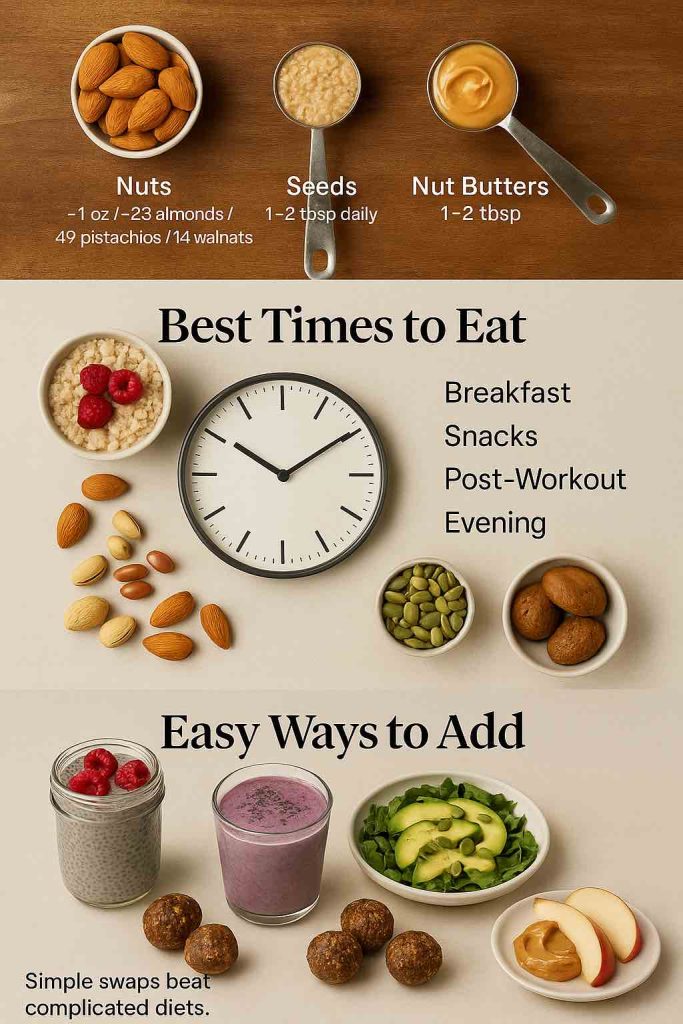
When joints hurt, daily choices matter. It’s natural to ask which foods to avoid with arthritis and which to lean on for relief. No single food causes or cures arthritis. Yet patterns add up. The right pattern calms inflammation. The wrong one turns up the volume. This guide stays practical. You’ll find a clear list of arthritis foods to avoid, short reasons, and easy swaps you can live with. Then, you’ll see what to add to your plate, so eating feels generous rather than strict.
Quick notes before we begin. Bodies differ. If one item here never bothers you, you may not need to cut it completely. And then – food works best alongside your care plan. Therefore, loop in your clinician, especially if you take disease-modifying drugs
⚠️ Educational medical disclaimer
This guide is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. It does not diagnose, treat, or replace care from your clinician. Always consult your healthcare professional—especially if you take DMARDs (e.g., methotrexate), blood thinners, have gout/kidney disease, diabetes, or other conditions. Stop any new food/supplement that seems to worsen symptoms and check with your clinician. In an emergency, seek urgent medical care.
How to use this list without becoming strict or stressed
Perfection is impossible; progress is powerful. Therefore, start with two or three changes you can keep and build from there. Moreover, think in patterns rather than “good” vs “bad.” The more your meals tilt toward fiber-rich plants, steady protein, whole grains, and olive oil—and the fewer ultra-processed, deep-fried, and sugar-heavy items you lean on—the better your joints and energy tend to feel. Finally, keep taste big: herbs, spices, citrus, garlic, and vinegar make healthy food craveable.
Before the list, a quick roadmap: first, prioritize pattern over perfection; small swaps compound. Second, read labels so you spot arthritis foods to avoid before they land in the cart. Finally, keep flavor high—because when meals taste great, healthier choices stick. For a step-by-step primer, see our post on how to follow an anti-inflammatory diet.
12 Foods to Avoid With Arthritis (and Better Choices)
Use these entries as modular blocks. Tackle the ones that show up most in your week, and adjust with your clinician’s advice.
1) Added sugars – a top food to avoid with arthritis
Why it matters: frequent sugar hits can amplify inflammatory signaling and, just as importantly, push weight upward—extra load that knees and hips must carry. Consequently, pain and fatigue often follow.
Where it hides: desserts, candy, flavored yogurts, granola bars, sweet sauces, “healthy” bakery muffins.
Label tips: on packaged foods, check “Added sugars.” Words like sucrose, corn syrup, dextrose, or malt syrup are clues.
Instead: fruit for daily sweetness; plain yogurt with berries; a small square of dark chocolate after dinner.
Learn more: Anti-inflammatory diet basics – Arthritis Foundation
Small cuts here quickly reduce a major share of the foods to avoid with arthritis in everyday routines.
Also Read: Cherries and Arthritis: Are Cherries Good for Arthritis?
2) Sugar-sweetened beverages
Why it matters: liquid sugar bypasses fullness signals; consequently, it’s easy to rack up calories without noticing. Meanwhile, sweet drinks crowd out water and unsweetened options.
Where it hides: regular soda, sweet tea, energy drinks, juice cocktails, coffee drinks with syrups.
Label tips: if sugar is a top-three ingredient, rethink it.
Instead: water, unsweetened tea/coffee, or sparkling water with citrus. For ideas that go beyond plain water, read our post on and try these anti-inflammatory drinks.
Plate help: Mediterranean diet guide – Mayo Clinic
3) Ultra-processed snacks and ready meals — everyday foods to avoid with arthritis
Why it matters: UPFs often combine refined starch, added sugar, sodium, and industrial fats. As a result, they pull your day away from the joint-friendly balance you want. Nevertheless, convenience can be non-negotiable; the trick is choosing better quick options.
Where it hides: instant noodles, packaged pastries, many “diet” snacks, freezer meals with long ingredient lists.
Label tips: multiple sweeteners, several refined oils, and flavor enhancers are red flags.
Instead: simple home meals most days; roasted pulses, nuts, or air-popped popcorn for crunch.
Everyday blueprint: The Ultimate Arthritis Diet – Arthritis Foundation
Because UPFs crowd out fiber and healthy fats, they’re among the foods to avoid with arthritis when you want calmer days.

4) Red and processed meats
Why it matters: these bring more saturated fat and, frequently, hefty sodium. In rheumatoid and osteoarthritis, that combo doesn’t help inflammation or heart health; meanwhile, large meat portions crowd out fish, beans, and plants.
Where it hides: bacon, sausages, deli meats, hot dogs, large steaks, salty jerky.
Label tips: “cured,” “smoked,” “salted,” or “nitrates/nitrites” usually signal processing.
Instead: fish, poultry, tofu/tempeh, or beans. If you love red meat, shrink the portion and frequency; make vegetables the star.
Care framework: 2019 ACR/AF Osteoarthritis Guideline (open access)
5) Deep-fried foods
Why it matters: deep frying adds oxidation products and extra calories; plus, fried meals usually arrive with refined sides and sugary drinks—a triple hit. Even so, you can keep the crunch with better methods.
Where it hides: fries, battered fish or chicken, tempura platters, doughnuts.
Label tips: on menus, “crispy,” “battered,” or “fried” almost always means deep oil.
Instead: bake, grill, pan-sear, or air-fry; season boldly with spices, citrus, garlic, and herbs.
Behavioral anchors: NICE Osteoarthritis Guideline NG226
Also Read: Apple Cider Vinegar for Arthritis & Joint Pain: Myths vs Facts
6) Refined grains
Why it matters: fast-digesting starches spike blood sugar and crowd out fiber-rich staples; consequently, inflammation control gets harder and energy swings wider.
Where it hides: white bread, many crackers, pastries, “breakfast” cookies, standard bakery muffins.
Label tips: choose products with “whole” as the first grain; be wary when “enriched wheat flour” leads.
Instead: oats, brown rice, quinoa, dense whole-grain breads, and legumes.
Neutral how-to: Mediterranean diet overview – British Dietetic Association
Swapping to whole grains steadily replaces several arthritis foods to avoid without feeling restrictive.
7) High-salt packaged foods — stealth arthritis foods to avoid
Why it matters: salt itself isn’t the sole culprit. Nevertheless, salty convenience foods travel with the same UPF pattern you’re reducing. Meanwhile, cardiometabolic health influences arthritis outcomes.
Where it hides: instant noodles, many canned soups, cured meats, snack mixes, flavored rice/pasta packets.
Label tips: if sodium tops ~20% DV per serving, consider a swap or portion control.
Instead: cook more at home; finish dishes with lemon, vinegar, pepper, herbs, and garlic to create brightness without extra sodium.
Lifestyle context: EULAR lifestyle recommendations – Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases
8) When omega-6–heavy processed oils dominate
Why it matters: omega-6 fats aren’t villains; however, low omega-3 intake combined with many omega-6-rich processed foods may tilt inflammatory pathways. Balance, therefore, helps more than bans.
Where it hides: packaged snacks, commercial baked goods, fast-food fryers, shelf-stable dressings.
Label tips: long ingredient lists with multiple refined seed oils and no omega-3 sources.
Instead: add omega-3s consistently—fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) or, if plant-forward, flax, chia, and walnuts. For an easy daily habit, read our post and see how to use flax seeds daily. Discuss supplements with your clinician if needed.
Evidence overview: Omega-3s in rheumatoid arthritis – review of trials (open access)
Also Read: Tomatoes and Arthritis: The Truth Unveiled.
9) Oversized portions
Why it matters: portion creep is quiet but powerful. Extra body mass increases joint load—especially at knees and hips—and pain often rises; consequently, trimming portions pays off even before the scale moves.
Where it hides: all-you-can-eat buffets, supersized combos, bottomless baskets, shareable plates that equal two meals.
Label tips: restaurant nutrition sheets (where available) help; otherwise, split dishes or box half.
Instead: use a plate rule—½ vegetables, ¼ protein, ¼ whole grains or starchy veg. Serve from the stove, not the table, to curb automatic seconds.
Trial data: 18-month knee OA RCT: weight↓, IL-6↓, load↓, pain↓
Managing portions is a quiet way to trim hidden foods to avoid with arthritis while easing joint load.
10) Fast-food “combo” meals
Why it matters: refined bun + fried side + sugary drink equals three problems in one order. Nevertheless, convenience is sometimes necessary; thoughtful edits blunt the impact.
Where it hides: value meals and “box” deals.
Label tips: watch the drink and side; they often double the trouble.
Instead: order a single item and pair it with salad and water; or make a lighter “copycat” at home with whole-grain buns and oven wedges.
Real-world program: Diet + exercise for knee OA – JAMA RCT
Deconstructing combos helps you skip multiple foods to avoid with arthritis in a single decision.
11) Alcohol (context with RA/OA medications)
Why it matters: for many with arthritis—especially those on methotrexate or other DMARDs—alcohol is mainly about liver safety and medication interactions. Therefore, your safest intake is individualized.
Where it hides: beer, wine, spirits, cocktails with sugary mixers.
Label tips: none on menus; set a personal cap in advance and alternate with water.
Instead: alcohol-free beer/spirits; seltzer with citrus; smaller pours with food.
Plain-English guidance: NHS – Methotrexate: common questions
Also Read: Gin Soaked Raisins for Arthritis
12) High-purine meats/seafood—only if your arthritis is gout
Why it matters: gout is a specific arthritis with clearer diet fingerprints. Organ meats; certain fish/shellfish (anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, trout, tuna); beer/spirits; and HFCS have stronger links to flares. If you live with RA or OA, do not borrow gout rules you may not need.
Where it hides: liver and sweetbreads; the fish above; sweetened beverages with HFCS; beer and some spirits.
Label tips: “sweetened with high-fructose corn syrup” is a clue.
Instead: portion-controlled lower-purine proteins, steady hydration, and your prescribed meds. For a detailed handout, read our post and see the gout diet: what to eat & what to avoid (PDF).
Neutral overview: CDC – Learn about gout
Why These Arthritis Trigger Foods Make Symptoms Worse
In brief, ultra-processed mixes, sugary inputs, and deep-fried methods push your pattern away from fiber, polyphenols, and healthy fats. Conversely, meals built on plants, lean or plant proteins, and whole grains tend to calm things down. Therefore, think subtraction and addition.
⚠️ Educational medical disclaimer
This guide is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. It does not diagnose, treat, or replace care from your clinician. Always consult your healthcare professional—especially if you take DMARDs (e.g., methotrexate), blood thinners, have gout/kidney disease, diabetes, or other conditions. Stop any new food/supplement that seems to worsen symptoms and check with your clinician. In an emergency, seek urgent medical care.
What to Eat When You’re Avoiding Foods That Worsen Arthritis
Lists of things to limit can feel punishing. Consequently, it’s vital to add foods that make the pattern satisfying. A Mediterranean-style approach—vegetables and fruit, whole grains, legumes, nuts and seeds, extra-virgin olive oil, and regular fish—hits that sweet spot. You get fiber and polyphenols for gut and immune health. You also get healthy fats for the heart, which matters in RA and OA. Meanwhile, it’s flexible enough for busy weeks. For ideas, browse our post and see these anti-inflammatory foods to add.

A repeatable plate (use at lunch and dinner):
- Half non-starchy vegetables (raw, roasted, sautéed, or soup).
- Quarter protein (fish, beans/lentils, tofu/tempeh, or poultry).
- Quarter whole grains or starchy veg (oats, brown rice, quinoa, sweet potato).
- Finish with olive oil, nuts, or seeds; drink water or unsweetened tea.
If you like an arthritis-specific map, this primer is helpful: The Ultimate Arthritis Diet – Arthritis Foundation. For a neutral “how-to,” the BDA’s overview is also clear: Mediterranean diet – British Dietetic Association.
When this plate is your default, the foods to avoid with arthritis become occasional treats instead of daily habits.
And for a step-by-step living guide, see our post how to follow an anti-inflammatory diet.
Supporting moves that make food changes work
Omega-3s as a steady habit: EPA/DHA from fish—and, when appropriate, supplements—show signals for less morning stiffness and fewer tender joints in inflammatory arthritis. Start with food; discuss supplements with your clinician if needed. Evidence recap: Omega-3s in RA – review (open access).
Weight and OA symptoms: even modest, sustained weight loss reduces knee or hip load and eases pain. Notably, trials show diet (± exercise) lowers inflammatory markers and improves function. For fundamentals and targets, see: ACR/AF OA Guideline and NICE NG226. For selected patients, medication-assisted loss can help; semaglutide produced greater weight loss and larger pain reductions in a 2024 trial: NEJM – semaglutide in obesity + knee OA.
Keeping Arthritis-Unfriendly Foods in Check—Day to Day
First, swap, don’t only subtract. If you drop soda, add sparkling water with citrus. If you skip deep-fried sides, add roasted vegetables with bold seasoning. Second, shape the default plate. When half the plate is plants, choices downstream get easier. Third, track briefly. Two to four weeks of notes on meals, sleep, stress, movement, and symptoms reveal patterns you can act on. Finally, partner with your clinician. Especially if you take DMARDs, manage multiple conditions, or consider supplements or weight-loss medication.
FAQs
1) What are the top foods to avoid with arthritis?
Generally, steer clear of ultra-processed snacks, sugary drinks, deep-fried foods, refined grains, and oversized portions. These patterns tend to drive inflammation and weight gain; therefore, your joints often feel worse.
2) What are the five worst foods for rheumatoid arthritis?
If we must pick five culprits: sugary drinks, deep-fried items, ultra-processed snacks, large portions of red/processed meats, and refined pastries. However, portion size and frequency matter as much as the food itself.
3) Which vegetables to avoid for arthritis?
There isn’t a universal “do-not-eat” veg list. That said, if nightshades (potatoes, tomatoes, peppers) seem to flare your symptoms, try a short remove-and-re-introduce test; otherwise, vegetables are allies.
4) Are there fruits to avoid with arthritis?
Not usually. Moreover, most fruits help due to fiber and polyphenols. If concentrated juices or dried fruit spike your sugar, choose whole fruit and watch portions.
5) What foods irritate arthritis pain the most?
Frequently: sugar-sweetened beverages, deep-fried fare, and highly processed snack foods. Consequently, reducing those while adding fiber-rich meals often helps.
6) What foods should be avoided with rheumatoid arthritis specifically?
The same culprits apply, but consistency matters more. Additionally, many people with RA feel better with regular omega-3-rich fish, fewer ultra-processed foods, and moderated alcohol—especially with DMARDs.
7) What foods to avoid with arthritis in hands?
There’s no hand-specific list. Even so, day-to-day inflammation drivers—sugary drinks, fried combos, and heavy processed meats—can worsen hand stiffness indirectly; small, steady swaps still help.
8) What foods to avoid with arthritis in hip (or knees)?
Again, no unique foods just for hips or knees. Nevertheless, trimming calorie-dense meals and fast-food combos reduces body load on weight-bearing joints, which often eases pain.
9) What foods to avoid with arthritis in fingers or feet?
Focus on the same pattern: fewer ultra-processed and fried foods, more plants, and balanced portions. Meanwhile, keep shoes comfortable and movement gentle to complement diet changes.
10) Is chicken bad for arthritis?
Not inherently. In fact, baked or grilled chicken can be a helpful protein swap compared with processed meats or fried options. However, skip heavy breading and sugary sauces.
11) Are potatoes bad for arthritis?
Not by default. But, large portions of fries or chips are a different story. Instead, try roasted new potatoes with olive oil and herbs—much friendlier for joint health.
12) Is corn bad for arthritis?
Plain corn in balanced portions is fine for most people. However, corn syrups in sweetened drinks and ultra-processed snacks can push you toward patterns you’re trying to avoid.
13) Are fried eggs bad for arthritis?
Eggs themselves aren’t the issue; rather, it’s the frying and the sides. Therefore, poach or soft-boil the eggs and pair them with vegetables or whole-grain toast.
14) Are pistachios bad for arthritis?
No—unsalted pistachios can be a smart snack. Nevertheless, watch portions if weight management is a goal, and avoid heavily salted or candy-coated versions.
15) What foods can make arthritis worse quickly?
For many readers: sugary beverages, deep-fried foods, and stacked fast-food combos. Consequently, swapping the drink to water and the side to salad can help almost immediately.
16) What foods to avoid for arthritis inflammation?
Think patterns: sugary drinks, refined pastries, ultra-processed snacks, and frequent fried meals. Meanwhile, build meals around vegetables, beans, fish, whole grains, and olive oil.
17) What foods to avoid for joint pain during flares?
During tougher weeks, keep meals simple and lower in salt and sugar. Moreover, choose baked/roasted proteins, lots of veg, whole grains, and steady hydration.
18) What are good alternatives to the foods to avoid with arthritis?
Swap soda → sparkling water with citrus; fries → roasted potatoes; deli meats → beans, fish, or grilled chicken; pastries → fruit + yogurt. Consequently, you’ll cut several triggers at once.
19) What foods to avoid for rheumatoid arthritis—a short list?
Prioritize cutting: sugar-sweetened drinks, deep-fried items, ultra-processed snacks, and frequent red/processed meats. Then, add omega-3 fish twice weekly for balance.
20) What foods to avoid for arthritis patients who eat out?
Avoid the “combo trap”: refined bun + fried side + sugary drink. Instead, order a single grilled item, add a side salad, and choose water or unsweetened tea.
21) What foods to avoid with rheumatism (older term for arthritis)?
“Rheumatism” is broad, but the same modern guidance applies. Therefore, trim ultra-processed foods, sugary beverages, and deep-fried items; then focus on fiber- and omega-3-rich meals.
22) What are bad foods for arthritis on one short list?
Sugary drinks, deep-fried foods, ultra-processed snacks, refined pastries, and large portions of processed meats. However, remember: frequency and portion size decide the real impact.
23) What are the five vegetables to avoid for arthritis?
There isn’t a universal five-veg blacklist. Nevertheless, if you notice consistent symptoms with a specific vegetable (for example, a nightshade), test it thoughtfully and re-introduce to confirm.
24) What foods to avoid with arthritis—Ayurveda perspective?
Ayurveda often suggests limiting overly heavy, fried, or very spicy foods, and favoring warm, digestible meals. Meanwhile, it encourages mindful eating, ginger, turmeric, and balanced routines—principles that align with many modern anti-inflammatory patterns.
25) What foods should be stayed away from with rheumatoid arthritis long term?
Stay mindful of daily habits: sugar-sweetened drinks, frequent fast-food meals, and oversized portions. Ultimately, the consistent foods to avoid with arthritis are the ones you eat every day, not the occasional treat.
26) What foods to avoid with arthritis if I want a quick start?
Begin with two moves: cut sugary beverages and swap deep-fried sides for roasted veg. Because those changes are simple and daily, they often deliver the fastest relief.
27) Do I need a strict arthritis avoid-food list, or can I be flexible?
Be flexible. After all, perfection is unnecessary. Instead, build a satisfying default plate and treat less-helpful foods as occasional, mindful choices.
28) Are there foods to avoid for arthritis in the morning vs at night?
Timing matters less than pattern. Even so, mornings go better with protein, fiber, and hydration; evenings go better with lighter, vegetable-forward plates rather than heavy fried takeout.
29) What’s the best way to remember the foods to avoid?
Think “F-S-U-R”: Fried, Sugary drinks/desserts, Ultra-processed snacks, Refined pastries/grains. Meanwhile, add plants, protein, and olive oil.
30) Finally, how do I balance life and the foods to avoid with arthritis?
Choose a default you love and return to it after birthdays, travel, and busy weeks. Because consistency beats intensity, your joints usually thank you over time.
⚠️ Educational medical disclaimer
This guide is for educational purposes only and is not medical advice. It does not diagnose, treat, or replace care from your clinician. Always consult your healthcare professional—especially if you take DMARDs (e.g., methotrexate), blood thinners, have gout/kidney disease, diabetes, or other conditions. Stop any new food/supplement that seems to worsen symptoms and check with your clinician. In an emergency, seek urgent medical care.