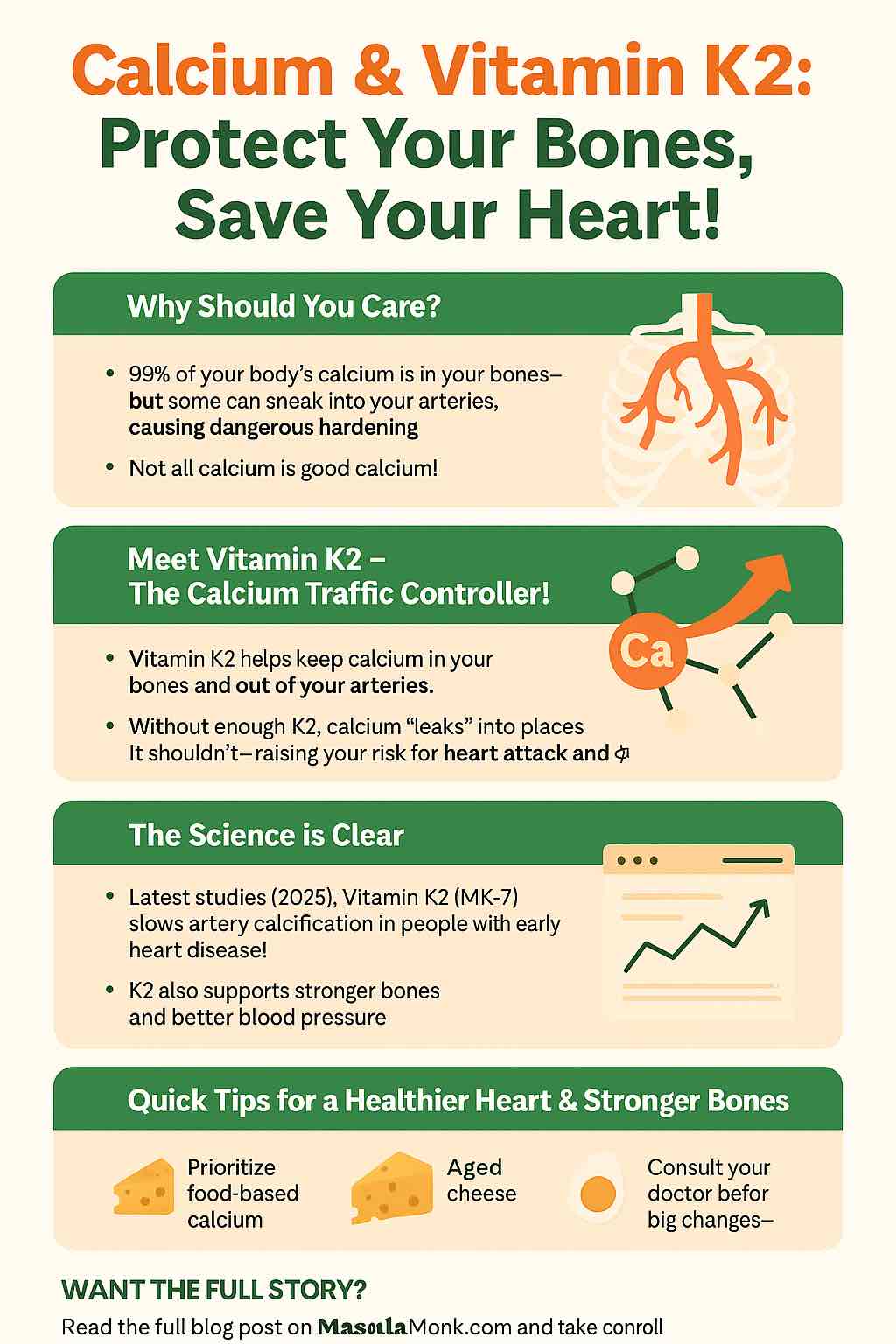
You probably know calcium is important for strong bones. You’ve seen the ads for calcium supplements and heard warnings about osteoporosis. But recently, another side to the story is emerging—one that connects our favorite bone-builder to heart health, and brings a largely ignored vitamin, K2, into the spotlight.
What if I told you that getting calcium wrong might not just fail your bones—it could harden your arteries?
And what if the missing puzzle piece for a strong heart and skeleton is a nutrient most people have never heard of?
Welcome to the intersection of calcium, vitamin K2, and vascular calcification—where the latest science is rewriting the rules of preventive health.
1. Calcium: Essential, But Not Always Innocent
For decades, the health community has sung the praises of calcium for bone strength. We need it—about 99% of the body’s calcium is stored in bones and teeth.
But here’s the twist:
When calcium ends up in your arteries instead of your bones, it can lead to vascular calcification—essentially, “hardening” of the arteries, which is a major risk factor for heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure.
How does this happen?
- Too much calcium in the blood (especially from supplements)
- Aging or certain diseases (e.g., chronic kidney disease)
- Not enough “calcium traffic controllers” to keep it in the right places
2. Vascular Calcification: A Silent Threat
Vascular calcification is the buildup of calcium in the blood vessel walls. Unlike soft plaque, this calcium is hard and unyielding—turning flexible arteries into stiff pipes.
Why should you care?
- It’s strongly linked to heart attacks, strokes, and even cognitive decline.
- Once started, it’s very hard to reverse.
Who’s at risk?
- Older adults
- People taking high-dose calcium supplements (especially without balancing nutrients)
- Patients with chronic kidney disease, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease
3. Enter Vitamin K2: The Master Traffic Controller
Vitamin K2 (especially in its MK-7 form) acts like the manager of a construction crew. It ensures calcium gets put into your bones and teeth—where it’s needed—and keeps it out of your arteries and organs, where it causes harm.
How does K2 work?
- Activates proteins (like matrix Gla protein/MGP and osteocalcin)
- These proteins literally bind up calcium and shuttle it to your skeleton
- Without K2, these proteins can’t do their job—so calcium “leaks” into arteries
Most people are low in K2—especially in Western diets, where sources like natto (fermented soybeans), aged cheese, and some animal foods are rare.
4. What Does the Latest Research Say? (2024–2025)
A. Calcium Alone Can Be Problematic
- Some studies link high-dose calcium supplements (without K2) to higher heart attack risk, particularly in older adults.
- Calcium from food doesn’t show this risk—likely because it’s absorbed more slowly and with co-factors like K2.
B. K2 Supplementation Shows Real Promise
- 2025 RCT: Over 2 years, 180 µg/day of MK-7 (a form of K2) in people with early artery calcification significantly slowed further progression compared to placebo. (Journal of Hypertension, 2025)
- K2 supplementation reduces levels of inactive MGP (a key biomarker), suggesting it’s helping prevent “calcium leaks” in arteries.
- Benefits are seen even in healthy people and those with early disease, not just those with severe calcification.
C. Special Populations:
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD): K2 shows some promise, though results are mixed. People with kidney problems are at especially high risk for vascular calcification.
- Postmenopausal women: K2 may improve arterial stiffness and blood pressure.
D. It’s Not Just About Bones or Heart—It’s About Both
- K2 (with D3) improves bone density while also protecting arteries—potentially solving the supplement “double-edged sword.”
5. Practical Takeaways: What Should You Do?
A. Get Calcium From Food First
- Dairy (if tolerated), leafy greens, tofu, sardines, almonds.
- Food-based calcium is paired with nutrients and absorbed gradually.
B. Don’t Overdo Calcium Supplements
- If you need a supplement (e.g., for osteoporosis), use the lowest dose required.
- Don’t take “just in case”—work with your healthcare provider to test your levels.
C. Add Vitamin K2 to the Mix
- Consider a supplement with MK-7 form (typically 90–200 µg/day)—especially if you’re taking calcium or vitamin D.
- Look for reputable brands, and take with a meal for best absorption.
- Natural food sources: Natto (a Japanese fermented food, by far the richest source), aged hard cheeses (Gouda, Edam), pastured egg yolks, goose liver.
D. Don’t Forget Vitamin D
- Vitamin D and K2 work together: D helps you absorb calcium; K2 helps you use it wisely.
- Many D3 supplements now include K2 for this reason.
E. If You’re on Blood Thinners…
- If you take warfarin (Coumadin), talk to your doctor before adding any K2—K vitamins affect how your medication works.
6. The Future: What to Watch For
The science is moving fast:
- Ongoing studies in people on dialysis, transplant patients, and those with high baseline calcification.
- Emerging evidence that tracking dp-ucMGP (the inactive, uncarboxylated form of MGP) may be a useful marker for K2 status and vascular health.
Guidelines are evolving, but leading researchers already suggest that K2 is a “missing link” in the prevention of both osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease.
7. Final Thoughts: A Smarter Way to Supplement
The old advice was simple: “Take more calcium!”
The new science says: “Balance your nutrients, respect the synergy, and put calcium where it belongs.”
Vitamin K2 might just be the unsung hero in your supplement routine—protecting both your bones and your arteries.
Your Action Plan:
- Check your sources: Get calcium from food first.
- Team up nutrients: If using supplements, add K2 (and D3) to the mix.
- Eat some fermented foods or aged cheeses.
- Ask your doctor about testing your vitamin D and calcium status, and discuss K2 if you have risk factors.
- Stay curious! Science keeps evolving, and so should your approach to health.
References / Further Reading
- Vossen LM, et al. “Menaquinone-7 slows down progression of coronary artery calcification in patients with mild-to-moderate coronary artery disease: A randomized controlled trial.” J Hypertens. 2025.
- Schurgers LJ, et al. “Vitamin K2: The essential bioactive form for vascular health?” Nutrients. 2023.
- Maresz K. “Vitamin K2 and cardiovascular health: A review of the latest evidence.” Open Access J. 2024.
Do you have questions about your supplement stack? Curious about practical ways to boost K2 naturally? Let’s continue the conversation in the comments below!
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace individualized medical advice. Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your supplement routine.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between vitamin K1 and K2?
Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) is found in leafy greens and helps with blood clotting. Vitamin K2 (menaquinone, especially MK-7) is found in fermented foods and some animal products, and it helps direct calcium into bones and away from arteries. K2 has a much stronger impact on vascular health than K1.
2. Can I get enough vitamin K2 from my diet?
Most Western diets are low in vitamin K2, unless you regularly eat natto (fermented soybeans), certain aged cheeses, or grass-fed animal products. Many people may benefit from a supplement, especially if at risk for osteoporosis or vascular calcification.
3. Is it safe to take calcium and vitamin K2 together?
Yes, taking calcium and vitamin K2 together is considered safe for most people. In fact, K2 helps ensure calcium is used properly by the body and doesn’t build up in the arteries.
4. Who should be especially careful about calcium supplementation?
People over 50, those with a history of heart disease, chronic kidney disease, or those already taking high-dose vitamin D should discuss calcium supplements with their doctor and consider balancing with K2 and magnesium.
5. What is the best form and dose of vitamin K2?
MK-7 is the most studied and bioavailable form. Doses of 90–200 µg/day are commonly used in research for heart and bone benefits.
6. How long does it take to see results from vitamin K2 supplementation?
Research shows changes in biomarkers (like dp-ucMGP) can occur within weeks, but slowing of arterial calcification or improvement in bone density typically takes 1–2 years of consistent use.
7. Should I take vitamin D with K2?
Yes, vitamin D helps absorb calcium and K2 helps put it in the right places. Many combination supplements include both for this reason.
8. Can vitamin K2 interact with medications?
Vitamin K2 can interfere with blood-thinning medications like warfarin. If you’re on any anticoagulant, consult your doctor before starting K2.
9. Is food-based K2 as effective as supplements?
Fermented foods like natto provide a high dose of K2, but many people find supplements more practical for consistent dosing—especially if they don’t enjoy these foods.
10. Is vascular calcification reversible?
It is very difficult to reverse once established. The main goal is to slow or prevent progression. Early intervention with diet, lifestyle, and possibly K2 is key.