expense of tenderness.
Why air fryer falafel is worth making
It fits beautifully into healthy falafel meals, lunch bowls, quick pita wraps, and meal prep routines. If you like this lighter direction, it pairs naturally with high-protein vegetarian meal prep ideas and plant-based protein meal prep inspiration, where chickpeas already play a valuable role.
Also Read: Keto Mocktails: 10 Low Carb, Sugar Free Recipes
Baked Falafel Recipe
Baked falafel is sometimes dismissed too quickly, usually because people expect it to behave exactly like fried falafel. It does not. Still, when approached on its own terms, it can be delicious, practical, and surprisingly satisfying.
What a baked falafel recipe does well
Baked falafel has several practical advantages. Larger batches are much easier to manage in the oven, and the process is notably less messy than frying. It also suits make-ahead cooking particularly well. Better still, baked falafel reheats nicely, which makes it a strong option for lunchboxes, grain bowls, and easy weeknight wraps.

How to bake falafel so it stays crisp and tender
Use a hot oven. Place the falafel on a lightly oiled tray or parchment. Brush or spray the tops with a little oil. Patties rather than thick balls usually bake more evenly. Turn them partway through so both sides color well.
What baked falafel tastes like
The crust is gentler, and the overall result is slightly drier than deep-fried falafel, though not unpleasantly so when the mixture itself is well balanced. In fact, baked falafel often shines most when served with generous sauces, crunchy vegetables, and warm bread or grains.
When a baked falafel recipe is the smart choice
When you want a healthy falafel recipe, when you are feeding more people at once, or when you want leftovers that hold up well the next day. It may not be the purest expression of the dish, yet it is one of the most practical.
Also Read: Slow Cooker Pork Tenderloin (Crock Pot Recipe) — 3 Easy Ways
How to Make Falafel with Canned Chickpeas
Since many cooks still want a canned chickpea falafel option, it is worth setting out a practical approach.
Use 2 cans of chickpeas, drained and dried very thoroughly. Reduce the onion slightly if you know yours is especially watery. Pulse carefully, because canned chickpeas go from chunky to mushy fast. Use chickpea flour a little more readily than you would in the dried-chickpea version. Prefer patties rather than balls. Then cook in the oven or air fryer rather than expecting the mixture to behave exactly like traditional fried falafel.

Tips for canned chickpea falafel
Dry the chickpeas as thoroughly as you can. Pat them dry with a clean towel if needed. Do not over-process. Chill the mixture before shaping. Use a binder sooner rather than later if the mix seems soft. Keep expectations honest and shape for the method rather than for tradition.
Why canned chickpea falafel turns mushy
Because the chickpeas are already cooked. They are softer, more hydrated, and easier to turn into paste. Once that happens, the interior loses the airy, crumbly quality that makes falafel feel so good. The goal, therefore, is not to make canned chickpeas behave like dried ones. The goal is to get the best possible shortcut version from the ingredient you have.
Will it be identical to an authentic falafel recipe made with soaked dried chickpeas? No. Can it still be tasty, crisp in places, and absolutely worth eating in a pita with salad and sauce? Certainly.
Also Read: Keto Hot Chocolate Recipe (Sugar-Free Hot Cocoa) + Best Homemade Mix
Why Falafel Falls Apart and How to Fix It
This is one of the classic falafel frustrations, and it nearly always comes down to structure and moisture.

The mixture may be too wet
Extra water from poorly drained chickpeas, very watery onion, or excessive herbs can all loosen the mixture. If the mix feels sticky and sloppy rather than cohesive, it needs help. A spoonful of chickpea flour can make a real difference.
The mixture may be too coarse
If the ingredients have not been pulsed enough, they may not bind. Falafel should not be puréed, but it does need enough processing for the particles to catch and hold together when pressed.
The mixture may need rest
Resting the mixture in the fridge gives it time to firm up. If shaping feels difficult, a half-hour of chilling often improves things.
The chickpeas may be the issue
Canned chickpeas are more prone to creating a softer mix that struggles in hot oil. That is one reason why so many cooks prefer dried chickpeas for a true homemade falafel recipe.
The oil may be part of the problem
If you are frying, oil that is not hot enough can weaken the structure before the exterior sets. Consequently, the falafel may seem as though it lacks binding when the real issue is that the crust never had a chance to form quickly enough.
Also Read: Dirty Martini Recipe (Classic, Extra Dirty, No Vermouth, Spicy, Blue Cheese, Tequila + Batched)
How to Keep Falafel from Turning Mushy
Mushy falafel is usually a sign that the mixture lost too much structure before it ever reached the pan or oven.
One common culprit is over-processing. Once chickpeas become a smooth paste, the interior tends to lose that delicate, crumbly quality. Another frequent cause is over-reliance on canned chickpeas. Since they are already cooked, they are easier to reduce to something dense and creamy.

Too much onion can also play a role, as can insufficient resting time. In some cases, falafel that looks mushy after cooking was not actually undercooked; it was simply too wet and too smooth going in.
The simplest prevention is this: start with soaked dried chickpeas, pulse rather than blend, drain everything well, and chill the mixture before shaping.
Also Read: Fish and Chips Reimagined: 5 Indian Twists (Recipe + Method)
How to Build More Flavor into a Homemade Falafel Recipe
Even when the texture is right, falafel can disappoint if it tastes muted. Fortunately, that is one of the easiest problems to fix.

Use enough herbs
A pale falafel interior often points to not enough parsley and cilantro. The herbs do not merely add freshness. They shape the identity of the dish.
Season assertively
Chickpeas are mild. Onion and herbs mellow as they cook. Salt, cumin, coriander, and garlic all need to be generous enough to remain clear in the finished falafel.
Smell the raw mixture carefully
You cannot eat it in the same carefree way you might taste a dressing, but you can smell it and assess the seasoning in that sense. Does it smell aromatic and warm? Or does it smell mostly like wet chickpeas? Your nose gives a useful clue.
Think about the whole plate
Falafel often sits alongside tahini, yogurt sauce, salad, pickles, hummus, and bread. The main falafel mixture should therefore be flavourful in its own right, but it does not need to carry the entire meal alone. Balance across the plate matters.
Also Read: Ravioli Recipe Reinvented: 5 Indian-Inspired Twists on the Italian Classic
Best Falafel Sauce Ideas for Wraps, Bowls, and Pita
Falafel without sauce can still be good. And then falafel with the right sauce becomes a complete meal.

Tahini sauce for falafel
This is the classic partner for falafel. Tahini mixed with lemon juice, garlic, water, and salt creates a sauce that is creamy yet bright. Its slight bitterness and richness work beautifully against the crisp shell and herb-forward center.
Yogurt sauce for falafel
A cool yogurt sauce offers a different kind of balance. It softens the warmth of cumin and coriander and pairs especially well with pita, salad, and crunchy vegetables. A cucumber-based version is even better on warm days. That is one reason why this Greek tzatziki sauce guide fits so naturally alongside falafel.
Cucumber yogurt sauce for falafel
If you want something especially fresh, a cucumber yogurt sauce is hard to beat. It brings coolness, moisture, and tang, all of which make it excellent for wraps and summer platters.
Creamy dairy-free options
If you want something richer without dairy, a tahini-forward mayo or a vegan herb sauce can be excellent. For readers who enjoy that style, the ideas in these vegan mayo variations can be adapted into very good sandwich and wrap sauces.
Spicy sauces
Falafel also welcomes heat. Harissa, chilli sauce, or a spicy yogurt dressing can shift the whole plate in a livelier direction. The warmth of the falafel base gives these sauces something solid to lean against.
Also Read: Croquettes Recipe: One Master Method + 10 Popular Variations
How to Serve Falafel in Pita, Wraps, Bowls, and Platters
One of falafel’s greatest strengths is how easily it slides into different meals. A batch made in the afternoon can become lunch, dinner, and leftovers the next day without feeling repetitive.

Falafel in pita bread
This is the classic arrangement for good reason. Warm pita, falafel, chopped tomato, cucumber, onion, herbs, tahini sauce, and perhaps a few pickles create a balance of crisp, creamy, bright, and warm. It feels complete in a way that many simple sandwiches do not.
Falafel wrap ideas
Wraps offer a slightly more flexible version of the same idea. Flatbread, lavash, or even tortillas can work if you are using what you have. Layer in lettuce, crunchy vegetables, sauce, and perhaps a spoonful of hummus. If you enjoy this lunch-friendly direction, plant-based sandwich inspiration and chickpea meal prep ideas make useful companions.
Falafel bowls for lunch or meal prep
For a lighter or more meal-prep-friendly route, serve falafel over rice, bulgur, couscous, quinoa, or greens. Add chopped vegetables, pickles, hummus, and sauce. A bowl can feel hearty or fresh depending on what you add, and it is an excellent home for air fryer falafel or baked falafel. If you like this format, this vegan bowl idea shows how satisfying sauce-and-grain bowls can be even outside a Mediterranean flavour profile.
Falafel platter
There is also something especially inviting about serving falafel as part of a broader spread. Place it alongside hummus, chopped salad, pickled onions, olives, warm bread, yogurt sauce, and a few herbs. Suddenly a simple chickpea preparation becomes the center of a table. That broader serving style connects naturally with your own guide to what to eat with hummus, which includes pairings that can sit comfortably beside falafel as well.
Falafel with playful twists
Once the classic version is secure, it can also be fun to explore other directions. Your post on falafel with Indian twists opens up a more inventive path without losing the core appeal of the dish.
Also Read: How to Make a Flax Egg (Recipe & Ratio for Vegan Baking)
Falafel and Hummus: One of the Best Pairings
This pairing deserves special mention because it is one of the most satisfying ways to serve falafel. Falafel brings crispness, warmth, and structure. Hummus brings creaminess, earthiness, and a soft counterpoint. Add pickles, lemon, chopped salad, and bread, and suddenly the plate has everything it needs.

What makes falafel and hummus work so well is contrast. One is crisp, the other smooth. One is herb-forward, the other mellow. And then one is hot, the other can be room temperature or cool. Together, they make each other better.
That is also why this pairing works across formats. It can be part of a platter, spread inside a wrap, spooned into a bowl, or layered into pita bread. It feels generous, complete, and deeply comforting without being complicated.
Also Read: Pork Tenderloin in Oven (Juicy, Easy, 350°F or 400°F) Recipe
Drinks That Pair Well with Falafel
Falafel is rich enough to appreciate something fresh and cooling on the side. Since the plate often includes tahini, hummus, bread, salad, and spice, a drink with brightness and lift feels especially welcome.

A minty, tangy option like jal jeera works surprisingly well, particularly in hot weather. Its cumin, mint, and citrus notes echo some of the aromatic qualities in the meal without competing with them. For a more playful summer table, a chilled mint-forward mocktail can also fit, though falafel rarely needs anything too sweet beside it.
In general, the most natural drink pairings are refreshing rather than rich. Think lemon, herbs, mint, cucumber, and cooling acidity rather than cream-heavy beverages.
Also Read: 19 Essential Kitchen Tools That Make Cooking Easier
Is Falafel Healthy? Fried vs Air Fryer vs Baked Falafel
Falafel occupies an interesting space in the kitchen because it can feel both hearty and wholesome at the same time. Much of that comes from its base. Chickpeas are a legume, and legumes are valued for protein, fiber, folate, iron, and other useful nutrients. If you enjoy reading more about the nutritional side of ingredients, both USDA FoodData Central and the NIH Office of Dietary Supplements glossary offer broad, reliable context around foods like chickpeas and legumes.

That said, whether falafel feels especially light or more indulgent depends on the method and the company it keeps.
Fried falafel is richer. Air fryer falafel and baked falafel are lighter. A pita packed with sauce can feel very different from a bowl of greens, chopped vegetables, and tahini. A platter with hummus, pickles, salad, and warm bread can be both nourishing and abundant.
The better way to think about healthy falafel is not by trying to strip it of pleasure. Instead, think in terms of balance. Use plenty of herbs. Do not under-season the mixture. Choose the method that fits your needs. Pair it with vegetables and sauces that add freshness rather than heaviness alone.
Why this is naturally a vegan falafel recipe
The falafel itself is usually vegan, because it is built from chickpeas, herbs, spices, onion, and garlic. The main thing to watch is what you serve with it. Tahini sauce keeps the whole meal vegan. Yogurt sauce, naturally, does not. Accordingly, vegan falafel is often less about changing the falafel itself and more about choosing the right accompaniments.
Why falafel is often gluten free
Falafel can also be gluten free, provided the binder and accompaniments cooperate. Chickpeas, herbs, and spices are naturally gluten free. If a recipe needs help holding together, chickpea flour is usually the easiest gluten free option. The falafel itself may be gluten free even when the pita is not.
Also Read: How to Cook Tortellini (Fresh, Frozen, Dried) + Easy Dinner Ideas
Falafel Recipe Variations: Green, Spicy, Mini, and Breakfast Falafel
Once the base technique feels familiar, falafel becomes an invitation to explore.

Green falafel
Increase the herb ratio for a brighter, more vivid interior. This version feels particularly fresh in wraps and bowls.
Spicy falafel
Add green chilli, red chilli flakes, or a little harissa to the mixture or the accompanying sauce. The chickpeas soften the heat nicely.
Mini falafel
Shape smaller balls for platters, snack boards, or party spreads. These are especially useful if you want falafel as part of a larger mezze table.
Falafel pockets
Stuff pita pockets with chopped salad, tahini, and smaller falafel pieces. This works well for packed lunches because the filling stays more contained.
Breakfast falafel
While not a traditional breakfast dish everywhere, falafel can be excellent in the morning with eggs, chopped tomatoes, yogurt sauce, herbs, and warm bread. The savory, spiced character suits a relaxed brunch surprisingly well.
Falafel and hummus
This pairing deserves mention again because it is so satisfying. Falafel with hummus, pickles, vegetables, and bread offers creamy, crisp, tangy, and earthy elements all in one plate. If you want more ideas in that direction, the pairings in what to eat with hummus make an easy extension.
Also Read: Steel Cut Oats vs Rolled Oats: Nutrition, Taste, Cooking & More
How to Make Falafel for Meal Prep
Falafel is one of the smartest foods to batch once you know the fundamentals.

Prepare the mixture ahead
The raw mixture can be made and chilled in advance, which makes shaping and cooking much easier the next day. This is especially helpful if you are using dried chickpeas and want to spread the work out.
Shape and freeze
You can shape falafel and freeze it on a tray before transferring it to a container. Later, you can fry, bake, or air fry smaller portions without starting from scratch.
Cook and store
Cooked falafel keeps well in the fridge for a few days. It is excellent for quick lunches when tucked into wraps or bowls with fresh vegetables and a sauce.
Reheat the right way
The oven or air fryer is the best route for reviving texture. The microwave softens the crust, which is not ideal unless speed matters more than crispness.
Build flexible meals around it
This is where falafel becomes especially useful. One batch can become pita sandwiches one day, bowls the next, and a snack plate later in the week. Because the base is so adaptable, meal prep rarely feels repetitive.
Also Read: How to make No-Bake Banana Pudding: No Oven Required Recipe
Homemade Falafel Recipe
Yield
About 18 to 24 falafel, depending on size
Prep time
25 minutes active time, plus soaking and chilling
Cook time
Varies by method
Ingredients for this Falafel Recipe
- 1 1/2 cups dried chickpeas
- 1 small onion, roughly chopped
- 4 to 6 garlic cloves
- 1 packed cup parsley
- 1/2 to 1 cup cilantro
- 2 teaspoons ground cumin
- 1 teaspoon ground coriander
- 1/2 to 1 teaspoon black pepper
- 1 1/2 to 2 teaspoons salt
- 1 to 2 tablespoons chickpea flour if needed
- 1 teaspoon baking powder, optional
- neutral oil for frying, or a little oil for brushing

Step-by-Step Method for this Falafel Recipe
- Soak the dried chickpeas in plenty of water overnight or up to 24 hours. Drain well.
- Add the chickpeas, onion, garlic, parsley, cilantro, cumin, coriander, salt, and pepper to a food processor.
- Pulse until the mixture is finely chopped and holds together when pressed, but do not purée it.
- If needed, add chickpea flour to help bind. Pulse briefly again.
- Chill the mixture for at least 30 minutes.
- Shape into balls or patties.
- Fry in hot oil until deeply golden, or cook in an air fryer or hot oven until crisp and cooked through.
- Serve hot with tahini sauce, yogurt sauce, pita, salad, and pickles.
Also Read: Sourdough Recipe: 10 Easy Bread Bakes (Loaves, Rolls & Bagels)
A Few Serving Menus Built Around the Falafel Recipe
Sometimes the easiest way to picture a recipe is to see how it can shape a full meal.

A simple weekday lunch
Air fryer falafel, chopped cucumber and tomato, tahini sauce, and warm pita.
A make-ahead office lunch
Baked falafel, greens, grains, pickled onions, hummus, and yogurt sauce packed separately.
A relaxed dinner platter
Fried falafel, warm bread, chopped salad, hummus, tahini, tzatziki, olives, and herbs.
A summer spread
Falafel wraps, crunchy slaw, yogurt sauce, herbs, and a cooling glass of jal jeera.
A creative vegetarian dinner
Classic falafel served alongside one of your Indian-inspired falafel variations for contrast and conversation.
Also Read: Baked Jalapeño Poppers (Oven) — Time, Temp & Bacon Tips
The Small Decisions That Improve a Falafel Recipe the Most
Once you have made falafel a few times, you begin to notice that the biggest improvements often come from surprisingly small adjustments.

Drying the chickpeas well matters.
Using enough herbs matters.
Stopping the food processor a little earlier matters.
Chilling the mixture matters.
Choosing patties for the oven and balls for frying matters.
Serving the falafel while still warm matters.
Adding enough sauce and crunch on the plate matters.
These are not glamorous insights, yet they are what turn a decent falafel recipe into one that becomes part of your regular cooking rhythm.
It is also worth saying that confidence changes the result. The first time, you may second-guess the texture, the seasoning, or the shape. The second time, you will already know more. The third time, you will make small decisions more naturally. Falafel rewards repetition in a very tangible way.
Also Read: Macaroni & Cheese Recipe: Creamy Stovetop, Baked & Southern
Falafel Recipe and the Pleasure of Repetition
Some recipes are enjoyable once and then forgotten. Falafel rarely belongs to that category. It tends to become more useful the more often you make it. The first time, you are learning the texture. The second time, you are refining the seasoning. The third time, you are already deciding whether the batch should become pita sandwiches, bowls, or a platter for friends.
That repeatability is part of what makes falafel so lovable. It adapts easily without losing the qualities that make it recognisable in the first place. A batch can become a quick lunch, a casual dinner, or the centerpiece of a table meant for sharing. On some days it leans more traditional; on others it takes on a slightly more flexible role. You can fry it for maximum crispness, air fry it for convenience, or bake it for meal prep, yet the heart of the dish remains the same: chickpeas, herbs, aromatics, spice, and that irresistible contrast between crust and center.
A good falafel recipe, then, is not only about one successful meal. It is about opening the door to many meals that follow naturally from the same set of ingredients.
Also Read: Blueberry Pancakes (6 Recipes) + Homemade Pancake Mix
A Final Word on Falafel Recipe
Falafel rewards care, though it does not demand fussiness. If you soak dried chickpeas, pulse the mixture to the right texture, season with confidence, and choose a cooking method that suits the meal you want, you are already most of the way there.

From there, the process stops feeling like effort and starts feeling like pleasure. One meal might see the falafel tucked into pita with salad and tahini, while the next turns it into a bowl with grains and pickles. It can sit beside tzatziki, pair beautifully with hummus, or anchor a fuller spread of sauces, vegetables, and bread. Some batches are worth keeping classic, whereas others invite a spicier, greener, or more playful variation the next time around.
What matters most is that the falafel feels alive. Crisp outside. Tender inside. Fragrant with herbs. Warm with spice. Worth making again.
And once you have that, you do not simply have a homemade falafel recipe. You have one of the most versatile, satisfying, and generous chickpea dishes a home kitchen can offer.
Also Read: Iced Coffee: 15 Drink Recipes—Latte, Cold Brew, Frappe & More
Falafel Recipe FAQs
1. What is falafel made of?
Falafel is usually made from chickpeas or fava beans, along with onion, garlic, parsley, cilantro, cumin, coriander, salt, and pepper. In many homemade versions, chickpeas are the main base, especially in a classic chickpea falafel recipe. Some variations also use a little chickpea flour or baking powder to improve texture. Although the ingredient list is fairly simple, the balance of herbs, aromatics, and seasoning is what gives falafel its distinct flavor.
2. What is falafel, exactly?
Falafel is a savory Middle Eastern dish made by grinding soaked legumes with herbs, aromatics, and spices, then shaping the mixture into balls or patties and cooking it until crisp outside and tender inside. It is often served in pita, wraps, bowls, or on a platter with salad and sauce. As a result, falafel can work as a snack, lunch, or full meal depending on how it is served.
3. How do you make falafel from scratch?
To make falafel from scratch, start by soaking dried chickpeas until they are plump but still firm. After that, pulse them with onion, garlic, herbs, and spices until the mixture is finely chopped and holds together when pressed. Then chill the mixture, shape it, and fry, bake, or air fry it. The key is to pulse rather than puree, because that keeps the texture light instead of pasty.
4. Do you need dried chickpeas for an authentic falafel recipe?
Traditionally, yes. An authentic falafel recipe is usually made with dried chickpeas that have been soaked but not boiled. That method creates a mixture with better texture and structure, which helps the falafel stay crisp outside and tender inside. By contrast, canned chickpeas are much softer, so they tend to produce a denser result.
5. Can you make falafel with canned chickpeas?
Yes, you can make falafel with canned chickpeas, though the texture will be different. Since canned chickpeas are already cooked, they are softer and wetter than soaked dried chickpeas. Because of that, canned chickpea falafel can turn mushy or dense if the mixture is over-processed. Even so, it can still work well for a quicker homemade falafel, especially in baked or air fryer versions.
6. Why does falafel fall apart?
Falafel usually falls apart when the mixture is too wet, too coarse, or not rested long enough before cooking. Occasionally, canned chickpeas are the reason, since they create a softer mixture that may struggle to hold shape. In other cases, the issue is simply that the ingredients were not pulsed enough. Chilling the mixture and adding a small amount of chickpea flour, if needed, often helps.
7. Why is my falafel mushy instead of crisp?
Mushy falafel usually happens when the chickpeas are too soft, the mixture is too wet, or the food processor turns everything into a paste. Canned chickpeas can cause this more easily than soaked dried chickpeas. Likewise, overcrowding an air fryer or baking tray can prevent the exterior from crisping properly. For better results, keep the mixture textured, drain ingredients well, and give each piece enough space while cooking.
8. How do you make falafel crispy?
For crisp falafel, start with the right texture in the mixture. It should be finely chopped and cohesive, not smooth. Then chill it before shaping. Fried falafel usually gives the crispiest shell, although air fryer falafel can also turn out very well if lightly oiled and spaced properly. In the oven, shaping flatter patties instead of thick balls helps create more surface area for browning.
9. Is air fryer falafel good?
Yes, air fryer falafel can be very good when made carefully. While it does not have exactly the same crust as deep-fried falafel, it still develops a nicely browned exterior and keeps the inside tender. For many home cooks, air fryer falafel is the best balance between convenience, lighter cooking, and satisfying texture. It is especially useful for weeknight dinners and meal prep.
10. How do you cook falafel in an air fryer?
To cook falafel in an air fryer, shape the mixture into small patties or compact balls, lightly oil the outside, and arrange them in a single layer with space between each piece. Then cook until browned and crisp, turning if your air fryer needs it. Since machines vary, it is best to check the first batch closely. Generally, air fryer falafel works best when the basket is not crowded and the falafel is not too thick.
11. Is baked falafel worth making?
Absolutely. Baked falafel does not taste exactly like fried falafel, yet it can still be delicious. It is particularly useful for larger batches, meal prep, and lighter meals. Moreover, baked falafel reheats well and works beautifully in bowls, wraps, and lunchboxes. A hot oven, a lightly oiled surface, and flatter patties all help improve the final texture.
12. Is falafel healthy?
Falafel can be part of a healthy meal, especially when made with plenty of herbs and served with vegetables, hummus, yogurt sauce, or tahini. Chickpeas bring fiber and plant-based protein, which makes falafel filling and satisfying. Naturally, fried falafel is richer than baked or air fried falafel, so the cooking method changes the overall feel of the meal. Even then, falafel can still fit easily into balanced vegetarian eating.
13. Is falafel vegan?
Most classic falafel recipes are vegan because they are made from chickpeas or fava beans, herbs, spices, and aromatics. That said, it is always worth checking the binder or sauce being served alongside it. The falafel itself is often vegan, whereas yogurt sauce or certain accompaniments may not be.
14. Is falafel gluten free?
Falafel can be gluten free, though it depends on the recipe. Chickpeas, herbs, and spices are naturally gluten free, but some recipes use flour as a binder. If you want gluten free falafel, chickpea flour is one of the easiest alternatives. Accordingly, it is always a good idea to check the ingredients if you are cooking for someone who avoids gluten.
15. What sauce goes best with falafel?
Tahini sauce is the classic choice for falafel. Its creamy, nutty, lemony flavor pairs beautifully with the crisp shell and herb-filled center. Still, falafel also works very well with yogurt sauce, tzatziki, spicy sauces, or even a creamy garlic dressing. The best option depends on whether you want the meal to feel more classic, cooling, or bold.
16. What do you serve with falafel?
Falafel goes well with pita, wraps, chopped salad, hummus, tahini sauce, pickles, yogurt sauce, slaw, and grain bowls. It can be the centerpiece of a simple lunch or part of a larger mezze-style spread. Depending on the occasion, you can serve it in pita bread, over rice or couscous, or alongside fresh vegetables and dips.
17. Can falafel be made ahead of time?
Yes, falafel is excellent for make-ahead cooking. You can prepare the mixture in advance and chill it until you are ready to shape and cook it. Alternatively, you can shape the falafel and freeze it for later. Cooked falafel also stores well, which makes it useful for quick lunches and easy dinners throughout the week.
18. Can you freeze falafel?
Yes, falafel freezes very well. In fact, one of the best ways to do it is to freeze the shaped, uncooked falafel first on a tray, then transfer it to a container once firm. That way, you can cook only as much as you need later. Cooked falafel can also be frozen, though freshly cooked falafel usually gives the best texture.
19. How do you reheat falafel so it stays crisp?
The best way to reheat falafel is in the oven or air fryer. That helps the outside crisp up again instead of turning soft. A microwave will warm it quickly, but it usually softens the crust. Therefore, if texture matters, the oven or air fryer is the better choice.
20. What is the difference between falafel balls and falafel patties?
Falafel balls are more traditional and are especially popular for frying. Falafel patties, on the other hand, are often easier for baking and air frying because they cook more evenly and expose more surface area to heat. The flavor is essentially the same, but the shape can affect the texture and the method that works best.
21. Can you make easy falafel at home without deep frying?
Yes, easy falafel can absolutely be made at home without deep frying. Air fryer falafel and baked falafel are both practical options, especially for home cooks who want less mess and lighter cooking. The most important thing is getting the mixture right first. Once that is in place, the cooking method becomes much easier to adapt.
22. What makes the best falafel recipe?
The best falafel recipe starts with the right chickpeas, plenty of fresh herbs, enough seasoning, and the right texture in the mixture. It should hold together well, cook up crisp outside, and stay tender inside. Beyond that, the best falafel recipe is the one that suits how you want to eat it, whether that means a traditional fried version, a homemade baked falafel, or a lighter air fryer falafel for everyday meals.
23. What is the difference between falafel and hummus?
Falafel and hummus both often begin with chickpeas, yet they become very different foods. Hummus is a smooth dip or spread, whereas falafel is a shaped mixture that is cooked until crisp. They are often served together because their textures contrast so well.
24. Can I use falafel in a wrap instead of pita?
Absolutely. Falafel works beautifully in wraps. In fact, wraps can be easier to eat than stuffed pita pockets because the filling stays more contained. Add lettuce, chopped vegetables, sauce, and hummus if you like, then roll everything tightly.
25. What herbs are best in a falafel recipe?
Parsley and cilantro are the classic herb combination. Parsley keeps the mixture fresh and green, while cilantro adds brightness and a slightly sharper edge. If you dislike cilantro, extra parsley is usually the best substitute rather than skipping herbs altogether.
26. Why is my falafel bland?
Falafel usually tastes bland when the mixture is under-seasoned or under-herbed. Chickpeas are mild, so they need enough salt, garlic, cumin, coriander, and fresh herbs to feel alive once cooked. Bland falafel is often not a structural problem at all. It is simply a seasoning problem.
27. Can I make mini falafel for a party?
Yes, mini falafel is excellent for platters and party food. Smaller pieces work especially well on mezze boards with hummus, tahini, pickles, olives, chopped salad, and warm bread. They also make it easier for guests to sample more than one sauce.
28. What is the best oil for frying falafel?
A neutral oil with a suitable frying profile works best. You want an oil that lets the herbs, spices, and chickpeas speak for themselves rather than adding a strong flavor of its own.
29. Can falafel be part of a vegetarian meal prep plan?
Very easily. Falafel is one of the best vegetarian meal prep options because it holds well, reheats nicely in the oven or air fryer, and works in wraps, bowls, and platter-style lunches. It is filling, flexible, and easy to pair with vegetables, sauces, and grains.
30. Why does homemade falafel become a repeat recipe?
Because once you understand the texture and the method, it pays you back in many forms. One batch can become a quick lunch, a casual dinner, a platter for guests, or several meal-prep boxes across the week. It is deeply versatile, satisfying, and far more generous than its ingredient list first suggests.