Ulcerative Colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that affects millions worldwide, causing symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, and fatigue. While medications remain the cornerstone of UC management, growing research highlights the essential role of nutrition, especially fruit intake, in symptom control and long-term gut health. But for many with UC, the simple act of eating an apple can be fraught with questions:
Which fruits are safe? Are some harmful? How do I balance nutrition and comfort?
Let’s break down the latest science and offer actionable guidance.
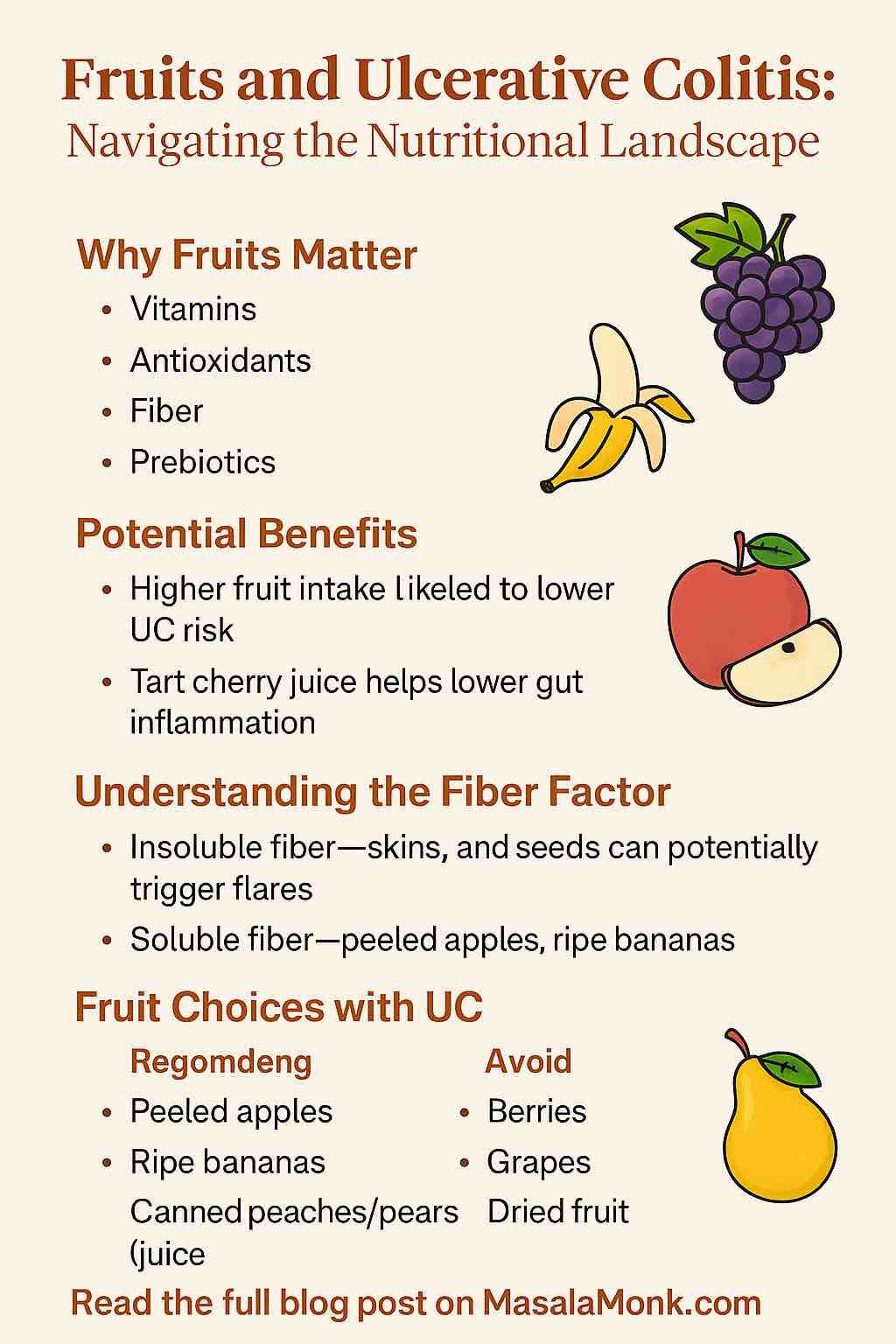
1. Why Fruits Matter in Ulcerative Colitis
Fruits are nutritional powerhouses:
- Vitamins and Minerals (vitamin C, potassium, folate)
- Antioxidants and Phytonutrients (anthocyanins, flavonoids)
- Fiber (soluble and insoluble)
- Prebiotics (nourish beneficial gut bacteria)
These nutrients collectively help repair tissues, reduce inflammation, and support overall well-being. In fact, population studies consistently show that diets rich in fruits and vegetables are associated with a lower risk of developing UC.
2. Fruit Intake and UC: What Does the Latest Research Say?
Population Insights:
- A recent meta-analysis found that people with higher fruit intake had a 31% reduced risk of UC compared to those with the lowest intake.
- Dried fruits and antioxidant-rich varieties (berries, cherries) show particularly promising effects in reducing risk (MDPI, 2024).
New Clinical Trials:
- Montmorency Tart Cherry Juice: In a groundbreaking human trial (2025), UC patients who consumed tart cherry juice daily for six weeks saw a 40% decrease in gut inflammation (measured by fecal calprotectin) and improved quality of life.
However, sugar content and small sample size mean it’s not a stand-alone solution. - Plant-Based Diets: Large cohort studies confirm an 8% lower risk of UC among people eating the most fruits and vegetables.
- Potatoes: Unexpectedly, recent UK research found that high potato intake correlated with a 51% higher risk of UC—suggesting not all plant foods are equal.
Emerging Science:
- Animal studies with jujube and strawberry tree fruits show they may protect against colitis, but these benefits are not yet proven in humans.
3. Understanding the Fiber Factor: Soluble vs. Insoluble
Fiber is central to how fruits impact UC.
- Insoluble fiber (skins, seeds, peels) can be irritating during flares, leading to gas, bloating, or diarrhea.
- Soluble fiber (flesh of apples, bananas, pears when peeled) is generally gentler, absorbs water, and can help bulk stools.
Key tip: Focus on soluble fiber sources during active symptoms and flares.
4. Practical Tips: Choosing and Preparing Fruits with UC
During Flare-Ups:
- Opt for low-fiber, gentle fruits: peeled apples, ripe bananas, canned peaches or pears (in juice, not syrup), well-cooked or poached fruits.
- Avoid: raw fruit skins, seeds, tough peels, dried fruit (unless you know you tolerate it), and high-insoluble-fiber options like berries or grapes.
In Remission:
- Gradually reintroduce a wider variety of fruits, including soft berries and dried fruits, in small amounts.
- Try blending fruits (smoothies) or cooking (compotes, applesauce) to improve tolerance.
General Guidelines:
- Listen to your gut: Everyone’s triggers are different. Keep a food and symptom diary to track reactions.
- Go slow: Reintroduce new fruits one at a time.
- Mind the juice: Fruit juices, even tart cherry, can be high in sugar and lack fiber—moderate your intake and dilute when possible.
- Stay hydrated: Especially if your fruit intake increases stool output.
5. Best Fruits for People with UC (Based on Current Evidence and Practicality)
| Fruit | When Best Tolerated | How to Prepare/Serve | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ripe Bananas | Flares, remission | Raw, mashed, in smoothies | Soluble fiber, potassium |
| Peeled Apples | Flares, remission | Steamed, applesauce, baked | Antioxidants, soluble fiber |
| Canned Peaches/Pears | Flares | Canned in juice, drained | Easy to digest, low fiber |
| Tart Cherries | Remission | Juice (diluted), dried (small amounts) | Anti-inflammatory polyphenols |
| Papaya/Mango | Remission, mild flares | Peeled, cubed | Enzymes, vitamins A & C |
| Blueberries (cooked) | Remission | Stewed, in oatmeal | Antioxidants |
| Watermelon (seedless) | Remission | Chilled, cubed | Hydration, vitamins |
6. Fruits to Approach with Caution (Especially During Flares)
- Raw apples, pears (with skin)
- Berries with seeds (strawberries, raspberries, blackberries)
- Grapes (due to skin/seeds)
- Dried fruits (unless very well tolerated)
- Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits; may irritate in some)
- Pineapple (can be tough and fibrous)
7. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I eat fruit during a UC flare-up?
Yes, but stick to low-fiber options like peeled apples, ripe bananas, and canned pears or peaches. Avoid raw skins, seeds, and tough or dried fruits, which can aggravate symptoms.
2. Which fruits are safest for UC patients?
Safest choices include peeled apples, ripe bananas, canned peaches/pears (in juice), and well-cooked fruits. These are easier to digest and less likely to irritate the gut.
3. Are there fruits I should avoid completely with UC?
Avoid fruits with tough skins or seeds (e.g., raw apples, berries, grapes) during active flares. Citrus fruits, dried fruits, and pineapple can also be triggers for some people.
4. Is fruit juice a healthy choice for UC?
Most fruit juices are high in sugar and lack fiber. If you use juice (e.g., tart cherry juice, which shows potential benefits), drink it diluted and in moderation, and monitor your tolerance.
5. How does fiber in fruit affect UC symptoms?
Insoluble fiber (skins, seeds) can irritate during flares. Soluble fiber (found in peeled apples, bananas) is gentler. Adjust your intake based on your symptoms.
6. Does eating fruit increase the risk of a UC flare?
No strong evidence suggests fruit itself triggers flares. Triggers are individual—track your reactions, and avoid fruits that consistently cause symptoms.
7. Can dried fruits be included in a UC diet?
Dried fruit is linked to a lower risk of UC in some studies, but it’s high in sugar and fiber. Start with small amounts, and only if you tolerate them well.
8. Should I remove the skins from all fruits?
During flares or if you’re sensitive, it’s best to remove skins and seeds. In remission, you may try reintroducing them slowly and see how your body reacts.
9. How can I safely reintroduce fruits after a flare?
Start with gentle, peeled, or cooked fruits. Add new types one at a time, monitor your body’s response, and increase variety as tolerated.
10. Are there any fruits with special benefits for UC?
Recent research suggests tart cherry juice may help lower gut inflammation, but moderation is key due to sugar content. All fruits have unique nutrients—variety and preparation are more important than any single “superfruit.”
8. Personalizing Your Fruit Journey: How to Find Your Sweet Spot
- Track: Keep a food/symptom journal for at least two weeks.
- Experiment: Try different preparations—raw, cooked, blended, peeled.
- Consult: Work with a dietitian experienced in IBD for tailored advice.
- Balance: Combine fruits with protein or healthy fats (e.g., yogurt, nut butter) to slow digestion and avoid sugar spikes.
9. Looking Ahead: The Future of Fruit & UC
Research is ongoing, and while promising results from tart cherry juice and plant-based diets are encouraging, there’s no universal “superfruit” for UC. Individual responses vary, and moderation is key.
Stay tuned for larger studies on fruit extracts, the microbiome, and how food can complement medication in managing UC. As science evolves, so will our understanding of which fruits heal, which to limit, and how to make eating both pleasurable and safe.
Final Thoughts:
Fruits, when chosen and prepared with care, can be an ally for people with ulcerative colitis. The key is to individualize your choices, listen to your body, and adapt your diet as your condition changes. With knowledge, experimentation, and guidance, you can find a fruit-filled approach that supports your gut health—one bite at a time.