Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects up to one in ten women of reproductive age worldwide. If you’ve been diagnosed, you know how complex and frustrating the condition can be—irregular cycles, hormonal swings, acne, stubborn weight gain, and, for many, insulin resistance.
But what if your kitchen spice rack held some powerful allies? Enter: ginger.
For centuries, ginger has been used for everything from nausea to colds. But did you know that modern research and thousands of women with PCOS are uncovering real, tangible benefits from adding ginger to your daily routine? Let’s explore the science, the stories, and exactly how you can use ginger as part of a holistic PCOS strategy.
Why Ginger? The Science
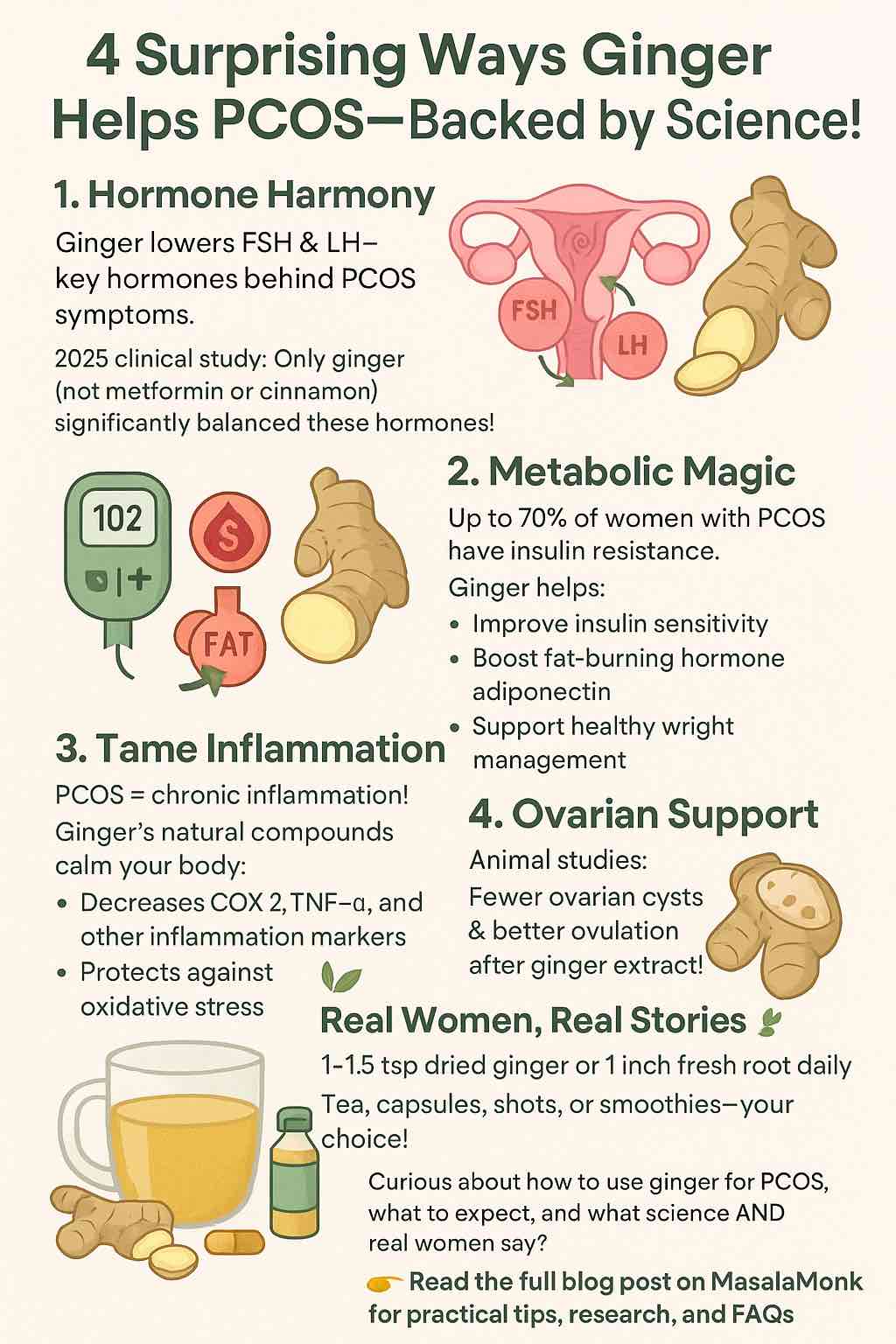
1. Hormone Harmony: How Ginger May Balance PCOS Hormones
PCOS is fundamentally a hormonal condition—characterized by imbalances like elevated androgens (testosterone), and disruptions to LH and FSH, two key pituitary hormones.
What research says:
A 2025 randomized controlled trial compared ginger, cinnamon, and metformin for PCOS. Remarkably, ginger was the only supplement that significantly reduced FSH, LH, and SHBG levels—all pivotal for cycle regulation. Metformin and cinnamon, by contrast, mainly improved insulin resistance and testosterone levels, but did not impact these cycle-driving hormones to the same extent.
Translation: Ginger may help “reset” your hormonal signaling—potentially supporting more regular cycles and ovulation.
2. Metabolic Magic: Improving Insulin Sensitivity and Blood Sugar
Up to 70% of women with PCOS struggle with insulin resistance. Ginger shines here, too.
In animal studies, ginger extract improved insulin sensitivity and raised levels of adiponectin, a hormone that boosts fat burning and lowers inflammation. Human trials echo these results, with many women reporting improved fasting glucose, weight management, and even reductions in BMI after regular ginger supplementation.
How does it work?
Ginger’s bioactive compounds—gingerols, shogaols—help your cells respond better to insulin and may slow down the absorption of glucose from your gut.
3. Inflammation & Oxidative Stress: Ginger’s Antioxidant Arsenal
Chronic inflammation is both a cause and consequence of PCOS, fueling everything from insulin resistance to acne and fatigue.
Ginger has been called an “anti-inflammatory powerhouse.” Its bioactive ingredients help lower key markers like COX-2, TNF-α, and CRP. Multiple reviews (including a sweeping 2024 systematic review of 65 studies) highlight ginger’s ability to lower oxidative stress and improve inflammation in PCOS.
4. Ovarian Support: Fewer Cysts, Better Ovulation
Animal studies are especially compelling: rats with PCOS given ginger extract showed fewer ovarian cysts and more healthy follicles, pointing to improved ovulation and ovarian function.
Real Women, Real Results: What the PCOS Community Says
Science is powerful, but sometimes what matters most is what real women experience in the day-to-day. Here are some highlights from women in the PCOS community:
- Cycle “Kickstarts”: Many report that ginger shots or tea helped bring back their periods—sometimes after weeks or months without a cycle. Most saw results within two weeks of consistent use.
- Blood Sugar Wins: Several shared that regular ginger helped curb cravings and support weight loss, especially when combined with a lower-carb or anti-inflammatory diet.
- Inflammation Relief: A cup of fresh ginger tea (or a daily ginger-turmeric shot) is a comforting, soothing ritual for many—and some say it helps with pain and bloating, too.
- Mild Side Effects: A small number experienced mild discomfort (e.g., leg aches with capsules), but side effects were rare.
“I boil fresh ginger root for a strong tea and sip it multiple times a day for several days. Always seems to do the trick…”
– Reddit user, r/PCOS
“Ginger and cinnamon 3x a day, and I lost weight and got my sugar down…”
– Reddit user, r/PCOS
How To Use Ginger for PCOS: Practical Tips
What Form?
- Fresh Ginger Root: Grated in tea, smoothies, or recipes.
- Powdered Ginger: Add to oatmeal, curries, or “golden milk” lattes.
- Ginger Capsules: For a standardized dose—great if you don’t love the taste.
- Ginger Shots: Home-made or store-bought (look for those with no added sugar).
How Much?
- Most clinical studies use the equivalent of 2–3 grams of dried ginger per day (about 1–1.5 teaspoons), or one-inch piece of fresh ginger root daily.
- For capsules, check labels—500 mg, 2–3x/day is common.
When & How Often?
- For hormonal and metabolic benefits, consistency matters: daily use for at least 8–12 weeks is recommended in studies.
- Some prefer ginger tea before meals to aid digestion and blood sugar control.
Combining Ginger with Other Approaches
- Many women see the best results when ginger is part of a broader PCOS plan—including regular movement, lower-carb or anti-inflammatory eating, and if prescribed, medications like metformin.
- Ginger pairs well with cinnamon, turmeric, and lemon—both for taste and for synergistic health benefits.
Are There Any Risks?
- Ginger is generally very safe, but high doses can cause mild GI upset, heartburn, or interact with blood-thinning medication.
- Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting a new supplement, especially if you’re on medication or pregnant.
Takeaway: Is Ginger Right for You?
If you’re looking for a natural, research-backed way to support your hormones, metabolism, and overall wellbeing with PCOS, ginger is a powerful (and tasty) ally. The latest research highlights unique hormonal effects you won’t get from metformin or cinnamon alone. And the lived experiences of real women suggest that, when used consistently and as part of a bigger plan, ginger might just help you feel a little more in control.
Try it for a few weeks: Brew a spicy-sweet tea, blend it into a morning smoothie, or add a daily capsule. Pay attention to how your body responds—and remember, PCOS is a marathon, not a sprint.
Have you tried ginger for PCOS? What’s worked for you? Share your experiences and let’s learn together.
References:
- Frontiers in Nutrition, 2025: Ginger vs Cinnamon vs Metformin for PCOS
- Antioxidants, 2024: Systematic Review on Ginger & Cinnamon in PCOS
- Reddit, r/PCOS Community Experiences
- ScienceDirect, 2023: Ginger in Letrozole-Induced PCOS Models
If you have more questions or want tailored guidance for your PCOS journey, leave a comment for the community!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How much ginger should I take daily for PCOS benefits?
Answer: Most studies use 2–3 grams of dried ginger per day (about 1–1.5 teaspoons of powdered ginger or a one-inch piece of fresh root). If using capsules, 500 mg two to three times daily is common. Always start with a lower dose to assess your tolerance.
2. How soon can I expect results from ginger for PCOS?
Answer: Many people report improvements in cycle regularity or inflammation within 2–4 weeks, but most clinical studies show benefits after 8–12 weeks of consistent daily use.
3. What is the best way to consume ginger for PCOS—tea, powder, or capsules?
Answer: All forms can be effective. Fresh or powdered ginger is great for teas, smoothies, or food. Capsules are convenient and offer standardized dosing, but choose high-quality, third-party tested supplements.
4. Are there any side effects or risks with ginger?
Answer: Ginger is generally safe for most people, but high doses can cause mild stomach upset, heartburn, or diarrhea. It may also interact with blood thinners. Consult your doctor if you’re pregnant, breastfeeding, or on medication.
5. Can ginger help with PCOS-related weight gain?
Answer: Research and user reports suggest ginger may support weight management by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation, which can indirectly help with weight loss as part of a healthy lifestyle.
6. Will ginger alone regulate my periods or fix my hormones?
Answer: Ginger can help support hormonal balance, but results are best when combined with a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and any prescribed medications.
7. Is it safe to combine ginger with metformin or other medications?
Answer: In most cases, yes, but always check with your healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions or side effects, especially if you’re on blood-thinning or diabetes medications.
8. Can men or people without PCOS benefit from ginger’s hormonal effects?
Answer: Ginger offers general anti-inflammatory and metabolic benefits for everyone, but most hormone-balancing research is specific to women with PCOS.
9. Can I take ginger if I’m trying to conceive or undergoing fertility treatments?
Answer: Ginger may support ovulation and hormonal balance, but consult your fertility specialist before adding new supplements during preconception or fertility treatments.
10. Are there any foods or supplements that work well with ginger for PCOS?
Answer: Yes—ginger pairs well with cinnamon, turmeric, inositol, and anti-inflammatory diets (rich in veggies, healthy fats, lean proteins). Many women see the best results when ginger is one part of a comprehensive wellness plan.













