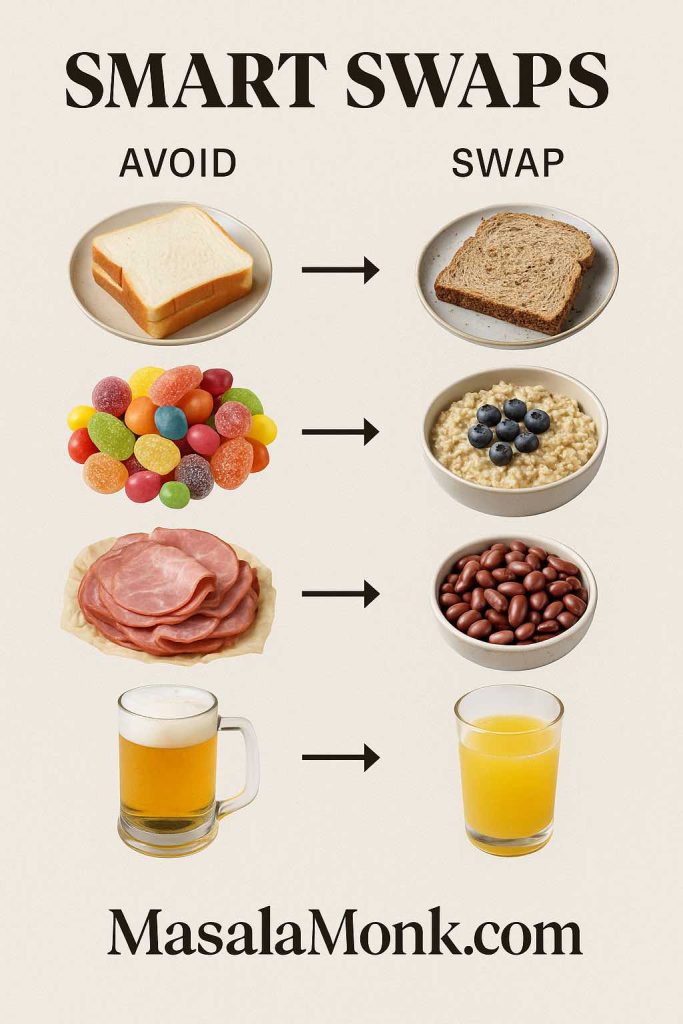
Foods to avoid with diverticulitis is the question everyone asks first, especially during a painful flare. Because the colon is inflamed, the safest route is to reduce roughage short-term, then step back up to a sustainable eating pattern as symptoms settle. To keep this both practical and evidence-based, the plan below follows the clinical arc you’ll see in the diverticulitis diet guidance from Mayo Clinic and the patient-friendly lists on the low-fiber diet page at MedlinePlus.
Free download: Grab the foods to avoid with diverticulitis printable guide (clear → low fiber → reintroduce) — download the PDF here.
However, before we map your meals, it helps to define the playing field. Diverticulosis refers to small pouches in the colon; diverticulitis is when those pouches become inflamed or infected. The day-to-day diet changes more with diverticulitis than with diverticulosis, because a flare typically needs gentler textures and lower fiber for a short time. For a quick overview of both conditions, bookmark diverticulosis and diverticulitis at MedlinePlus, then come back here to put the plan into action.
⚠️ Educational information — not medical advice.
This article is for general education only and does not replace advice from your own clinician. Do not start, stop, or delay medical care because of what you read here. If you have a flare, worsening pain, fever, vomiting, or other urgent symptoms, contact your healthcare provider or local emergency services.
The 3-Phase Path That Makes Eating Simpler (and Safer)
Because the bowel needs rest first and fiber later, think in phases. This structure reduces guesswork, prevents “forever bans,” and gives you a clear way to reintroduce foods after the worst has passed. Before you start, save the foods to avoid with diverticulitis one-page checklist for quick reference — FREE PDF download.
Phase 1: Clear Liquids (Short and Purposeful)
At the peak of pain, you’ll start with clear liquids so your gut can calm down. That means broth, strained soups, gelatin, pulp-free juices, oral rehydration solution, tea, and water. Use the official clear-liquid diet list at MedlinePlus when you’re unsure what “counts” as clear. Because this stage is only to reduce irritation, keep it brief unless your clinician advises otherwise.
Pptional “full liquids” bridge (if solids still feel rough) : A short, clinician-guided step on full liquids (strained creamy soups, milkshakes, puddings) can help some people between Phases 1 and 2. MedlinePlus
Phase 2: Low-Fiber (48–72 Hours for Many People)
As soon as symptoms begin easing, transition to low-fiber choices: eggs, poached fish, tender chicken, white toast, plain pasta, white rice, peeled/cooked vegetables, applesauce, and yogurt or cottage cheese if tolerated. The aim here is small, gentle meals, typically five to six times per day, so you’re nourished without overloading the bowel. For precise “allowed/avoid” lists, rely on the low-fiber diet guide at MedlinePlus.
Phase 3: Step-Up and Reintroduce (Bridge Back to Normal)
Once pain and tenderness subside, begin adding fiber back—slowly. Start with soft fruits (for instance, a ripe banana), oatmeal, well-cooked vegetables, and lighter grains. As you feel more normal, scale toward your long-term pattern. If you want a quick reassurance that this progression is standard, skim the Mayo Clinic overview of the diverticulitis diet.
Also Read: Fiber in Food.
⚠️ Educational information only — not medical advice. Always consult your clinician for diagnosis, treatment, and personalized diet guidance.
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis During a Flare (Temporary List)
This is the section most readers jump to, so let’s be direct. The following foods to avoid with diverticulitis apply during an active flare and early recovery. They are not permanent bans; they’re temporary guardrails that reduce irritation while the colon heals. Prefer a quick checklist? Download the FREE PDF and keep it handy during your flare.
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis: Whole Grains and Bran
Although whole grains are fantastic after recovery, they’re too fibrous during a flare. Replace brown rice, whole-wheat breads, bran cereals, and quinoa with refined grains—white rice, white toast, plain pasta—for a short stretch. The low-fiber diet list at MedlinePlus shows the exact swaps.
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis: Raw Skins, Tough Salads, and Corn
Raw skins and hearty salads add texture you don’t want right now. Choose peeled, cooked, or canned fruit/veg (packed in water or juice). If you want help picking fruit by phase and texture, use our internal explainer Fruits and Diverticulitis: What You Can and Can’t Eat to make practical choices you’ll actually enjoy.
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis: Beans and Legumes (For Now)
Legumes are high-fiber and often gas-forming, so press pause during the flare. Later, when you’re stepping up, you can reintroduce in small portions—for example, puréed lentil soup—and gauge comfort.
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis: Nuts, Seeds, and Popcorn (During the Flare)
This one causes the most confusion. During the flare, skip rough, seedy textures; nevertheless, the old instruction to avoid these forever is outdated. Current gastroenterology guidance does not recommend routine avoidance between flares. For clarity and confidence, do read the AGA clinical guidance on acute diverticulitis and a simple myth explainer from Cleveland Clinic.
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis: Very Spicy Sauces (If They Aggravate Symptoms)
Capsaicin tolerance is individual. If hot sauces, red-chile curries, or extra-spicy pickles worsen cramping or urgency, shelve them for now. Later, re-introduce gradually.
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis: Carbonated Drinks and Alcohol (If They Bloat or Hurt)
Some people feel fine; others notice more gas or discomfort. Treat these as optional avoids during the flare and early recovery. Then, test small reintroductions.
Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis: Tough, Fatty, or Fried Foods
Heavily fried items and tough cuts of meat can linger and irritate. Choose poached fish, omelets, soft tofu, or tender chicken prepared simply. For small meal frameworks, see the diverticulitis diet overview at Mayo Clinic.
If you want a second perspective while you’re still in the flare, our related article What Are the 10 Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis? acts as a quick reminder list you can consult when your energy is low.
⚠️ Educational information only — not medical advice. Always consult your clinician for diagnosis, treatment, and personalized diet guidance.
The Big Myth: “No Nuts, Seeds, or Popcorn Ever Again”
Because this myth is so persistent, it deserves its own short section. For years, people were told that nuts, seeds, and popcorn could lodge in diverticula and cause attacks. However, modern guidance and prospective data do not support this. After a flare has resolved, there is no need for routine avoidance. To understand the shift in thinking, here are two straightforward references:
Practically, that means treat nuts, seeds, and popcorn as foods to avoid with diverticulitis only during an active flare, then reintroduce them cautiously once you’re well.
Building Flare-Friendly Plates (Then Stepping Back Up)
Now that you know the foods to avoid with diverticulitis in the heat of the moment, here’s how to build real meals and move forward without guesswork.
Day 0–1: Clear Liquids with Purpose
Sip broth, pulp-free juices, oral rehydration solution, tea, gelatin, and water. Space fluids evenly, and don’t push this phase longer than advised. If you need a simple checkpoint, the clear-liquid diet list from MedlinePlus is easy to scan when you’re tired.
Day 2–3: Low-Fiber Meals in Small, Frequent Portions
Think two ounces of protein + one low-fiber side, several times a day:
- Soft scrambled eggs with white toast
- Poached fish with white rice and peeled, cooked carrots
- Lactose-free yogurt or cottage cheese if tolerated
- Applesauce or plain custard for easy dessert
When in doubt, recheck the low-fiber diet page at MedlinePlus for examples. Do read out post on How to Eat 100 Grams of Protein a Day.
Day 4–6: Step-Up Starts
Add ripe banana, oatmeal (if comfortable), well-cooked vegetables, and lighter grain swaps (for instance, part white/part brown). The Mayo Clinic diverticulitis diet overview is a helpful reassurance that you’re on the expected path.
Day 7–10: Toward Maintenance
Reintroduce beans via puréed soups first, then small portions of whole beans; add soft salads and raw fruit skins only when comfortable. If spicy food, carbonated drinks, or alcohol seem irritating, rein them in and try again later. For a balanced perspective on individual “trigger” stories, have a look at the short Q&A on no universal trigger foods in the Mayo Clinic expert answers.
⚠️ Educational information only — not medical advice. Always consult your clinician for diagnosis, treatment, and personalized diet guidance.
Between Flares: Fiber, Fluids, and a Pattern You Can Live With
After you recover, shift your focus from foods to avoid with diverticulitis to foods that keep you regular and comfortable: whole grains, beans, fruits, vegetables, and nuts and seeds—added gradually, with plenty of water. For a quick primer on why fiber matters (and how different types act), use The Nutrition Source by Harvard’s explanation of Fiber and its types.
Because readers often ask about produce first, it helps to provide a guided path. If you want a practical, food-by-food tour that slots into everyday Indian meals and snacks, do read our internal article Fruits and Diverticulitis: What You Can and Can’t Eat. That piece shows how to move from cooked/peeled items back to crunchy, raw, high-fiber favorites without a panic spiral every time you crave a salad.
Fiber Supplements: When (and How) to Use Them
Food first is ideal; nevertheless, some people benefit from a soluble fiber supplement after symptoms settle. Psyllium is often best tolerated. Crucially, go low and slow:
- Start with 1 rounded teaspoon daily for 3–4 days
- Increase to 2 teaspoons if comfortable
- Then move to 1 tablespoon, paired with a full glass of water each time
Talking about Psyllium, do read Psyllium Husk (Isabgol/Ispaghula) Side Effects: Risks, Benefits & How to Take It Safely.
This dovetails with a gentle food reintroduction. It’s also consistent with individualized recovery advice in the AGA guidance on acute diverticulitis.
Readers also ask about flax and chia. During a flare, they’re simply too fibrous. Later, they can be excellent additions—especially ground flax for its soluble fraction. If you want approachable, phase-aware ideas, link to our how-to with recipes: How to Incorporate Flax Seeds. Moreover, if you enjoy chia puddings, wait until you’re clearly in remission, then begin with half portions and extra fluids. In the meantime, do explore our post on 10 Creative Chia Pudding Recipes for Every Taste.
Specific Foods People Ask About
Bananas (A Gentle Bridge Food)
A ripe banana is often a friendly step-up fruit once you leave strict low-fiber eating. Because texture and tolerance both matter, advance at your comfort speed. Do read more about How Much Potassium Is in a Banana? Nutrition Facts, Comparisons & Benefits.
Leafy Salads, Cabbage, Lettuce, and Corn
These can be later-phase reintroductions. Start with cooked, finely chopped cabbage or soft lettuce blends, keep portions small, and observe your response before scaling up.
Coffee, Chocolate, Very Spicy Food, Carbonation, and Alcohol
Because individual tolerance varies so much, the best approach is limit if they aggravate symptoms, then retest in small amounts. This avoids needless permanent bans while respecting what your body tells you. For balance and clarity, you can link readers to the concise reminder of “no universal trigger foods” in Mayo Clinic’s expert answers.
Nuts, Seeds, and Popcorn (After Recovery)
Again, they are foods to avoid with diverticulitis during a flare, not forever. In remission, no routine avoidance is advised. Provide readers with confidence by linking to AGA guidance and Cleveland Clinic’s myth explainer.
⚠️ Educational information only — not medical advice. Always consult your clinician for diagnosis, treatment, and personalized diet guidance.
Why This Approach Beats Rigid “Never” Lists
First, the phase model is how major institutions guide patients to calm a flare and transition safely. A short stint on clear liquids, a handful of days on low-fiber, then a gradual climb back to fiber is exactly what you’ll see outlined in the Mayo Clinic diverticulitis diet and the MedlinePlus low-fiber diet.
Second, permanent bans on nuts, seeds, and popcorn aren’t supported by current evidence. After recovery, no routine avoidance is recommended—show readers the shift with the AGA management guidance and the plain-English overview from Cleveland Clinic.
Finally, personalization matters. There is no single list of foods that prevents attacks in everyone. A balanced message—limit what bothers you, progress slowly, hydrate well—is more realistic and more humane. If someone needs a succinct reminder of that point, link to Mayo Clinic’s expert Q&A on trigger foods.
When to Call Your Clinician (and What to Watch)
Diet helps, but medical care is critical if you have fever, severe pain, vomiting, or worsening symptoms, or if things don’t improve after a few days of the clear-to-low-fiber approach. A plain-language condition overview is here: Diverticulitis at MedlinePlus. Use it as your “when in doubt” reference. After the immediate problem is under control, shift focus to daily habits—fiber (added slowly), fluids, movement, sleep, and stress regulation—because those patterns usually matter more than any single food.
Free download: Grab the foods to avoid with diverticulitis printable guide (clear → low fiber → reintroduce) — download the PDF here.
Recap You Can Act On Today
- During a flare, foods to avoid with diverticulitis include whole grains and bran, raw skins and tough salads, beans and legumes, nuts/seeds/popcorn (for now), very spicy sauces, carbonation and alcohol if they aggravate you, and tough or heavily fried foods.
- Move from clear liquids → low-fiber → reintroduction. Use Mayo Clinic’s diverticulitis diet as your north star and verify food lists with MedlinePlus: low-fiber diet and MedlinePlus: clear-liquid diet.
- After recovery, no routine ban on nuts, seeds, or popcorn; see AGA guidance and Cleveland Clinic myths vs facts.
- In the long term, build a high-fiber, well-hydrated pattern; learn how fiber works at Dietary Fiber (The Nutrition Source, Harvard), then add real foods you enjoy.
- For practical produce choices and kitchen ideas, lean on our internal guides: Fruits and Diverticulitis: What You Can and Can’t Eat, What Are the 10 Foods to Avoid with Diverticulitis?, and How to Incorporate Flax Seeds.
⚠️ Education only. This article is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always speak with your healthcare provider about your specific situation.
FAQs
1) What are the top foods to avoid with diverticulitis during a flare?
During an active flare, temporarily avoid high-roughage items such as whole grains and bran cereals; raw fruit and vegetable skins; large raw salads and corn; beans and lentils; nuts, seeds, and popcorn; very spicy, capsaicin-heavy sauces; carbonated drinks and alcohol if they aggravate you; and tough, fatty, or heavily fried foods. Then, as symptoms settle, reintroduce fiber gradually.
2) How long should I follow a clear-liquid phase before moving on?
Briefly. Use clear liquids for a short window—typically one to two days—until severe pain eases and you can tolerate more. Next, progress to a low-fiber phase for a few days, and finally transition back toward your usual, higher-fiber pattern as comfort returns.
3) What does a low-fiber day actually look like?
Think small, gentle meals 5–6 times per day: soft scrambled eggs with white toast, poached fish with white rice and well-cooked peeled vegetables, yogurt or cottage cheese if tolerated, and simple desserts like applesauce or custard. Portion control plus hydration helps you advance smoothly.
4) Are nuts, seeds, and popcorn permanently foods to avoid with diverticulitis?
No. During a flare, yes—skip rough, seedy textures. However, after symptoms resolve, routine long-term avoidance isn’t generally recommended. Instead, reintroduce slowly, note your tolerance, and drink plenty of fluids as you bring back fiber.
5) Is coffee one of the foods to avoid with diverticulitis?
It depends. Caffeine can stimulate the gut in some people. During a flare, you might limit or pause coffee; afterwards, reintroduce gradually and observe your body’s response. Similarly, chocolate can be stimulating for some but well tolerated by others—personalization is key.
6) Are bananas okay, or should they go on my list of foods to avoid with diverticulitis?
Ripe bananas are often gentle during the step-up phase after clears and low-fiber. Start with small portions, then scale as tolerated. Green or very firm bananas can be more fibrous, so add those later in recovery.
7) What about chia or flax seeds?
During a flare, avoid them—they’re very high in fiber. Later, introduce small amounts (e.g., a teaspoon of ground flax) with additional fluids. Increase slowly over several days; if gas or discomfort occurs, pause and retry later.
8) Are dairy products safe during a flare?
Many people tolerate simple, lower-lactose options such as yogurt or cottage cheese during the low-fiber phase. Nevertheless, if dairy worsens bloating or cramps for you, skip it temporarily and use other protein sources like eggs, tofu, or tender chicken.
9) Which grains are best right after a flare?
Begin with refined grains—white rice, plain pasta, white toast, cream of wheat—because they’re lower in fiber and gentler on an irritated bowel. Then, step up to oats, blended grains, and eventually whole grains as you feel better.
10) Are beans always foods to avoid with diverticulitis?
Only during the flare. Beans and lentils are fiber-rich and can cause gas early on. Later, consider puréed legume soups in small servings before returning to intact beans; go slowly to limit discomfort.
11) Do carbonated drinks and alcohol belong on my personal “avoid” list?
Sometimes. Bubbles may increase bloating; alcohol may aggravate symptoms for some. During a flare, it’s reasonable to limit both. Subsequently, reintroduce cautiously—try smaller portions, sip with food, and monitor how you feel.
12) Should I worry about black pepper or spices?
Milder seasonings and black pepper are often fine. Very spicy, capsaicin-heavy dishes can bother an irritable gut, especially during a flare. Therefore, reduce heat temporarily; then, as you improve, titrate spice back to taste.
13) What’s a simple 10-day progression I can follow?
- Days 0–1: clear liquids.
- Days 2–3: low-fiber meals in small, frequent portions.
- Days 4–6: step-up foods such as ripe banana, oatmeal (if tolerated), and well-cooked vegetables.
- Days 7–10: begin transitioning toward maintenance—gradually add whole grains, small portions of beans, and raw textures as comfortable.
14) How much water should I drink while I reintroduce fiber?
Hydration matters. As you add fiber, increase fluids to help stool move comfortably. A steady intake spread through the day generally works better than large, infrequent gulps.
15) Which fiber supplements are best after recovery?
Many people find soluble fiber—especially psyllium—well tolerated once symptoms resolve. Start low (e.g., a teaspoon daily), increase slowly over several days, and always pair with a full glass of water. Avoid starting supplements during an acute flare.
16) Can I follow a low FODMAP diet for diverticulitis?
Low FODMAP is designed for IBS symptom management, not specifically for diverticulitis. Even so, some individuals use it in remission to troubleshoot gas and bloating. If you try it, do so with professional guidance and still aim for adequate fiber over time.
17) Are leafy salads, cabbage, and corn automatically foods to avoid with diverticulitis?
During the flare, yes—because raw, high-fiber, or tough textures can irritate. However, after you improve, you can reintroduce these foods—first cooked and finely chopped, then gradually less processed—as your tolerance allows.
18) Do oats and oatmeal help or hurt?
It varies. Oatmeal is often a friendly bridge food in the step-up phase; it contains soluble fiber that can be soothing for some. Nonetheless, if it causes bloating, try smaller portions or wait a few days before trying again.
19) What about cheese, butter, and ghee?
Butter and ghee are fats without fiber; a little may be fine, though large amounts or very greasy meals can feel heavy. Many cheeses are tolerable in the low-fiber phase, but if you experience cramping or loose stools, reduce or pause and reassess later.
20) Are potatoes, crackers, or plain toast acceptable early on?
Yes—plain, low-fiber versions are common in the low-fiber phase. For instance, peeled mashed potatoes, plain salted crackers, and white toast often work well. Later, shift to higher-fiber choices as you recover.
21) Are foods to avoid with diverticulitis different from foods to avoid with diverticulosis?
Yes. Diverticulitis (active inflammation) calls for temporary low-fiber eating. Diverticulosis (no active inflammation) usually benefits from a higher-fiber pattern to support regularity and stool form. In short: flare = gentler textures; remission = fiber forward.
22) Do I need a “printable list of foods to avoid with diverticulitis” for the fridge?
It can help. A one-page checklist that separates flare foods (temporary avoids and allowed items) from remission foods (fiber-forward staples) reduces decision fatigue and makes shopping easier—especially when you’re not feeling your best.
23) How can I personalize the list of foods to avoid with diverticulitis?
Track your response. Keep a brief notes app or card for two weeks as you reintroduce foods. Record what you ate, portion size, timing, water intake, and how you felt. Because sensitivity is individual, your personal “avoid for now” list may be shorter—or longer—than someone else’s.
24) What’s the single biggest mistake people make?
Staying on clear liquids or ultra-low-fiber foods too long. That can leave you fatigued and constipated once the flare settles. Progress—cautiously but consistently—through the phases so you’re moving toward a sustainable, fiber-inclusive pattern.
25) When should I call my clinician instead of tweaking food?
Immediately seek medical advice if pain worsens, fever develops, you’re vomiting, you cannot keep fluids down, or you’re not improving after a few days of phased eating. Diet is supportive, but medical care comes first when red flags appear.
26) Can I exercise while advancing my diet?
Light movement—gentle walks, easy stretching—often aids regularity and comfort once acute pain decreases. Nevertheless, avoid strenuous core work during a flare. Resume normal activity gradually as you feel better.
27) Will probiotics help, or are they on the list of foods to avoid with diverticulitis?
They’re not foods, and evidence is mixed. Some people feel better with a simple probiotic in remission; others notice no change. If you experiment, introduce one product at a time, keep notes, and stop if symptoms worsen.
28) How do I bring back flavor without triggering symptoms?
Start with mild seasonings—ginger, turmeric, cumin, fresh herbs, a squeeze of lemon—rather than very hot chilies. Additionally, choose moist cooking methods (poaching, braising, steaming) to keep proteins tender and easy to digest.
29) What’s a smart “first grocery list” after a flare?
White rice, plain pasta, white bread, eggs, tender fish or chicken, yogurt or lactose-free alternatives, peeled/cooked vegetables, applesauce, ripe bananas, oatmeal (if tolerated), broth, oral rehydration solution, and plenty of still water. Next, add higher-fiber staples as you step up.
30) Bottom line: what should I remember about foods to avoid with diverticulitis?
During a flare, prioritize gentle textures and temporarily avoid roughage; then, as symptoms ease, reintroduce fiber slowly with solid hydration. Over time, aim for a balanced, higher-fiber pattern that you can maintain—always guided by your own tolerance and your clinician’s advice.