Turmeric, the vibrant golden spice that gives curry its signature hue, has long been hailed as a superfood with a wide range of health benefits. From fighting inflammation to boosting brain function, its active compound curcumin has earned a place in both traditional and modern medicine. But in recent years, one particular question has been on the rise: Is turmeric good for your liver?
With the liver being your body’s primary detox organ, maintaining its health is essential. As liver diseases like nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) become more prevalent, many are turning to natural remedies like turmeric for support. But what does the latest science actually say?
In this deep dive, we explore the research-backed benefits, the potential risks, and what you need to know before adding turmeric to your wellness routine.
The Liver and Its Role in Health
Your liver is a powerhouse. It processes everything you consume, filters toxins, produces bile for digestion, regulates blood sugar, stores essential nutrients, breaks down fats, and plays a key role in metabolism and immune system function. With such a vital role, it’s no wonder that even minor liver dysfunction can impact your overall health—causing symptoms ranging from fatigue and digestive issues to hormonal imbalances and cognitive problems.
Liver issues are on the rise globally due to poor diets, sedentary lifestyles, alcohol use, and environmental toxins. Conditions like NAFLD, alcoholic liver disease, hepatitis, and cirrhosis are becoming increasingly common, making proactive liver care more important than ever.
Turmeric’s Active Ingredient: Curcumin
The primary bioactive compound in turmeric is curcumin, which comprises about 2–8% of most turmeric preparations. Curcumin is known for its strong anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and even anticancer properties. However, curcumin’s poor natural bioavailability means it is rapidly metabolized and eliminated from the body. To address this, many supplements are combined with piperine (an extract from black pepper), phospholipids (like in Meriva formulations), or nanoparticles to improve absorption.
Curcumin modulates several cellular signaling pathways, including those involved in inflammation (e.g., NF-κB), oxidative stress (e.g., Nrf2), and apoptosis (programmed cell death). These mechanisms are especially relevant in the context of liver diseases, where inflammation and oxidative damage are key drivers.
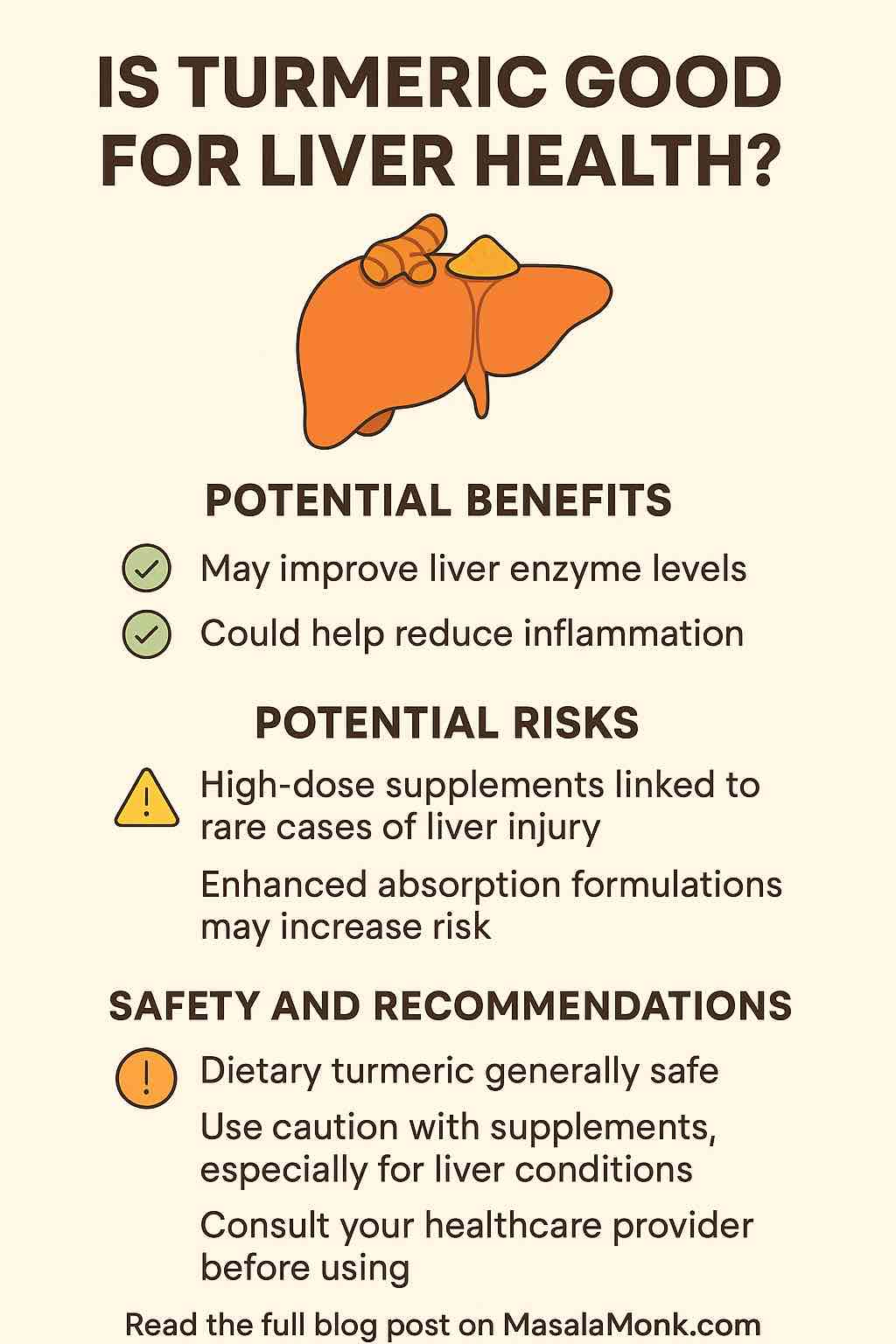
What the Science Says: Turmeric and Liver Health
1. Promising Benefits
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD):
One of the most compelling areas of study is turmeric’s potential to help those with NAFLD—a condition affecting an estimated 25% of the global population. In a 2021 double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, participants taking 2 grams of turmeric extract daily for 8 weeks experienced notable improvements in liver enzyme levels (AST, ALT), lipid profiles (triglycerides, LDL), and markers of inflammation. This suggests turmeric could play a role in reducing liver fat accumulation and improving overall liver function.
Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis:
Chronic liver inflammation often leads to fibrosis—the buildup of scar tissue—which, if unchecked, progresses to cirrhosis. Preclinical studies in rodents show that curcumin inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation and reduces the expression of fibrotic markers like TGF-β and collagen. These findings hint at curcumin’s potential to slow or reverse the progression of liver scarring.
Detoxification Support:
Curcumin may enhance the activity of detoxifying enzymes such as glutathione-S-transferase (GST) and superoxide dismutase (SOD). By supporting these detoxification pathways, turmeric helps the liver neutralize and eliminate harmful substances, including heavy metals and environmental pollutants.
Reduction of Oxidative Stress:
Oxidative stress is a major factor in liver damage. Curcumin’s antioxidant properties help counteract oxidative damage by neutralizing free radicals and upregulating the expression of antioxidant enzymes. This not only supports liver health but also protects against cellular aging and DNA damage.
Anti-inflammatory Effects:
Chronic inflammation is central to the progression of nearly all liver diseases. Curcumin reduces the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6, TNF-α, and CRP, which are elevated in conditions like hepatitis and fatty liver. It also inhibits the activation of the NF-κB pathway, a major driver of chronic inflammation.
2. The Cautionary Side
Despite these compelling benefits, turmeric is not without risks—especially in supplement form.
Reports of Liver Injury:
Recent years have seen an increase in reports linking turmeric supplements to acute liver injury. Although these cases are rare, some have been severe, resulting in hospitalization, liver failure, and even death. Most incidents involved high-dose curcumin supplements, often combined with bioavailability enhancers like piperine or formulated using advanced technologies such as liposomal encapsulation.
Why the Risk Exists:
When turmeric is taken in food amounts, it is well-tolerated by most people. However, concentrated extracts can pose problems for certain individuals—particularly those with pre-existing liver conditions or genetic predispositions. Supplements that enhance curcumin absorption may increase the compound’s systemic levels far beyond what the body is used to handling, potentially triggering adverse reactions.
Regulatory Warnings:
The Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) and other health bodies have issued formal warnings about the risk of liver injury from curcumin-containing products. They recommend that anyone with liver disease or on liver-metabolized medications exercise caution and consult a healthcare provider before use.
How to Safely Use Turmeric for Liver Support
- Stick to dietary sources: Using turmeric in cooking is not only safe but beneficial. It can be added to curries, soups, rice dishes, smoothies, and teas for everyday wellness.
- Choose supplements wisely: If opting for a supplement, select reputable brands that use third-party testing and provide transparent labeling.
- Avoid megadoses: More isn’t always better. Stay within recommended dosages and avoid combining with other potent liver-impacting herbs or medications without guidance.
- Monitor for side effects: Watch for symptoms like fatigue, yellowing of the skin, or dark urine—potential signs of liver stress—and discontinue use if they occur.
- Consult a professional: Especially important for those with chronic health conditions, existing liver concerns, or who are on multiple medications.
Turmeric in Context: A Holistic Liver Health Strategy
Turmeric can play a supportive role, but it should be part of a broader approach to liver care. Key strategies include:
- Eating a nutrient-rich, anti-inflammatory diet featuring fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Limiting alcohol intake and avoiding processed foods high in sugar and trans fats.
- Staying hydrated to assist the liver’s filtration process.
- Regular physical activity, which has been shown to improve liver enzyme levels and reduce liver fat.
- Getting regular checkups to monitor liver health through blood tests like AST, ALT, and GGT.
Conclusion: Is Turmeric Good for Your Liver?
Yes—with conditions.
Turmeric is a powerful spice with legitimate potential to support liver health. It can reduce inflammation, fight oxidative stress, and help improve liver function markers—especially in individuals with early-stage liver concerns like NAFLD. However, it’s not a one-size-fits-all remedy. The risk of liver injury from high-dose supplements—though rare—is real and should not be ignored.
As with any supplement, balance is key. Incorporate turmeric mindfully into a healthy lifestyle, and consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new regimen—especially if you’re dealing with liver disease or taking liver-metabolized medications.
Click-worthy Tip: Want to try turmeric for liver health? Start with golden milk or turmeric tea—delicious, soothing, and easy on the liver!
Call to Action:
Found this helpful? Share this post and help someone else take charge of their liver health. Got questions or personal experiences with turmeric? Drop a comment below—we’d love to hear your story!
FAQs: Turmeric for Liver Health
1. Can turmeric actually detox the liver?
Turmeric doesn’t “detox” the liver in the way some marketing suggests, but its active compound, curcumin, can support the liver’s natural detoxification pathways by enhancing antioxidant enzymes like glutathione and reducing oxidative stress.
2. How much turmeric should I take for liver health?
For general wellness, 500–2,000 mg of curcumin extract per day is commonly used in studies. However, it’s best to start with dietary turmeric and consult your healthcare provider before starting supplements—especially for liver-specific concerns.
3. Is turmeric safe for people with existing liver disease?
Turmeric in food amounts is generally safe. However, curcumin supplements can pose risks for people with liver disease, especially in high doses or combined with piperine. Always consult a healthcare professional before using supplements.
4. Are turmeric supplements better than turmeric in food?
Supplements contain concentrated curcumin and may offer stronger anti-inflammatory effects. However, they also carry a higher risk of side effects. Dietary turmeric is safer and still beneficial when consumed consistently.
5. Can turmeric cause liver damage?
Yes, in rare cases. High-dose turmeric supplements, particularly those with enhanced absorption formulas (like with piperine), have been linked to acute liver injury in some individuals.
6. How long does it take to see liver health benefits from turmeric?
Clinical trials suggest improvements can appear in as little as 8 weeks when turmeric is taken consistently, particularly in people with NAFLD or elevated liver enzymes.
7. What are signs of turmeric-related liver stress?
Watch for jaundice (yellowing skin or eyes), dark urine, abdominal pain, fatigue, or nausea. If these symptoms appear, stop use immediately and seek medical help.
8. Is turmeric better than milk thistle for liver health?
Both offer unique benefits. Milk thistle (silymarin) has a longer history in liver support, while turmeric (curcumin) offers broader anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Some formulations combine both for synergistic benefits.
9. Should turmeric be taken with food or on an empty stomach?
Turmeric is best taken with food, especially fats, to enhance absorption and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort. Many supplements also include black pepper extract (piperine) to improve bioavailability.
10. Can I drink turmeric tea daily for liver support?
Yes! Turmeric tea or “golden milk” is a gentle, daily way to support liver health without the risks associated with high-dose supplements. Just avoid adding too much sugar or dairy if you’re managing liver conditions.