Iron rich vegetables are some of the most powerful foods you can add to your diet to boost hemoglobin and fight anemia naturally. Iron itself is one of the most vital nutrients for the body because it helps create hemoglobin — the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Without enough of it, you may feel constant fatigue, dizziness, low immunity, and in many cases, develop iron deficiency anemia.
For those following a vegetarian or plant-based lifestyle, iron rich vegetables become even more important. While plants provide non-heme iron, which is absorbed less efficiently than heme iron from meat, the good news is that absorption can be improved easily. For example, combining these vegetables with vitamin C–rich foods like lemon, bell peppers, or tomatoes significantly increases iron uptake.
As a result, by choosing the right vegetables — and preparing them smartly — you can naturally raise your hemoglobin levels, regain energy, and protect long-term health. In this guide, we’ll cover the top 10 iron rich vegetables, along with simple pairing tips, meal ideas, and practical ways to make them work in your daily diet.
👉 If you’re new to the basics, first check out our detailed guide on Iron Deficiency Symptoms & Top 10 Vegan Iron Rich Foods That Can Help.
Why Iron Rich Vegetables Matter for Anemia & Hemoglobin
Iron in food appears in two forms. Heme iron (from meat/fish) absorbs more efficiently; non-heme iron (from plants) absorbs less, however, a few simple habits close that gap quickly. For example, pairing iron foods with vitamin C (lemon, oranges, tomatoes, bell peppers) significantly improves absorption. In addition, light cooking can reduce certain compounds (like oxalates) that otherwise compete with iron.
Meanwhile, if you’re seeing warning signs—persistent tiredness, pale skin, shortness of breath—address intake sooner rather than later. For a full checklist, see our symptoms guide:
15 Signs You Are Iron Deficient
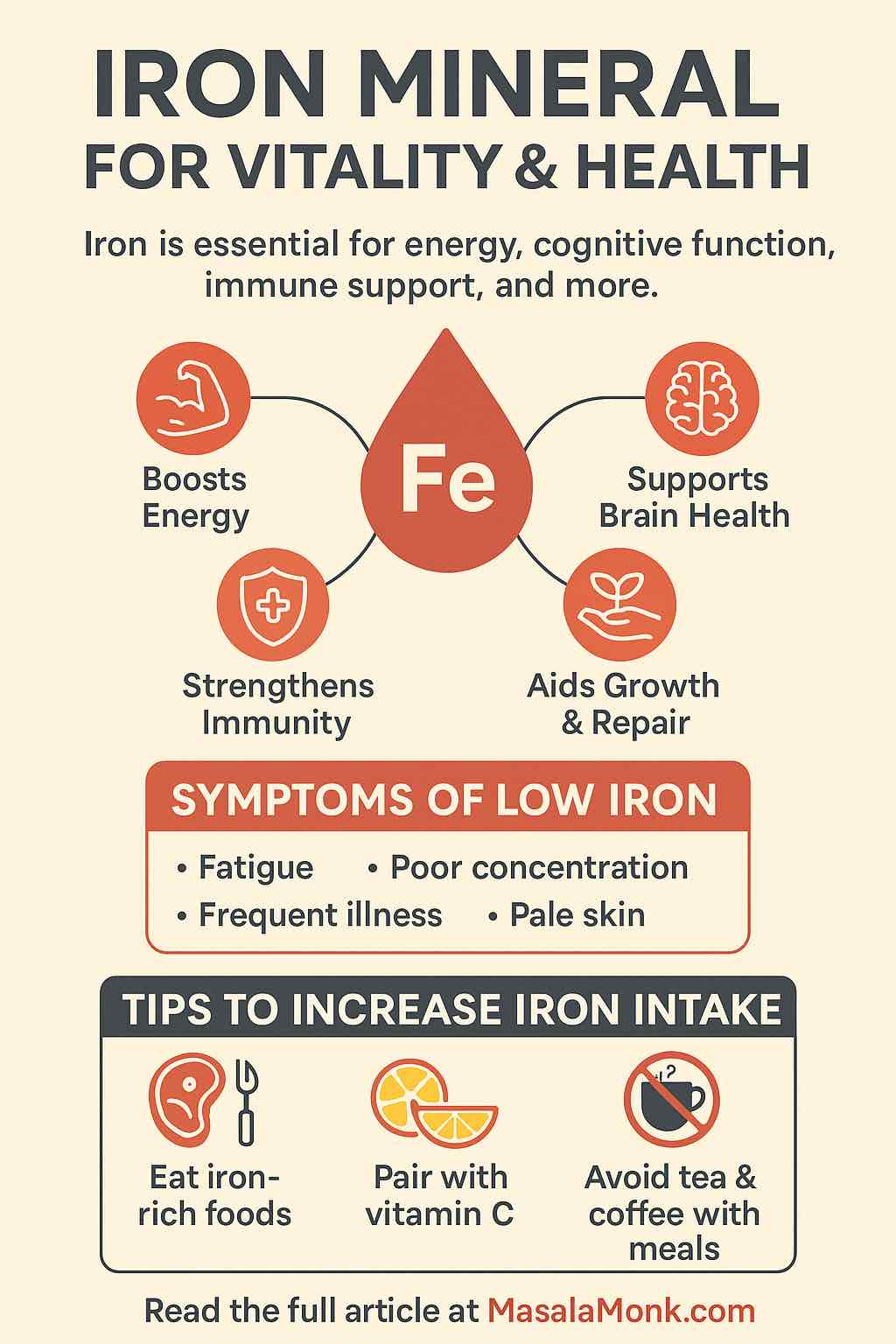
Finally, if you want the bigger picture on why iron touches energy, immunity, and even cognition, this explainer connects the dots:
Iron: The Mineral for Vitality and Health
Daily Iron Needs (and a realistic plant-based target)
As a reference point, adult men generally need ~8 mg/day, while women of child-bearing age need ~18 mg/day. Because plant iron is less bioavailable, vegans/vegetarians often aim higher. This can sound daunting at first; however, with the vegetable choices below—and smart pairings—you’ll find it’s very achievable.

10 Iron-Rich Vegetables for Boosting Hemoglobin and Fighting Anemia
When it comes to improving hemoglobin levels naturally, vegetables high in iron are some of your best allies. Each of the foods below not only provides plant-based iron but also adds extra nutrients that support energy, circulation, and red blood cell production.
1. Spinach – An Iron Powerhouse for Fighting Anemia
To begin with, spinach is one of the most celebrated vegetables rich in iron. A single cup of cooked spinach offers nearly 6 mg of iron, making it one of the best plant-based sources available. Moreover, it is also loaded with folate and vitamin C, which help in red blood cell formation.
As a result, lightly cooking spinach (instead of eating it raw) reduces oxalates and allows your body to absorb more iron. Therefore, pairing spinach with lemon juice or tomatoes boosts absorption significantly.
2. Kale – Iron-Rich Green Vegetable for Anemia and Hemoglobin Support
In addition, kale is another excellent food high in iron, delivering about 1.5 mg per cooked cup. While it may not match spinach in iron content, it provides vitamin K, calcium, and vitamin C, making it especially beneficial for women’s health.
Unlike spinach, kale contains fewer oxalates, and therefore more of its iron is readily absorbed. For example, adding kale to soups or stir-fries with bell peppers ensures both iron and vitamin C work together.
3. Beet Greens – An Overlooked Source of Plant-Based Iron
Often thrown away, beet greens are surprisingly rich in iron, providing around 2.7 mg per cooked cup. In fact, they also contain magnesium, potassium, and vitamin A, all of which enhance circulation and oxygen delivery.
For best results, sauté beet greens with garlic and finish with lemon juice. As a result, the vitamin C improves iron uptake naturally.
4. Swiss Chard – Colorful Iron for Healthy Blood
Swiss chard is both vibrant and nutrient-packed. One cooked cup offers nearly 4 mg of iron, and in addition, it contains magnesium and vitamin C. Unlike some other greens, Swiss chard already combines non-heme iron with vitamin C, which means it supports its own absorption.
Therefore, pairing it with lentils in a warm stew doubles the iron boost and helps fight anemia effectively.
5. Broccoli – Low Iron but High in Absorption Power
On the other hand, broccoli may not be the highest in iron (around 1 mg per cooked cup), but it provides a powerful advantage: vitamin C. This makes broccoli one of the best companions for improving iron absorption from other foods.
Moreover, it is also rich in folate and fiber, supporting long-term blood health. For example, a broccoli and chickpea stir-fry finished with lime is both delicious and iron-friendly.
6. Brussels Sprouts – Tiny Iron-Rich Vegetables for Hemoglobin Boost
Brussels sprouts deliver about 1.2 mg of iron per cooked cup. More importantly, they naturally combine iron with vitamin C and antioxidants, which makes them excellent for raising hemoglobin.
For a practical idea, roast Brussels sprouts with olive oil and sprinkle pumpkin seeds on top. As a result, you’ll stack two strong iron sources in one dish.
7. Mustard Greens – Peppery Leaves Rich in Iron
Furthermore, mustard greens are packed with about 1.5 mg of iron per cooked cup, plus vitamin A and vitamin C. Their spicy flavor makes them a versatile addition to meals while strengthening immunity and circulation.
For example, combining mustard greens with lentils or beans creates a hearty vegetarian dish that delivers steady iron intake.
8. Collard Greens – Slow and Steady Hemoglobin Support
Collard greens, a staple in Southern cooking, contain around 2.2 mg of iron per cooked cup. In addition, they’re rich in calcium and fiber, which makes them a well-rounded choice for long-term health.
Therefore, simmering collards with tomatoes naturally improves iron absorption while enhancing flavor.
9. Pumpkin – A Seasonal Vegetable with Iron Power
Surprisingly, pumpkin provides about 1.4 mg of iron per cooked cup. More importantly, it also contains vitamin A and antioxidants that boost immunity and red blood cell production.
Don’t forget pumpkin seeds — they are even richer in iron, delivering around 2.5 mg per ounce. As a result, roasting the seeds or blending pumpkin into soups gives you an easy way to fight anemia.
10. Beetroot – Iron-Rich Root Vegetable to Build Blood and Hemoglobin
Lastly, beetroot may not be extremely high in iron (about 1 mg per cooked cup), but it plays a unique role. Its natural nitrates improve circulation and oxygen delivery, which complements iron’s effect on hemoglobin.
For example, drinking beetroot juice with citrus fruits is an excellent way to refresh your body while improving iron absorption.
How to Improve Absorption from Iron Rich Vegetables (Simple, practical, proven)
Even strong plant-based iron sources underperform if absorption is blocked. Therefore, build these habits into your routine:
- Add vitamin C whenever possible. Lemon juice, oranges, tomatoes, kiwi, strawberries, bell peppers—add to salads, dals, sautés, and sauces.
- Time your tea/coffee. Enjoy them between meals, not with them; tannins and polyphenols reduce iron uptake.
- Cook with cast-iron sometimes. Especially for tomato-based dishes; you’ll get a small, natural iron lift.
- Soak/sprout/ferment when applicable. These steps lower phytates in grains/legumes, which can otherwise compete with iron.
- Mix categories. A plate with greens and legumes and vitamin-C veg consistently outperforms a single food alone.
👉 Explore more tips in our companion post: Iron: The Mineral for Vitality and Health.

High-Iron Vegetarian Meal Ideas (Stack veggies the smart way)
- Spinach-tomato dal + lemony kale salad
Iron from spinach + vitamin C from tomatoes/lemon = better uptake. - Broccoli-chickpea stir-fry over quinoa
Crucifer + legume + whole grain; finish with lime to amplify absorption. - Collards in tomato-onion base + roasted Brussels
Cook low and slow, then add a citrusy slaw on the side for more C. - Pumpkin-chard coconut curry + cucumber-pepper salad
Rich, comforting, and cleverly paired with fresh vitamin-C veg.
Common Iron Mistakes (and quick fixes)
- Relying on one “hero” food. Instead, rotate greens (spinach, kale, chard, collards) and layer legumes, seeds, and vitamin-C veg.
- Sipping tea/coffee with meals. Shift them 60–90 minutes away from iron-rich plates.
- Eating all greens raw. Light cooking often improves usable iron from leafy veg.
- Forgetting vitamin C. Add citrus, tomatoes, or peppers to practically every iron-focused dish.
- Skipping variety. A week of mixed iron rich vegetables consistently outperforms a single daily salad.
Final Thoughts
If you’ve been struggling with low energy, frequent dizziness, or pale skin, iron deficiency might be the culprit. Instead of rushing to supplements right away, start by adding these iron rich vegetables to your daily meals. They are natural, nourishing, and effective at building hemoglobin and fighting anemia.
And remember—iron absorption is just as important as intake, so always combine your veggies with vitamin C sources.
👉 Want to explore beyond vegetables? Check out:
- Iron Deficiency Symptoms & Top 10 Vegan Iron Rich Foods That Can Help
- Iron: The Mineral for Vitality and Health
FAQs on Iron-Rich Vegetables and Anemia
1. Which vegetable has the highest iron content?
Spinach tops the list, providing around 6 mg of iron per cooked cup. Swiss chard and beet greens are also excellent choices with high iron levels.
2. Can vegetables alone cure anemia?
Vegetables can significantly improve iron intake and help manage anemia, especially when combined with vitamin C–rich foods. However, in severe cases, medical treatment and supplements may also be required.
3. How can I increase iron absorption from vegetables?
Pair iron-rich vegetables with vitamin C foods like citrus, tomatoes, or bell peppers. Avoid tea, coffee, and excessive dairy around meals, as they can block iron absorption.
4. Are iron-rich vegetables enough for pregnancy?
They are a valuable part of a pregnancy diet, but often doctors recommend iron supplements as well since iron needs are very high during pregnancy.
5. Which iron-rich vegetables are best for kids?
Spinach, broccoli, pumpkin, and beetroot are kid-friendly when added to soups, smoothies, or purees. Pairing them with fruits like oranges improves absorption.
6. Do cooked vegetables lose their iron content?
No, iron is a stable mineral and doesn’t get destroyed by cooking. In fact, lightly cooking vegetables like spinach reduces oxalates, making iron easier to absorb.
7. Can vegetarians rely only on vegetables for iron?
Yes, vegetarians can meet their iron needs with vegetables, legumes, seeds, and fortified foods, as long as they also include vitamin C for better absorption.
8. What fruits go well with iron-rich vegetables?
Citrus fruits (oranges, lemons, grapefruits), strawberries, and pomegranates are great options. They provide vitamin C, which enhances iron absorption from veggies.
9. Are green juices good for anemia?
Yes. Juices made with spinach, kale, or beetroot combined with lemon or orange juice can provide a quick, easily absorbed source of iron and vitamin C.
10. How long does it take to improve hemoglobin with diet?
It varies by individual and severity of anemia. With consistent intake of iron-rich vegetables and supportive foods, hemoglobin levels can start improving in 4–6 weeks.
References & Further Reading
For those who want to explore more about iron-rich vegetables, anemia, and hemoglobin health, here are some trusted resources:
- Iron and Vitamin C: The Perfect Pair – Michigan State University Extension
Explains how vitamin C dramatically improves non-heme iron absorption from vegetables. - Spinach and Iron Content – URMC Health Encyclopedia
Details on how much iron spinach provides and why it’s considered an anemia-fighting superfood. - Plant-Based Foods Higher in Iron Than Steak – Real Simple
A practical list of vegetarian foods that rival or beat meat in iron content. - Iron Absorption and the Role of Vitamin C – JAMA Network
Scientific research highlighting how vitamin C influences iron absorption rates. - Iron Deficiency Anemia – StatPearls, NCBI Bookshelf
An evidence-based medical overview of anemia, symptoms, and dietary solutions. - Vegetarian Nutrition and Iron Requirements – Wikipedia
Covers nutrition needs for vegetarians, including iron requirements and absorption strategies. - Iron-Rich Foods for Vegetarians – Prevention.com
A lifestyle-oriented guide to the best iron-rich foods for vegetarians and vegans.