You probably know coriander—also called cilantro—as the green leafy herb sprinkled over curries, tacos, or salads. But what if I told you this humble kitchen staple is far more than just a flavor enhancer? From regulating blood sugar to protecting your skin, coriander is quietly earning its place as a true wellness powerhouse.
Let’s dive deeper into what makes coriander so special, how modern science is validating ancient wisdom, and—most importantly—how you can harness its full potential in your everyday life.
The Botanical Backstory: What’s in a Name?
First, a quick clarification: “Coriander” refers to the entire plant (leaves, stems, and seeds). In North America, the fresh leaves are called “cilantro,” while the seeds are called “coriander.” In most of the world, “coriander” covers both.
Coriander (Coriandrum sativum) has been cultivated for over 7,000 years—ancient Egyptians, Greeks, Romans, and Ayurvedic healers all prized it for its culinary and medicinal powers. But what does today’s science say?
The Nutritional Profile: Tiny Herb, Mighty Nutrients
Coriander is surprisingly nutrient-dense. Here’s a snapshot of what you get in a modest serving:
- Leaves (per ¼ cup):
- 16% Daily Value (DV) of Vitamin K
- Good source of Vitamin A, C, and E
- Fiber, calcium, manganese, iron, and 11 essential oils
- Seeds (per tablespoon):
- High in dietary fiber
- B-vitamins (esp. folate, riboflavin)
- Iron, magnesium, manganese
- Flavonoids and polyphenols like quercetin, linalool, and terpinene
But coriander’s real magic lies beyond basic nutrition. Let’s explore the science.
Proven Health Benefits: What the Research Reveals
1. Blood Sugar Control and Diabetes Support
Several randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shown that daily coriander seed powder (as little as 1g/day) can:
- Lower fasting blood sugar
- Improve insulin sensitivity
- Reduce total cholesterol and triglycerides
For example, a 6-week double-blind study in people with type-2 diabetes found fasting glucose dropped from ~156 to ~130 mg/dL. Cholesterol and triglyceride levels improved significantly as well. These effects are attributed to coriander’s ability to activate insulin-producing enzymes and boost antioxidant defenses.
Practical Tip:
If you have prediabetes or diabetes, consider adding 1g of coriander seed powder (about ¼ tsp) to your morning routine. Sprinkle it into smoothies, yogurt, or warm lemon water. (Check with your doctor first if you’re on medication!)
2. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Power
Coriander is rich in antioxidants—especially quercetin, terpinene, and linalool—which help fight oxidative stress and inflammation. Research shows that coriander intake increases plasma antioxidant capacity and reduces cell damage markers like malondialdehyde.
Why it matters:
Oxidative stress is linked to heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. Coriander’s unique compounds may help buffer these risks.
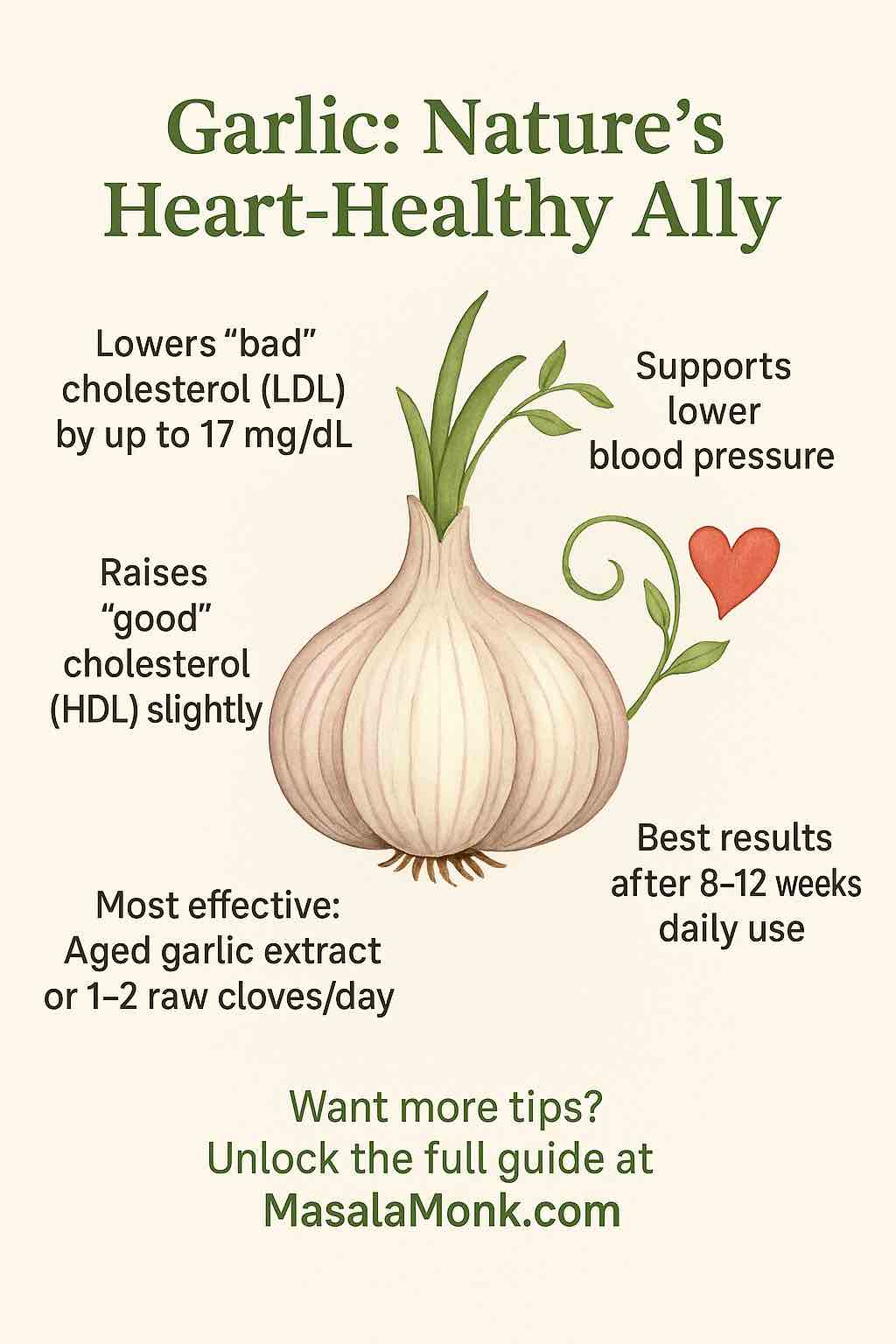
3. Heart Health: Lowering Cholesterol and Blood Pressure
Animal and human studies suggest coriander can:
- Lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and total cholesterol
- Improve HDL (“good”) cholesterol
- Reduce blood pressure via diuretic and vascular effects
Practical Tip:
Use ground coriander seeds in salad dressings, dips, or spice blends to help keep your heart happy.
4. Digestive Aid and Gut Health
Coriander has been used for centuries as a digestive tonic. Modern science backs this up:
- Stimulates digestive enzymes and juices
- Relieves bloating and gas
- Eases indigestion and supports gut motility
Quick Remedy:
Make a simple coriander tea:
- 1 tsp coriander seeds, lightly crushed
- Steep in hot water for 5–10 minutes
- Add a squeeze of lemon and a dash of honey
5. Immune and Antimicrobial Benefits
Coriander extracts have demonstrated antimicrobial activity against common pathogens like E. coli, Salmonella, and Staph. They also help modulate immune responses and reduce inflammatory cytokines.
6. Brain and Mood Support
Emerging research indicates coriander may help protect the brain:
- Neuroprotective: Animal studies show reduced seizure activity, improved memory, and less anxiety.
- Molecular mechanisms: Certain coriander compounds activate potassium channels involved in calming overexcited neurons.
7. Skin, Bone, and Eye Health
- Skin: Coriander seed oil has been shown to reduce UV-induced irritation and accelerate skin repair.
- Bone: High vitamin K and calcium content support strong bones.
- Eyes: Vitamin A and antioxidant content aid in protecting vision.
Real-Life Ways to Use Coriander Every Day
1. Fresh Leaves (Cilantro)
- Chop and sprinkle over soups, salads, tacos, or curries
- Add to green smoothies or pesto for a fresh zing
2. Seeds
- Toast and grind for use in spice blends, rubs, and marinades
- Simmer in lentil dishes, stews, or herbal teas
3. Lemon-Coriander Water
Try this trendy wellness infusion for metabolism and detox support:
- Soak 1 tsp coriander seeds overnight in water
- In the morning, add a squeeze of lemon
- Strain and drink on an empty stomach
Reported benefits include better digestion, less bloating, and gentle detoxification.
Recipe: Cooling Coriander-Mint Chutney
Perfect for digestion, blood sugar balance, and a flavor kick!
Ingredients:
- 1 cup fresh coriander leaves
- ½ cup mint leaves
- 1 green chili
- 1 small piece of ginger
- 2 tbsp lemon juice
- Salt to taste
- Water to blend
Method:
- Combine all ingredients in a blender.
- Blend to a smooth paste. Add water as needed.
- Store in the fridge for up to 3 days.
Who Should Be Cautious?
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Large medicinal doses not recommended
- People on diabetes or blood pressure meds: Monitor closely, as coriander may amplify effects
- Allergy: Rare, but possible
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new herbal supplement, especially if you have chronic conditions or take prescription drugs.
The Bottom Line: Coriander is More Than a Flavor
From ancient remedies to modern clinical trials, coriander proves itself as a true wellness ally. Whether you’re managing blood sugar, aiming for heart health, boosting immunity, or just want to spice up your meals, coriander offers a tasty, evidence-based way to nourish your body.
So next time you see that bunch of cilantro or those tiny golden seeds, remember: you’re holding a powerhouse of health in your hands!
Have You Tried Coriander for Wellness?
Share your favorite recipes, tips, or experiences in the comments below. Let’s spread the word about this mighty herb—your body (and taste buds) will thank you!
References:
- Healthline: Coriander Benefits
- PharmEasy: Health Benefits of Coriander
- Clinical trial (PMC10220854)
- Times of India: Lemon-Coriander Seed Water
- ResearchGate: Coriander and Diabetes
- Nutraceutical Business Review: Skin Study
Ready to add more coriander to your life? Try the recipes above and let me know how it goes!
FAQs: Coriander – Nutritional & Health Benefits
1. What is the difference between coriander and cilantro?
Coriander refers to the entire plant (Coriandrum sativum). In North America, the fresh leaves are called cilantro, while the dried seeds are known as coriander. In other regions, both the leaves and seeds may simply be called coriander.
2. How much coriander should I consume daily for health benefits?
Research suggests that about 1 gram (approximately ¼ teaspoon) of coriander seed powder daily can be beneficial for blood sugar and cholesterol. Fresh leaves can be used liberally in meals.
3. Can coriander help with blood sugar control?
Yes, several human trials indicate that coriander seeds may help lower fasting blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity, especially in people with prediabetes or type-2 diabetes. Always consult your doctor if you have a medical condition or are on medication.
4. What are the best ways to include coriander in my diet?
Add fresh leaves to salads, soups, or smoothies. Use ground seeds in spice blends, curries, or herbal teas. Try making lemon-coriander water by soaking seeds overnight and adding lemon juice in the morning.
5. Is coriander safe for everyone?
Coriander is safe in normal food amounts for most people. However, those who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking blood sugar/blood pressure medication should use caution and consult a healthcare provider before taking medicinal doses.
6. Are there any potential side effects of consuming coriander?
Coriander is generally well-tolerated. Rarely, it can cause allergic reactions or mild digestive upset. Excessive consumption may lower blood sugar or blood pressure too much in sensitive individuals.
7. Does coriander really help with weight loss?
Coriander seeds, especially in combination with lemon water, may support metabolism and reduce water retention, but no single food will cause weight loss without healthy diet and lifestyle habits.
8. Can coriander improve skin health?
Yes, coriander seed oil and fresh leaves have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Studies show coriander seed oil can reduce skin irritation and help with healing.
9. Does cooking coriander destroy its nutrients?
Some delicate vitamins (like vitamin C) in coriander leaves are sensitive to heat, so add fresh leaves at the end of cooking. Seeds retain their nutrients and flavor even when toasted or cooked.
10. How do I store fresh coriander to keep it fresh longer?
Wrap rinsed leaves in a paper towel and store them in a sealed bag or container in the refrigerator. Alternatively, place stems in a jar of water and cover loosely with a plastic bag.