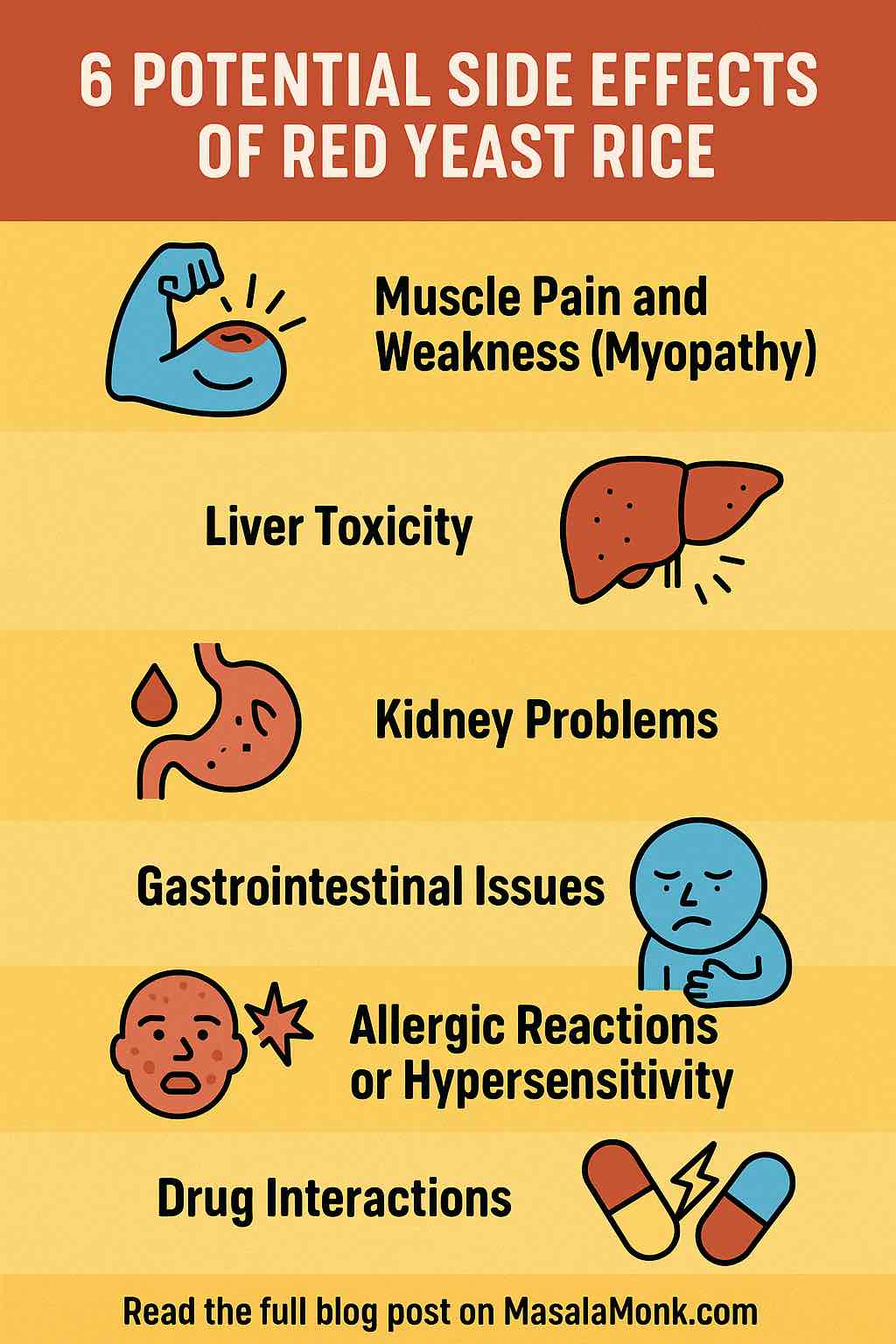
Red yeast rice (RYR) has earned a reputation as a powerful natural remedy for managing cholesterol. Used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries, this fermented rice product contains monacolin K, a substance chemically identical to the prescription drug lovastatin. This means it can reduce LDL (“bad”) cholesterol effectively—but also that it may carry similar side effects. In recent years, high-profile health incidents and new research have cast a spotlight on the safety and regulation of red yeast rice supplements. If you’re considering adding RYR to your health regimen, read on for a practical, research-backed exploration of its potential risks.
1. Muscle Pain, Weakness, and Rhabdomyolysis
One of the most well-documented and serious side effects of red yeast rice is its impact on muscles. Because monacolin K behaves like a statin, it can lead to muscle-related issues such as:
- Myalgia: General muscle pain or tenderness.
- Weakness or fatigue: Especially after physical exertion.
- Rhabdomyolysis: A rare but life-threatening condition where muscle fibers break down and release harmful proteins into the bloodstream, potentially causing kidney damage.
A 2025 report by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) confirmed that even a daily intake of 3 mg of monacolin K can trigger these effects in sensitive individuals. These risks increase when RYR is taken alongside other statins, certain antibiotics, or with heavy physical activity.
Tip: If you notice unexplained muscle pain or dark-colored urine while taking RYR, stop immediately and consult a healthcare professional.
2. Liver Toxicity and Enzyme Elevation
Another concern shared with statins is the risk of liver damage. While not common, some users of red yeast rice have experienced:
- Elevated liver enzymes (AST, ALT)
- Fatigue
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Nausea and abdominal discomfort
Recent case studies (2024) from clinical settings reported multiple hospitalizations for acute hepatitis linked to red yeast rice. Although reversible, liver damage can be serious if not caught early.
Tip: Get your liver function tested regularly if you’re using RYR long-term.
3. Kidney Damage and Contamination Scandals
Kidney damage can result directly from rhabdomyolysis or from exposure to toxins sometimes found in red yeast rice products. The most concerning is citrinin, a mycotoxin with known nephrotoxic (kidney-damaging) and potentially genotoxic properties.
Even more alarming was the 2024 Kobayashi Pharmaceutical scandal in Japan, where over 500 people were hospitalized and at least 80 died after consuming contaminated red yeast rice supplements containing puberulic acid, a potent fungal toxin.
Tip: Choose brands that are third-party tested and explicitly free of citrinin or other contaminants. Look for quality certifications (e.g., USP, NSF).
4. Gastrointestinal Side Effects
Like many supplements and medications, red yeast rice can irritate the gastrointestinal tract. Common complaints include:
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Stomach cramps
- Diarrhea
- Heartburn
These effects are generally mild and tend to subside with continued use or dosage adjustment. A 2024 study published in Frontiers in Pharmacology found that combining red yeast rice with certain herbal compounds reduced both muscle and GI side effects.
Tip: Take RYR with food to minimize stomach upset, and start with a low dose to test tolerance.
5. Allergic Reactions and Hypersensitivity
Although rare, allergic reactions have been reported. These may manifest as:
- Skin rash or itching
- Swelling of the face or throat
- Difficulty breathing
In sensitive individuals, immune responses can also trigger elevated creatine kinase (CK) levels, which is a marker for muscle stress.
Tip: Discontinue use and seek medical attention if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction.
6. Dangerous Drug Interactions
Red yeast rice can interact with many medications, increasing the risk of adverse effects. Key interactions include:
- Statins: Doubling up can amplify side effects.
- CYP3A4 inhibitors: Drugs like erythromycin, ketoconazole, or grapefruit juice can raise monacolin K levels to dangerous levels.
- Anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin): May increase bleeding risk.
- Niacin or fibrates: Raises the risk of muscle toxicity.
Tip: Always consult your doctor or pharmacist before combining RYR with prescription medications.
Practical Recommendations
- Do your homework: Research the brand and look for third-party testing.
- Start low: Begin with the lowest effective dose.
- Monitor health markers: Check liver enzymes, kidney function, and muscle symptoms.
- Stay informed: Regulations are evolving; keep up with updates from FDA, EFSA, and other health bodies.
Conclusion: The Bottom Line Red yeast rice is often marketed as a safer, “natural” alternative to statins. But natural doesn’t always mean harmless. With risks that mirror prescription drugs and the added concern of contamination, users must approach red yeast rice with informed caution. If you’re managing high cholesterol, consult your healthcare provider to weigh the benefits and risks—and consider lifestyle and dietary changes that support heart health alongside or in place of supplements.
Stay safe, stay informed, and choose wisely.
🔍 FAQs: Red Yeast Rice – Risks, Safety, and Use
1. Is red yeast rice safe to take daily?
It depends. While many people tolerate low doses well, daily use—especially above 3 mg of monacolin K—can cause liver, muscle, or kidney issues. Long-term use should always be monitored by a healthcare provider.
2. How does red yeast rice lower cholesterol?
Red yeast rice contains monacolin K, which inhibits the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, just like statin drugs. This reduces the production of cholesterol in the liver, effectively lowering LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels.
3. Can I take red yeast rice with a statin?
No. Taking red yeast rice with a statin can double the dose of monacolin K, significantly increasing the risk of side effects like muscle damage and liver toxicity. Always consult your doctor before combining them.
4. What are signs that red yeast rice is affecting my liver or kidneys?
Look for yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, persistent fatigue, nausea, or swelling in the legs. These may indicate liver or kidney issues and require immediate medical attention.
5. Is red yeast rice a regulated supplement?
Not consistently. In the U.S. and many other countries, red yeast rice is sold as a dietary supplement, meaning it is not subject to the same safety, efficacy, or purity standards as prescription drugs. This can lead to potency variations or contamination (e.g., with citrinin).
6. Who should not take red yeast rice?
Avoid RYR if you are:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding
- Taking statins or CYP3A4 inhibitors
- Have liver or kidney disease
- Have a history of muscle disorders
Always consult your physician before use.
7. How can I find a safe red yeast rice supplement?
Choose products that are third-party tested (e.g., USP, NSF, ConsumerLab) and labelled as free from citrinin. Avoid unknown or unverified brands, especially those not transparent about monacolin K content.
8. Can red yeast rice cause allergic reactions?
Yes, though rare, allergic reactions may include rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Discontinue use and seek medical help immediately if symptoms appear.
9. What is the safest dose of red yeast rice?
Doses below 3 mg of monacolin K per day are considered lower risk, but even at this level, adverse effects have occurred. Some guidelines recommend using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible.
10. Is red yeast rice better than statins?
It can be effective for mild cholesterol reduction, especially for people who cannot tolerate statins. However, it’s less predictable, less regulated, and may lack the comprehensive cardiovascular protection shown in clinical trials of statins.