We reach for rice or quinoa because both are comforting. They carry flavor, welcome vegetables and both of them make a plate feel complete. Yet, when you compare them closely, they behave differently in your body and in your kitchen. This guide unpacks quinoa vs rice with practical numbers, plain language, and easy cooking moves you can use tonight.
Although both are starches, they do not play the same role. Quinoa brings more protein and more fiber. Rice, especially white rice, brings a softer texture and a neutral base. As a result, each shines in different meals. In the sections below, you will see where quinoa wins. You will also see where rice still fits beautifully. Most importantly, you will learn how to choose the right base for your goals and your taste.
Before we dive in, remember one key fact. Quinoa is a seed. It cooks like a grain, but botanically it is not a cereal. This small detail explains some of its unique traits. It also explains why its protein and fiber numbers stand out.
Also Read: Glycemic Index (GI) VS Glycemic Load (GL)
Quinoa vs Rice: the short, honest take
Let’s set the stage with a clear summary. Then we will build details under it.
- Quinoa offers more protein and fiber per cooked cup. Therefore, it usually keeps you full longer.
- White rice is slightly lower in calories per cup. It tastes neutral. It lets sauces and curries take center stage.
- For steadier energy, quinoa, brown rice, and basmati are generally better picks than standard white or jasmine.
If you want more context on varieties, skim our explainer on basmati rice and glycemic index. For a simple primer on blood sugar and carbs, read Harvard’s guide to carbohydrates and blood sugar. Both links will help you turn this article into action.
Quinoa vs Rice: nutrition, per cooked cup
Numbers make decisions easier. Let’s compare typical cooked portions you see in bowls and plates.
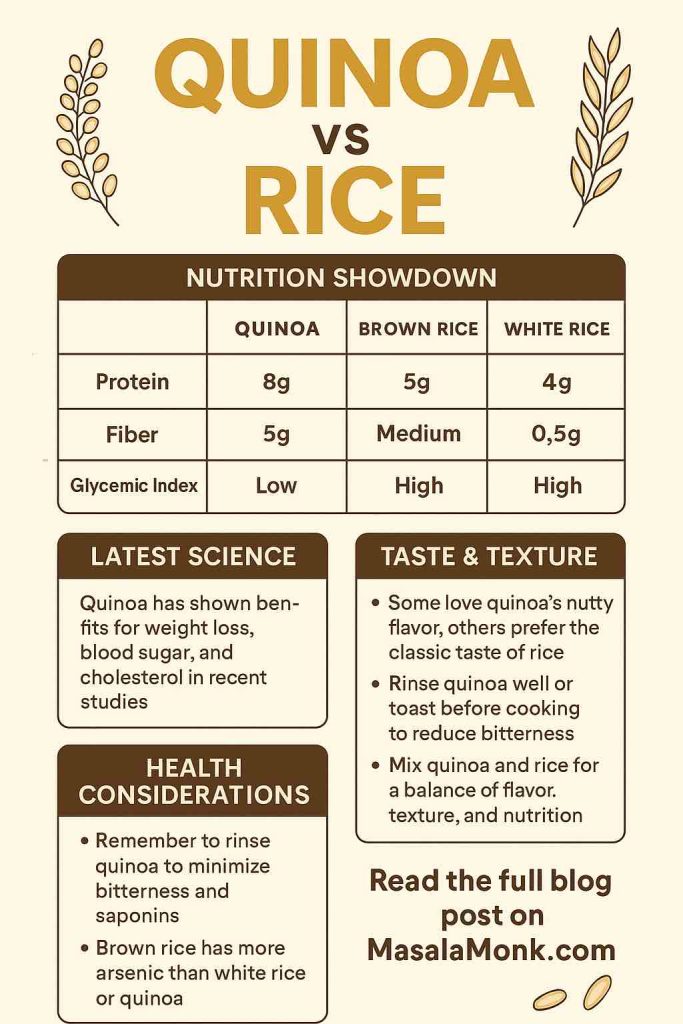
- Quinoa (1 cup cooked): about 222 kcal, ~39 g carbs, ~8 g protein, and ~5 g fiber. You can verify at USDA/MyFoodData for quinoa and read context at Harvard’s quinoa feature.
- White rice (1 cup cooked): around 205 kcal, ~45 g carbs, ~4 g protein, and <1 g fiber. See USDA/MyFoodData for white rice.

Which has fewer calories per cup? White rice does, by a modest margin.
Which supports fullness better? Quinoa does, because of protein and fiber.
Is quinoa lower carb than rice? Per cup, quinoa has slightly fewer carbs than many white rices. The gap is small. The bigger win is quinoa’s fiber and protein.
Prefer metric? No problem. Per 100 g cooked, quinoa averages about 4.4 g protein and ~2.8 g fiber. White rice averages roughly 2.7 g protein and ~0.4–0.6 g fiber. Consequently, quinoa sticks a bit longer and often delivers better satiety. Rice, meanwhile, usually needs support from protein and vegetables to keep hunger steady and digests faster unless you add partners like beans, tofu, eggs, fish, or chicken.
Now step back. Nutrition is not only macros. Micronutrients matter. So do amino acids. Quinoa offers a broader amino acid profile and helpful minerals. Rice offers consistency, digestibility, and a clean flavor stage. Therefore, let your meal goal guide your choice. Are you building a lean, filling bowl for lunch? Quinoa might serve you well. Are you plating a rich curry that needs a soft base? White or basmati rice may be perfect.
Also Read: Glycemic Index and Secrets of Weight Loss

Quinoa vs Rice: per cup and per 100 g at a glance
Per cup (cooked)
| 1 cup cooked | Calories | Carbs | Protein | Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinoa (~185 g) | ~222 | ~39 g | ~8 g | ~5 g |
| White rice (~158 g) | ~205 | ~45 g | ~4 g | <1 g |
| Brown rice (~195 g) | ~216 | ~45 g | ~5 g | ~3.5 g |
Source the quinoa and white rice figures from USDA/MyFoodData for quinoa and USDA/MyFoodData for white rice. Values vary by brand and moisture, but the pattern remains stable.
Tip: Use the cup table for quick menu planning. Use the gram table below for macro tracking.
Per 100 g (cooked)
| Food (100 g) | Calories | Carbs | Protein | Fiber |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quinoa | ~120 | ~21.3 g | ~4.4 g | ~2.8 g |
| White rice | ~130 | ~28.3 g | ~2.7 g | ~0.4–0.6 g |
| Brown rice | ~123 | ~25.6 g | ~2.7–2.9 g | ~1.6–1.8 g |
| Basmati (white) | ~121–130 | ~25–28 g | ~2.7–3.0 g | ~0.4–0.8 g |
| Jasmine (white) | ~129–135 | ~28–30 g | ~2.7–3.0 g | ~0.4–0.8 g |
These tables helps in calories vs carbs vs protein comparison. They also support quick menu planning. If you build bowls by volume, the per-cup table helps. If you track macros by weight, the 100 g snapshot helps more. You can now place the base that matches your day.
Glycemic index in quinoa vs rice (and why it matters)
The glycemic index (GI) estimates how fast a carb-rich food raises blood sugar. As a rule of thumb, ≤55 is low, 56–69 is medium, and ≥70 is high. For clear definitions and practical examples, read Harvard’s overview on carbohydrates and blood sugar. If you want to look up specific foods or brands, use the University of Sydney GI database.

Here is the part that matters for your day.
- Quinoa is generally low-GI, often reported around the low 50s. Its fiber and protein contribute to that steadier curve. That is why quinoa bowls often feel satisfying for longer.
- Rice spans a wide range. Brown rice averages around the low-to-medium boundary. Standard white rice sits medium on average. Basmati often lands lower among white rices. Jasmine tends to land higher.
Here it is important to keep on mind cooking changes starch, GI can shift with methods. Cooling cooked rice and then reheating increases resistant starch. That change can soften the post-meal rise for some people. Pairings matter too. When you add protein, fiber, and healthy fats, digestion slows. Therefore, you can keep rice in rotation and still aim for steady energy.
Summarizing GI in quinoa vs rice
- What is the GI of quinoa vs rice? Quinoa is generally low-GI (often ~53). Rice varies widely by type.
- Which rice types run lower GI? Brown rice often averages ~55. Basmati is frequently lower among white rices.
- Which rice types run higher GI? Jasmine tends to be higher. Many standard white rices fall in the medium range.
Is quinoa healthier than rice for blood sugar? Often yes, because quinoa starts low-GI and brings fiber and protein. However, brown rice and basmati can also be smart picks. Therefore, choose variety first, then use cooking methods that encourage steadier curves.
If you want practical levers, walk through our guide to reducing the glycemic impact of rice. You will see how cook → cool → reheat, slightly firmer texture, and protein-fiber pairings smooth the ride. For a neutral, health-organization perspective on using GI wisely, review Diabetes UK’s GI overview.
GI by rice variety (white, brown, basmati, jasmine)
Variety matters. So do cultivar and cooking. Here is a quick comparison you can trust.
- White rice (general): medium GI on average. Soft and easy to over-serve.
- Brown rice: low-to-medium GI. More fiber than standard white. Chewier bite and nutty notes.
- Basmati (white): often lower GI among white rices. Higher amylose helps keep grains separate.
- Jasmine (white): often higher GI. Plush texture and a perfumed aroma.
For a broader context on GI and health outcomes, skim Harvard’s overview of rice. For brand or product specifics, check entries in the University of Sydney GI database.
How cooking and pairing change GI (so rice stays in your life)
Small technique shifts change how grains behave.

- Cook → cool → reheat. Cooling cooked rice forms resistant starch. That starch resists digestion and can blunt the spike.
- Keep grains slightly firm. Very soft grains digest faster. Slightly firmer grains slow things down.
- Pair smartly. Add protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Beans, tofu, eggs, fish, chicken, vegetables, nuts, and seeds all help.
- Mind portions. A modest scoop leaves room for vegetables and protein. You get the texture you love without losing balance.
For a clear walkthrough, open our practical guide on reducing rice’s GI. The methods are simple, repeatable, and budget-friendly.
Quinoa vs Rice for different goals
This section folds several “which is better” questions directly into the guidance. That way, you decide by goal, not by hype.
Quinoa vs Rice for fullness and everyday nutrition
Which is healthier, rice or quinoa, for satiety? Quinoa usually wins. If satiety is your priority, start with quinoa. It delivers more protein and more fiber per cup. Those two levers slow digestion. They also help curb snack cravings later. For the full panel, compare USDA/MyFoodData for quinoa with USDA/MyFoodData for white rice. For a friendly overview, read Harvard Nutrition Source on quinoa.
Even so, rice can still support fullness when you structure the plate. First, add bulk with non-starchy vegetables. Next, add protein. Then finish with a little fat for flavor and texture. Together, those pieces change how the whole meal feels.
What about brown rice vs quinoa? That contest is closer. Brown rice is a whole grain with moderate fiber and low-to-medium GI. However, quinoa still edges it on protein and often on fiber per cup. If you love the chew of brown rice, you can still get great meals. Just add beans or tofu to push protein higher.
Quinoa vs Rice for steady energy and blood sugar
If you want stable post-meal energy, lean on low- or medium-GI bases. Quinoa is a reliable choice. Brown rice and basmati are strong options too. Moreover, dial in technique. Use the cook-cool-reheat sequence. Keep grains a touch firm. Pair with protein, vegetables, and healthy fats. For a clean, balanced view from a health organization, read Diabetes UK on the GI.
Does quinoa have a lower GI than jasmine rice? Usually yes. Jasmine often trends higher. If you love jasmine for aroma, balance the plate. Add vegetables and protein. Keep the serving controlled.
Quinoa vs Rice for weight management
Is quinoa better than rice for weight loss? Sometimes. Weight management is about patterns, not single foods. Still, the base matters. White rice is slightly lower in calories per cup than quinoa. That small edge can help when you want a lighter base. However, quinoa’s higher protein and fiber can improve fullness. Consequently, the “better” choice depends on the rest of the plate.
Here are two simple frameworks:
- Quinoa-forward bowl: quinoa base + beans or tofu + mixed vegetables + yogurt-tahini dressing + lemon.
- Light rice bowl: modest scoop of white or basmati rice + vegetable-heavy stir-fry + lean chicken or shrimp + crunchy side salad.
Is quinoa more filling than rice? Often yes. The protein and fiber explain that feeling. But remember preference and texture. If rice helps you enjoy more vegetables and lean protein, that also supports the goal. If you want more structure, explore our guide on choosing the best rice for weight loss. It shows how to set portions and choose cooking methods that support a calorie plan.
Quinoa vs Rice for bodybuilding and training days
Training changes needs. Sometimes you want faster carb delivery. Other times you want meals that stick. Therefore, match the base to the session.
- Around training: white or basmati rice digests a bit faster. That can help when you need quick refueling. Pair with lean protein and a small amount of fat.
- Away from training: quinoa brings more protein and fiber. That helps fullness as you spread meals through the day. Add legumes, eggs, tofu, or fish for extra protein.
As always, test and notice. Your body will tell you which base supports your work.
Also Read: Quinoa for Weight Loss: Benefits, Nutrition, and How to Cook Ideas
Quinoa vs Rice by variety (white, brown, basmati, jasmine)
As the risk of repeating ourselves, however for sake of more clarity on topic, let’s now fold some comparisons directly into short, practical sub-sections. Each one answers “which is better” in the specific context.
Quinoa vs White Rice
White rice is plush and neutral. It absorbs sauces and lets other flavors lead. On average, it is medium GI and low in fiber. Therefore, watch portions. Pair it with vegetables and protein. In contrast, quinoa is typically lower GI and higher in protein and fiber. It brings a nutty note and a slight pop to each bite.
For facts while you cook, keep USDA/MyFoodData for white rice open in a tab. For quinoa context, browse Harvard Nutrition Source on quinoa. If you want a broad view of rice varieties, read Harvard Nutrition Source on rice.
When to choose which: use white rice when the dish is rich and saucy. Use quinoa when you want the base to contribute protein and fiber. Or mix them half-and-half for a balanced compromise.
Quinoa vs Brown Rice
Here the gap narrows. Brown rice is a whole grain. It keeps the bran and germ. As a result, it carries more fiber and micronutrients than standard white rice. Its GI usually sits in the low-to-medium band. If you enjoy the chewier bite and nutty flavor, it can anchor meals beautifully. Quinoa still edges brown rice on protein and fiber per cup. That edge can aid fullness when calories are tight.
For averages and a sensible overview, see Harvard’s rice page. For a narrative comparison of brown and white rice, skim Harvard Health’s head-to-head explainer.
When to choose which: pick brown rice when you want the rice experience with extra texture and a friendlier GI. Pick quinoa when you want more protein, more fiber, and quicker cooking.
Quinoa vs Basmati Rice
Among white rices, basmati is a standout. It often lands lower on the GI spectrum than many standard white rices. Higher amylose helps keep grains separate. The aroma is a bonus. If you want a white rice experience with a gentler curve, basmati is a smart choice. For deeper detail and cooking notes, open our basmati GI analysis. If you want brand-specific values, search the University of Sydney GI database.
When to choose which: pick basmati when you want long, separate, fragrant grains. Pick quinoa when you want more protein and fiber in the base. Or serve basmati with lentils or chickpeas to boost protein and fiber.
Also Read: ‘Quinoa’ Instead of ‘Chicken’: 5 High Protein Plant-Based Meal Prep Ideas
Quinoa vs Jasmine Rice
Jasmine rice is aromatic and soft. It is lovely with Thai curries and dishes that want a perfumed base. However, jasmine tends to sit higher on the GI than basmati and many brown rices. Therefore, if blood sugar steadiness is a priority, choose jasmine less often. For variety differences and a clear overview, read Harvard’s rice page.
When to choose which: pick jasmine for aroma and softness. Pick quinoa when you want steadier energy and extra protein.

Other rice styles in brief (so you can branch out)
There are so many rice varieties, it’s hard to cover them all, however some of the more popular ones and which keep trending every now and then are covered below in comparison with Quinoa.
Wild rice vs quinoa
Wild rice is a grass seed, much like quinoa is a seed. It brings a chewy bite and an earthy, nutty flavor. It has more protein than many standard white rices. Choose wild rice when you want texture and a whole-grain feel. Choose quinoa when you want more protein per cup and a faster cook.
Red and black rice vs quinoa
Red and black rices keep their bran. They bring color, antioxidants, and a bit more fiber than standard white rice. They usually land in the medium-GI range. Choose them when you want a classic rice experience with extra character. Choose quinoa when you want more protein and a typically lower GI.
Parboiled rice vs quinoa
Parboiled rice is steamed in the husk before milling. That process helps retain some nutrients. It also tends to keep grains separate and can yield a lower GI than standard white rice. Use parboiled rice when you want distinct grains for pilaf. Use quinoa when you want higher protein and fiber in the base.
Cauliflower rice and shirataki rice vs quinoa
Cauliflower and shirataki “rice” are low-calorie substitutes, not grains. They drastically reduce carbs and calories. However, they change texture and flavor. Use them for low-carb meals or as volume extenders. Use quinoa or rice when you want true grain structure and lasting fullness.
Also Read: Healthy Oat Protein Bars – 5 Easy No Sugar Recipes for Snacks
Taste, texture, and kitchen behavior (so your swaps stick)
Food should satisfy. Numbers help, but flavor keeps habits alive. Therefore, pay attention to texture and taste.
Quinoa tastes nutty with a gentle chew. Rinse it well to remove saponins. For extra depth, toast the dry grains for a minute or two. Then add water. A 1:2 quinoa-to-water ratio works for many cooks. Simmer until you see tiny germ rings and the pot looks just dry. Cover and rest for five minutes. Finally, fluff and season. A drizzle of olive oil and a squeeze of lemon go a long way.

White rice is soft and neutral. It lets sauces sing and stews shine. Brown rice is chewier and slightly nutty. Basmati cooks fragrant and separate, which makes it ideal for pilafs. Jasmine is plush and perfumed, perfect for Thai and Southeast Asian flavors.
If you are not ready for a full swap, start gently. Mix half quinoa and half rice. The bowl will feel familiar yet more filling. Over time, you can push the ratio toward your goals without losing comfort.
Does quinoa taste like rice? Not exactly. It is nuttier and slightly chewy. However, with the right dressing or sauce, most eaters enjoy the swap quickly.
Real-world plates you can build tonight
Real life asks for simple moves, you do not need new recipes to start. You only need patterns that repeat well, here are patterns that work.
Protein-forward quinoa bowl
Base: quinoa. Add roasted chickpeas or grilled tofu. Pile on vegetables. Finish with a yogurt-tahini drizzle and lemon. Because quinoa brings protein and fiber, the bowl satisfies. For more ideas, see quinoa meal-prep ideas.
Light, saucy rice bowl
Base: a modest scoop of white or basmati rice. Top with a vegetable-heavy stir-fry. Add lean chicken or shrimp. Add a crunchy side salad. The plate stays light yet complete.
Basmati pilaf with legumes
Toast basmati with spices. Simmer until long and separate. Fold in cooked lentils and herbs. Serve with a bright cucumber salad. The dish tastes rich but lands gently.
Half-and-half “transition” bowl
Mix equal parts cooked quinoa and cooked brown rice. Add roasted vegetables, a protein, and a nutty dressing. You get rice comfort and quinoa’s staying power.
Cold grain salad for busy weeks
Toss cooked and cooled quinoa with chopped greens, beans, cucumbers, tomatoes, olives, and a lemon vinaigrette. Store for lunches. Because quinoa holds texture, the salad keeps well. For higher-protein patterns, explore high-protein quinoa strategies.
Quinoa vs Rice: cooking smarter for better curves
You can improve rice’s glycemic profile without abandoning it, which means you can keep rice and still aim for steady energy. Use these simple levers.
- Cook → cool → reheat. Resistant starch goes up. The glycemic hit can soften.
- Pair with protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Beans, eggs, tofu, fish, chicken, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds slow digestion.
- Keep texture slightly firm. Very soft grains digest faster.
- Scale portions down. A smaller scoop plus more vegetables often feels better.
- Prefer lower-GI choices. Basmati and brown rice are friendlier than standard white or jasmine.
For step-by-step help, read reducing the glycemic impact of rice. For a neutral, health-org perspective on using GI well, see Diabetes UK’s GI overview.
Pantry, storage, and prep notes that make the habit easy
Logistics shape success. Set up your kitchen so good choices happen on autopilot.
- Store uncooked grains in airtight jars away from heat and light.
- Cool cooked grains quickly, then refrigerate within two hours.
- Use cooked grains within three to four days, or freeze flat for later.
- Reheat with a splash of water and cover to restore moisture.
- Batch once; eat many times. Cook big on one night. Portion into containers. Rotate through bowl formulas all week.
- Season simply. Try lemon zest, garlic, toasted cumin, turmeric, parsley, cilantro, sesame, or a spoon of pesto. Little touches amplify flavor.
When you cook a pot, cook a little extra. Future-you will thank present-you.
Pulling it together: how to choose with confidence
You now have the facts and the levers. Let’s convert them into confident choices.
- Choose quinoa when you want more protein and fiber, generally lower GI, and a base that can stand on its own in bowls and salads. For numbers and context, revisit USDA quinoa and Harvard’s quinoa guide.
- Choose brown or basmati rice when you want a classic rice experience with a gentler glycemic impact than standard white. For a balanced overview of varieties, see Harvard’s rice page.
- Choose white rice when you need a lighter-calorie, neutral base that keeps the spotlight on the main dish. Then round out the plate with vegetables and protein so the meal satisfies and digests steadily. For exact cup-for-cup figures, compare white rice per cup with quinoa per cup.
If blood sugar steadiness is a priority, focus on technique. Cook, cool, and reheat. Keep grains slightly firm. Pair with protein and vegetables. Favor lower-GI varieties. For simple steps, use our guide to reducing rice’s GI. For a neutral, health-org stance on GI, read Diabetes UK’s overview.
Finally, keep cooking joyful. Food is fuel, but it is also comfort. Try one new method this week. Swap in a half-and-half mix. Add a bright pickle or a crunchy salad. Notice how the plate feels. Then iterate. With a little curiosity, quinoa vs rice stops being an argument. It becomes a flexible toolkit you can use with ease.
FAQs
1) What is the glycemic index of quinoa vs rice?
Generally, quinoa sits in the low-GI range, while rice varies widely by type. Consequently, brown and basmati rice tend to be friendlier than standard white or jasmine. Even so, cooking, cooling, and reheating can shift the numbers a bit.
2) Which is healthier overall: quinoa or rice?
It depends on your goal. Typically, quinoa wins on protein, fiber, and a steadier blood-sugar response. However, white rice is slightly lower in calories per cup and works well as a neutral base when portions and pairings are smart.
3) Is quinoa better than rice for weight loss?
Often, yes—because quinoa’s extra protein and fiber can improve fullness. Nevertheless, a modest serving of rice with plenty of vegetables and lean protein can also fit well.
4) Brown rice vs quinoa: which should I choose?
Both are solid. Brown rice offers a whole-grain experience with chew and moderate fiber. Meanwhile, quinoa usually brings more protein and fiber per cup. Therefore, choose by texture preference and how long you want the meal to keep you satisfied.
5) Basmati rice vs quinoa: which has the advantage?
Each brings different strengths. Basmati often lands lower on the GI spectrum among white rices and has a fragrant, separate grain. Conversely, quinoa adds more protein and fiber. As a result, you might even combine them.
6) Jasmine rice vs quinoa: which supports steadier energy?
Typically quinoa. Jasmine rice is delicious and plush, yet it often trends higher on the GI scale. Thus, if you choose jasmine, balance the plate with vegetables, protein, and mindful portions.
7) Does quinoa have fewer carbs than rice?
Per cooked cup, quinoa usually has slightly fewer carbs than many white rices. Still, the difference is small. Instead, quinoa’s bigger edge is its protein and fiber.
8) Quinoa vs white rice: which has fewer calories?
White rice, by a modest margin. Even so, quinoa often feels more filling thanks to its higher protein and fiber content.
9) Protein in quinoa vs rice: how do they compare?
Quinoa commonly provides about twice the protein per cup compared with white rice. Consequently, it can help when you want more protein from the base itself.
10) Fiber in quinoa vs brown rice: who wins?
Quinoa usually edges out brown rice on fiber per cup. Nevertheless, both beat standard white rice. Therefore, either can help you build more satisfying bowls.
11) What is the difference between quinoa and rice?
Botanically, quinoa is a seed that cooks like a grain, while rice is a cereal grain. Hence, quinoa tends to carry more protein and fiber, whereas rice delivers a softer, more neutral canvas.
12) Is quinoa better than rice for diabetics?
Often yes, due to lower GI and higher fiber. That said, brown rice and basmati can also be sensible choices. Furthermore, pairings, portions, and cooking methods matter just as much.
13) Which is better for bodybuilding or training days: quinoa or rice?
It depends on timing. Around workouts, white or basmati rice can digest a bit faster. Conversely, away from training, quinoa’s extra protein and fiber can help with satiety across the day.
14) Quinoa vs rice for weight loss: what portion strategies work?
First, keep the base modest. Next, pack in vegetables. Then, add lean protein and a little fat for flavor. Consequently, both quinoa bowls and rice bowls can fit your plan.
15) Wild, red, or black rice vs quinoa: how do these compare?
These colorful rices retain more of the grain and usually bring extra texture and character. Even so, quinoa still tends to offer more protein per cup. Thus, choose based on flavor and the role you want the base to play.
16) Parboiled rice vs quinoa: which should I use?
Parboiled rice often cooks into separate grains and can be gentler than some standard white rices. Nevertheless, quinoa remains stronger on protein and fiber. Therefore, pick parboiled for pilafs and quinoa for protein-forward bowls.
17) Cauliflower rice or shirataki rice vs quinoa: which is “lighter”?
Those substitutes are extremely low in calories and carbs. However, they change texture and flavor dramatically. Meanwhile, quinoa behaves like a true grain and offers staying power. Hence, use the alternatives for very low-carb plates and quinoa for fuller meals.
18) Does quinoa taste like rice?
Not exactly. Quinoa is nutty with a slight chew; rice is softer and more neutral. That said, with dressings, sauces, and herbs, the swap feels natural surprisingly quickly.
19) Can I mix quinoa and rice in one dish?
Absolutely. In fact, a half-and-half mix is an easy transition strategy. As a result, you get rice’s familiarity and quinoa’s extra protein and fiber in the same bowl.
20) Is quinoa more expensive than rice?
In many markets, yes, because quinoa is less widely grown and processed differently. Even so, mixing quinoa with rice or using quinoa for specific meals can manage cost while preserving benefits.
21) Quinoa vs rice calories per 100 g vs per cup: which view should I use?
Use the per 100 g view for precise macro tracking. Alternatively, use the per cup view for quick home cooking decisions. Either way, keep consistency in your method.
22) Which is healthier: brown rice or quinoa?
Often quinoa, thanks to protein and fiber. Nonetheless, brown rice remains a strong whole-grain option. Therefore, rotate both and pick based on texture, budget, and the rest of the plate.
23) Is quinoa or rice better for beginners who want steadier energy?
Start with quinoa or basmati, since both usually support a smoother glucose response than many standard white rices. Additionally, keep portions steady and add protein.
24) Why do cooking methods change the GI of rice?
Because heat, cooling, and reheating alter starch structure. Specifically, cooling increases resistant starch, which resists digestion. Consequently, the post-meal rise can be gentler.
25) How do I choose between quinoa and rice on busy weeks?
Plan for versatility. Batch-cook one pot of quinoa and one of rice. Then, alternate: quinoa bowls on high-satiety days; rice bowls when you want a lighter base or faster digestion.