Are you searching for natural ways to supercharge your weight loss journey and boost your overall health? Two ingredients stand out for their ancient reputations and modern scientific attention: turmeric and apple cider vinegar (ACV). You may have seen countless social media claims, but what does current research actually say? How can you use these tools safely and effectively in daily life? Let’s dive in.
Why Turmeric and Apple Cider Vinegar?
Turmeric, the golden spice revered in Ayurveda and Asian cuisine, is famed for its active compound curcumin—a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory. Meanwhile, ACV, made by fermenting apples, has gone from folk remedy to wellness staple, touted for everything from weight loss to digestive support. Both have generated waves of research in recent years—so what’s hype and what’s real?
Turmeric: The Science Behind the Golden Spice
1. Metabolic Benefits and Weight Management
Recent umbrella reviews and meta-analyses published in 2025 have strengthened the case for curcumin’s role in metabolic health:
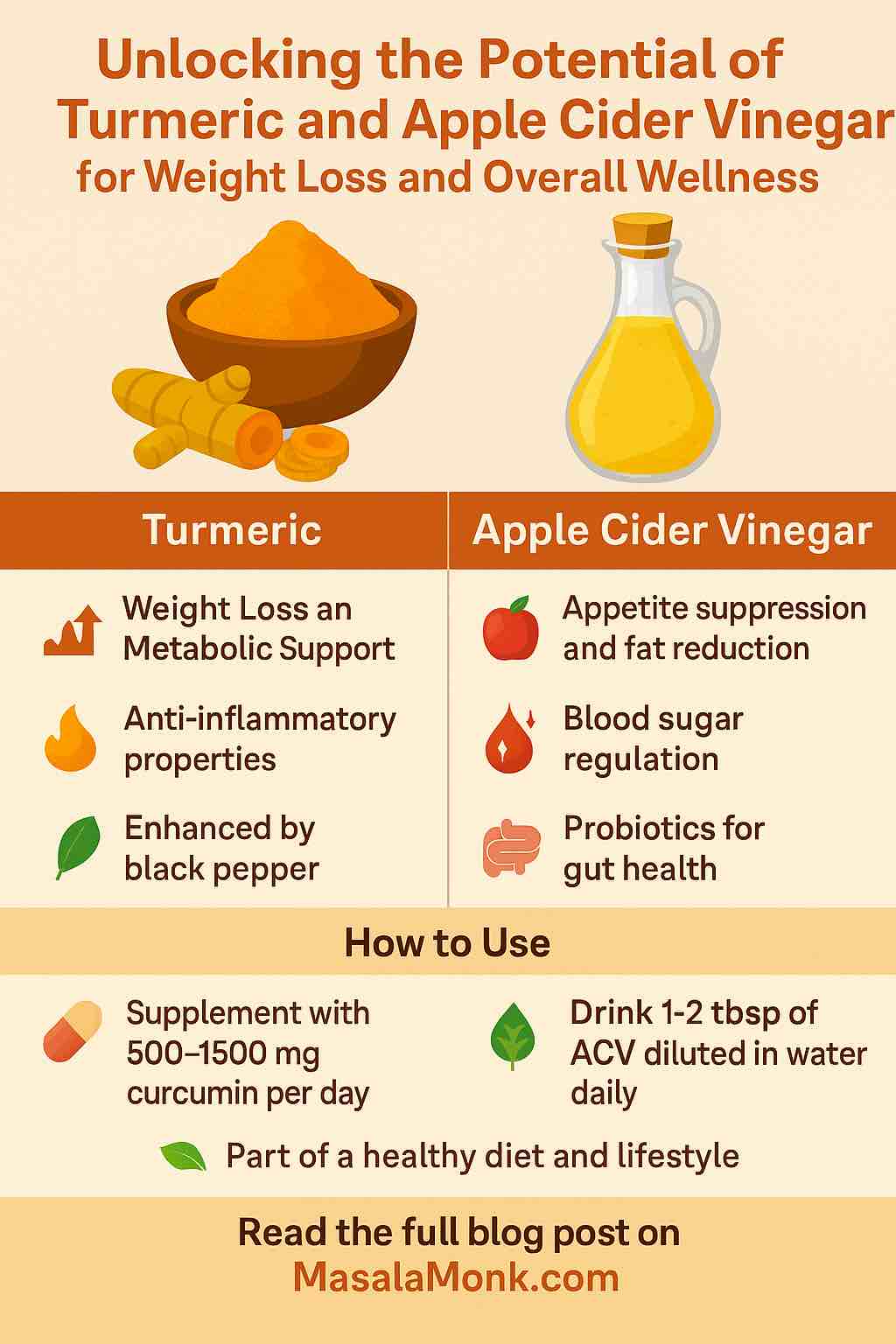
- Weight Loss: Studies show curcumin supplementation can lead to modest reductions in body weight (≈1 kg), BMI (~0.3), and waist circumference (~1–2 cm). While not a miracle cure, these results are significant for those seeking sustainable, healthy changes—especially when paired with diet and exercise.
- How it Works: Curcumin suppresses inflammation, a key player in obesity, and may inhibit new fat cell formation. It also activates AMPK, a “master switch” that boosts fat burning, and modulates the gut-brain axis, potentially influencing appetite and mood.
- Synergy with Exercise: The latest RCTs show the combination of curcumin and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) improves body composition and metabolic markers even more than exercise alone.
2. Broader Wellness Effects
- Inflammation & Oxidative Stress: Curcumin is a powerful anti-inflammatory—helpful for joint pain, skin health, and reducing risks of chronic diseases.
- Insulin Sensitivity: Beneficial for blood sugar control, especially in people with prediabetes or metabolic syndrome.
- Mood and Brain Health: New studies are exploring curcumin’s role in supporting mood, reducing anxiety, and protecting the brain against age-related decline.
3. How to Use Turmeric Safely
- Bioavailability Is Key: Curcumin is poorly absorbed alone. For best results, choose a supplement with black pepper extract (piperine) or opt for “enhanced bioavailability” formulas.
- Dosing: Most research uses 500–1500 mg curcumin per day. For food-based use, add 1–2 teaspoons of ground turmeric to curries, soups, or smoothies—always with a pinch of black pepper.
- Safety: Turmeric is safe for most, but high doses can cause digestive upset or (very rarely) liver issues. If pregnant, on blood thinners, or managing gallstones, consult your doctor.
Apple Cider Vinegar: What Does the Evidence Say?
1. ACV and Weight Loss—Fact vs. Fiction
- Recent Trials: A 2024–2025 clinical trial in young adults found daily ACV (5–15 mL, diluted in water) led to 6–8 kg weight loss, significant drops in BMI, body fat, and waist measurements over just 12 weeks—regardless of dose.
- How it Works: Acetic acid, the main component, may suppress appetite, slow digestion, and stabilize blood sugar, making you feel fuller and reducing total calorie intake. Some studies showed those drinking ACV ate ~400 calories less per day!
2. Other Wellness Benefits
- Blood Sugar & Cholesterol: ACV can blunt post-meal blood sugar spikes and modestly lower cholesterol in some people.
- Digestive Health: Raw, unfiltered ACV contains probiotics that may support gut health.
- Satiety & Cravings: By slowing stomach emptying, ACV can reduce cravings and the urge to snack.
3. How to Use ACV Safely
- Dosing: Start with 1 teaspoon (5 mL) in a large glass of water before meals; you can work up to 1–2 tablespoons (15–30 mL) per day if well tolerated.
- Always Dilute: Never drink ACV straight—it can erode tooth enamel, burn the throat, and worsen acid reflux if undiluted.
- Safety Tips: Rinse your mouth after, use a straw, and avoid if you have chronic kidney disease or ulcers. Check with your doctor if you’re on medications (especially insulin, diuretics, or heart meds).
Turmeric & ACV Together: A Potent Pair?
There’s no direct research on their synergy, but using both as part of a healthy lifestyle may provide complementary benefits: turmeric fights inflammation and supports metabolism; ACV helps control appetite and blood sugar. Together, they can be a powerful (and delicious) part of your wellness routine.
Practical Ways to Add Turmeric and ACV to Your Day
1. Morning Wellness Shot
- 1 cup warm water
- 1 tbsp ACV (unfiltered, with “mother”)
- ½ tsp ground turmeric
- Pinch of black pepper
- Juice of ½ lemon
- (Optional) 1 tsp honey or a splash of maple syrup
Mix well and drink on an empty stomach.
2. Golden ACV Salad Dressing
- 1 tbsp ACV
- 1 tsp Dijon mustard
- ½ tsp turmeric
- 1 tbsp olive oil
- Pinch of pepper
- Whisk and drizzle over greens.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Smoothie
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- ½ tsp turmeric
- 1 small banana
- ½ cup pineapple
- ½ tbsp ACV
- Pinch of black pepper
- Blend and enjoy!
4. Easy Ways to Boost Intake
- Add turmeric to rice, scrambled eggs, roasted veggies, or teas (“golden milk”).
- Use ACV in marinades, vinaigrettes, or add a splash to sparkling water.
FAQs
- Can turmeric and apple cider vinegar really help with weight loss?
Answer: Yes, both can modestly aid weight loss according to recent studies, but results are best when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise. Neither is a miracle solution on its own. - How much turmeric and apple cider vinegar should I take daily?
Answer: Research suggests 500–1500 mg curcumin (turmeric extract) per day, and 1–2 tablespoons (15–30 mL) of ACV diluted in water. Start small to assess tolerance. - What is the best way to consume turmeric for absorption?
Answer: Pair turmeric with black pepper (which contains piperine) or choose a supplement labeled as “enhanced bioavailability.” Cooking with healthy fats also helps absorption. - Can I take turmeric and ACV together?
Answer: Yes, they can be combined safely in drinks or recipes, as long as you don’t exceed recommended doses and have no contraindications. - Are there any side effects or risks?
Answer: Turmeric is safe for most, but high doses may cause stomach upset or interact with blood thinners. ACV can erode tooth enamel and irritate the throat if undiluted. Always dilute ACV and avoid excessive use. - Who should avoid turmeric or ACV?
Answer: Those with gallbladder disease, bleeding disorders, or on certain medications should avoid high-dose turmeric. ACV should be avoided by people with ulcers, acid reflux, or chronic kidney disease. - Is it better to use supplements or whole foods?
Answer: Both are beneficial. Supplements ensure consistent dosing, while whole foods provide additional nutrients and culinary variety. Use supplements for therapeutic effects and whole foods for general wellness. - Does ACV need to be organic or unfiltered?
Answer: For maximum probiotic benefit, choose raw, unfiltered ACV with the “mother.” Organic is preferred but not mandatory for effectiveness. - How soon can I expect to see results?
Answer: Most studies report noticeable effects in 8–12 weeks when used consistently along with lifestyle changes. - Can I use turmeric and ACV for general wellness even if I’m not trying to lose weight?
Answer: Absolutely! Both support anti-inflammation, gut health, blood sugar balance, and overall vitality regardless of weight loss goals.
Key Takeaways
- Turmeric and ACV are both backed by modern science for supporting modest weight loss, better metabolism, and overall wellness.
- Their greatest benefits come as part of a healthy lifestyle—including a balanced diet and regular movement.
- Use practical recipes and dosing, watch for side effects, and choose quality sources.
- Remember: There’s no miracle shortcut, but these time-tested ingredients can make healthy habits easier—and tastier!
Have you tried turmeric or ACV in your routine? What’s your favorite way to use them? Share in the comments!













