In recent years, the buzz around probiotics and gut health has exploded — and for good reason. Our gut is home to trillions of microorganisms that do much more than just help digest food. They influence everything from immunity and mood to inflammation levels throughout the body.
Among these tiny but mighty microbes, probiotics stand out as the beneficial bacteria that can tip the balance toward better health. This blog post delves deep into how probiotics support gut health, their powerful role in reducing inflammation, and why this matters for your overall well-being.
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are live microorganisms, mostly beneficial bacteria and some yeasts, that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. Think of them as the “good guys” in your gut community, helping to keep harmful bacteria in check and supporting digestive health.
Common probiotic strains include:
- Lactobacillus species (e.g., Lactobacillus acidophilus)
- Bifidobacterium species (e.g., Bifidobacterium bifidum)
- Saccharomyces boulardii (a beneficial yeast)
You can get probiotics from fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and supplements.
Understanding the Gut Microbiome: Your Inner Ecosystem
Your gut microbiome is a vast ecosystem of trillions of microbes living primarily in the large intestine. This diverse microbial community plays a crucial role in:
- Digesting complex carbohydrates and fibers
- Producing essential vitamins (like Vitamin K and B vitamins)
- Training the immune system to recognize harmful invaders
- Maintaining the integrity of the gut lining
A healthy, balanced microbiome supports smooth digestion and a strong immune system. When this balance is disrupted — a condition known as dysbiosis — it can lead to digestive issues, increased inflammation, and chronic disease.
How Probiotics Promote Gut Health
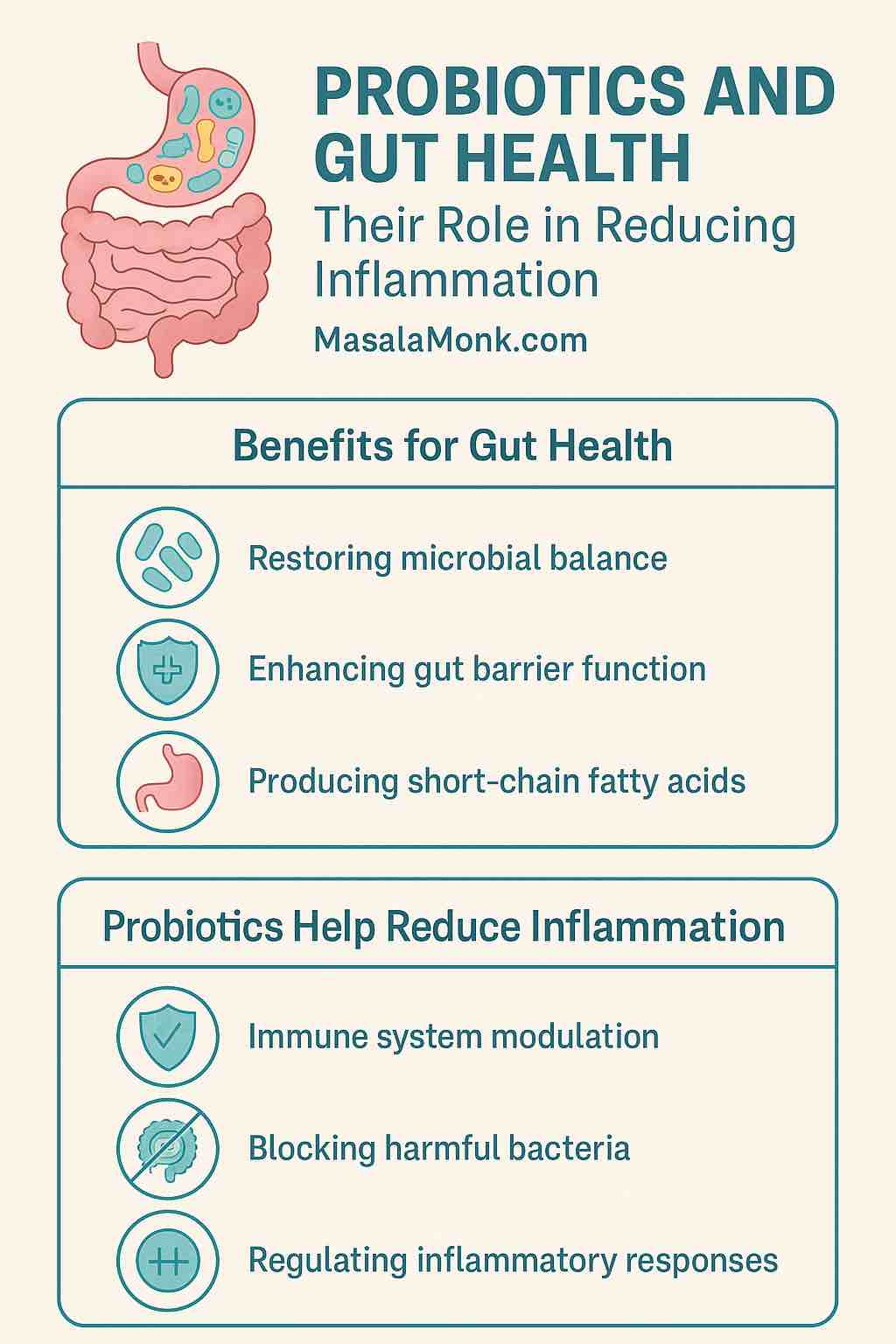
1. Restoring Microbial Balance
Many factors, such as antibiotics, poor diet, stress, and infections, can disrupt the gut microbiome, allowing harmful bacteria to proliferate. Probiotics help restore this balance by replenishing beneficial microbes and crowding out pathogens.
2. Enhancing the Gut Barrier Function
The gut lining acts as a protective barrier that selectively allows nutrients to pass into the bloodstream while keeping harmful substances out. Probiotics encourage the production of tight junction proteins that seal the gaps between intestinal cells, preventing “leaky gut” — a condition where toxins and microbes leak into the bloodstream, triggering inflammation.
3. Modulating the Immune System
The gut contains around 70% of the body’s immune cells. Probiotics interact with immune cells to help regulate immune responses, promoting tolerance to harmless antigens while boosting defenses against pathogens. This immune modulation is key to reducing excessive inflammation.
4. Producing Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
Probiotics ferment dietary fibers into SCFAs like butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These molecules are vital for gut health as they:
- Provide energy for colon cells
- Reinforce gut barrier integrity
- Have potent anti-inflammatory properties by regulating immune signaling
Probiotics and Inflammation: What’s the Link?
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, aimed at healing and defense. But when inflammation becomes chronic, it can contribute to various diseases, including autoimmune conditions, allergies, metabolic syndrome, and even mental health disorders.
The gut microbiome — and probiotics specifically — influence inflammation through several pathways:
Immune System Modulation
Probiotics promote the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines (such as IL-10) and suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines (like TNF-alpha and IL-6). This helps keep immune responses balanced and prevents excessive inflammation.
Blocking Harmful Bacteria
By competing for nutrients and adhesion sites in the gut, probiotics inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria that can trigger inflammation.
Protecting the Gut Barrier
A healthy gut lining prevents endotoxins — toxic substances from bacteria — from leaking into circulation. This reduces systemic inflammation often linked to metabolic and autoimmune diseases.
Regulating T-Regulatory Cells
Probiotics support the function of T-regulatory cells, which are immune cells that suppress overactive inflammatory responses and maintain immune tolerance.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Probiotic Benefits
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
Clinical studies have demonstrated that probiotics, including multi-strain blends like VSL#3 and E. coli Nissle 1917, can reduce inflammation and help maintain remission in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease patients.
Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity
Probiotic supplementation has been associated with improved insulin sensitivity, reduced markers of systemic inflammation (like C-reactive protein), and better weight management outcomes.
Allergies and Asthma
Early probiotic intervention in infants may reduce the risk of developing allergic diseases by shaping the immune system’s tolerance mechanisms.
Mental Health and the Gut-Brain Axis
Emerging research shows that certain probiotics can reduce neuroinflammation linked to depression and anxiety, highlighting the intimate connection between gut health and mental well-being.
How to Incorporate Probiotics into Your Diet
Foods Rich in Probiotics
- Yogurt: Choose varieties labeled with “live and active cultures.”
- Kefir: A fermented milk drink loaded with probiotics.
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage with beneficial bacteria.
- Kimchi: Spicy Korean fermented vegetables.
- Miso: Fermented soybean paste used in Japanese cuisine.
- Tempeh: Fermented soybean cake, great protein source.
Probiotic Supplements
Supplements can be a convenient way to boost probiotic intake. Look for products with clinically studied strains, guaranteed CFU counts, and proper storage instructions.
Things to Keep in Mind
- Strain specificity: Not all probiotics have the same effects. Benefits depend on the particular strain(s) used.
- Individual differences: Each person’s microbiome is unique, so probiotic responses vary.
- Safety: Probiotics are generally safe for most people but should be used with caution by immunocompromised individuals.
- Prebiotics matter: Dietary fibers (prebiotics) feed probiotics and help them flourish.
Final Thoughts
The gut is more than just a digestive organ — it’s a powerhouse of immune regulation and inflammation control. Probiotics, as essential members of this ecosystem, play a vital role in nurturing gut health and keeping chronic inflammation in check.
By including probiotic-rich foods or supplements in your daily routine, you’re supporting a balanced microbiome, a strong gut barrier, and a modulated immune system — all of which contribute to better health and disease prevention.
Taking care of your gut means taking care of your whole body.
FAQs
1. What are probiotics and why are they important for gut health?
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria and yeasts that help maintain a balanced gut microbiome. They support digestion, strengthen the gut barrier, and modulate the immune system, which helps reduce inflammation and promote overall health.
2. How do probiotics help reduce inflammation in the body?
Probiotics reduce inflammation by promoting anti-inflammatory immune responses, suppressing harmful bacteria that trigger inflammation, strengthening the gut lining to prevent toxin leakage, and producing short-chain fatty acids that have anti-inflammatory effects.
3. Which probiotic strains are best for reducing inflammation?
Strains like Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Saccharomyces boulardii have shown anti-inflammatory properties. Multi-strain probiotic blends like VSL#3 are also effective, especially in inflammatory bowel conditions.
4. Can probiotic-rich foods provide the same benefits as supplements?
Yes, probiotic-rich fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi naturally contain beneficial bacteria that support gut health. However, supplements can provide targeted strains and higher doses for specific health concerns.
5. How long does it take to notice the effects of probiotics on inflammation?
Results vary depending on the individual, probiotic strain, and health condition. Some may notice digestive improvements within days, while reduction in chronic inflammation could take several weeks to months of consistent use.
6. Are probiotics safe for everyone?
Generally, probiotics are safe for most people. However, those with weakened immune systems, severe illnesses, or recent surgery should consult a healthcare provider before starting probiotics.
7. What is “leaky gut” and how do probiotics help?
Leaky gut is a condition where the intestinal lining becomes permeable, allowing toxins and bacteria to enter the bloodstream and trigger inflammation. Probiotics enhance the gut barrier by promoting tight junction proteins that seal intestinal cells together.
8. How does diet affect the effectiveness of probiotics?
Diet plays a crucial role. Consuming prebiotics—fibers that feed probiotics—like garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus helps probiotics thrive. A diet high in processed foods and sugar can disrupt the microbiome and reduce probiotic benefits.
9. Can probiotics help with specific inflammatory diseases like IBD or arthritis?
Research suggests probiotics can aid in managing inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) by reducing gut inflammation. Some evidence indicates potential benefits for autoimmune and inflammatory conditions like arthritis, but more studies are needed.
10. Should probiotics be taken daily, and is there a risk of becoming dependent on them?
Daily probiotic intake can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, especially after antibiotics or during illness. There is no evidence of dependence; however, maintaining a healthy diet is equally important to support natural gut bacteria.











