In a world dominated by pharmaceuticals, it’s refreshing to rediscover natural remedies that have stood the test of time. Kalonji, also known as Nigella sativa, black seed, or black cumin, is one such wonder seed. Revered in traditional medicine and increasingly validated by modern science, Kalonji seeds offer a treasure trove of health benefits that make them a must-have in your kitchen and wellness routine.
In this post, we take a deep, research-backed dive into the top six health benefits of Kalonji, with a practical lens for daily life application.
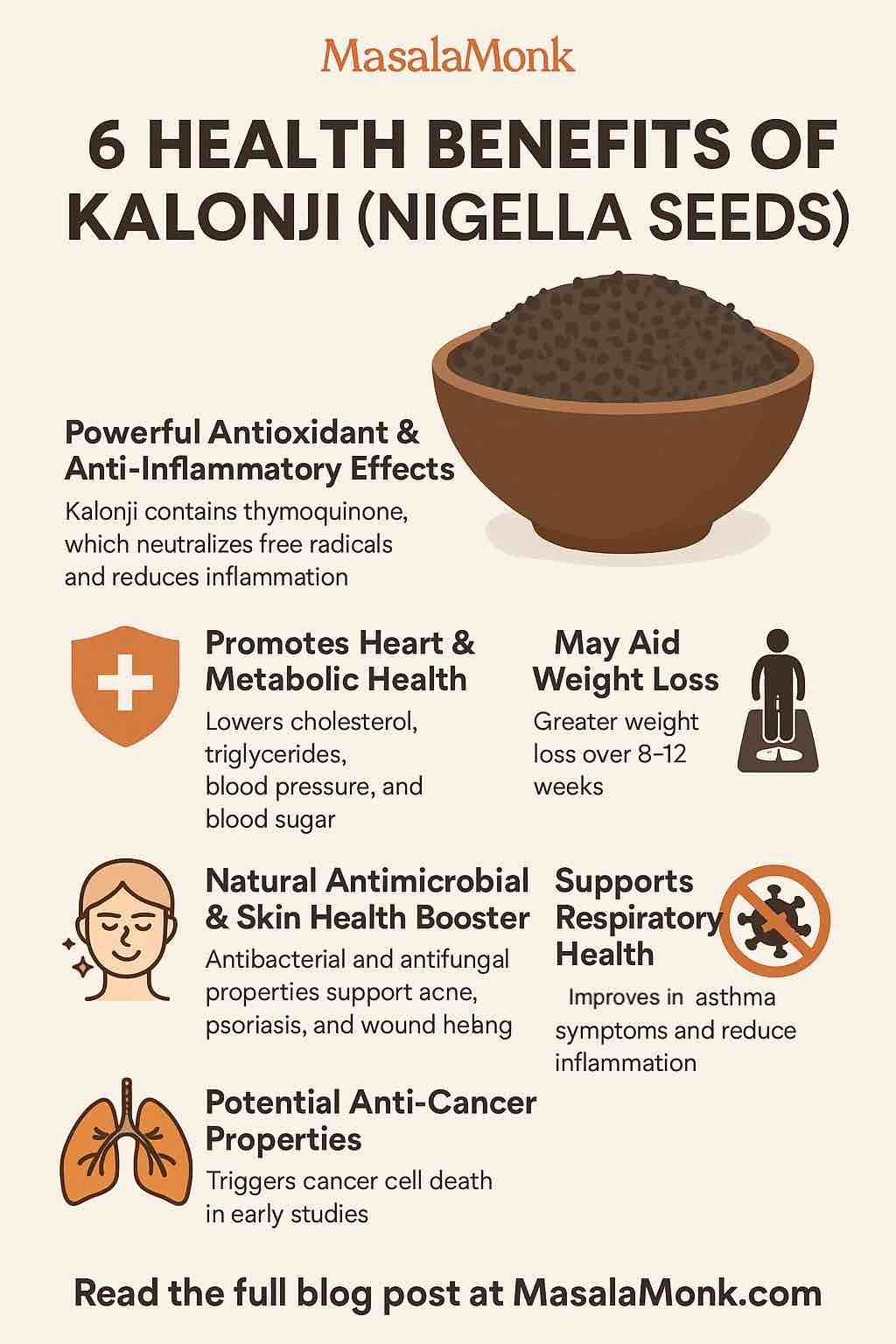
1. Cardiometabolic Health: A Natural Ally for Your Heart and Metabolism
Modern clinical studies (2023-2025) have confirmed that Kalonji significantly improves key markers of cardiometabolic health, including:
- Lowering LDL (“bad”) cholesterol
- Reducing triglycerides
- Improving fasting blood glucose and HbA1c
- Decreasing blood pressure
Practical Tip: Add 1/2 to 1 teaspoon of Kalonji seeds (toasted lightly) into your morning smoothie, yogurt, or sprinkle over salads. If you prefer oil, 1 to 2.5 mL per day is a typical dosage.
2. Blood Sugar Control: A Diabetic-Friendly Supplement
Multiple 2024–2025 randomized controlled trials suggest that Nigella sativa helps reduce HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose, and insulin resistance — making it particularly useful for people with Type 2 Diabetes or prediabetes.
How it works: Thymoquinone, the key active compound, improves insulin sensitivity and supports pancreatic beta-cell function.
Practical Tip: Pair a small dose (1–2 g of seed powder) with your main meals for glycemic balance. Always consult your doctor before adding it if you’re on anti-diabetic medication.
3. Potent Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects
Kalonji seeds are rich in thymoquinone, carvacrol, and other potent antioxidants. These compounds reduce oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha and IL-6, implicated in various chronic conditions such as arthritis, neurodegeneration, and metabolic syndrome.
Practical Tip: Make a tea by steeping 1 tsp of crushed Kalonji seeds in hot water with a slice of ginger and lemon. Sip this after heavy meals or during inflammation flare-ups.
4. Respiratory Relief: Asthma, Allergies & More
Recent trials (2024) have found that Kalonji oil helps reduce asthma severity and allergic symptoms by acting as a bronchodilator and immunomodulator. It improves FEV1 (a marker of lung function) and reduces inflammatory markers in the respiratory tract.
Practical Tip: Mix 1/2 teaspoon of Kalonji oil with honey and take it once a day during allergy season or when experiencing mild respiratory symptoms.
5. Skin Health and Wound Healing
From acne and eczema to vitiligo and wounds, Kalonji’s antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects make it an excellent addition to your skincare routine. Studies show topical use can reduce acne severity and speed up healing.
Practical Tip: Apply a mixture of Kalonji oil and aloe vera gel to affected skin areas. For acne, dab a small amount directly onto the pimple.
6. Immune System Modulation
Emerging research from 2024–2025 demonstrates that Kalonji boosts immune responses by increasing CD4+ T cells and modulating key cytokines. This may explain its historical use in preventing infections and supporting recovery from illness.
Practical Tip: During cold and flu season, take 1 teaspoon of Kalonji oil with warm water and a pinch of turmeric to enhance your body’s natural defense mechanisms.
Final Thoughts
Kalonji is not a miracle cure, but when used consistently and wisely, it can complement modern treatments and enhance overall wellness. Whether you’re managing blood sugar, improving heart health, supporting your immune system, or taking care of your skin — this tiny seed packs a powerful punch.
Important Reminder: Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have existing conditions or take medications.
So next time you’re stocking up your pantry, don’t forget to add Kalonji — a humble seed with heavyweight benefits.
Have you tried Kalonji? Share your experience or questions in the comments!
🔍 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the best way to consume Kalonji for health benefits?
The most common ways include consuming whole seeds (toasted or raw), seed powder, or Kalonji oil. It can be added to food or taken directly in small doses. Oil is especially popular for skin, respiratory, and immune uses.
2. How much Kalonji should I take daily?
Typical daily doses are 1–3 grams of seeds or 1–2.5 mL of oil. Always start with the lower end and increase gradually. Consult a healthcare provider if you have any medical conditions.
3. Can Kalonji be taken with other supplements or medications?
Yes, but caution is advised. Kalonji may interact with medications for diabetes, hypertension, or immune suppression. Always check with your doctor before combining it with pharmaceuticals.
4. Is Kalonji safe for children or pregnant women?
While small dietary amounts are likely safe, therapeutic doses of Kalonji oil or powder should be avoided during pregnancy and in young children unless under medical supervision.
5. Does Kalonji help with weight loss?
Studies show Kalonji can modestly support weight loss by improving metabolism and reducing appetite, especially when paired with a healthy diet and exercise.
6. Can Kalonji cure diseases like diabetes or cancer?
No. Kalonji is not a cure, but it may help manage symptoms or reduce risk factors. It should be seen as a complementary therapy, not a replacement for medical treatment.
7. How long does it take to see results from Kalonji?
Some benefits, like improved digestion or reduced bloating, may appear in days. Others, such as blood sugar control or skin improvement, typically require consistent use over 4–12 weeks.
8. What does Kalonji taste like?
It has a slightly bitter, peppery flavor with hints of oregano and onion. It blends well with savory dishes, pickles, and bread toppings.
9. Can I apply Kalonji oil directly to the skin?
Yes, it can be used topically, especially when mixed with carrier oils like coconut or aloe vera gel. Do a patch test first to check for sensitivity.
10. Where can I buy good-quality Kalonji?
Look for organic, cold-pressed Kalonji oil and whole seeds from trusted herbal or Ayurvedic retailers. Ensure there are no additives or fillers.