A healthy gut is the foundation of overall well-being. In the world of health and wellness, the focus on gut health has taken center stage, and for good reason. While kombucha and kefir often steal the spotlight, India has its own traditional gut-healing elixir – Kanji. Kanji is a fermented north Indian beverage considered to be great for the stomach and is a must-have in winters as it not only soothes our system from all the binge eating we do in this season but also heats our body.
Why is Gut Health Important?
The gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption, metabolism, and immunity. Poor gut health can lead to bloating, indigestion, and more severe issues like leaky gut syndrome or autoimmune conditions. Fermented foods and drinks like kaanji introduce beneficial bacteria into the digestive system, helping to balance the gut microbiome and promote better digestion.
What is Kanji?
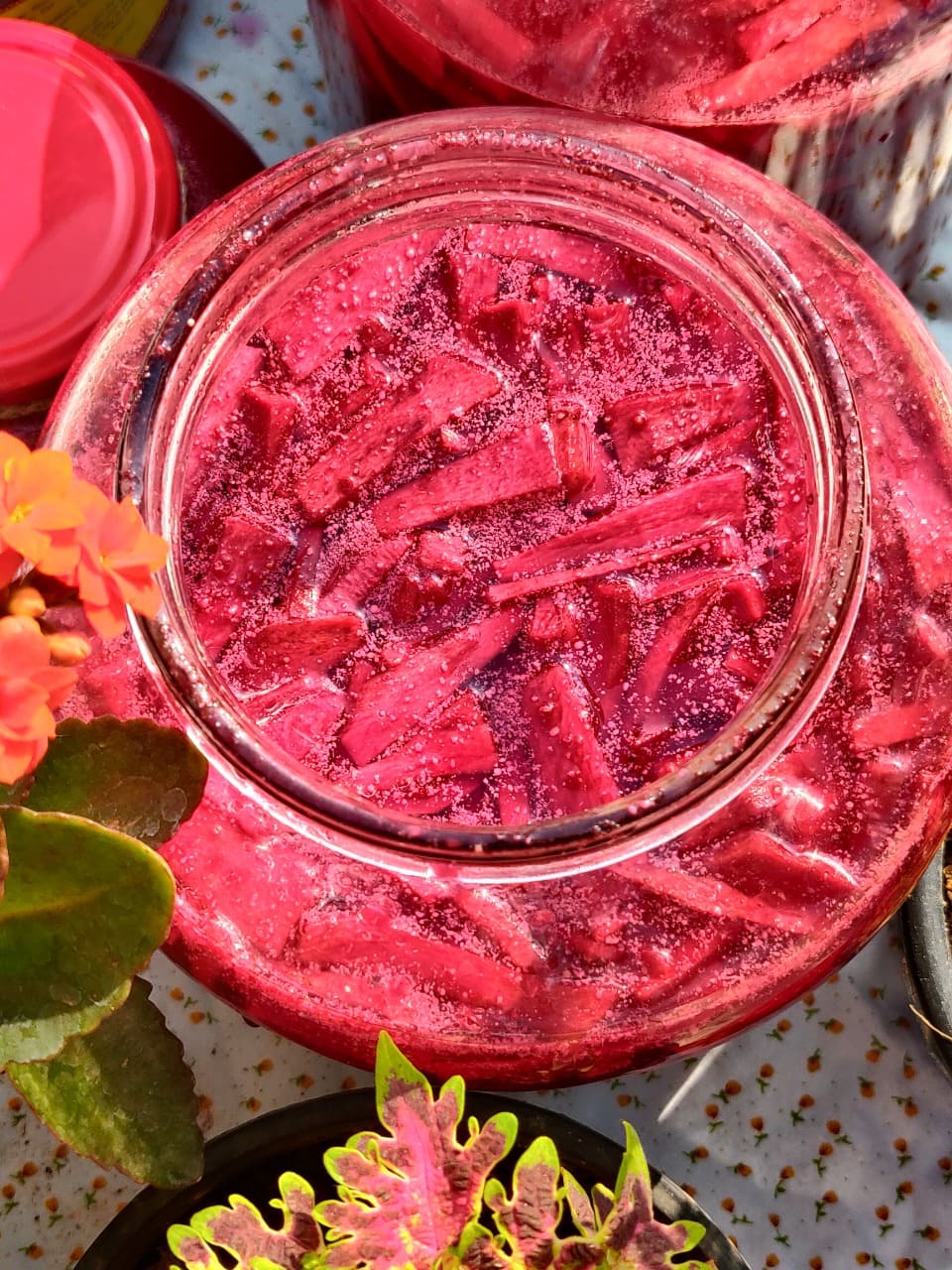
Kanji is a traditional North Indian fermented drink made primarily from black carrots, mustard seeds, and water, with a blend of spices that give it a tangy, pungent flavor. Often consumed during the winter and spring months, this vibrant, probiotic-rich drink is not only delicious but also incredibly beneficial for gut health. Also known as Khatairn in the Sindhi language.
Health Benefits of Kaanji:
- Rich in Probiotics:
The fermentation process of kanji creates natural probiotics, which help replenish good bacteria in the gut. This improves digestion and helps in the absorption of essential nutrients. - Boosts Immunity:
A healthy gut contributes to a robust immune system. By consuming kaanji regularly, you are arming your body with the necessary defenses to fight off common illnesses. - Detoxifies the Body:
Kanji acts as a natural detoxifier. Its antioxidant properties help flush out toxins from the body, promoting clearer skin and better organ function. - Aids Digestion and Reduces Bloating:
The natural enzymes in kanji support digestion, prevent constipation, and reduce bloating. It also helps in balancing stomach acid, which can alleviate acid reflux. - Anti-Inflammatory Properties:
The mustard seeds and spices used in kanji have anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation in the gut and the body.
How to Make Kaanji at Home:
Making kanji is simple, and the best part is you can customize it to your liking. Here’s a quick recipe:
Ingredients:
• 4-5 black carrots (or regular carrots if unavailable)
• 1-2 beets (optional for extra color)
• 1 tbsp mustard seeds (coarsely ground)
• 1 tbsp black salt
• 1 tsp red chili powder
• 5 cups of water
Method:
- Wash and peel the carrots and beets. Cut them into long sticks.
- In a large glass jar, add the carrots, beets, mustard seeds, black salt, and chili powder.
- Pour in the water and stir well.
- Cover the jar with a muslin cloth and let it ferment for 4-5 days in sunlight. Stir daily.
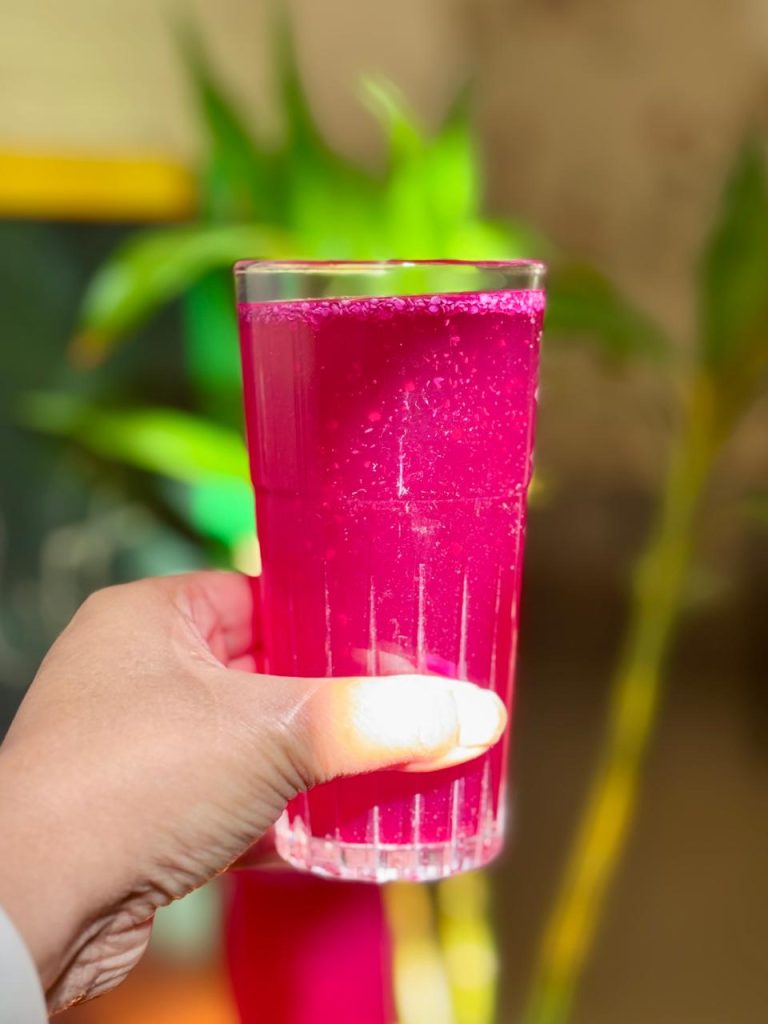
- Once fermented, strain the drink and refrigerate. Enjoy chilled!
And if you don’t want go through the hassle of making kanji at home try this Kaali Gajar Kanji – 100% Natural and Homemade from Masala Monk
Kanji is more than just a refreshing drink; it’s a time-honored tradition that nurtures our gut and overall health. As we embrace global trends of kombucha and fermented teas, let’s not forget the power of our own desi drinks. By incorporating kanji into your diet, you’re not just drinking for taste – you’re drinking for health.
Raise a glass to good health with kanji – your gut will thank you!