When you’re pregnant, hydration is more than just a health tip — it’s a daily necessity. Your body needs extra fluids to support increased blood volume, amniotic fluid, and the growth of your baby. But sometimes, plain water isn’t enough. That’s when the best electrolyte drinks for pregnancy can help keep you energized, balanced, and feeling your best.
Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium play a vital role in muscle function, fluid balance, and even nerve health. The challenge? Not every electrolyte drink is pregnancy-safe. Many popular sports drinks are packed with sugar, caffeine, or artificial sweeteners, which may not be ideal for expecting mothers.
Pregnancy is a time to care for yourself with intention, and hydration plays a central role. For a broader overview of balanced nutrition, you can also explore our pregnancy nutrition guide.
In this guide, we’ll explore safe, natural, and effective electrolyte drinks that you can enjoy during pregnancy. From traditional remedies like buttermilk to modern options like Pedialyte, this is your go-to resource for pregnancy-safe hydration.
Why Electrolytes Matter in Pregnancy
Pregnancy often brings new challenges: morning sickness, fatigue, heat intolerance, or even dizziness. These are times when water alone may not be enough. Electrolytes step in to:
- Restore hydration after vomiting or sweating.
- Prevent muscle cramps (especially in legs and back).
- Support healthy blood pressure.
- Maintain energy levels and reduce fatigue.
Think of electrolytes as tiny helpers that allow your body to use the water you drink more efficiently. In fact, hydration is especially crucial in the first trimester when nausea and fatigue are common. Pairing electrolyte support with first trimester nutrition basics can make a real difference.
According to Verywell Health, dehydration during pregnancy can even lead to complications like low amniotic fluid and preterm contractions — making electrolyte balance all the more important.
The 5 Best Natural Electrolyte Drinks for Pregnancy
1. Coconut Water: Nature’s Hydration Choice
Coconut water is often called “nature’s sports drink” — and for good reason. It’s naturally rich in potassium and magnesium, which help restore balance and fight fatigue.
- Why it helps: Light, refreshing, and gentle on the stomach.
- How to use: Drink fresh tender coconut water whenever possible. Packaged versions should be unsweetened and preservative-free.
- Pregnancy tip: Keep a coconut handy for hot afternoons — it cools you down while providing essential minerals.
2. Homemade Electrolyte Drink: Safe and Simple
A homemade electrolyte drink is one of the safest choices, because you control exactly what goes in.
Easy Recipe:
- 2 cups of water
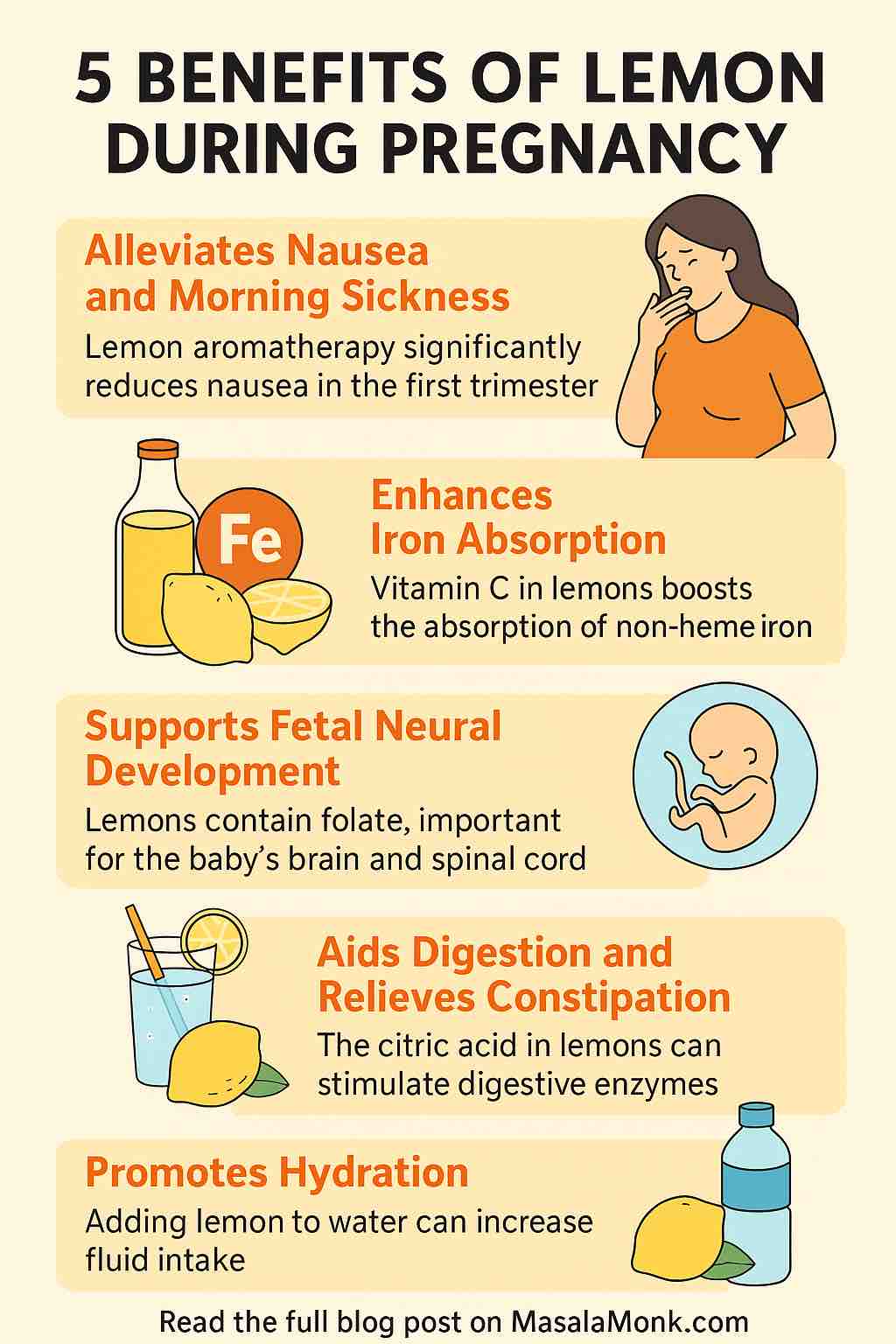
- Juice of half a lemon
- A pinch of pink Himalayan salt
- 1–2 teaspoons honey or jaggery
- Why it helps: Sodium and potassium from the salt restore balance, while lemon adds vitamin C. Honey provides quick, natural energy.
- Pregnancy tip: Carry it in a flask for long days — it’s a clean, affordable alternative to packaged drinks.
3. Buttermilk (Chaas): Traditional Hydration
Buttermilk, or chaas, is a timeless Indian drink perfect for cooling down and staying hydrated.
- Electrolyte benefits: Calcium, sodium, and potassium.
- Why it helps: Soothes digestion, prevents acidity, and keeps the body cool.
- How to use: Blend curd with water, add salt, roasted cumin powder, and coriander leaves.
- Pregnancy tip: If bloating is a concern, thin it with extra water for easier digestion.
4. Fresh Fruit-Infused Water
Plain water can feel boring, which often makes it hard to drink enough. Fruit-infused water solves that problem while boosting electrolyte content.
- Best fruits to try: Orange slices, watermelon, cucumber, strawberries.
- Why it helps: These fruits provide potassium and magnesium naturally.
- Pregnancy tip: Prepare a jug in the morning, sip all day. It encourages hydration without extra calories or sugar.
If you’d like fun, refreshing variations, try these hydrating electrolyte mocktails made with cucumber and mint — perfect for pregnancy-safe sipping.
5. Fresh Juices with a Pinch of Salt
Fresh fruit and vegetable juices — such as orange, pomegranate, or carrot juice — can double as electrolyte drinks when prepared smartly.
- Why it helps: Adds potassium, magnesium, and natural sugars.
- How to use: Always dilute juices with water and add a tiny pinch of salt to boost electrolyte value.
- Pregnancy tip: Stick to fresh, homemade juices — packaged juices often hide added sugars.
For another delicious twist, explore folate-rich pregnancy mocktails that combine hydration with essential prenatal nutrients.
Are Electrolyte Drinks Safe During Pregnancy?
Yes — but safety depends on the type.
- Safe options: Coconut water, buttermilk, homemade electrolyte drinks, fruit-infused water.
- Use caution with: Packaged sports drinks. Many contain caffeine, high sodium, or artificial sweeteners.
- Rule of thumb: If you can make it at home or choose a clean-label brand, it’s more likely to be safe.
Always consult your doctor before adding electrolyte powders or supplements to your daily routine.
Popular Packaged Electrolyte Drinks — Are They Pregnancy-Safe?
Many women wonder about popular electrolyte brands. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Pedialyte – Often recommended for dehydration and morning sickness. Usually safe in moderation.
- LMNT Electrolytes – Very high in sodium; not recommended unless prescribed by your doctor.
- Liquid I.V. Hydration Multiplier – Convenient, but check sweeteners and sodium levels. Use sparingly.
- Ultima Replenisher – Sugar-free, clean-label, and often considered one of the safer packaged options.
⚠️ Important: Always check ingredients. Avoid anything with caffeine, artificial sweeteners (like aspartame or sucralose), or added stimulants.
Homemade vs. Store-Bought Electrolyte Drinks
- Homemade: Customizable, natural, and safe. You know exactly what you’re drinking.
- Store-bought: Convenient for emergencies or travel, but requires careful label checks.
For everyday hydration, homemade and natural sources like coconut water or buttermilk are your best bets. Save packaged options for when you really need them.
When Should You Use Electrolyte Drinks in Pregnancy?
Electrolyte drinks aren’t necessary every day, but they can be a lifesaver in specific situations:
- After morning sickness or vomiting.
- On hot, humid days when you’re sweating more.
- During prenatal workouts or yoga.
- If you’re feeling dizzy, weak, or unusually tired.
Think of electrolyte drinks as your hydration backup plan — not a replacement for water, but a complement when you need an extra boost.
Electrolytes are especially helpful after morning sickness episodes. You might also find relief from these morning sickness-friendly foods that support hydration and digestion.
Electrolyte Drinks During Labor & Recovery
Labor can be long and physically draining. Many women find that sipping on light electrolyte drinks helps them stay energized and hydrated through contractions.
- Best options for labor: Coconut water, diluted fresh juice, or Pedialyte.
- Why it matters: Electrolytes help maintain energy, support muscle contractions, and aid recovery.
After delivery, especially if you’re breastfeeding, electrolyte-rich drinks can continue to support hydration and milk production.
Alongside fluids, many women prefer light meals like third-trimester nourishing soups for comfort and sustained energy as labor approaches.
Conclusion
Pregnancy is a time when every choice you make for your body also impacts your baby. Hydration is one of the simplest ways to support both your health and your little one’s development. Choosing the best electrolyte drinks for pregnancy means focusing on safe, natural, and nourishing options.
- Everyday choices: Coconut water, buttermilk, homemade mixes, fruit-infused water, fresh juices.
- Occasional use: Pedialyte or clean-label electrolyte powders, but only with medical guidance.
Learn more about Pedialyte in our post on Pedialyte and Electrolytes for Diarrhea.
💧 Stay hydrated, listen to your body, and keep your choices simple. When in doubt, go natural — because sometimes the best solutions really are the simplest.
Further Reading & References
Staying hydrated during pregnancy is about finding balance — choosing drinks that are safe, natural, and nourishing. If you’d like to explore more expert guidance and practical ideas, here are some trusted resources:
- Pregnancy hydration and dehydration risks — Verywell Health explains why hydration is so important during pregnancy, from preventing fatigue to reducing complications like low amniotic fluid. (Verywell Health)
- Electrolytes explained — What are electrolytes, and why do they matter for pregnancy wellness? This guide breaks down sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium in simple terms. (Verywell Health)
- Choosing safe electrolyte drinks — Not all sports drinks are created equal. Vogue highlights how to pick electrolyte drinks that are low in sugar and free from additives. (Vogue)
- Electrolyte powders and sodium caution — Some powders contain more sodium than you need. Health.com breaks down what to watch out for before adding them to your routine. (Health.com)
- Liquid I.V. and pregnancy safety — Healthline discusses whether Liquid I.V. and similar hydration multipliers are safe during pregnancy. (Healthline)
- Electrolytes while pregnant — The Mother Runners share practical insights into why electrolytes are essential for energy, nausea relief, and overall pregnancy health. (The Mother Runners)
💡 For more natural, wellness ideas, check out our dedicated pregnancy collection on MasalaMonk.com.