In the quest for simple, natural weight management solutions, ancient wisdom and modern nutrition sometimes intersect in unexpectedly delightful ways. Enter the “Fig-tastic Overnight Soak”—the practice of soaking dried figs (Anjeer) overnight and eating them first thing in the morning. Hailed for its digestive and metabolic benefits by Indian grandmothers and increasingly recommended by nutritionists, this habit is creating a buzz. But what does the science say? Does this ritual really help with weight loss? And how can you integrate it into your routine for maximum effect?
Let’s peel back the layers, blending expert insight, cultural wisdom, and user experiences to see if soaked figs deserve a spot in your morning routine.
The Nutritional Powerhouse: Why Figs?
Figs are more than just a sweet treat. Each dried fig is packed with:
- Dietary Fiber: Both soluble and insoluble, supporting gut health and fullness.
- Natural Sugars: Offering gentle energy—less processed than added sugars.
- Micronutrients: Including calcium, magnesium, potassium, iron, and vitamin K.
- Polyphenols & Antioxidants: Plant compounds with anti-inflammatory and anti-aging potential.
But what makes soaking them special? Soaking figs overnight softens them, activates enzymes, and may make certain nutrients more bioavailable, while reducing anti-nutrients like tannins and phytates. The water also absorbs water-soluble vitamins and minerals.
What Does Science & Tradition Say About Soaked Figs for Weight Loss?
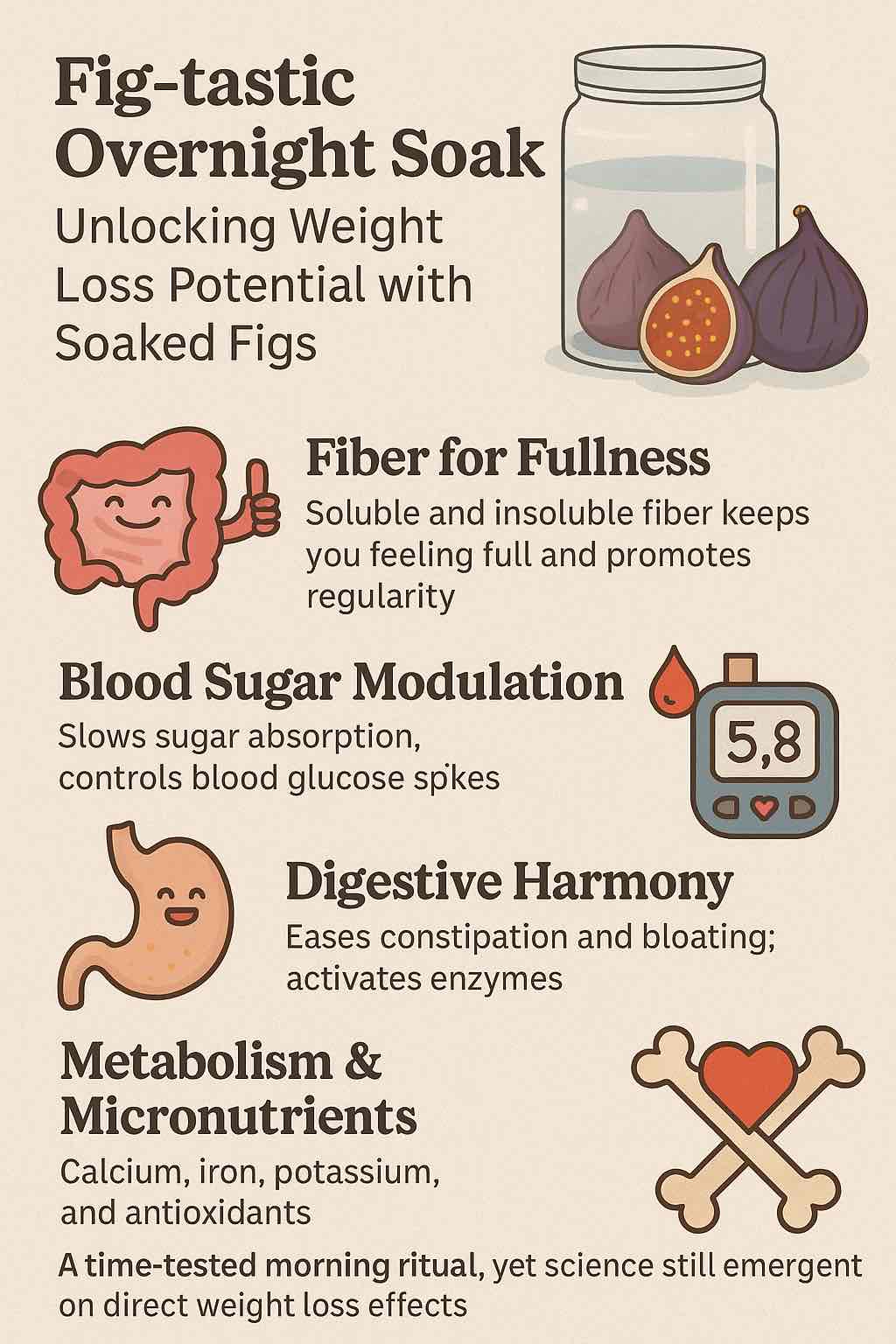
1. Fiber for Fullness
Soaked figs are an excellent source of fiber, which:
- Slows digestion and sugar absorption.
- Keeps you fuller for longer, naturally curbing snacking.
- Supports regular bowel movements—critical for a healthy metabolism and a flatter belly.
2. Blood Sugar Modulation
The fiber in figs helps slow the release of sugars, preventing rapid spikes and crashes in blood glucose. This is essential for:
- Reducing cravings.
- Supporting insulin sensitivity (important in weight management).
3. Digestive Harmony
Soaking figs enhances their digestibility. Many users and practitioners report:
- Relief from constipation.
- Reduced bloating.
- A “light” feeling in the gut that supports energy throughout the day.
4. Metabolism & Micronutrients
Figs are loaded with minerals like calcium, iron, and potassium—vital for bone health, heart health, and optimal muscle function. There are claims (especially in Ayurveda) that figs, particularly when soaked, can gently boost metabolism, especially when paired with saffron.
5. What Do Studies Show?
- Direct, high-quality clinical trials on soaked figs and weight loss in humans are lacking.
- Animal studies and population surveys suggest dried figs support a healthy gut, improve cholesterol profiles, and may aid in satiety and weight management.
- Some small human trials show dried fruits (including figs) are linked to lower BMI and waist circumference, but causality isn’t confirmed.
6. Cultural Practice
In India and the Middle East, eating soaked figs (with or without saffron) has long been a gentle, morning ritual believed to:
- “Cleanse” the gut.
- Provide sustained energy.
- Support clear skin and strong hair.
- Offer a low-calorie start to the day.
Real-World Results: What Users Say
“It worked very well for my digestion. I’m overweight and was worried about sugar, but with only two figs I didn’t gain weight—felt lighter instead.” — User on Practo
“After two weeks, my cravings dropped and I noticed I wasn’t reaching for snacks by mid-morning.” — Community member, OurFigs forum
“Constipation gone. Energy steady. I still watch my overall calories but soaked figs make mornings easier.” — Dietitian feedback, Indian Express
Common themes:
- Improved bowel movements and reduced bloating.
- Feeling fuller, fewer cravings.
- No reports of weight gain with 1–2 figs per day.
- Benefits plateau or reverse (bloating, sugar overload) if more than 2–3 figs are consumed daily.
How To Do The “Fig-tastic Overnight Soak” — A Step-by-Step Guide
- Choose Your Figs:
Use unsweetened dried figs (avoid those with added sugars). Turkish or Indian Anjeer figs work well. - Soak:
- Place 2 dried figs in a glass or ceramic cup.
- Cover with about 250 mL (1 cup) filtered water.
- For extra flavor and potential metabolic benefit, add 2–3 saffron strands (optional).
- Let soak overnight (8–10 hours) at room temperature.
- Morning Ritual:
- On waking, eat the figs and drink the soaking water.
- Wait 20–30 minutes before your regular breakfast.
- For blood sugar balance, follow with protein and healthy fat (e.g., Greek yogurt, nuts, eggs, or a smoothie).
- Repeat daily for at least 1–2 weeks and observe changes.
Pro Tips & Variations
- Busy mornings? Soak figs in a portable jar and eat them at work or school.
- Add to breakfast bowls: Chop soaked figs into oatmeal or yogurt.
- Try a fig smoothie: Blend soaked figs with almond milk and a scoop of protein powder.
- Combine with nuts: For a “trail mix” effect that’s both satisfying and sustaining.
How to Track Your Results
For best results, treat this like a little “self-experiment.” Here’s how:
- Log your daily fig intake and note how you feel after breakfast and at midday.
- Track bowel habits, cravings, energy, and weight for at least a week.
- Adjust: If you feel bloated or gassy, drop to 1 fig daily or skip a day.
- If diabetic or sensitive to sugar, monitor blood glucose (test before and after breakfast).
Who Should Be Careful?
- People with IBS or sensitive digestion: Figs are high in FODMAPs and may cause gas in some.
- Diabetics: Though figs are fiber-rich, they still contain natural sugars—monitor your response carefully.
- Those on blood thinners: Figs are high in vitamin K, which can interact with medications like warfarin.
- Allergy-prone individuals: Figs can rarely trigger reactions in people sensitive to latex or birch pollen.
Always check with your doctor if you’re starting any new dietary habit, especially if you have chronic conditions.
The Bottom Line
Soaked figs offer a practical, gentle, and tasty way to support digestive comfort, appetite control, and steady energy—potentially making them a helpful ally in weight management. While direct clinical evidence is still emerging, tradition, nutrition science, and user experience all point to a daily “Fig-tastic Soak” as a low-risk, high-reward addition to a healthy lifestyle.
Here’s your simple starter ritual:
- Soak 2 figs overnight.
- Enjoy figs and soaking water upon waking.
- Follow with protein/fat-rich breakfast.
- Track your own results, and adjust as needed.
With mindful use and realistic expectations, the humble fig might just help make your mornings (and your waistline) a little more fantastic!
Have you tried the Fig-tastic Overnight Soak? Share your story in the comments below, or ask questions about customizing your morning ritual!
FAQs: Fig-tastic Overnight Soak
1. How many soaked figs should I eat daily for weight loss?
Most experts and traditional practitioners recommend 2 dried figs per day, soaked overnight. More than 2–3 can lead to excess calories or digestive discomfort.
2. Should I drink the water in which figs are soaked?
Yes! The soaking water contains some water-soluble nutrients and is traditionally consumed along with the figs for maximum benefit.
3. Can people with diabetes eat soaked figs?
In moderation (1–2 figs), most people with diabetes can safely consume soaked figs due to their fiber content and low-to-moderate glycemic index. Always monitor your blood sugar and consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
4. What time of day is best to eat soaked figs?
Eating soaked figs first thing in the morning on an empty stomach is most common. This supports digestive regularity and may help curb mid-morning cravings.
5. Will soaked figs alone help me lose weight?
Soaked figs can support weight management by promoting satiety and digestive health, but no single food causes weight loss. Combine figs with a balanced diet, physical activity, and portion control for best results.
6. Can I soak figs with other ingredients, like saffron or nuts?
Yes! Adding a few saffron strands may add antioxidants and a pleasant flavor. You can also pair soaked figs with nuts or yogurt for a balanced breakfast.
7. What if I experience bloating or discomfort?
Figs are high in fiber and FODMAPs, which may cause gas or bloating for some people. If this happens, reduce to 1 fig daily or skip a day, and monitor your symptoms.
8. Are fresh figs as effective as dried, soaked figs?
Fresh figs are also nutritious but may not be available year-round. Dried figs (soaked) are easier to digest and offer a more concentrated source of nutrients and fiber.
9. Is there scientific evidence supporting soaked figs for weight loss?
Direct clinical studies on soaked figs and weight loss are lacking. Most benefits are based on the nutritional profile of figs and user experiences. More research is needed for definitive claims.
10. Can children or elderly people have soaked figs?
Yes, in moderation. For children, 1 soaked fig is sufficient. Elderly individuals may benefit from the fiber and minerals, but should ensure figs are soft and easy to chew. Always check for allergies or sensitivities.