If you’ve ever spent time on a treadmill or reading fitness blogs, you’ve probably come across the term “fat-burning heart rate.” Maybe you’ve seen charts in your gym with color-coded zones, or maybe your smartwatch pings you, congratulating you on hitting the elusive “fat burn.” But what does this actually mean, and—more importantly—does training in this zone really help you lose fat faster?
Let’s cut through the noise and look at the latest science (and practical strategies) for making the fat-burning heart rate work for you.
Understanding the Basics: What Is the Fat-Burning Heart Rate?
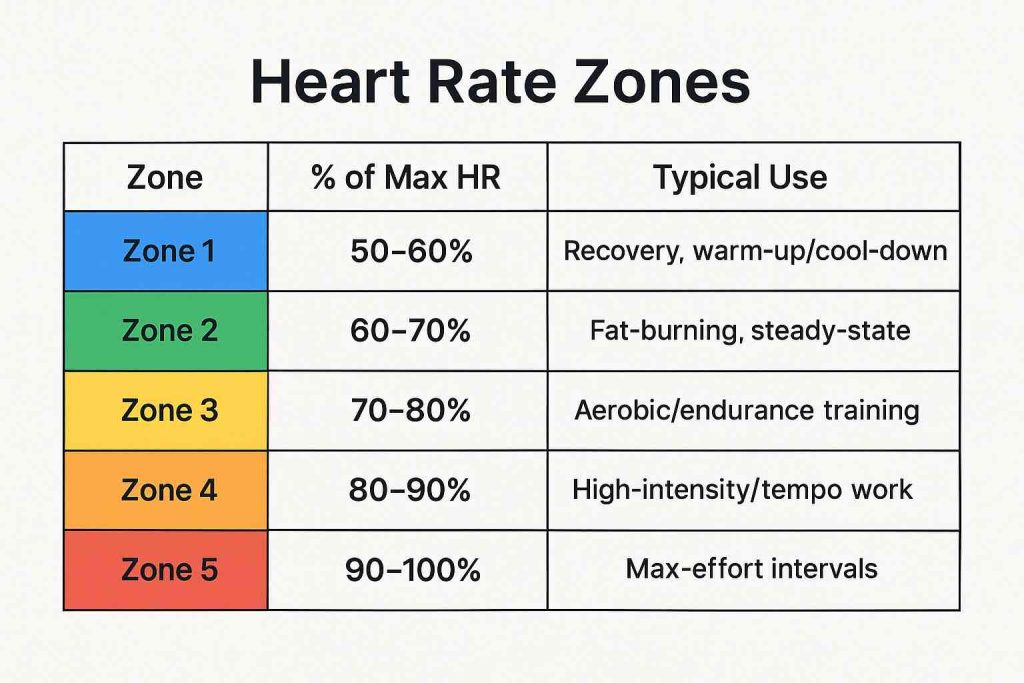
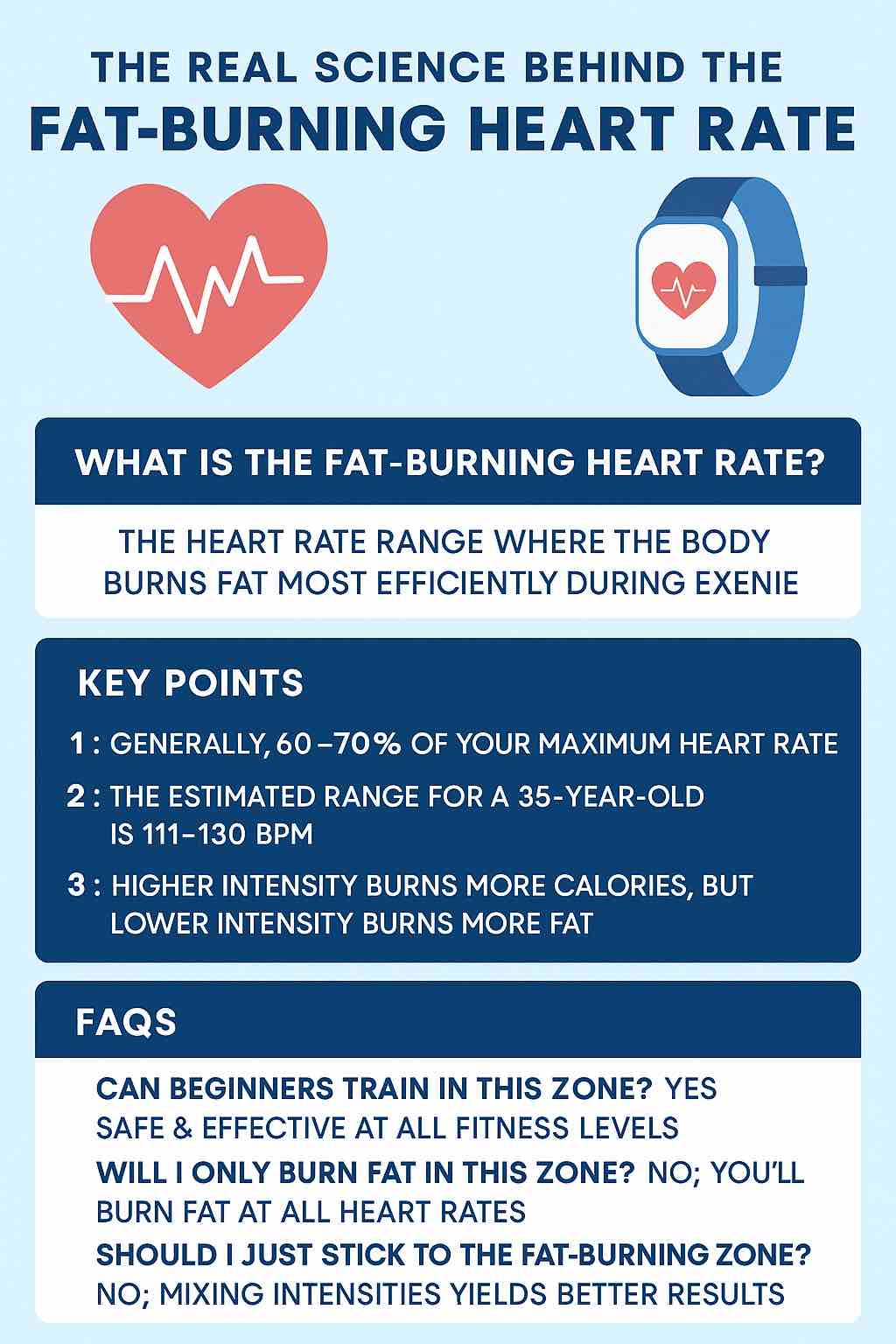
At its core, the fat-burning heart rate is a target range where your body is thought to use more fat for energy, as opposed to carbohydrates. It’s not that you aren’t burning fat at other heart rates, but this particular range maximizes the proportion of calories coming from fat.
- Traditionally: The “fat-burning zone” is about 60–70% of your maximum heart rate (MHR).
- Why this range? At lower intensities, your body relies more on fat for fuel. As intensity increases, carbs become the primary energy source.
How to Calculate Your Fat-Burning Zone
Step 1: Estimate your Maximum Heart Rate (MHR)
- The classic formula is 220 minus your age.
- Example: If you’re 35, your MHR ≈ 185 beats per minute (bpm).
Step 2: Find 60% and 70% of your MHR
- 185 × 0.6 = 111 bpm
- 185 × 0.7 = 130 bpm
Your fat-burning zone: 111–130 bpm
Tip: Most fitness trackers and smartwatches will do this math for you!
What’s New in 2025? The Science Has Evolved
Research in the last few years has clarified several key points:
- Zone 2 Training (the “fat-burning zone”) remains the gold standard for building an aerobic base and improving metabolic health.
- This is NOT a myth. It is still crucial for long-term fat utilization and endurance.
- But: Individual “fat-max” (where fat burning actually peaks) varies.
- Some people burn the most fat at slightly lower or higher heart rates than the traditional 60–70% MHR.
- Fitness, genetics, and metabolic health all play a role.
- Clinical testing (lab treadmill with a mask) can identify your true fat-max, but for most people, the 60–70% range is a good starting point.
- High-Intensity Training: While higher heart rates burn more calories (and more carbs), total fat loss over time often depends on both intensity AND volume. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is great for efficiency, but Zone 2 is more sustainable and accessible for most.
Practical Application: How to Actually Use the Fat-Burning Zone
1. Use Zone 2 for Longer, Sustainable Workouts
- Why: You can maintain Zone 2 intensity for 30–90+ minutes, which means you burn more total fat during a single session compared to a short HIIT burst.
- How: Try brisk walking, easy jogging, steady cycling, or swimming at a pace where you can still hold a conversation.
- Tip: You should be breathing heavier than at rest, but not gasping.
2. Layer in High-Intensity for Best Results
- Why: Intervals at higher heart rates (Zone 4/5) spike calorie burn, improve VO₂ max, and trigger “afterburn” (EPOC).
- How: 1–2 HIIT sessions a week—think sprints, hill runs, or high-resistance cycling for 20–60 seconds, followed by easy recovery.
- Tip: The rest of your week should still focus on Zone 2!
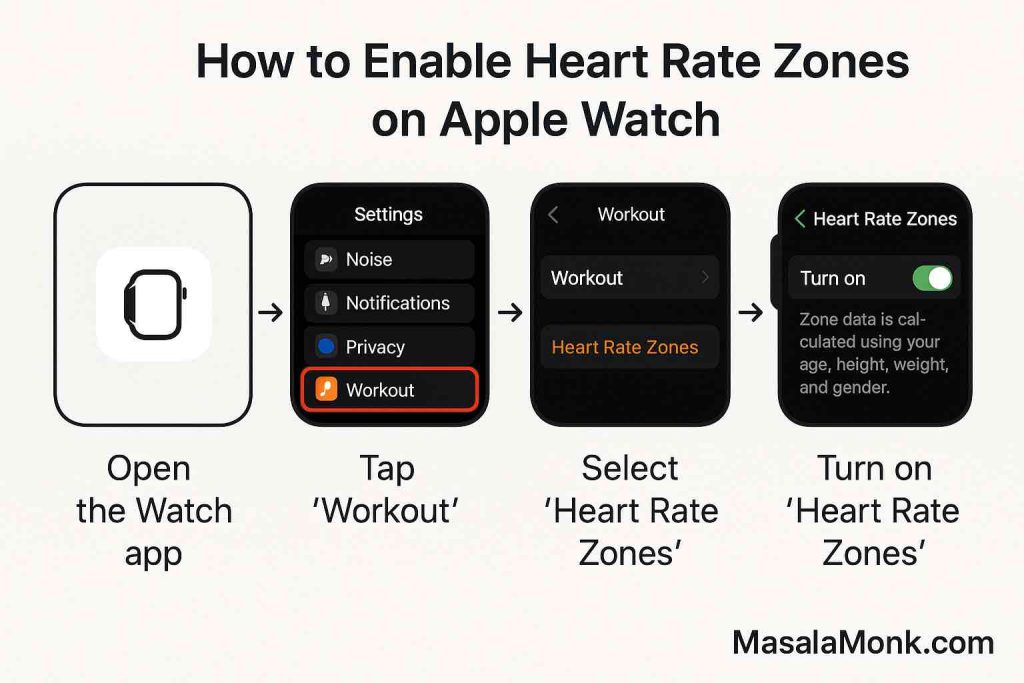
3. Track Your Heart Rate—But Don’t Obsess
- Use a heart rate monitor, fitness band, or smartwatch for real-time feedback.
- Most devices have built-in zone alerts and graphs.
- If you don’t have a device, use the “talk test:”
- Zone 2 = conversational pace
- Zone 3+ = can only speak in short phrases
4. Make It a Habit
- Aim for 150–300 minutes of Zone 2 cardio per week (per major health guidelines).
- Mix in 1–2 higher intensity sessions for variety and metabolic benefit.
- Be consistent: The magic is in showing up, not in any single “perfect” workout.
Busting the Biggest Fat-Burning Myths
Q: Can you ONLY lose fat by staying in the fat-burning zone?
A: No! Fat loss depends on overall calorie deficit. Higher zones burn more total calories per minute, but Zone 2 allows you to go longer, making it a cornerstone for sustained fat loss.
Q: Is the 220 – age formula accurate?
A: It’s a general estimate. Actual MHR can vary by 10–20 beats. Use it as a guideline, not gospel. Personalized lab testing gives the best accuracy, but isn’t necessary for most people.
Q: Should I just do Zone 2 forever?
A: No! Variety is key. Zone 2 for endurance and health, higher zones for intensity and performance. Both have a place in a balanced program.
Q: Does the fat-burning zone work for everyone?
A: Individual differences matter. Age, fitness, genetics, and even day-to-day factors like sleep and nutrition can shift your “fat-max.” Use feedback and adjust as you go.
Beyond Cardio: Other Fat-Loss Essentials
- Strength training: Builds muscle, increases resting metabolic rate, supports long-term fat loss.
- Sleep & stress management: Chronic stress or poor sleep can blunt fat-burning hormones and drive cravings.
- Nutrition: You can’t out-train a bad diet. Whole foods, lean protein, fiber, and hydration are your foundation.
Action Plan: Your Next Steps
- Calculate your zone: Use the formula or your wearable.
- Plan your week: Schedule 3–5 Zone 2 sessions (30–60 minutes each), plus 1–2 higher-intensity workouts.
- Monitor progress: Watch for changes in endurance, recovery, and body composition—not just the scale.
- Stay flexible: Adjust as you get fitter. Your “zone” may change!
- Celebrate the wins: Consistency and progress are far more important than perfection.
Final Thoughts
The fat-burning heart rate is a useful concept—but it’s not a magic bullet. Use Zone 2 as your “base camp,” add intensity as needed, and remember: the best exercise is the one you’ll keep doing. If you have a smartwatch, let it guide you—but don’t forget to listen to your body too.
Want a sample workout plan, or tips for integrating heart rate training into your routine? Drop a comment or message me!
Sources & Further Reading
- VeryWell Health: Fat-Burning Heart Rate
- TechRadar: How to Use Heart Rate Zones
- Mount Sinai: Fat Burning Variability
- Mayo Clinic: Exercise Intensity
- VeryWell Health: Zone 2 Training
Ready to train smarter? Find your zone and get moving—fat loss, energy, and endurance await!
FAQs
1. What is the fat-burning heart rate zone?
It’s the heart rate range—usually 60–70% of your estimated maximum heart rate—where your body uses a higher proportion of fat for energy during exercise.
2. How do I calculate my fat-burning heart rate?
Subtract your age from 220 to get your estimated max heart rate, then multiply by 0.6 and 0.7 to get your fat-burning range in beats per minute.
3. Do I only burn fat in the fat-burning zone?
No. You burn fat at all heart rates, but this zone maximizes the percentage of energy from fat. Higher intensities burn more calories and can boost fat loss overall.
4. Can I lose weight faster if I always stay in the fat-burning zone?
Not necessarily. Total calorie burn and a consistent calorie deficit drive fat loss. The fat-burning zone is sustainable for longer workouts, but mixing intensities is usually more effective.
5. Is the 220-minus-age formula accurate?
It’s a useful estimate but not precise for everyone. Your true maximum heart rate can vary, so listen to your body and adjust if needed.
6. Should I use a fitness tracker to monitor my heart rate?
Yes! Wearables help you stay in your target zone and make workouts more effective, though you can also use the “talk test” if you don’t have a tracker.
7. How often should I train in the fat-burning zone?
Aim for 3–5 sessions per week, 30–60 minutes each. Add 1–2 higher-intensity sessions weekly for variety and results.
8. Can beginners use heart rate zones?
Absolutely! Zone 2 (fat-burning) is ideal for beginners—low impact, safe, and builds aerobic fitness.
9. Does strength training help with fat loss too?
Yes. Building muscle increases your resting metabolism, supporting long-term fat loss—even when you’re not working out.
10. What else matters for fat loss besides heart rate?
Consistent movement, balanced nutrition, strength training, good sleep, and stress management are all key for lasting results.