Ghee has been at the heart of Indian kitchens for millennia. But in recent years, it’s not just grandmothers who are talking about this golden elixir—nutritionists, athletes, and foodies across the world are adding ghee to their daily rituals. If you’ve wandered through a health food aisle or scrolled Instagram lately, you’ve seen the buzzwords: A2 Desi Cow Ghee and A2 Bilona Ghee.
But what do these labels really mean? Are they worth the premium price? And which one deserves a place in your kitchen?
Let’s break it down—without hype, but with practical insights, recent science, and a nod to ancient wisdom.
A2 Desi Cow Ghee: What Is It, Really?
A2 Desi Cow Ghee is made from the milk of indigenous Indian breeds—such as Gir, Sahiwal, or Rathi cows—which naturally produce the A2 beta-casein protein. This is in contrast to the A1 protein found in many Western dairy breeds.
Why do people care about A2? Some research links A1 beta-casein to digestive issues and inflammation for sensitive individuals, while A2 is considered easier on the gut. But here’s the catch: during ghee-making, most milk proteins (including A2 and A1) are removed, making ghee almost pure fat. So, for most people, “A2” in ghee is mainly a sign of origin and ethical farming, not a game-changer for those with dairy protein sensitivities.
Bottom line:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee means ghee made from the milk of Indian, grass-fed, “A2” cows. It’s usually higher in good fats and nutrients than regular ghee, especially if sourced from reputable brands.
A2 Bilona Ghee: The Gold Standard
Now, let’s talk about A2 Bilona Ghee—the superstar of Ayurvedic tradition.
What Makes the Bilona Method Special?
The Bilona method is a two-step, slow, labor-intensive process:
- Whole milk from A2 cows is first made into yogurt (curd).
- The yogurt is churned to extract cultured butter.
- This butter is slowly simmered over low heat to produce ghee.
This process, unlike the industrial “cream-to-ghee” shortcut, not only honors tradition but, according to many experts and some emerging research, preserves more nutrients, antioxidants, and flavor. The fermentation step also introduces beneficial enzymes and a richer, deeper taste.
What’s So Great About Bilona Ghee?
- Higher in Butyric Acid: Butyrate is great for gut health and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- More CLA (Conjugated Linoleic Acid): May support metabolism and heart health.
- Rich, Cultured Flavor: If you’ve tasted it, you know—it’s more aromatic, almost “caramelized.”
- Ayurvedic Value: Considered a “Rasayana” (rejuvenator), used in healing rituals, massages, and even eye therapies.
- Clean Label: Usually made by smaller producers, free of additives and preservatives.
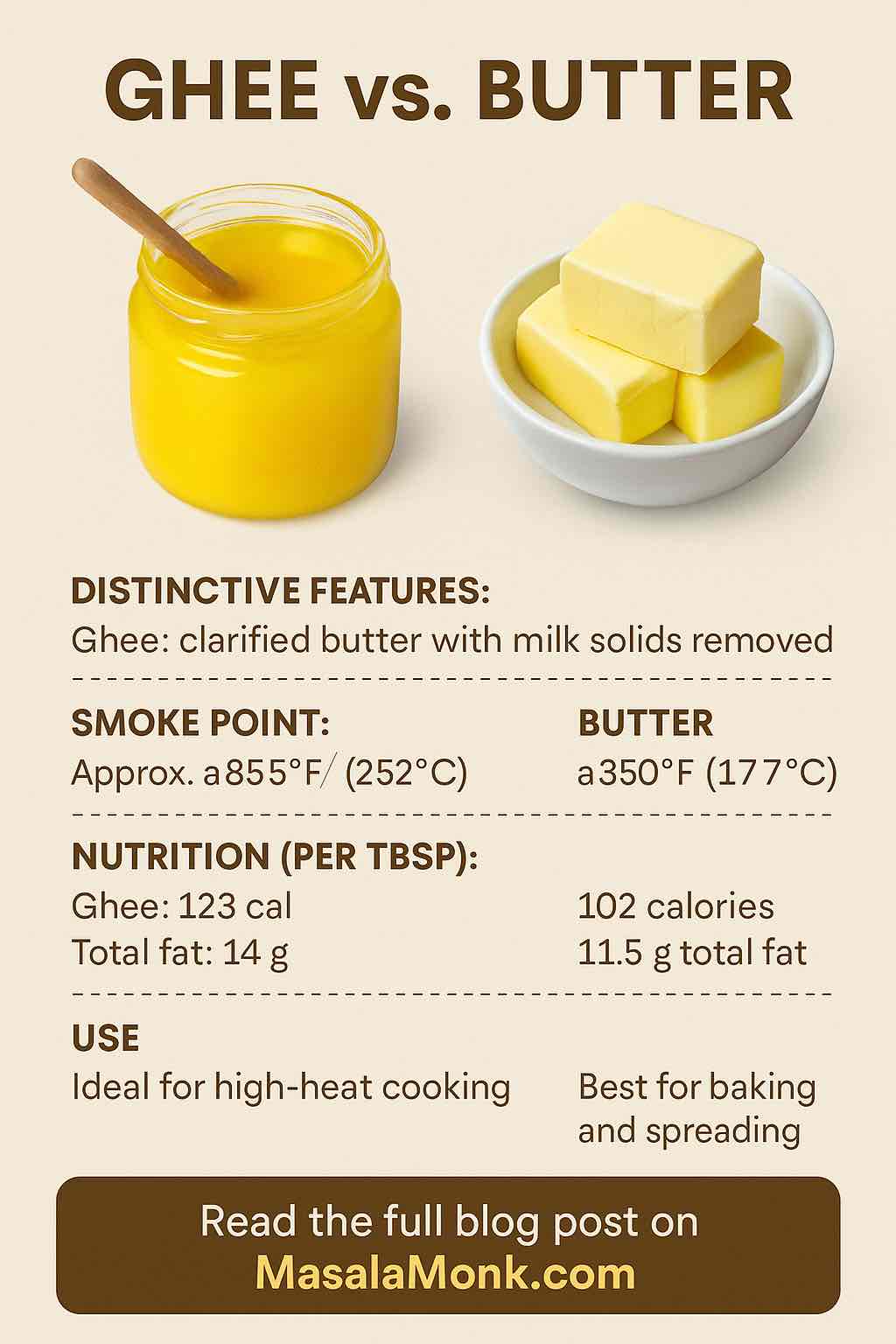
How Do They Compare? [Practical Table]
| Attribute | A2 Desi Cow Ghee | A2 Bilona Ghee |
|---|---|---|
| Source | A2 desi cow milk | A2 desi cow milk |
| Process | Cream-to-ghee or Bilona | Always traditional Bilona method |
| Taste | Buttery, nutty | Deeper, “cultured,” complex |
| Nutrition | High, but process-dependent | Highest; preserves more nutrients |
| Gut Health | Good | Superior (more butyrate/CLA) |
| Ayurvedic Value | Moderate | Highest |
| Price | Lower | Premium (due to labor-intensive) |
| Best Use | Everyday cooking | Finishing, ritual, health boosting |
Buying Guide: What to Look For
With demand booming (the Indian A2 ghee market is growing at over 22% per year!), labels are getting creative. Here’s how to shop smart:
- Check the Source: Look for the cow breed, and confirm it’s “A2 desi.” Ask brands for traceability.
- Look for “Bilona” and “Curd Churned”: The gold standard is “Bilona” or “cultured ghee.” “Cream to ghee” skips the fermentation.
- Ingredient List: Should list only “milk” or “curd” (no additives).
- Packaging & Transparency: Smaller batches, glass jars, and third-party certifications are a plus.
- Lab Tests: Some premium brands publish test results for butyric acid/CLA.
Pro Tip:
If it’s very cheap, it’s probably not genuine Bilona ghee!
How to Use Each Ghee
- A2 Desi Cow Ghee:
Perfect for frying, sautéing, baking, tadkas, or drizzling on dal and roti. Great for daily cooking if you want better nutrition than standard ghee. - A2 Bilona Ghee:
Best enjoyed where you can taste and feel the difference: on steamed rice, kichdi, in bulletproof coffee, Ayurvedic rituals, or just a spoonful for gut health.
The Science: What Do Recent Studies Say?
- Ghee is almost pure fat—so A2/A1 proteins are nearly absent, making both suitable even for those sensitive to casein (unless the allergy is severe).
- Traditional Bilona ghee tends to have higher butyric acid and CLA, more antioxidants, and a richer flavor profile, according to recent 2024-25 lab studies by premium brands.
- Ghee in moderation supports digestion, immunity, and anti-inflammatory pathways; Ayurveda’s 3000-year track record is now being validated by modern science.
Verdict: Which One Should You Choose?
For most households:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee is a smart upgrade from regular ghee—nutritious, tasty, and affordable.
For health seekers, Ayurveda followers, or anyone who wants the best:
A2 Bilona Ghee is the ultimate choice. The traditional method delivers on flavor, nutrition, and holistic benefits—if your budget allows.
Final Thoughts: Ghee for the Modern Kitchen
Don’t get lost in the marketing maze. Buy the best quality you can, from brands you trust. Whether you choose A2 Desi Cow Ghee or go all-out for A2 Bilona, you’re honoring an age-old tradition that’s as relevant today as it was centuries ago.
Pro Tip:
Try both! Use A2 Bilona ghee for special meals or rituals, and A2 Desi Cow ghee for everyday cooking.
Ready to Taste the Difference?
If you found this guide helpful, share it with friends or leave your ghee stories in the comments. Let’s keep the tradition—and the flavor—alive!
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) and Answers
1. What is the main difference between A2 Desi Cow Ghee and A2 Bilona Ghee?
Answer:
A2 Desi Cow Ghee is made from the milk of indigenous Indian (A2) cow breeds, while A2 Bilona Ghee is made using the traditional Bilona process (curd-churning) with A2 milk. Bilona Ghee usually retains more nutrients and has a richer, deeper flavor because of its method of preparation.
2. Does A2 Ghee actually contain the A2 protein?
Answer:
No, by the time ghee is made, almost all milk proteins (including A2 and A1 casein) are removed. The “A2” label refers to the milk source, not the protein content of the final ghee. This means people with casein sensitivity can often consume ghee, but those with severe dairy allergies should consult a doctor.
3. Why is Bilona Ghee considered healthier?
Answer:
The Bilona method involves fermenting milk to curd and then churning it to obtain butter, which is slowly cooked into ghee. This traditional process helps preserve short-chain fatty acids like butyrate, as well as CLA and fat-soluble vitamins, making it richer in nutrients and more beneficial for gut health.
4. Is there a noticeable taste difference between the two?
Answer:
Yes. A2 Bilona Ghee has a more complex, “cultured,” and sometimes slightly caramelized flavor due to the fermentation and slow-cooking process. A2 Desi Cow Ghee (not made by Bilona) tends to be more neutral, but still richer than regular ghee.
5. Can I use both types of ghee for regular cooking?
Answer:
Absolutely. Both types are suitable for everyday cooking, frying, and baking. Many people use A2 Desi Cow Ghee for daily meals and reserve A2 Bilona Ghee for special recipes, finishing touches, or Ayurvedic rituals because of its flavor and nutrient density.
6. Why is Bilona Ghee more expensive?
Answer:
The Bilona process is labor-intensive and yields less ghee per liter of milk compared to the industrial cream-to-ghee process. This, along with the use of A2 desi cow milk (which is costlier), results in a higher price for Bilona ghee.
7. How can I verify if a ghee is genuinely made by the Bilona process?
Answer:
Check for clear labeling such as “Bilona,” “cultured,” or “curd-churned.” Look for brands that offer transparency about their process, publish lab test results, and share details about the breed and feeding practices. Avoid suspiciously cheap products and those with vague sourcing information.
8. Are there any side effects to consuming ghee?
Answer:
Ghee is high in saturated fat and calories, so moderation is key—especially for those managing cholesterol or weight. For most people, high-quality ghee is beneficial when used wisely. Individuals with severe milk allergies should avoid ghee or consult a healthcare provider.
9. Is A2 Bilona Ghee suitable for people following keto, paleo, or Ayurvedic diets?
Answer:
Yes! A2 Bilona Ghee is highly valued in Ayurvedic, keto, and paleo diets due to its nutrient profile, lack of lactose and casein, and ability to support fat metabolism. It’s a versatile and healthy fat source for most dietary approaches.
10. Can children and elderly people benefit from A2 Bilona Ghee?
Answer:
Yes. In moderate amounts, A2 Bilona Ghee can support digestion, immunity, bone health, and brain function in all age groups. Its traditional use in infant foods and elderly diets is well-documented, but always adjust portions based on individual health needs.