Gut health is more than just avoiding bloating or indigestion—it’s the cornerstone of overall wellness. New research continues to reveal how a balanced digestive system supports immunity, brain function, mental health, and even chronic disease prevention. But when inflammation takes over the gut, the consequences can ripple throughout the body.
In this post, we’ll dive deep into what gut inflammation is, what causes it, the symptoms to watch for, and how to support your digestive system through food, lifestyle, and cutting-edge nutritional science.
🌿 What Is Gut Inflammation?
Gut inflammation refers to an immune response within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. It’s your body’s way of trying to fight off harmful triggers, whether from diet, bacteria, toxins, or chronic stress. While short-term inflammation can be protective, chronic inflammation can damage the intestinal lining, disrupt digestion, and lead to serious conditions like:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Leaky Gut Syndrome
- Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
🚨 Common Symptoms of Gut Inflammation
Many people are unaware they’re dealing with gut inflammation because the symptoms often overlap with common digestive issues. Here’s what to watch out for:
- Bloating and gas
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Food intolerances
- Brain fog or fatigue
- Skin issues (eczema, acne)
- Joint pain
- Frequent infections
If you’re experiencing a mix of these, your gut may be inflamed and in need of healing support.
🔬 What Causes Gut Inflammation?
1. Unhealthy Diet
- High-fat, processed foods impair gut lining and trigger immune cells within 48 hours.
- Low-fiber diets reduce microbial diversity, weakening gut resilience.
- Excess sugar and artificial sweeteners fuel the growth of harmful bacteria.
2. Antibiotic Overuse
Antibiotics don’t just kill bad bacteria—they also wipe out beneficial microbes, leaving your gut vulnerable to imbalance (dysbiosis).
3. Chronic Stress
The gut-brain axis links emotional health with digestive function. Stress alters gut permeability and microbial composition, increasing inflammation.
4. Environmental Factors
Pollution, food additives, pesticides, and a sedentary lifestyle have all been linked to increased gut inflammation.
5. Alcohol and Smoking
Both irritate the gut lining and disrupt microbial balance, leading to chronic inflammation and increased disease risk.
🥦 Healing Your Gut: Diet First
✅ Anti-Inflammatory Superfoods
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which actively reduces gut inflammation.
- Ginger: Soothes the digestive tract and supports enzyme activity.
- Fennel Seeds: Reduce gas and bloating.
- Green Tea: High in antioxidants that calm gut tissue.
- Yogurt (with live cultures): Boosts probiotics and immune support.
✅ Fiber-Rich Foods
Whole plant foods feed your gut microbes and strengthen your intestinal lining.
- Oats, apples, flaxseeds
- Beans, lentils, leafy greens
- Bananas, onions, garlic (rich in prebiotics)
❌ Foods to Avoid
- Refined sugar and white carbs
- Trans fats and fried foods
- Gluten (for those sensitive)
- Dairy (for those intolerant)
- Processed meats and alcohol
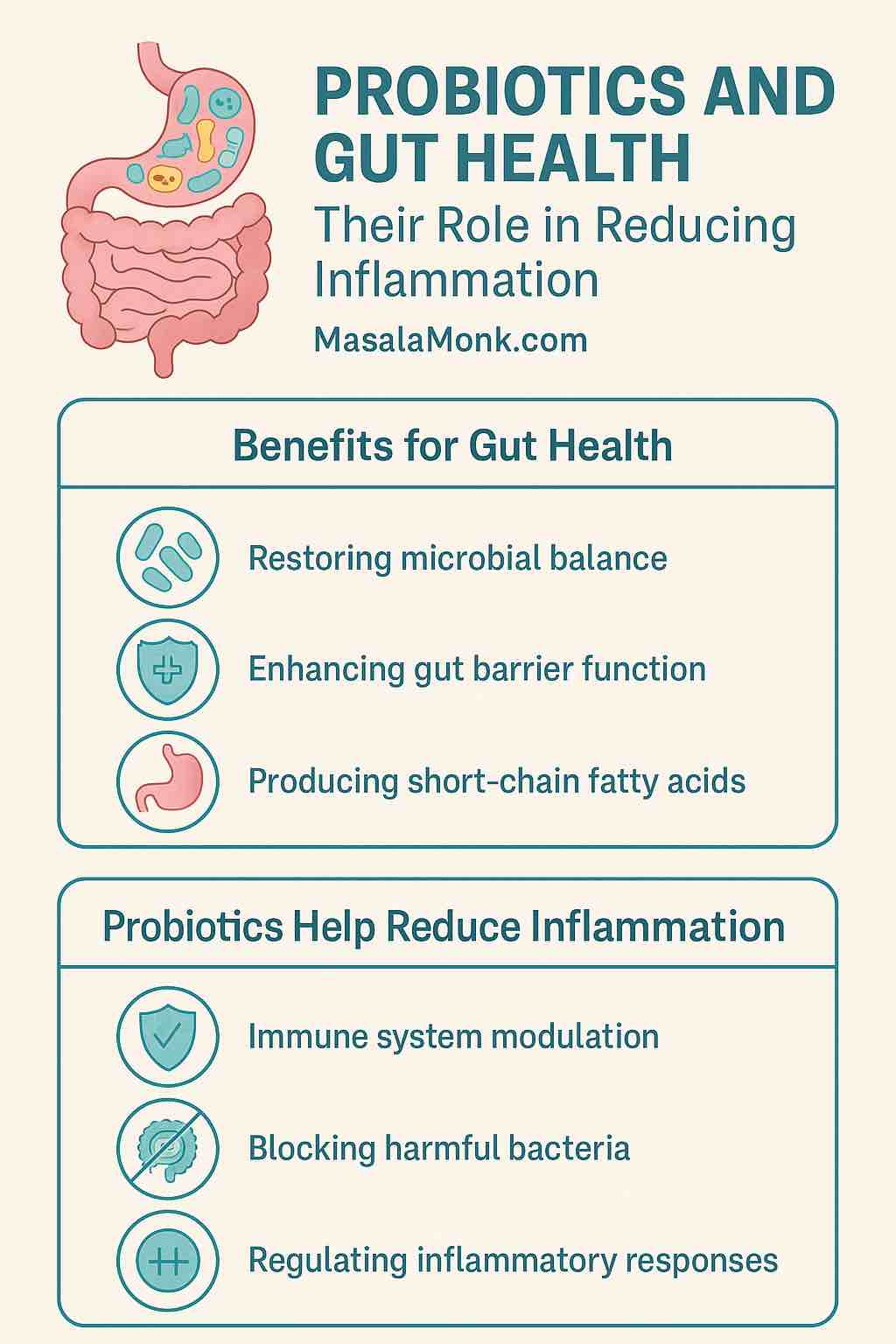
🧬 The Rise of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics
🔹 Probiotics
Live bacteria found in yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and supplements that help restore gut flora.
🔹 Prebiotics
Plant fibers (like in garlic, onions, leeks) that feed beneficial bacteria.
🔹 Synbiotics
Combining probiotics + prebiotics to maximize gut restoration.
🔹 Postbiotics
Bioactive compounds released by good bacteria that help repair the gut lining and lower inflammation.
🧠 Gut-Brain Connection: Mental Health Starts in the Gut
Emerging research confirms that your gut bacteria play a direct role in brain health. An inflamed or dysbiotic gut has been linked to:
- Anxiety and depression
- Mood swings
- Sleep disorders
- Brain fog
Balancing your microbiome can support neurotransmitter production (like serotonin) and reduce inflammation-driven mood issues.
🏃♂️ Lifestyle Tips for a Happy Gut
1. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity boosts microbial diversity and reduces stress-related inflammation.
2. Sleep Well
Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep to support circadian rhythms and gut healing.
3. Manage Stress
Try meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or time in nature to soothe your nervous system and gut.
4. Hydrate
Water helps flush out toxins and supports nutrient absorption.
🧪 Advanced Therapies and Personalized Nutrition
Science is heading toward microbiome-based personalized nutrition, where your gut bacteria determine what foods you should eat for optimal health. Companies are now offering gut microbiome testing kits to help guide these decisions.
In the future, expect to see:
- Gut-specific AI nutrition plans
- Targeted synbiotic supplements
- Precision anti-inflammatory therapies
📌 Final Thoughts
Your gut is your body’s command center for immunity, metabolism, and even mental health. Inflammation in the gut isn’t just a digestive issue—it’s a systemic health concern. But the good news? It’s manageable and reversible with the right dietary and lifestyle changes.
If you’ve been feeling “off” lately, your gut may be trying to tell you something. Listen closely, eat wisely, and care for your inner ecosystem.
💬 10 Frequently Asked Questions
1. What foods quickly reduce gut inflammation?
Turmeric, ginger, green tea, yogurt, leafy greens, and omega-3 rich foods are among the best.
2. Can stress cause gut inflammation?
Yes. Chronic stress disrupts the gut-brain axis and alters microbial balance.
3. Is gut inflammation the same as IBS?
Not exactly. IBS is a functional disorder that can be influenced by inflammation, but they’re not identical.
4. How can I test for gut inflammation?
Stool tests, blood tests (CRP), and endoscopies can help diagnose inflammation.
5. Are probiotics enough to heal the gut?
They’re helpful, but best combined with prebiotics, anti-inflammatory foods, and lifestyle changes.
6. Does gluten cause gut inflammation?
It can for sensitive individuals or those with celiac disease or non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
7. Can gut inflammation lead to weight gain?
Yes. Inflammation impacts metabolism and insulin sensitivity, contributing to fat storage.
8. Are fermented foods good for gut health?
Yes. They provide beneficial bacteria that support microbiome diversity.
9. How long does it take to heal gut inflammation?
It varies, but with consistent changes, many see improvement in 4–8 weeks.
10. Can children have gut inflammation?
Yes, especially with poor diet, antibiotics, or allergies. Early intervention is key.
📌 Blog Tags
gut inflammation, digestive health, anti-inflammatory diet, probiotics, prebiotics, leaky gut, IBS, IBD, gut microbiome, fermented foods, gut brain axis, chronic inflammation, turmeric, healing the gut