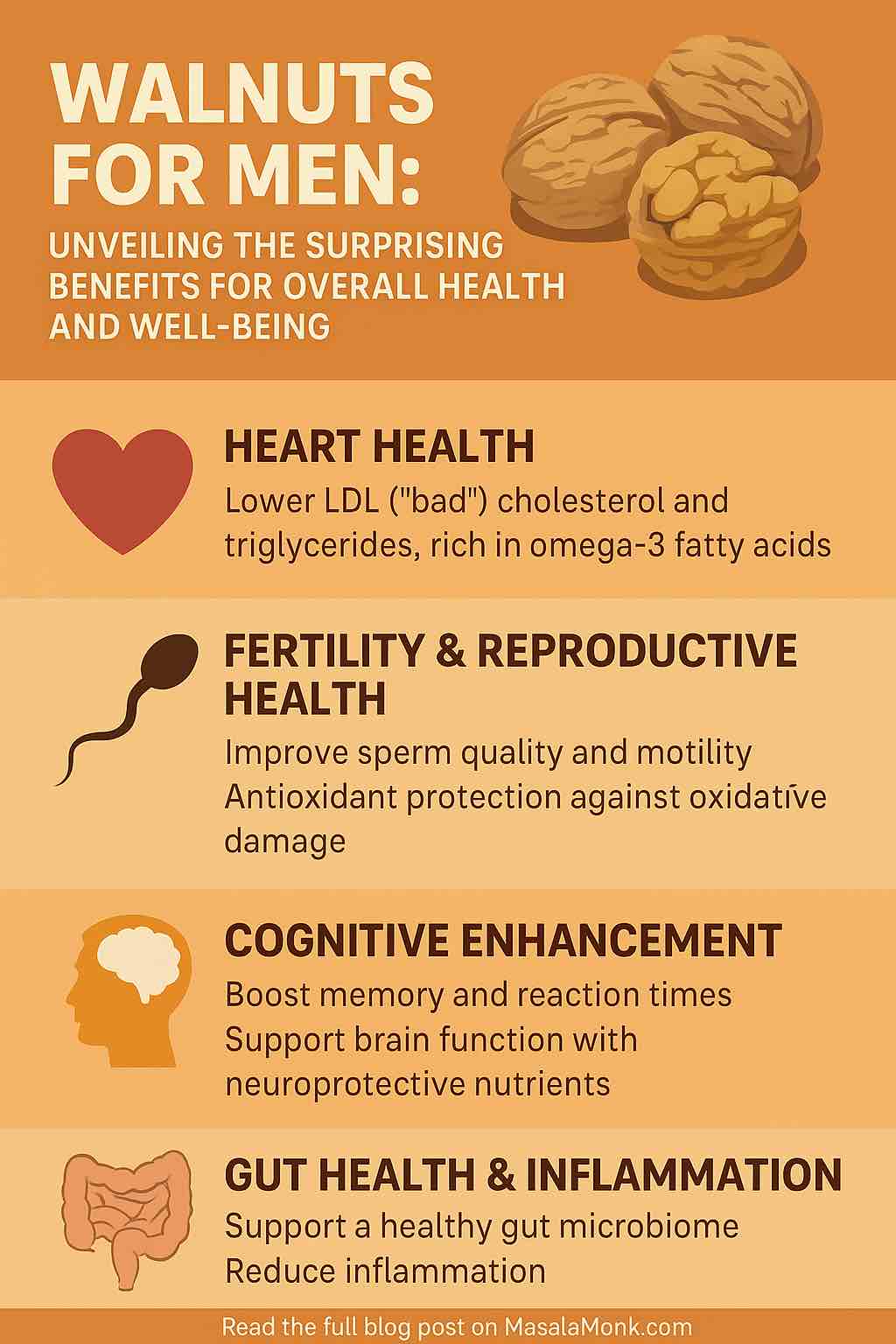
When it comes to natural superfoods for men, few things are as underrated yet powerful as the humble walnut — or Akhrot, as it’s often called. Packed with healthy fats, plant protein, and potent antioxidants, walnuts have been celebrated for centuries as “brain food.” For more on the mind–food connection, see Nourish Your Brain: The Benefits of Nuts and Walnuts for Cognitive Function. But walnut benefits for men extend far beyond sharper focus and memory.
For men, walnuts can be especially transformative. They play a role in supporting heart health (American Heart Association / Circulation AHA Journals), boosting markers of fertility (Biology of Reproduction (RCT) Oxford Academic), and may support metabolic health (Nutrients PMC). Add in their ability to aid weight management via satiety and provide sustained energy, and you have a nut that deserves a permanent place in every man’s diet.
This guide dives deep into the many ways walnuts enhance men’s health. From their nutritional profile to their role in heart, brain, and sexual wellness, we’ll cover everything you need to know about walnut benefits for men. We’ll also explore walnut oil, soaked walnuts, and how walnuts compare with other popular nuts like almonds.

Before we get into specific health benefits, let’s first understand what makes walnuts such a nutrient powerhouse.
Nutritional Value of Walnuts – Why Men Need Akhrot in Their Diet
Walnuts aren’t just another snack. They are one of the richest plant-based sources of omega-3 fatty acids, an essential nutrient linked to better circulation, improved brain function, and reduced inflammation.
Walnuts aren’t just another snack. They’re one of the richest plant-based sources of omega-3 (ALA)— learn more in Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA): for Bone, Brain, and Heart Health, linked to better vascular function and lower inflammation (USDA FoodData Central – see walnut entry; also California Walnuts 100 g factsheet). Per 100 g you typically get ~654 kcal, ~15 g protein, ~65 g fat (predominantly polyunsaturated), ~7 g fiber, and ~9 g ALA. Beyond healthy fats & Fiber, walnuts provide protein, antioxidants, and a range of vitamins and minerals that work together to promote overall health. These nutrients work together to support overall health.
For men, this combination is particularly valuable. Omega-3s and antioxidants protect the heart and blood vessels, while protein helps build and repair muscles. Minerals like magnesium and zinc play an essential role in energy production, testosterone support, and reproductive health. This makes walnuts a simple but powerful way to cover multiple wellness needs in one bite.
If you’re exploring nuts broadly, Benefits of Nuts and Seeds – Protein-Packed Superfoods is a handy primer.

Nutritional Benefits of Walnuts for Men’s Health
Walnuts deliver a balance of macronutrients and micronutrients that support men’s vitality. The high content of polyunsaturated fats, especially alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), makes them one of the best plant-based options for cardiovascular health. Zinc and magnesium support hormone production and immune strength, while B vitamins and antioxidants help combat stress and fatigue.
Unlike many calorie-dense snacks that provide little nutritional value, walnuts offer energy that actually fuels the body in a healthy way. For men juggling busy schedules, workouts, or demanding jobs, even a handful of walnuts can provide lasting energy without a sugar crash.
For practical ways to use them daily, try these 4 Recipes for Nutritious Nut-Infused Smoothies (don’t miss the Strawberry-Walnut smoothie).
Walnuts Nutrition Facts – Calories, Protein, and Healthy Fats
Here’s a closer look at the nutrition in walnuts (per 100 grams):
(Primary sources: USDA FDC / CWC factsheet (100 g).)
| Nutrient | Amount | Why It Matters for Men |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | ~654 kcal | High energy for active lifestyles |
| Protein | ~15 g | Supports muscle growth and recovery |
| Fat | ~65 g (mostly polyunsaturated) | Essential for testosterone, heart, and brain health |
| Omega-3 (ALA) | ~2.5 g | Improves circulation & reduces inflammation. See ALA guide. |
| Fiber | ~7 g | Supports digestion & weight control |
| Magnesium | ~158 mg | Important for testosterone and energy production |
| Zinc | ~3 mg | Boosts reproductive health and immunity |
| Vitamin B6 | ~0.5 mg | Enhances brain function & hormone balance |
| Antioxidants (Polyphenols) | High | Protects cells from aging & oxidative stress |
As you can see, walnuts aren’t just calorie-dense — they are nutrient-dense. They fuel the body while nourishing it at the same time. For men, that means better stamina, stronger immunity, and long-term protection against lifestyle diseases.
Now that we’ve explored the nutritional value of walnuts, it becomes clear why they have such a wide range of positive effects. Let’s move into the specific health benefits of walnuts for men, beginning with their role in keeping the heart strong and healthy.
Walnut Benefits for Men’s Health – From Heart to Hormones
Walnuts aren’t just nutritious on paper; their impact on men’s health is backed by research and centuries of traditional wisdom. Whether it’s the heart, brain, or reproductive system, walnuts bring measurable benefits. Here’s how they support different aspects of men’s health.
Walnut Benefits for Men’s Heart Health
Cardiovascular health is one of the biggest concerns for men, and walnuts are a natural ally. Thanks to their rich omega-3 fatty acid content, walnuts help reduce bad cholesterol (LDL). Multiple controlled trials and a large 2-year RCT in older adults show walnut intake reduces LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and improves lipoprotein profiles, supporting cardiovascular risk reduction (Circulation / AHA WAHA Trial; AHA news summary here). Some trials also show improved endothelial function, relevant for circulation (Diabetes Care).

Better blood flow doesn’t just protect the heart — it also boosts stamina and energy. A diet that regularly includes walnuts has been linked to a lower risk of heart disease, making them one of the simplest foods men can add for long-term heart health.
For a broader dietary context that includes nuts, see Guide to the Mediterranean Diet. For weight and heart overlap, The Role of Nuts and Seeds in Weight Management & Overall Health is a useful read.
Walnut Benefits for Men’s Brain Function and Focus
It’s no coincidence that the shape of a walnut resembles the human brain. Walnuts are packed with polyunsaturated fats, antioxidants, and vitamin B6, all of which support memory, focus, and may support overall cognitive function. Deep-dive here: Nuts for Brain Health: Unleashing Nature’s Brain-Boosting Snacks. Want ideas you can make in five minutes? Try these Omega-3 Boosting Morning Smoothies (Flax + Walnuts).
For men managing demanding careers or studying under pressure, eating walnuts daily can enhance mental clarity and reduce fatigue. The omega-3 fatty acids in walnuts are particularly important for protecting against age-related cognitive decline, making them valuable not just for young men but also for older adults aiming to keep their minds sharp.

Observational analyses in nationally representative data link walnut consumption with better cognitive test performance in adults (Journal of Nutrition, Health & Aging). While causality can’t be claimed from cross-sectional data, the signal aligns with walnuts’ ALA and polyphenols.
Walnut Benefits Sexually – Boosting Fertility and Stamina
One of the most talked-about areas of walnut benefits for men is sexual health. Studies suggest that regular walnut consumption can improve sperm quality, motility, and overall reproductive vitality. This is largely due to their zinc and omega-3 content, both of which are crucial for testosterone production and reproductive function. For a broader men’s-hormone perspective, see Boosting Testosterone Naturally: 6 Tips & 4 Supplements.
Improved circulation from walnuts’ heart-friendly fats also benefits sexual stamina. For men looking for natural ways to enhance fertility and vitality, walnuts are a simple and safe addition to the diet.

A randomized controlled trial showed that adding 75 g walnuts/day for 12 weeks improved sperm vitality, motility, and morphology in healthy men (Biology of Reproduction (RCT); PubMed record here). Follow-up clinical research also reports motility gains in infertile men (Fertility & Sterility). These are among the strongest walnut benefits for men with direct male-reproductive endpoints.
Walnuts for Weight Loss and Men’s Fitness Goals
Despite being calorie-dense, walnuts can fit into weight-management plans via satiety when portioned. Their combination of protein, healthy fats, and fiber helps men feel fuller for longer, reducing the temptation for unhealthy snacking. For recipes that make this easy, see Walnuts for Weight Loss: 5 Keto Morning Smoothie Recipes and an overview in Walnuts and Weight Loss: Nurturing Health with Nature’s Powerhouse.
For fitness-focused men, walnuts provide sustained energy for workouts and recovery. Eating a few walnuts before or after exercise can boost performance and aid muscle repair, making them a perfect addition to a balanced diet.
Walnuts are energy-dense but promote satiety (protein + fiber + PUFAs) and, in long trials, did not cause weight gain while improving lipids (Circulation / AHA WAHA Trial).
Walnuts for Men with Diabetes and Metabolic Concerns
Men who struggle with blood sugar regulation can benefit greatly from walnuts. Research indicates that walnuts may improve insulin sensitivity and help control fasting blood sugar levels.
Their high fiber and healthy fat content slow down the absorption of sugar in the bloodstream, making them a safe and beneficial snack for men with type 2 diabetes or those at risk. Including walnuts regularly can support better metabolic health and reduce the risk of complications.

In adults with metabolic syndrome, 45 g/day for 16 weeks improved HDL-C and lowered fasting glucose (Nutrients (clinical trial)). Other work shows better endothelial function in type 2 diabetes with a walnut-enriched diet (Diabetes Care) and improved glycemic markers in at-risk adults (BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care).
Suggested Reading: Glycemic Index (GI) VS Glycemic Load (GL) and also have a look at Low Glycemic Index (GI) Foods List: PDF for Free Download!.
Moving to next section:
While raw walnuts themselves are incredibly beneficial, their oil deserves special mention. Extracted through cold pressing, walnut oil concentrates many of the same nutrients and offers additional uses for men’s health, skin, and overall vitality.
Walnut Oil Benefits for Men – Cold-Pressed Goodness for Health and Vitality
Walnuts themselves are a superfood, but their oil is equally impressive. Extracted through cold pressing, walnut oil retains most of the nut’s essential fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins. For men, this golden oil brings benefits not only when consumed but also when applied to the skin and hair.
Curious about processing methods and where walnut oil fits among cooking oils? See Comparing 10 Types of Edible Oil Popular in India and What are ‘Fats’? (myths & facts).

Walnut Oil Benefits for Men’s Heart and Cholesterol Levels
Just like eating raw walnuts, consuming walnut oil can improve cardiovascular health. It is rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid that helps reduce inflammation, lower bad cholesterol, and support better circulation.
For men who prefer a lighter way to include walnuts in their diet, adding a spoonful of walnut oil to salads or drizzling it over cooked dishes can deliver heart-healthy benefits without adding bulk. This makes it a smart choice for busy lifestyles where maintaining heart health is essential.
Walnut oil supplies ALA similar to the nuts and can be used as a finishing oil to help meet omega-3 targets (nutrient basis: USDA / CWC data). Human outcome trials are far stronger for whole walnuts than for the oil alone—so oil is a convenient complement, not a substitute.
Walnut Oil Benefits for Men’s Skin and Hair
Walnut oil isn’t just for cooking — it’s also widely used in skincare and grooming. Rich in antioxidants, vitamin E, and omega-3s, it may help nourish the skin, help prevent dryness, and may even reduce signs of premature aging.
For men dealing with rough skin, shaving irritation, or dryness, walnut oil can act as a natural moisturizer. When massaged into the scalp, it may improve circulation and supports healthier hair growth, making it a natural remedy for thinning or weak hair.
Evidence here though is limited/mostly cosmetic or theoretical (vitamin E/PUFA content).
Walnut Oil Benefits Sexually and for Men’s Vitality
Because walnut oil improves blood circulation, it can indirectly support sexual health and stamina. Better circulation enhances energy levels and may contribute to improved performance. While research is still growing in this area, traditional medicine has long considered walnut oil as a natural booster for men’s vitality.
For men looking for natural ways to enhance both internal health and external wellness, walnut oil offers a versatile option — beneficial in the kitchen and on the grooming shelf.
Moving into next section:
Now that we’ve explored walnut oil, let’s return to the nut itself. The way you eat walnuts can make a big difference in how much benefit you actually get. Should you eat them raw, soaked, in the morning, or at night? Let’s break it down.
How to Eat Walnuts Daily – Best Practices for Men’s Health
Walnuts are versatile, but how you eat them can change how much benefit you get. For men, choosing between raw and soaked walnuts, the right time of day, and the ideal quantity can make a noticeable difference.
Soaked Walnuts Benefits for Men vs. Raw Walnuts
Many people wonder whether walnuts should be eaten raw or soaked overnight. Both forms are beneficial, but soaking walnuts has an extra edge. When walnuts are soaked, their tannins (which can sometimes cause a bitter taste) are reduced, making them easier to digest. Soaking also activates enzymes that may improve nutrient absorption. Read More the same here: Unleashing the Power of Soaked Walnuts: Discover the Nutritional Benefits.

For men with sensitive digestion, soaked walnuts may be the better option. Raw walnuts, on the other hand, are quick, crunchy, and still packed with nutrients. Both provide omega-3s, antioxidants, and protein — so the choice comes down to personal preference and digestive comfort.
Soaking can improve palatability for some; robust bioavailability data are limited. The key is consistent intake within calorie needs. (No strong RCTs available).
Benefits of Eating Walnuts in the Morning vs. Night
The timing of walnut consumption also matters. Eating walnuts in the morning provides a steady release of energy and can help reduce cravings throughout the day. This is especially helpful for men managing weight or looking for a natural energy boost before work or workouts.
Eating walnuts at night, however, comes with its own benefits. Walnuts contain melatonin, a natural sleep regulator. Consuming a few walnuts before bedtime may improve sleep quality and support overnight recovery.

For most men, combining both approaches — a few soaked walnuts in the morning and a handful of raw walnuts or walnut oil in the evening — can maximize benefits.
Morning for satiety/energy; evening is fine too. For quick morning options, don’t miss 4 Nut-Infused Smoothie Recipes.
Note: walnuts contain melatonin, but clinical sleep outcomes are not well-established.
How Many Walnuts Should Men Eat Daily?
The question of quantity is important. Walnuts are nutrient-dense, but also calorie-dense, so moderation is key. Most experts recommend 4 to 7 walnuts per day for men. This amount is enough to provide essential nutrients without adding excess calories.
For men aiming to improve fertility, brain health, or heart function, consistency is more important than volume. A small daily serving, taken regularly, is far more effective than eating large amounts occasionally.

Practical guidance from cardiometabolic trials ranges from ~28–56 g/day (1–2 ounces), with the WAHA trial using ~30–60 g; fertility RCT used 75 g/day. Suggest a real-world target ~28–42 g/day unless calories allow more. (Circulation / WAHA; Biology of Reproduction).
Getting into the next section:
Of course, walnuts aren’t the only nuts competing for attention. Many men compare them with almonds or even other varieties like black walnuts. Let’s see how they stack up.
Walnuts Compared to Other Nuts – Are They the Best Choice for Men?
Nuts in general are a cornerstone of healthy eating, but not all nuts are the same. Walnuts stand out because of their unique nutrient profile, yet many men wonder: are they better than almonds or other varieties of walnuts?
Almonds vs. Walnuts Benefits for Men’s Health
Almonds are often the go-to nut for men focusing on fitness, but walnuts bring a set of benefits that almonds can’t match.
- Almonds are rich in vitamin E, calcium, and monounsaturated fats, which support skin health and strong bones.
- Walnuts, on the other hand, are the only nuts with a significant amount of plant-based omega-3 fatty acids. This makes them superior for heart health, brain support, and male fertility.
For specifics, see Almonds Nutrition Facts 100g & Glycemic Index Impact and Best Nuts for Weight Loss.

For men aiming for all-round wellness, combining both nuts can be the smartest choice. Almonds protect skin and bones, while walnuts take care of the heart, brain, and reproductive system.
Almonds excel in vitamin E and monounsaturated fat; walnuts are unique for ALA omega-3 and consistent LDL-C improvements in trials (Circulation / WAHA; umbrella review of nut trials: Nutrients 2023). Use both for complementary benefits.
Black Walnut Benefits vs. English Walnuts for Men
Not all walnuts are the same. The two most common varieties are English walnuts (the type most people eat daily) and black walnuts (a more earthy, slightly bitter variety).
- English walnuts are milder in taste and packed with polyunsaturated fats, antioxidants, and protein. They are ideal for daily consumption.
- Black walnuts are richer in certain phytochemicals and have been used in traditional remedies for gut health and detoxification. They are less common in regular diets but can add variety and additional nutrients.
For men, English walnuts provide the most researched benefits for heart, brain, and reproductive health, while black walnuts are worth trying for their digestive and cleansing properties.
Most human data are on English (Persian) walnuts; black walnut claims are mainly compositional/traditional.

Moving into the next section:
Interestingly, the use of walnuts for men’s health isn’t just modern science. Traditional systems like Ayurveda have long considered akhrot a food for vitality and longevity. Let’s explore that perspective.
Akhrot Benefits in Ayurveda and Traditional Medicine for Men
Long before modern nutrition science, walnuts (akhrot) were recognized in traditional healing systems for their ability to strengthen the body and mind. In Ayurveda, Unani, and Persian medicine, walnuts were often prescribed to men for vitality, fertility, and overall health.
Akhrot Benefits for Men’s Vitality
In Ayurveda, akhrot is classified as a food that balances Vata and supports Ojas — the essence of vitality and immunity. For men, this translates into better stamina, stronger immunity, and improved reproductive health. Eating a few soaked walnuts daily was often recommended as a tonic for strength and endurance.
Akhrot Benefits for Reproductive and Sexual Health
Walnuts have long been considered an aphrodisiac in traditional medicine. They were believed to improve sperm quality, increase stamina, and support hormonal balance. Modern studies echo these ancient beliefs, showing that walnut consumption can indeed improve reproductive health in men.
Akhrot as a Brain and Nerve Tonic
Because of their rich omega-3 content and unique shape, walnuts were also linked with brain health in ancient medicine. They were believed to sharpen memory, calm the nerves, and reduce stress — benefits that men balancing work and family life still need today.
Walnuts’ healthy fats and polyphenols make them a smart addition to a brain-focused diet (see Foods for Memory and Brain Health).
Other Traditional Uses of Akhrot
Beyond men’s vitality, walnuts were also used for:
- Improving digestion and gut health
- Reducing joint pain
- Enhancing skin glow when used as oil or paste
These uses highlight how deeply walnuts were integrated into traditional wellness practices — not just as food, but as a natural remedy.
Finally moving to to conclusion:
With both modern research and traditional wisdom pointing to their power, walnuts truly deserve superfood status. Let’s wrap up with why every man should make them a part of his daily routine.
Conclusion – Why Every Man Should Add Walnuts (Akhrot) to His Routine
From heart protection and sharper brain function to enhanced reproductive health and improved fitness, walnuts truly live up to their reputation as a superfood for men. Backed by both traditional wisdom and modern science, akhrot delivers a rare combination of nutrients — omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, protein, and essential minerals — that directly support men’s health needs.
For men concerned about stamina, fertility, or simply maintaining long-term vitality, even a small daily serving can make a difference. Just 4 to 7 walnuts a day — whether raw, soaked, or in the form of cold-pressed walnut oil — is enough to boost energy, balance hormones, and protect against chronic diseases.
What makes walnuts even more valuable is their versatility. They can be eaten on their own, added to breakfast bowls, blended into smoothies, or used as a drizzle of walnut oil over salads. However you choose to enjoy them, consistency is key.
The bottom line? Walnuts are more than just a snack — they’re an investment in men’s health. By making them a regular part of your diet, you’re not only fueling your body today but also building a foundation for strength, vitality, and longevity in the years to come.

Frequently Asked Questions on Walnut Benefits for Men
1. Are walnuts good for men’s health?
Yes, walnuts are excellent for men’s health. They provide omega-3 fatty acids, protein, and minerals that support the heart, brain, and reproductive system. Regular consumption improves circulation, reduces bad cholesterol, and strengthens immunity. In short, the walnut benefits for men are both wide-ranging and scientifically proven.
Trials show LDL-C reduction and vascular benefits (Circulation / AHA) and an RCT supports sperm quality gains (Biology of Reproduction). These are core walnut benefits for men.
2. How many walnuts should a man eat daily?
Most experts recommend 4 to 7 walnuts per day. This amount is enough to provide nutrients like magnesium, zinc, and antioxidants without adding excess calories. Eating this small serving consistently is far more effective than consuming large amounts occasionally.
Most cardiovascular trials use ~1–2 oz (28–56 g/day); fertility RCT used 75 g/day (Circulation; Biology of Reproduction).
3. Do walnuts increase testosterone levels in men?
Walnuts don’t directly raise testosterone, but they contain nutrients such as zinc, magnesium, and healthy fats that support hormonal balance. These factors help maintain optimal testosterone levels and overall vitality in men.
4. What are the sexual health benefits of walnuts for men?
Studies suggest that walnuts may improve sperm quality, motility, and reproductive function. Their omega-3s also improve circulation, which supports stamina and performance. This makes sexual health one of the most important walnut benefits for men.
5. Is it better to eat soaked walnuts or raw walnuts?
Both forms are healthy, but soaked walnuts are easier to digest and may allow better nutrient absorption. Raw walnuts are crunchy, quick, and equally nutrient-rich. Men with sensitive digestion may prefer soaked walnuts.
6. Should men eat walnuts in the morning or at night?
Walnuts can be eaten at both times. Morning consumption provides lasting energy, helps curb cravings, and supports weight management. Eating walnuts at night supports better sleep because they contain melatonin, a natural sleep regulator.
7. Are walnuts good for men with diabetes?
Yes, walnuts can be beneficial for men with diabetes. Their fiber and healthy fats slow down sugar absorption, which helps regulate blood sugar. Eating walnuts regularly may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of complications.
Some trials in metabolic syndrome/at-risk adults show lower fasting glucose and better endothelial function with walnut intake (Nutrients; Diabetes Care; BMJ Open DRC).
8. How do walnuts compare with almonds for men’s health?
Almonds are excellent for vitamin E and bone health, while walnuts are superior for omega-3 fatty acids, brain support, and reproductive health. Together, they make a powerful combination. But when it comes to fertility and heart health, walnut benefits for men are more significant than almonds.
9. What are the benefits of walnut oil for men?
Cold-pressed walnut oil supports heart health, improves cholesterol, and provides omega-3s in an easy-to-use form. Externally, it nourishes skin, strengthens hair, and may even enhance vitality. Walnut oil is a versatile way for men to enjoy the benefits of akhrot.
10. Do walnuts help with weight loss for men?
Yes, walnuts can support weight management. Their combination of protein, fiber, and healthy fats helps men feel fuller for longer, reducing the urge to snack on unhealthy foods. Despite being calorie-dense, they are excellent for sustainable weight control.