Inflammation is the body’s natural defense mechanism — a vital process that helps heal injuries and fight off infections. But when inflammation lingers too long, it becomes chronic, silently fueling numerous health problems such as heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, and even mental health disorders.
This is where omega-3 fatty acids come into play — nature’s powerful anti-inflammatory agents. Found abundantly in fatty fish, certain nuts, and seeds, omega-3s have captured scientific attention for their profound role in reducing chronic inflammation and promoting overall health.
In this post, we’ll dive deep into the science behind omega-3 fatty acids, explore how they combat chronic inflammation, and offer practical tips to harness their benefits in your daily life.
What Is Chronic Inflammation and Why Does It Matter?
Before understanding how omega-3s work, it’s important to grasp what chronic inflammation really means.
Inflammation is the immune system’s response to harmful stimuli—like pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Acute inflammation is short-lived and beneficial, marked by redness, swelling, and pain that fade as healing occurs.
Chronic inflammation, however, is low-grade and persistent. Instead of protecting, it causes ongoing damage to tissues and organs. This silent inflammation has been linked to:
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis
- Type 2 diabetes
- Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s
- Some cancers
Reducing chronic inflammation is a key strategy in preventing and managing these diseases.
Meet Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Inflammation Fighters
Omega-3 fatty acids are a group of polyunsaturated fats essential to human health. The main types include:
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA)
EPA and DHA are primarily found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, while ALA is sourced from plant foods such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
Our bodies can convert ALA into EPA and DHA, but the process is inefficient, making direct dietary intake of EPA and DHA critical.
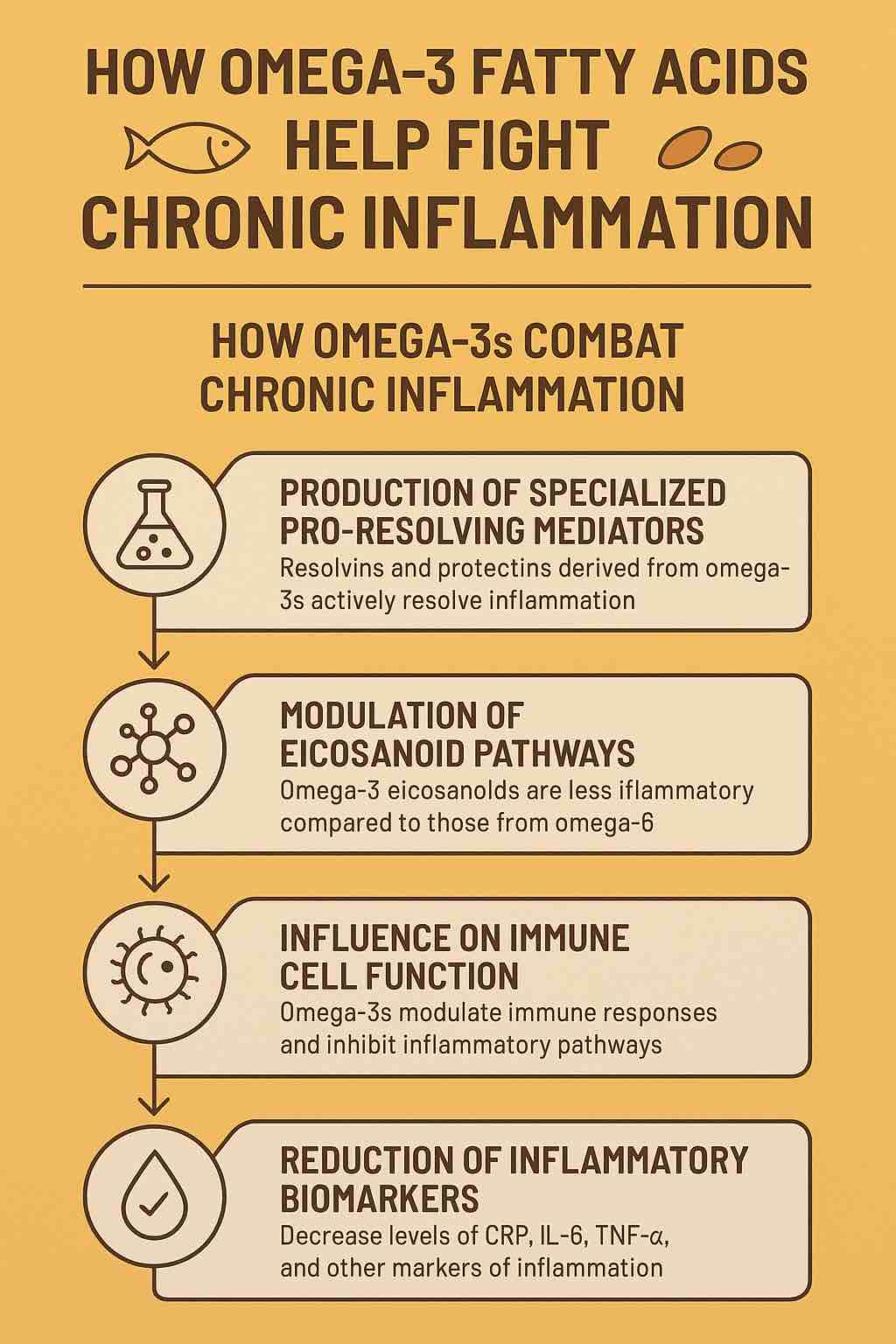
How Do Omega-3s Combat Chronic Inflammation?
Omega-3s employ several remarkable mechanisms to reduce chronic inflammation:
1. Production of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs)
Once consumed, EPA and DHA are transformed into molecules called resolvins, protectins, and maresins—collectively known as Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators.
Unlike classic anti-inflammatory drugs that block inflammation, these SPMs actively resolve inflammation by:
- Inhibiting pro-inflammatory molecules
- Clearing out dead cells and debris
- Promoting tissue repair
This resolution process helps restore immune balance without suppressing it entirely.
2. Modulating Eicosanoid Pathways
Eicosanoids are signaling molecules derived from fatty acids that regulate inflammation.
Omega-6 fatty acids, common in processed foods, tend to produce pro-inflammatory eicosanoids. Omega-3s, on the other hand, lead to less inflammatory or even anti-inflammatory eicosanoids.
By shifting this balance toward omega-3 derived eicosanoids, omega-3s help dial down the inflammatory response.
3. Regulating Immune Cell Function
Omega-3s influence immune cells like macrophages and T-cells by affecting receptor signaling (e.g., Toll-like receptors and TNF-alpha receptors). This modulation reduces the activation of inflammatory pathways and dampens chronic inflammation.
4. Lowering Inflammatory Biomarkers
Studies show that omega-3 supplementation can significantly decrease levels of:
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
- Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)
These markers are often elevated in chronic inflammatory conditions and serve as measurable signs of inflammation reduction.
Health Benefits Beyond Fighting Inflammation
Omega-3 fatty acids contribute to health far beyond inflammation control:
- Heart Health: Lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure, and decrease risk of heart attacks.
- Brain Function: Support cognitive health, reduce depression risk, and may slow cognitive decline.
- Joint Health: Alleviate symptoms of arthritis, reducing joint pain and stiffness.
- Liver Health: Improve liver fat levels and reduce inflammation in fatty liver disease.
How to Get Enough Omega-3s in Your Diet
To enjoy these benefits, aim to incorporate omega-3-rich foods into your diet:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, anchovies — aim for at least two servings per week.
- Plant Sources: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, hemp seeds, and algae-based supplements.
- Supplements: Fish oil or algae oil capsules can help, especially for those who don’t consume enough omega-3 foods. Consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements.
Tips for Maximizing Omega-3 Benefits
- Choose wild-caught fatty fish where possible for better nutrient profiles.
- Grind flaxseeds before eating to improve absorption.
- Balance omega-6 intake by reducing processed foods and oils high in omega-6.
- Pair omega-3 rich meals with antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables to further reduce inflammation.
Final Thoughts: Harness the Power of Omega-3s to Fight Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a stealthy threat to health, but omega-3 fatty acids offer a natural, scientifically-backed way to combat it.
By understanding their powerful anti-inflammatory mechanisms and making omega-3s a regular part of your diet, you can support your body’s defenses and promote long-term well-being.
Ready to take control of inflammation? Start by adding more omega-3 rich foods to your plate today.
For more detailed insights, recipes, and wellness tips on omega-3s and inflammation, visit MasalaMonk.com. Your journey to better health starts here!
FAQs on How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Help Fight Chronic Inflammation
1. What are omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential polyunsaturated fats that the body cannot produce on its own. They must be obtained through diet or supplements and include EPA, DHA (mostly from fish), and ALA (from plant sources).
2. How do omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation?
They reduce inflammation by producing specialized molecules called resolvins and protectins that help resolve inflammation, modulating inflammatory pathways, and lowering inflammatory biomarkers such as CRP and TNF-alpha.
3. Which foods are the best sources of omega-3s?
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are the richest sources. Plant-based options include flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and algae-based supplements.
4. How much omega-3 should I consume daily?
Most health organizations recommend about 250-500 mg combined EPA and DHA daily for healthy adults, which can typically be met by eating fatty fish twice a week. Individual needs may vary.
5. Can omega-3 supplements replace dietary sources?
Supplements can be helpful, especially for those who don’t eat fish, but whole foods provide additional nutrients and benefits. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements.
6. Are omega-3s safe for everyone?
For most people, omega-3s are safe when consumed in recommended amounts. However, high doses may interact with blood-thinning medications, so consult your doctor if you have any health conditions or take medications.
7. How quickly can omega-3s reduce inflammation?
While some effects on inflammatory markers can be seen within weeks, significant benefits often take several months of consistent omega-3 intake.
8. Can omega-3s help with arthritis symptoms?
Yes, omega-3s have been shown to reduce joint pain and stiffness in rheumatoid arthritis by decreasing inflammation.
9. Do plant-based omega-3s provide the same benefits as fish-based ones?
ALA from plants must be converted into EPA and DHA in the body, but conversion rates are low. Algae-based DHA supplements can be a direct plant-based alternative.
10. How do omega-3s compare to anti-inflammatory drugs?
Omega-3s help resolve inflammation naturally without suppressing immune function like some drugs do, making them a beneficial complement for long-term inflammation management.













