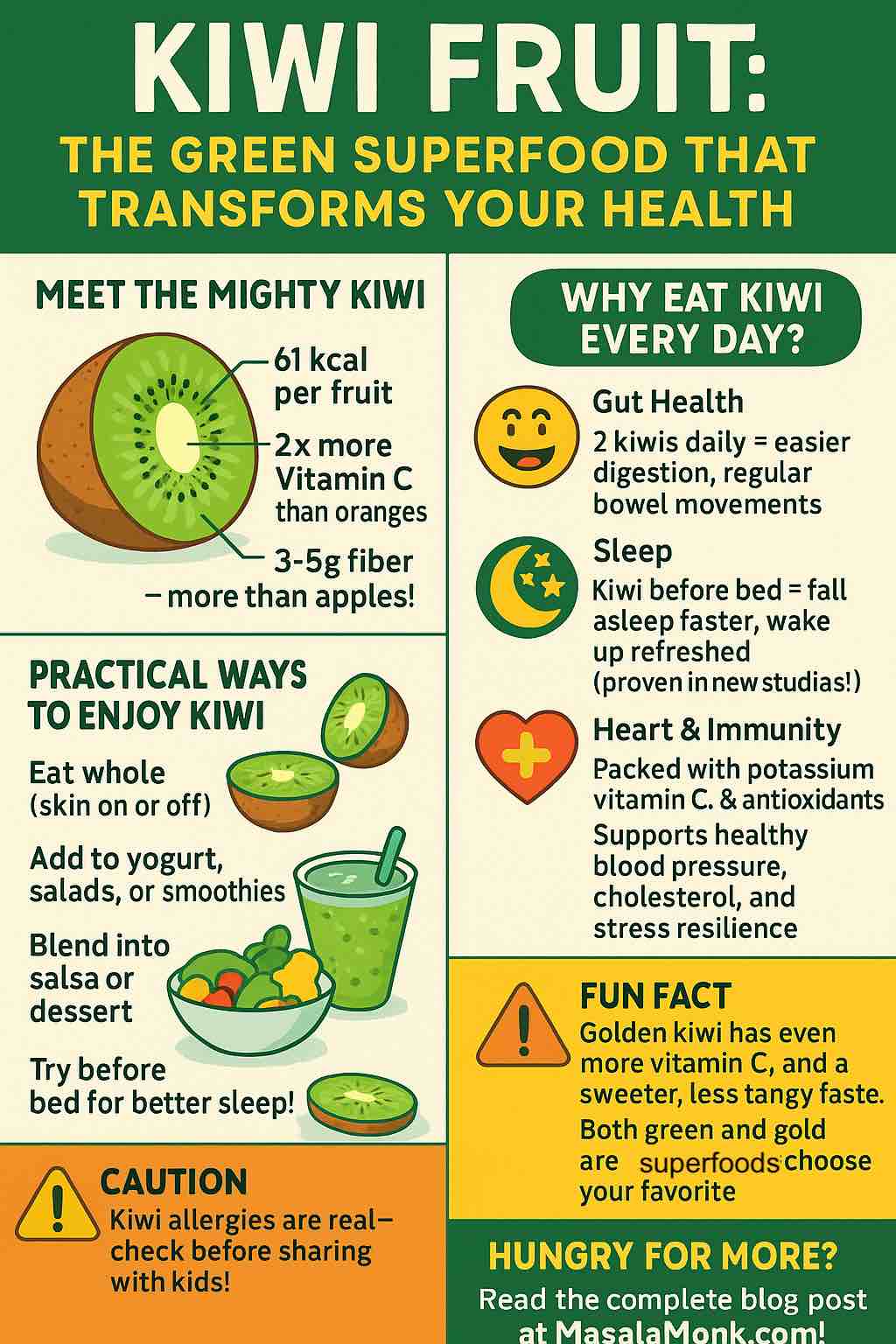
Few foods are as beloved—and as hotly debated—as the humble potato. Whether you’re a fan of the classic white potato (think mashed potatoes at Thanksgiving) or the vibrant sweet potato (hello, sweet potato fries), chances are you’ve wondered: Which is healthier? Which is better for my goals? Does it really matter how I cook them?
Today, we’re peeling back the layers on both spuds—exploring nutrition, health effects, cooking tips, and the real story behind the hype. Get ready for some surprises, a few myth-busters, and plenty of practical tips you can use at your next meal.
Nutrition Showdown: White Potato vs. Sweet Potato
Let’s start with the basics—a head-to-head comparison.
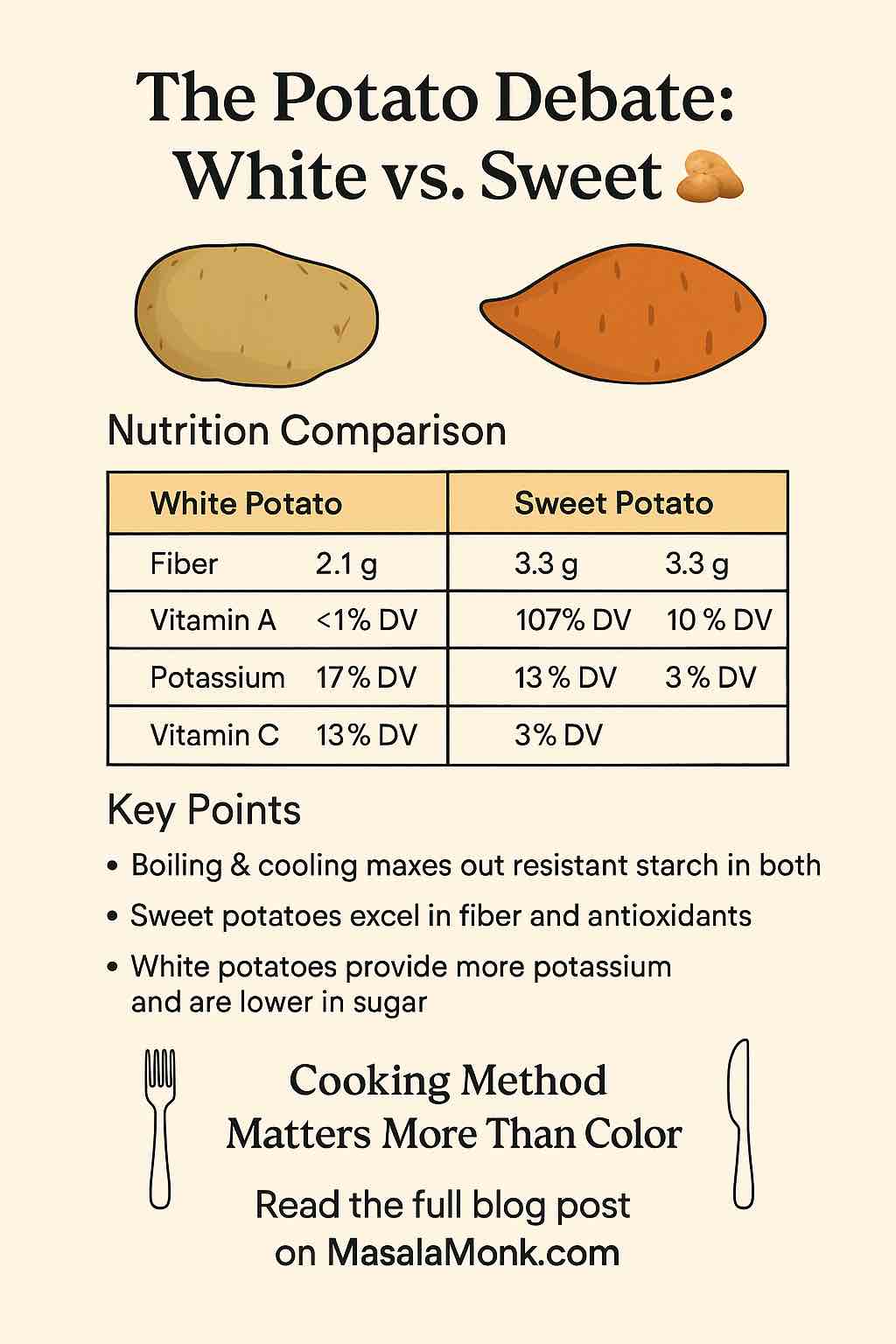
| Nutrient (per 100g, cooked) | White Potato | Sweet Potato |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 87 | 90 |
| Carbohydrates | 20g | 21g |
| Fiber | 2.1g | 3.3g |
| Protein | 2g | 2g |
| Fat | 0.1g | 0.2g |
| Potassium | 17% DV | 10% DV |
| Vitamin C | 13% DV | 3% DV |
| Vitamin A | <1% DV | 107% DV |
| Antioxidants | Moderate | High (esp. in colored varieties) |
Key Takeaways:
- Both are nutritious, low-fat, and loaded with healthy carbs.
- Sweet potatoes win big on fiber and vitamin A (beta-carotene).
- White potatoes bring more potassium and vitamin C to the table.
Glycemic Index: The Truth About Blood Sugar
You may have heard that potatoes are “bad for blood sugar”—but the full story is more nuanced:
- White potatoes have a variable glycemic index (GI), ranging from moderate (~56, for boiled red potatoes) to very high (up to 111, for baked russets). The GI jumps if you bake, fry, or mash.
- Sweet potatoes generally score lower, especially when boiled (GI ~44), but can still spike blood sugar if baked or mashed (GI up to ~91).
Practical tip:
How you cook your potatoes matters more than which type you eat! Boil and cool them (think potato salad) to maximize resistant starch and blunt the blood sugar spike.
Resistant Starch: Your Gut’s Secret Weapon
Here’s a little-known potato superpower: when you cook and cool potatoes (white or sweet), they form “resistant starch.” This special fiber-like carb:
- Feeds your gut bacteria (prebiotic effect)
- Promotes satiety and may help with weight control
- Improves insulin sensitivity over time
- Reduces inflammation in the gut
Studies show that cooled potato salad or reheated boiled potatoes (not fried) are gut-health gold. So don’t toss those leftovers—chill them and give your microbiome a treat!
Antioxidants and Unique Nutrients
- Sweet potatoes—especially the orange and purple types—are packed with antioxidants, including beta-carotene (vitamin A) and anthocyanins. These protect your cells from oxidative damage and support immune health.
- White potatoes contain their own beneficial compounds, like vitamin C, potassium, and glycoalkaloids, which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Color tip: The deeper the color (think purple or deep orange), the more antioxidants you’ll get!
Which Potato Fits Your Goals?
Trying to boost vitamin A?
- Go sweet potato—especially orange or purple varieties.
Need more potassium (for blood pressure, muscle health)?
- White potatoes are your friend—more potassium than a banana!
Watching blood sugar?
- Boiled and cooled potatoes of any type are best.
- Always pair potatoes with healthy fats (olive oil) and protein (beans, eggs, fish) to slow sugar absorption.
Want a fiber boost and gut health?
- Sweet potatoes have the edge, but cooled white potatoes also deliver.
Cooking Matters More Than Color
Let’s bust a myth:
Frying, over-baking, or drowning potatoes in cream, butter, or sugar cancels out most health benefits, no matter the type.
Healthiest Ways to Prepare Potatoes:
- Boil with the skin on: Preserves fiber and nutrients.
- Cool and eat as salad: Maximizes resistant starch.
- Roast with olive oil and herbs: Boosts flavor without adding junk.
- Pair with protein/fiber: Slows down the blood sugar rise.
Want a next-level hack? Try cold potato salad with a vinegar-based dressing—great for gut health and blood sugar control.
Busting Common Myths
- Are white potatoes “bad” for you?
No! They’re a real food—nutritious and filling if prepared well. - Are sweet potatoes “superfoods”?
They’re excellent for vitamin A and antioxidants, but variety matters most. No single food can be a magic bullet! - Should you avoid potatoes for weight loss or diabetes?
No, but portion size and cooking style matter. Use boiled or cooled potatoes, moderate your portions, and skip the heavy toppings.
Real-World, Practical Advice
- Rotate your spuds: Variety = better nutrition and less boredom.
- Shop for color: Try purple, orange, yellow, and white varieties for a rainbow of nutrients.
- Meal-prep hack: Boil a big batch, cool, and store for use in salads, quick breakfasts, or sides all week.
- Don’t peel unless you have to: The skin holds much of the fiber and nutrients.
2024–2025 Science Snapshot
- Recent studies confirm that both white and sweet potatoes offer gut, metabolic, and anti-inflammatory benefits—if you cook them wisely.
- Resistant starch is gaining buzz as a “postbiotic” powerhouse for gut health, especially in cooled potatoes.
- Glycemic impact can be minimized through preparation—not just by switching spud types.
Conclusion: Which Potato Wins?
Here’s the final word: Both white and sweet potatoes can be part of a healthy, enjoyable diet.
Your best bet? Eat a mix, focus on smart cooking, and savor every bite.
The real winner: You, when you enjoy potatoes as part of a balanced, diverse diet!
Recipe Ideas to Try
- Zesty Potato Salad
- Boiled baby potatoes (white or sweet), cooled
- Chopped red onion, celery, parsley
- Olive oil, lemon, Dijon mustard dressing
- Sprinkle of seeds or chopped eggs for protein
- Oven-Roasted Rainbow Fries
- Mixed wedges of white, orange, and purple potatoes
- Toss in olive oil, smoked paprika, rosemary
- Roast at 425°F until crisp
- Sweet Potato Breakfast Hash
- Diced sweet potatoes, sautéed with onions, bell pepper
- Add black beans and spinach
- Top with a poached egg for a full meal
What’s your favorite way to enjoy potatoes? Share your thoughts, questions, or your best recipe below! Let’s keep the spud conversation growing.
FAQs
1. Are sweet potatoes really healthier than white potatoes?
Sweet potatoes offer more vitamin A and fiber, while white potatoes provide more potassium and vitamin C. Both are healthy if prepared well—neither is automatically “better” than the other.
2. Which type of potato is better for managing blood sugar?
Boiled and cooled sweet potatoes have the lowest glycemic impact, but boiled and cooled white potatoes are also good. Preparation is key: avoid frying or baking at high temps for either type.
3. Can I eat potatoes if I’m trying to lose weight?
Yes, in moderation. Potatoes are filling and nutrient-dense. To support weight loss, boil or roast them (not fry), keep the skin on, and avoid heavy, high-calorie toppings.
4. What is resistant starch, and how do I get more of it from potatoes?
Resistant starch forms when potatoes are cooked and then cooled. It feeds gut bacteria and can improve insulin sensitivity. Potato salad (with cooled, boiled potatoes) is a great source.
5. Are potato skins good for you?
Yes! Potato skins are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Unless you have to peel them, leave the skin on for the best nutritional value.
6. Do sweet potatoes have more sugar than white potatoes?
Yes, sweet potatoes have slightly more natural sugars, but they also have more fiber, which slows the absorption. The total carb content is very similar between the two.
7. What’s the healthiest way to cook potatoes?
Boiling with skins on, cooling, and then eating as a salad or reheating is the healthiest. Roasting with olive oil and herbs is also great. Avoid deep frying and loading with butter, cream, or cheese.
8. Can potatoes be part of a diabetic-friendly diet?
Yes, if portion sizes are reasonable and preparation is healthy (boiled, cooled, roasted). Pair potatoes with lean protein and healthy fats to help control blood sugar.
9. Do colored potatoes (like purple or red) have extra health benefits?
Colored potatoes (especially purple and orange) are higher in antioxidants like anthocyanins and beta-carotene, offering extra cellular protection.
10. Is it better to eat potatoes hot or cold?
Cold (or gently reheated) potatoes contain more resistant starch, which is better for gut health and lowers the glycemic impact. Hot potatoes are still healthy, but for extra benefits, try them chilled or as leftovers.