If you’re searching for prune juice for constipation, you’re likely hoping for relief that’s simple, safe, and fast. Good news: both prune juice and prunes can help many people get regular again. For adults, a practical starting point is ½–1 cup (120–240 mL) of prune juice once daily or 4–6 prunes, alongside a full glass of water. Many notice improvement within a few hours to 24 hours. For maintenance, prunes often shine; for “I need help today,” prune juice is easy to sip and gentle on the stomach. In this guide, you’ll learn exactly how prune juice for constipation works, how it compares with whole prunes, how much to take, what to do in pregnancy and infancy, and when to escalate care.
Friendly disclaimer
This article is general information, not medical advice. If you’re dealing with persistent or severe constipation, if you’re pregnant, or if you’re considering any remedy for an infant or newborn, please consult your healthcare professional for individualized guidance.
Does prune juice really work?
Yes—often. To begin with, a randomized controlled trial found that dried prunes improved stool frequency and softness more than psyllium in adults with mild to moderate constipation. Participants tolerated prunes well and found them palatable. If you like reading the source, skim the randomized trial of prunes vs. psyllium.
Moreover, the “why” is straightforward. The benefits come from sorbitol, fiber, and polyphenols. Sorbitol is a natural sugar alcohol that gently pulls water into the bowel (an osmotic effect) and softens stool. Fiber adds bulk and softness, which supports regularity. Polyphenols—plant compounds—may also nudge gut motility. For clarity, a classic composition review reports that prunes contain about 14.7 g of sorbitol per 100 g and ~6.1 g of fiber per 100 g, while prune juice contains ~6.1 g sorbitol per 100 g but very little fiber because most is filtered out. If you want the nutrient specifics, see the composition of prunes and prune juice and this concise overview of prune composition and nutrition (PDF).
In short, prune juice for constipation tends to act because of sorbitol, which draws water into the bowel. Prunes for constipation bring sorbitol plus fiber, which helps maintain softer, bulkier stools over time.
Also Read: Bananas for Constipation: Ripe vs Green, Timing & What Works
How much prune juice for constipation? (Adults)
Let’s make this friction-free. Start low, be kind to your gut, and adjust slowly.

Prune juice (adults):
- Start with ½–1 cup (120–240 mL) once daily.
- If nothing changes after 24–48 hours, increase by ~½ cup.
- Many people notice effects within a few hours to 24 hours.
- If gas or cramping shows up, take a step back.
Whole prunes (adults):
- Begin with 4–6 prunes (≈40–60 g) per day.
- If needed, go to 8–10 prunes, spaced through the day.
- Always pair with a full glass of water.
Meanwhile, evidence suggests prunes increase stool weight and frequency and are generally well tolerated in adults with infrequent stools or low fiber intake. For a quick snapshot, peek at this short report on tolerance and stool output with prunes.
Timing tips that help:
- Try your serving in the morning and allow unhurried bathroom time. Breakfast naturally triggers the gastrocolic reflex.
- Keep meals fiber-forward: oats, legumes, vegetables, fruit, nuts, and seeds.
- Drink enough water. Dehydration is a quiet saboteur of stool softness.

Taken together, these habits make prune juice for constipation act more predictably and more gently.
Also Read: Prune Juice Unveiled: 5 Surprising Reasons It Supports Weight Loss
Prunes vs. prune juice: which should you choose?
It depends on your goal—and your preference.
- Choose prune juice when you want something easy to drink and possibly faster acting. Each sip delivers sorbitol without much bulk.
- Choose whole prunes when you want maintenance. Fiber plus sorbitol supports a softer, bulkier stool day after day.
- Choose the option you’ll actually stick with. Consistency always wins.

By contrast, if blood sugar is on your mind, whole prunes often make sense because fiber helps blunt glucose spikes compared with filtered juice. Portion still matters, of course.
And remember the head-to-head trial: prunes beat psyllium on frequency and consistency. If you like a food-first approach, that’s strong real-world proof in your corner. Here’s that prunes vs. psyllium study again.
Also Read: Hemorrhoids High Fiber Diet: Best Foods, What to Avoid, and a 7-Day Plan
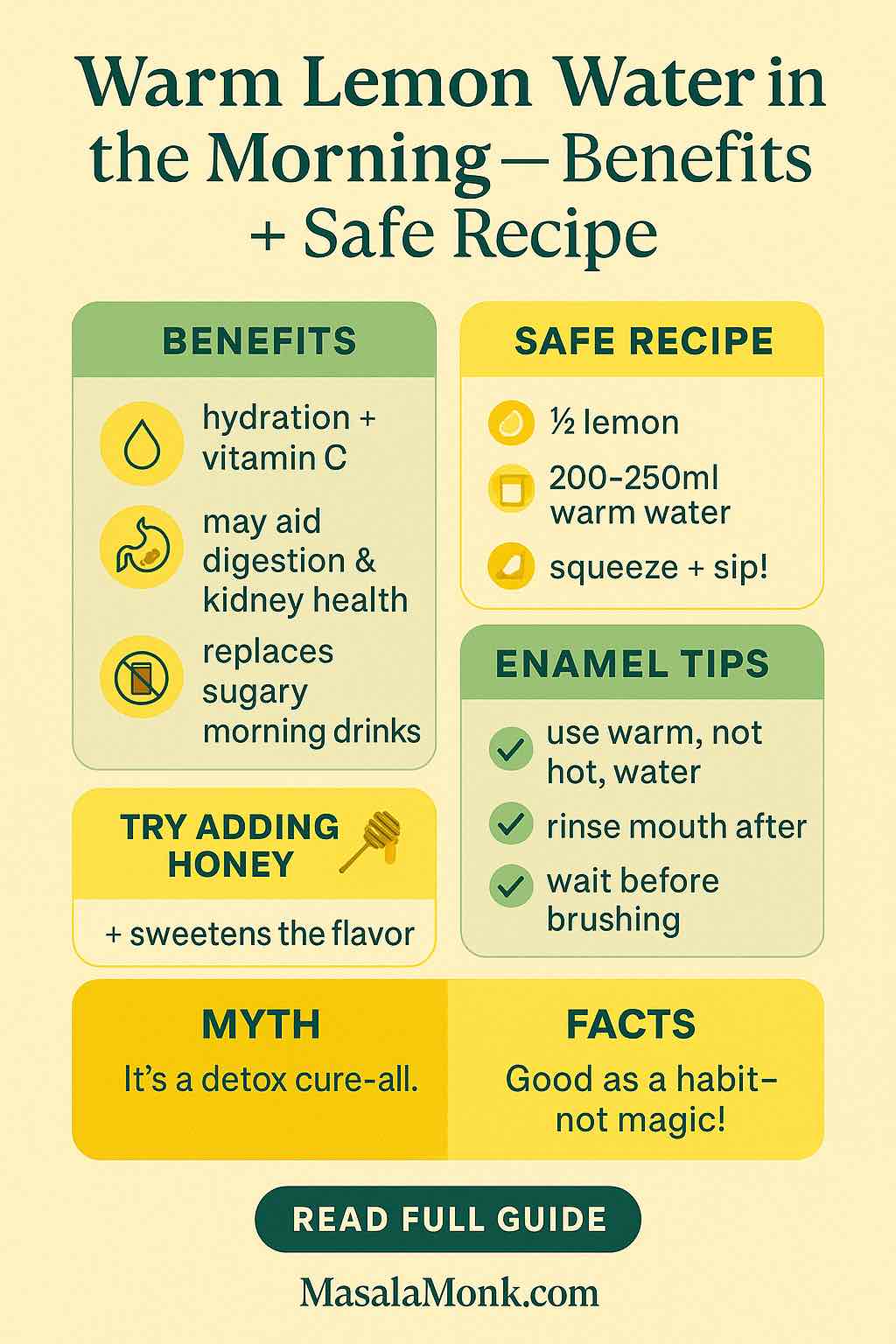
Does warming prune juice help?
Sometimes comfort matters. Warm prune juice can feel soothing and easier to sip. That said, the active effect still comes from sorbitol; temperature doesn’t change the chemistry. If warming the glass helps you drink it consistently, do it. If not, chilled prune juice works just as well. For a deeper look at the mechanism, revisit how sorbitol and fiber work in prunes and prune juice.

Is it safe to drink prune juice daily?
For most healthy adults, yes—when portions are modest. Side effects are usually dose-related: gas, cramping, or loose stools signal that it’s time to reduce your serving. If you live with diabetes or carefully watch carbohydrates, favor whole prunes or smaller juice portions; pairing meals with protein or fat also helps.
Even so, if you keep needing large daily amounts of prune juice for constipation and still feel stuck, step back. Focus on hydration. Lift your fiber at meals. Add a short daily walk. Then, if symptoms persist, consider next steps with your clinician. The American Gastroenterological Association and American College of Gastroenterology outline a stepwise plan for chronic idiopathic constipation that often begins with osmotic laxatives such as PEG 3350, followed by other options as needed. You can read the framework in the AGA/ACG guideline on chronic idiopathic constipation or skim a plain-language constipation guideline summary.
Think of prune juice for constipation as your gentle daily aid. If diet alone doesn’t fix it, the guideline gives you a safe, logical ladder to climb—without guesswork.
Also Read: Significance of Fiber in Diet: Understanding Its Health Benefits
A simple plan you can start today
Because a plan beats good intentions, here’s a five-step routine that uses prune juice for constipation or whole prunes as the anchor and layers in habits that actually move the needle.
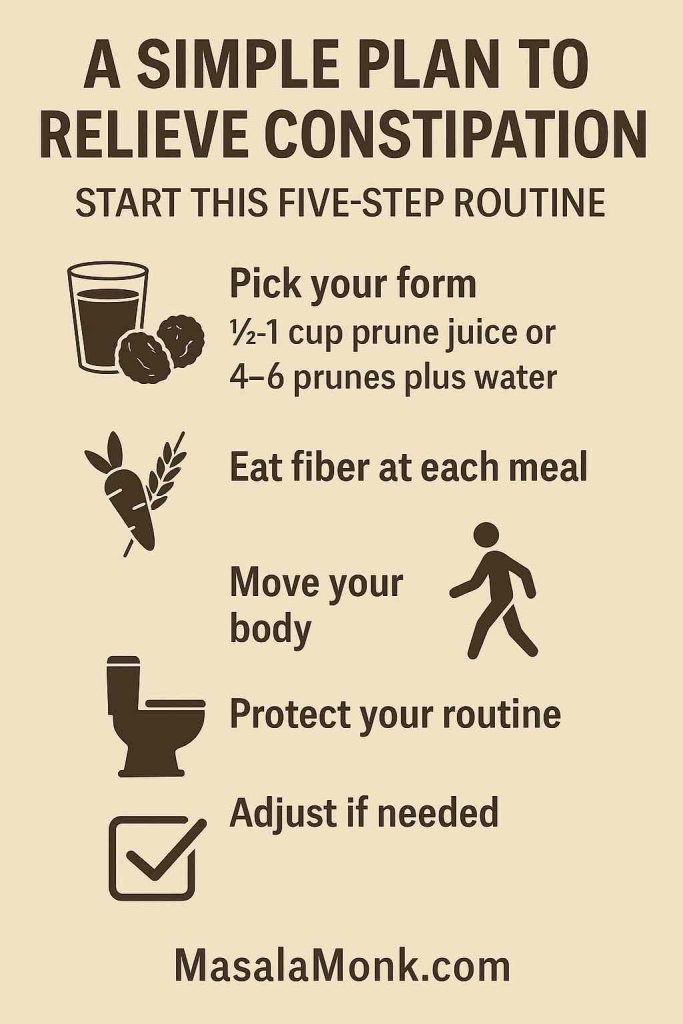
- Pick your form.
Choose ½–1 cup prune juice or 4–6 prunes in the morning. Add a full glass of water. Set aside relaxed bathroom time. - Eat fiber at each meal.
- Breakfast: oatmeal with ground flax or chia.
- Lunch: lentil soup or a chickpea-vegetable bowl.
- Dinner: a hearty veg side (beans, greens, carrots, broccoli).
- Snacks: fruit you enjoy—kiwi is a regularity favorite.
This keeps stools softer so prune juice for constipation does not have to work alone.
- Move your body.
Even a 10–20 minute walk helps. A brief stroll after meals can be enough. Movement nudges the bowel and lowers stress. - Protect your routine.
Create a consistent “bathroom window” daily. Don’t strain. If it helps, use a small footstool to elevate your knees. - Adjust after 24–48 hours.
If there’s little change, increase the dose gently—another ½ cup of juice or 2–3 prunes. If cramps or loose stools appear, reduce the dose. - Escalate if needed.
If there’s no meaningful improvement by 48–72 hours, consider guideline-supported OTC choices and speak with your clinician. The structured approach is here: the 2023 AGA/ACG constipation guideline.
Step by step, this plan is simple, sustainable, and respectful of your schedule.
Also Read: Psyllium Husk (Isabgol/Ispaghula) Side Effects: Risks, Benefits & How to Take It Safely
What about fresh plums—do plums make you poop?
Fresh plums are hydrating and contain some sorbitol and fermentable fiber. They’re great for everyday eating and gentle regularity. Nevertheless, prunes and prune juice are usually more effective when you’re truly constipated because prunes are concentrated and prune juice is easy to take when you don’t feel like chewing. If you want ideas for everyday use, try this friendly, practical read on plum nutrition and benefits.
Many readers keep both on hand: prunes in the pantry for routine, prune juice in the fridge for “today.” That way prune juice for constipation is available when you need speed, and prunes help keep things moving over the long term.
Infants and prune juice: please read this first

Here, precision matters. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends no fruit juice for infants under 12 months unless there’s a specific clinical reason. In other words, do not give juice to a young baby for general health; use it only if your pediatrician recommends it for constipation and provides exact dosing and dilution instructions. You can verify that policy in the AAP statement on fruit juice in infants and children and their family-facing summary, where the AAP stands on fruit juice.
In practice, some pediatric pathways allow tiny, diluted amounts of apple or pear juice in young infants with constipation, but only with clinician supervision. Prune juice may be considered a little later, again in small, diluted amounts. If your baby is ≥6 months and on solids, many clinicians prefer pureed prunes over juice because the child gets both fiber and sorbitol in a spoon-fed form. Above all, if your baby has vomiting, fever, blood in stool, a swollen belly, or poor weight gain, call your pediatrician right away.
For parents thinking long term, gentle food habits—once solids begin—can help the whole family. If you want soft, adaptable blends and easy tips (choose ingredients your pediatrician has cleared), explore these pregnancy and family-friendly digestion ideas.
Pregnancy and prune juice: reasonable, food-first steps
Constipation is common in pregnancy. Hormones, iron supplements, and a shifting routine all play a role. To begin with, a food-first plan is ideal: modest servings of prunes or prune juice, more water, fiber-rich meals, and comfortable movement as your provider approves.

If symptoms persist despite those steps, stool softeners such as docusate are generally considered safe in pregnancy; stimulant laxatives are used more cautiously. For balanced medical context, see the Mayo Clinic overview on pregnancy constipation and their clear guide to nonprescription laxatives.
To that end, small daily habits still matter. Mini meals with produce, steady hydration, and gentle walks stack up. If you want a friendly, food-based primer to personalize, try these pregnancy nutrition and digestion tips.
Safety, side effects, and sensible limits
Most people tolerate prune juice for constipation and prunes well. Still, a few guardrails keep things comfortable.
- Common effects: Gas, cramping, and loose stools—each is dose related. If they appear, reduce your serving.
- Medications and conditions: If you have chronic GI disease, are fluid-restricted, or live with complex medical conditions, talk with your clinician before relying on large daily amounts.
- Daily use: Modest daily portions are fine for many healthy adults. However, if you need frequent, large “rescue” doses, it’s time to step up to a structured plan. The AGA/ACG guideline offers a safe path forward.
Beyond those basics, remember that stress, sleep, and routine affect the gut. Even brief walks, a calmer morning rhythm, and a consistent bathroom window can improve results—and they pair well with prune juice for constipation.
Also Read: What is Metamucil? Best Time to Take, Side Effects, and More
Red flags: when to call a clinician
Seek medical advice promptly if you have any of the following:
- No bowel movement for more than 3–4 days with discomfort.
- Severe abdominal pain, vomiting, or fever.
- Blood in the stool.
- Unintentional weight loss or a persistent, new change in bowel habits.
- Worsening constipation in pregnancy or older age despite food and OTC measures.
These symptoms deserve timely attention. If diet isn’t enough, use the clinical roadmap here: the 2023 AGA/ACG constipation guideline.
Putting it all together—so it sticks
Let’s land the plane with something you can trust and actually do today.
- Keep prune juice for constipation as your quick helper. Use ½–1 cup to start, then adjust gently.
- Keep prunes for constipation as your daily anchor. Use 4–6 prunes with water; scale up slowly if needed.
- Build meals with fiber: vegetables, beans, whole grains, fruit, and seeds.
- Move gently every day. Even short walks matter.
- Protect your bathroom routine: a calm morning, a few minutes, no straining.
- If there’s little change after 48–72 hours, escalate thoughtfully with your clinician using the guideline above.
Ultimately, simple, consistent habits tend to win. Your gut likes rhythm. A morning glass of prune juice for constipation can be that rhythm starter. A handful of prunes can be your maintenance plan. Add a glass of water. Eat more plants. Take a short walk. Give yourself unhurried time in the bathroom. These steps are small, yet together they often work better than any single trick.
On balance, that’s the promise here: everyday choices that bring steady comfort, plus a clear path if you need more help. Start today, listen to your body, and adjust with care. If you need backup, you now know exactly where to turn—and which questions to ask—so you can get relief, stay regular, and get back to living your life.
Friendly medical disclaimer
This article offers general information to help you make informed choices about prune juice for constipation and related diet strategies. It is not a diagnosis or personalized medical advice. Please speak with your healthcare professional if you have ongoing or severe symptoms, complex medical conditions, or questions about treatments—especially if you are pregnant, older, or considering any remedy for an infant or newborn.
Sources
- Randomized controlled trial: prunes outperform psyllium on stool frequency and consistency — prunes vs. psyllium RCT.
- Mechanism and composition (sorbitol, fiber, polyphenols): composition of prunes and prune juice; overview of prune composition and nutrition (PDF).
- Clinical escalation framework: AGA/ACG guideline on chronic idiopathic constipation; constipation guideline summary.
- AAP policy on infant juice: AAP statement on fruit juice; family-facing AAP summary.
- Pregnancy context and OTC options: Mayo Clinic on pregnancy constipation; Mayo Clinic on laxatives.
FAQs
1) Does prune juice for constipation actually work?
Yes. It helps many people. Sorbitol draws water into the bowel. Meanwhile, prunes add fiber that softens stool. Together, they often relieve mild constipation.
2) How much prune juice for constipation should adults start with?
Begin with ½–1 cup (120–240 mL) once daily. Afterward, reassess symptoms in 24–48 hours. If needed, increase by about ½ cup. Avoid large jumps.
3) How fast does prune juice for constipation work?
Often within a few hours, though sometimes up to 24 hours. Consequently, give it a day before changing your dose.
4) Is warm prune juice better than cold?
Not really. However, warmth can feel soothing. The active effect comes from sorbitol, not temperature.
5) Are prunes or prune juice better for constipation?
Both help. On the other hand, prunes offer fiber plus sorbitol for maintenance. Prune juice is convenient and may act sooner.
6) How many prunes should I eat for constipation?
Start with 4–6 prunes daily. Additionally, drink a full glass of water. If needed, move to 8–10, spaced through the day.
7) Is it safe to drink prune juice every day?
Usually, yes—in modest amounts. Still, if you get gas or loose stools, cut back. Ultimately, consistency beats high doses.
8) Does prune juice have fiber?
Very little. The fiber remains mostly in whole prunes. Therefore, for fiber, eat prunes; for sorbitol, drink juice.
9) Can prune juice constipate you?
Rarely. Yet overuse may cause cramps or diarrhea instead. As a rule, adjust your dose gently.
10) Do plums make you poop?
Sometimes. Fresh plums contain sorbitol and water. Nevertheless, dried prunes and prune juice for constipation are typically stronger options.
11) What is the best juice for constipation besides prune?
Pear and apple juices contain sorbitol too. Moreover, kiwi smoothies can help due to fiber. Hydration helps all options work better.
12) What’s the best prune juice for constipation—any features to look for?
Choose 100% prune juice with no added sugar. If possible, pick a brand you’ll actually drink daily. Likewise, shelf-stable or refrigerated both work.
13) Is sugar-free or “light” prune juice better?
Maybe. Reduced-sugar versions can be easier for those watching carbs. However, ensure the serving still provides adequate sorbitol.
14) Do dried prunes soften stool?
Yes. In fact, fiber plus sorbitol softens and bulks stool. Consequently, many people use prunes for regularity maintenance.
15) Should I drink prune juice in the morning or at night?
Morning often works well. After breakfast, the gastrocolic reflex helps. Nevertheless, choose a time you can keep every day.
16) Can I mix prune juice with Miralax (PEG 3350)?
Often, yes—short term and as advised by a clinician. Additionally, keep fluids up. If symptoms persist, seek medical guidance.
17) Is prune juice a stool softener or a laxative?
Functionally, both. Technically, it acts as an osmotic laxative via sorbitol. Meanwhile, whole prunes behave like a natural stool softener because of fiber.
18) Can infants have prune juice for constipation?
Use caution. For young infants, follow a pediatrician’s guidance only. Alternatively, older babies on solids often try pureed prunes first.
19) Can newborns drink prune juice?
No. For newborns, consult a pediatrician for safe options. In any case, do not give juice without medical advice.
20) How much prune juice for infants who are older?
Only if a clinician recommends it. Even then, amounts are tiny and typically diluted. Above all, follow professional dosing exactly.
21) Is prune juice safe during pregnancy?
Generally, in food-like portions, yes. Furthermore, hydration, fiber, and gentle movement matter. If constipation persists, discuss safe OTC options with your provider.
22) Can prunes or prune juice cause gas?
Yes, occasionally. Sorbitol can ferment. Therefore, start low—then titrate slowly. Pair with water to reduce discomfort.
23) Can prunes make you constipated?
Unlikely. Nonetheless, very large servings without water may backfire. Balance prunes with fluids and regular meals.
24) What if prune juice for constipation doesn’t work after two days?
First, confirm fluids and fiber. Next, increase the dose modestly. If still stuck after 48–72 hours, consider clinician-guided OTC options.
25) Is a prune smoothie for constipation helpful?
Often, yes. Blend whole prunes with yogurt, oats, or seeds. Consequently, you’ll add fiber and fluids together.
26) Does plum juice help with constipation?
Sometimes. However, prune juice usually contains more sorbitol per serving. Therefore, prune juice for constipation tends to be more reliable.
27) Are prune tablets, pills, or concentrates effective?
They can be, yet responses vary. Tablets may lack fiber. Concentrates may be potent. Accordingly, start low and watch tolerance.
28) What’s the best way to use prune juice as a laxative?
Begin with ½–1 cup daily. Then, wait 24–48 hours. If needed, increase slowly. Meanwhile, drink water and keep meals fiber-rich.
29) Should I warm prune juice for constipation at night?
You can. Warmth may relax you. Even so, the key is the consistent sorbitol dose, not timing alone.
30) Can I drink prune juice every morning for regularity?
Yes, many people do. Likewise, some alternate days with whole prunes. Ultimately, choose the routine you’ll stick to.
31) Do prunes help bowel movements in the long run?
Yes. Fiber plus sorbitol supports ongoing regularity. Besides, they’re portable and easy to portion.
32) Can prune juice help with gas or does it make gas worse?
Both can occur. Initially, small servings may cause gas. Consequently, start low, sip slowly, and increase as tolerated.
33) Is prune juice as good as prunes for constipation?
It depends. For speed, prune juice may help first. For maintenance, prunes often win. Ideally, use both strategically.
34) How do I avoid diarrhea from prune juice?
Go slow. For example, start at ½ cup. Additionally, space servings and hydrate. Reduce the dose at the first sign of urgency.
35) What’s better than prunes for constipation if food fails?
If food strategies stall, consider clinician-approved OTC options. Meanwhile, keep water and fiber steady to support those tools.
36) Do plums make you constipated?
Not typically. Still, very low fluid intake may firm stool. Therefore, pair plums with water and other high-fiber foods.
37) Should I choose pitted prunes or whole prunes with pits?
Choose pitted for convenience and safety. Similarly, measure portions easily. Quality and fiber content remain comparable.
38) Does prune juice for constipation work for everyone?
No remedy works for all. Nevertheless, many benefit. If not, reassess dose, hydration, fiber, and timing. Then, consider professional advice.
39) When should I stop home measures and call a clinician?
Stop and call if you have severe pain, vomiting, blood in stool, fever, weight loss, or no improvement after 48–72 hours.
40) What daily routine pairs best with prune juice for constipation?
Morning dose, water, fiber at meals, a short walk, and a calm bathroom window. In short, keep it simple and consistent.