Kiwi fruit, with its unique sweet-tart flavor and vibrant green or golden flesh, has long been a favorite in fruit salads and tropical desserts. But in 2025, science is making it clear: this small, fuzzy fruit is one of the most impressive “functional foods” you can put on your plate. Whether your goals are better digestion, improved sleep, heart protection, glowing skin, or simply eating smarter, kiwi delivers—and often in ways you might not expect.
Let’s take a deep, practical dive into why eating kiwi every day could change your health, your habits, and your life.
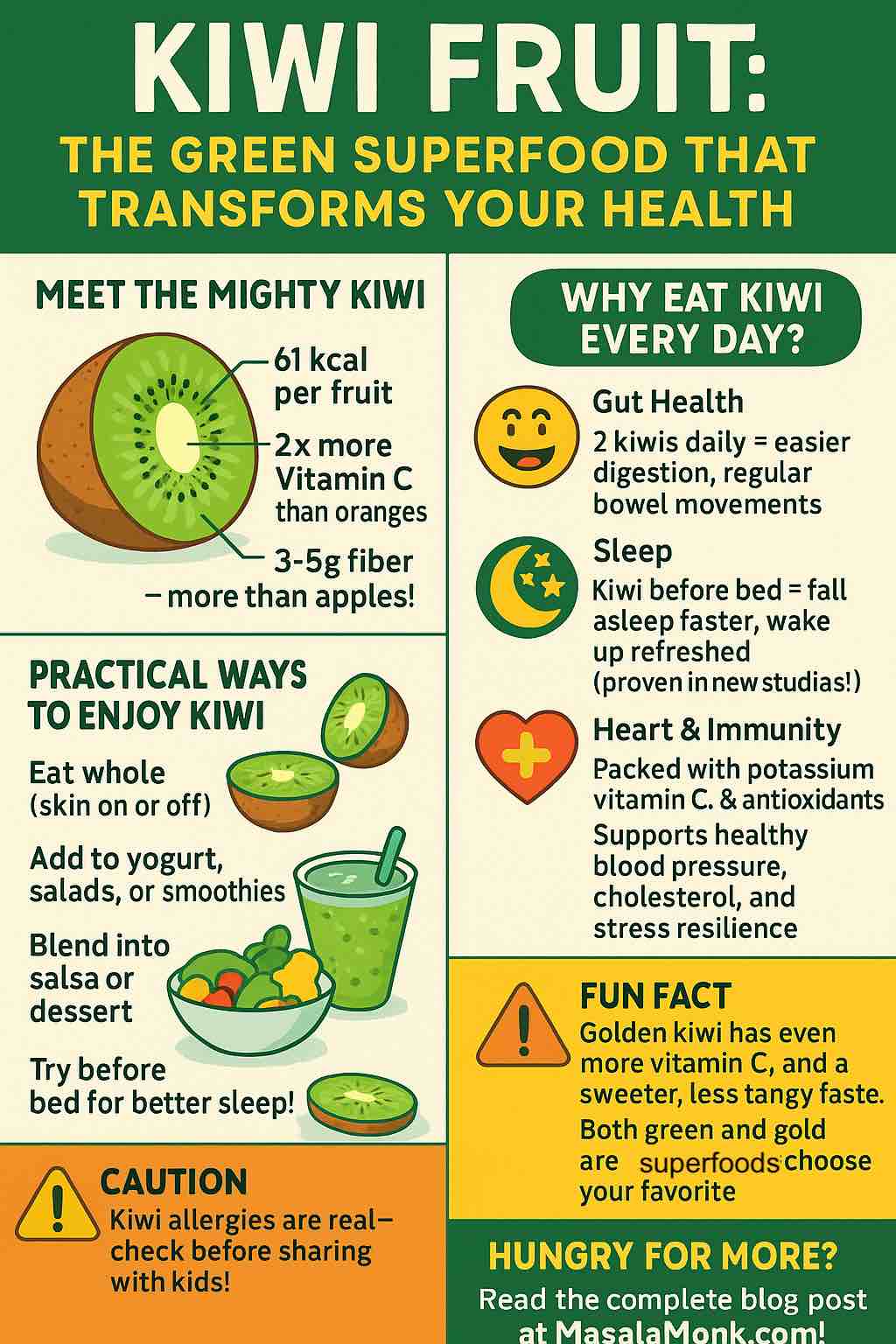
Kiwi Nutrition Facts: What’s Inside the Fuzz?
It’s easy to underestimate kiwi due to its size, but inside is a nutritional goldmine:
- Calories: ~61 kcal (per 100g, about 1 medium kiwi)
- Carbohydrates: 15g (natural sugars + valuable fiber)
- Fiber: 3–5g (both soluble and insoluble types for gut health)
- Protein: 1.1g
- Fat: 0.5g
- Vitamin C: 90–110mg (100–200% of daily needs—golden kiwis can reach up to 160mg)
- Vitamin K: 30–40mcg (supports blood and bone health)
- Potassium: 215–312mg (more than a banana per calorie)
- Vitamin E: 1.5mg (one of the few fruits with natural vitamin E)
- Folate, Copper, Magnesium, Calcium: In smaller but significant amounts
- Antioxidants: Rich in lutein, zeaxanthin, carotenoids, and polyphenols
Key detail: The edible skin contains extra fiber, vitamin E, and powerful phytonutrients. If you can handle the fuzzy texture, scrub and eat the whole fruit for maximum benefits.
How Kiwi Supercharges Your Health: New Science in 2025
1. Digestion & Gut Health: More Than Just Fiber
Kiwi has become a star in digestive health—not just for its fiber, but also for actinidin, a unique enzyme that breaks down proteins in your stomach. This means better digestion, less bloating, and more comfortable meals—especially for those who get gassy or heavy after eating animal protein or legumes.
Recent studies in the US, New Zealand, and Asia show:
- Two green kiwis a day significantly improve stool frequency and consistency, relieving both occasional and chronic constipation.
- Kiwi outperformed psyllium (a common fiber supplement) in clinical trials, providing greater relief from abdominal discomfort and straining.
- The fruit acts as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria, and boosts short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) production, supporting colon health and reducing inflammation.
Practical tip: Try a “kiwi breakfast shot”—eat one or two kiwis (with skin, if you like) on an empty stomach with water before your first meal.
2. Sleep: The Surprising Nighttime Superfood
Struggling to fall or stay asleep? Kiwi is quickly becoming the go-to bedtime snack.
Latest research (2024–2025) reveals:
- Eating 1–2 kiwis about one hour before bed helps people fall asleep faster, increases total sleep time, and improves sleep efficiency.
- This effect has been confirmed in adults, children, and even people with insomnia or overweight/obesity.
- The sleep boost is thought to come from the combination of natural serotonin, vitamin C, folate, and antioxidants—plus some gentle carbs that help your brain make melatonin.
Lifestyle tip: Replace your late-night cookie or ice cream with sliced kiwi, maybe topped with a sprinkle of cinnamon or a little yogurt.
Real-world example: A university trial with students found that after two weeks of evening kiwi, participants reported feeling more refreshed and alert in the morning, with less grogginess.
3. Heart Health & Metabolism: Small Fruit, Big Protection
Heart disease remains the world’s top killer, but simple daily changes add up. Kiwi offers several cardiovascular benefits:
- Its high potassium content helps lower blood pressure by counteracting sodium.
- Studies confirm that eating kiwi daily can lower triglycerides, reduce platelet aggregation (less clot risk), and modestly raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol.
- Kiwis are naturally low in sodium and fat, with a low glycemic index (~40), so they’re ideal for people with hypertension, prediabetes, or metabolic syndrome.
Actionable tip: Add kiwi to your post-workout smoothie or salad to replenish potassium and speed up muscle recovery.
Fun fact: In a study, people who ate three kiwis a day for eight weeks saw measurable improvements in blood pressure and blood lipids compared to those eating apples.
4. Mood, Immunity & Daily Energy: Vitamin C in Overdrive
Kiwi is one of the best natural sources of vitamin C—beating out oranges, strawberries, and many “superfoods” by weight.
- Just two kiwis provide more than enough vitamin C for a whole day, supporting your immune system and helping your body fight viruses and heal wounds.
- Vitamin C also reduces the impact of stress, improves mood, and assists your body in making collagen for healthy skin and joints.
- A 2025 trial in young adults found that regular kiwi consumption improved mood, reduced fatigue, and boosted vitality—sometimes in as little as four days.
Tip for busy days: Bring kiwis to work or class as a portable, vitamin-packed snack. They’re less messy than oranges and need no prep if you eat the skin.
5. Skin, Eye, and Longevity Benefits
- Kiwis contain lutein and zeaxanthin, carotenoids important for long-term eye health and protection against age-related macular degeneration.
- Their vitamin E and C combo helps repair and rejuvenate skin, fighting oxidative damage and keeping your complexion bright.
- New research also links regular kiwi intake to lower risk of some cancers, especially colorectal, thanks to fiber and unique antioxidant compounds that protect gut cells.
Pro aging hack: Try eating kiwi skin-on for a beauty and gut boost, or blend it into your smoothies for extra nutrients.
6. Cancer Prevention and Overall Longevity
While no single fruit is a cure-all, kiwi’s mix of fiber, vitamin C, and plant antioxidants is being actively studied for cancer prevention, especially of the colon. Emerging evidence suggests:
- People who eat kiwis daily have a statistically lower risk of developing colorectal cancer.
- The combination of antioxidants and fiber appears to reduce inflammation and support healthy cell turnover.
Practical application: If you have a family history of colorectal cancer or want to improve long-term gut health, make kiwi a daily staple.
How to Eat More Kiwi: Practical Tips for Every Lifestyle
Raw and Simple:
- Halve and scoop with a spoon for a portable snack.
- Eat the skin for extra fiber—just scrub well before eating.
In Salads:
- Add sliced kiwi to mixed greens, feta cheese, walnuts, and a citrus vinaigrette for a refreshing lunch.
On Breakfast:
- Top Greek yogurt, overnight oats, or cottage cheese with sliced kiwi, seeds, and honey.
In Smoothies:
- Blend one or two kiwis with spinach, banana, pineapple, and coconut water for a bright, tangy boost.
Salsas and Dips:
- Mix chopped kiwi with avocado, jalapeño, red onion, and cilantro for a colorful salsa—perfect for grilled fish, chicken, or tacos.
Desserts:
- Layer kiwi with whipped coconut cream, berries, and toasted nuts for a quick, healthy dessert.
As Dried Snacks:
- Slice thin and dehydrate for tangy, chewy “kiwi chips” (kids love these!).
For Better Sleep:
- Try two kiwis an hour before bed—plain or with a bit of cinnamon or dark chocolate shavings.
Kiwi in Real Life: Building a Healthy Routine
Here are a few sample ways to add kiwi to your daily rhythm:
The “Kiwi Two-a-Day” Challenge:
Start your morning and end your evening with a kiwi. Track your digestion, sleep, and energy for two weeks—most people notice real improvements.
Meal Prep Hack:
Buy a bag of kiwis every week. Wash them all at once. Store ripe ones in the fridge and eat as snacks, or slice over meals.
For Families:
Let kids try kiwis with the skin (cut into fun shapes if needed). The unique taste and texture can help expand picky eaters’ palates.
Fitness & Recovery:
Post-workout, blend kiwi with protein powder, leafy greens, and coconut water for the ultimate recovery shake.
For Travelers:
Kiwi travels well—bring a couple in your bag for flights or road trips to avoid unhealthy airport snacks.
Risks and Precautions: Who Should Be Careful?
- Allergies: Some people, especially those allergic to latex or other fruits (like banana or avocado), can react to kiwi. Symptoms range from mild itching to severe reactions. Try a small amount first if unsure.
- Blood Thinners: Kiwi is high in vitamin K, which can interfere with warfarin and similar medications. If you’re on blood thinners, consult your doctor about how much is safe.
- Oral Irritation: The actinidin enzyme can make your mouth tingle, especially if you’re sensitive—peeling may help.
Final Thoughts: Should You Eat Kiwi Every Day?
If you’re searching for a practical, delicious, and research-backed way to improve your diet and your health, kiwi fruit is hard to beat. Its blend of fiber, vitamin C, antioxidants, and plant enzymes offers real-life benefits for digestion, sleep, mood, skin, and heart health—often in ways you’ll actually feel.
Eating just one or two kiwis a day is simple, affordable, and fits into almost any diet—vegan, paleo, low-FODMAP (in moderation), or just plain healthy eating.
Try it for two weeks. You might sleep better, smile more, and feel lighter—inside and out.
Ready to make kiwi a habit? Pick up a few on your next grocery run and start experimenting. Your gut, heart, and mind will thank you!
FAQs About Kiwi Fruit
1. Can you eat kiwi skin, and is it healthy?
Yes, the skin is edible and actually boosts the fiber, vitamin E, and antioxidant content of each fruit. Just wash it thoroughly before eating. The texture is fuzzy, but you can rub off some of the hairs if you prefer. If you have a sensitive mouth, start with the skin of golden kiwis, which is smoother.
2. How many kiwis should I eat per day for health benefits?
Most research supports eating 1–2 kiwis per day for noticeable benefits to digestion, sleep, and immunity. Clinical studies often use this amount, and it’s generally safe for most healthy adults and children.
3. Are green and golden kiwis nutritionally different?
Yes. Green kiwis are higher in fiber and contain more actinidin (an enzyme aiding protein digestion). Golden kiwis are sweeter, less acidic, and contain even more vitamin C and some extra antioxidants. Both are excellent for health, so choose based on your taste and texture preference.
4. Is kiwi safe for people with allergies?
Kiwi can trigger allergies, especially in people sensitive to latex, avocados, bananas, or birch pollen. Symptoms can include itching, tingling, or swelling in the mouth. If you have any known food allergies or experience symptoms, consult your doctor before adding kiwi to your diet.
5. Can kiwi help with constipation and gut health?
Yes. Kiwi’s unique mix of fiber and the actinidin enzyme has been shown to improve bowel regularity, soften stools, and relieve constipation—sometimes outperforming fiber supplements. Eating two green kiwis daily can benefit most people with sluggish digestion.
6. Does eating kiwi really help you sleep better?
Recent clinical studies show that eating 1–2 kiwis about an hour before bed can help you fall asleep faster, sleep longer, and improve sleep quality. Kiwi contains serotonin and antioxidants that contribute to these benefits.
7. Is kiwi fruit good for people with diabetes?
Kiwi has a low glycemic index (around 40), meaning it causes only a gentle rise in blood sugar. It’s rich in fiber, which also helps with blood sugar control. Most people with diabetes can include kiwi as part of a balanced diet, but portion control is still important.
8. How should I store kiwi to keep it fresh?
Keep unripe kiwis at room temperature to ripen (speed this up by placing them next to apples or bananas). Once ripe, move them to the refrigerator, where they’ll stay fresh for up to a week.
9. Can I give kiwi to young children or babies?
Yes, but introduce it gradually to check for any reactions. Remove the skin for babies and cut the fruit into small pieces to reduce choking risk. Kiwi is a great source of vitamin C and fiber for growing kids.
10. Are there any medications or health conditions that make kiwi unsafe?
If you take blood thinners (like warfarin), kiwi’s vitamin K can interfere with your medication. People with a history of kidney stones may also want to moderate intake due to oxalate content. Always consult your healthcare provider if you have concerns.













