If you’re a coffee lover who’s ever found yourself dashing to the bathroom more often than you’d like, you’re not alone. Coffee is woven into the fabric of our mornings, workdays, and social rituals, but what does this beloved beverage do to your urinary health? From increased frequency to bladder irritation, let’s dive into the real-world impact of coffee on our bodies—combining science, recent research, and firsthand stories to help you make the best decisions for your daily brew.
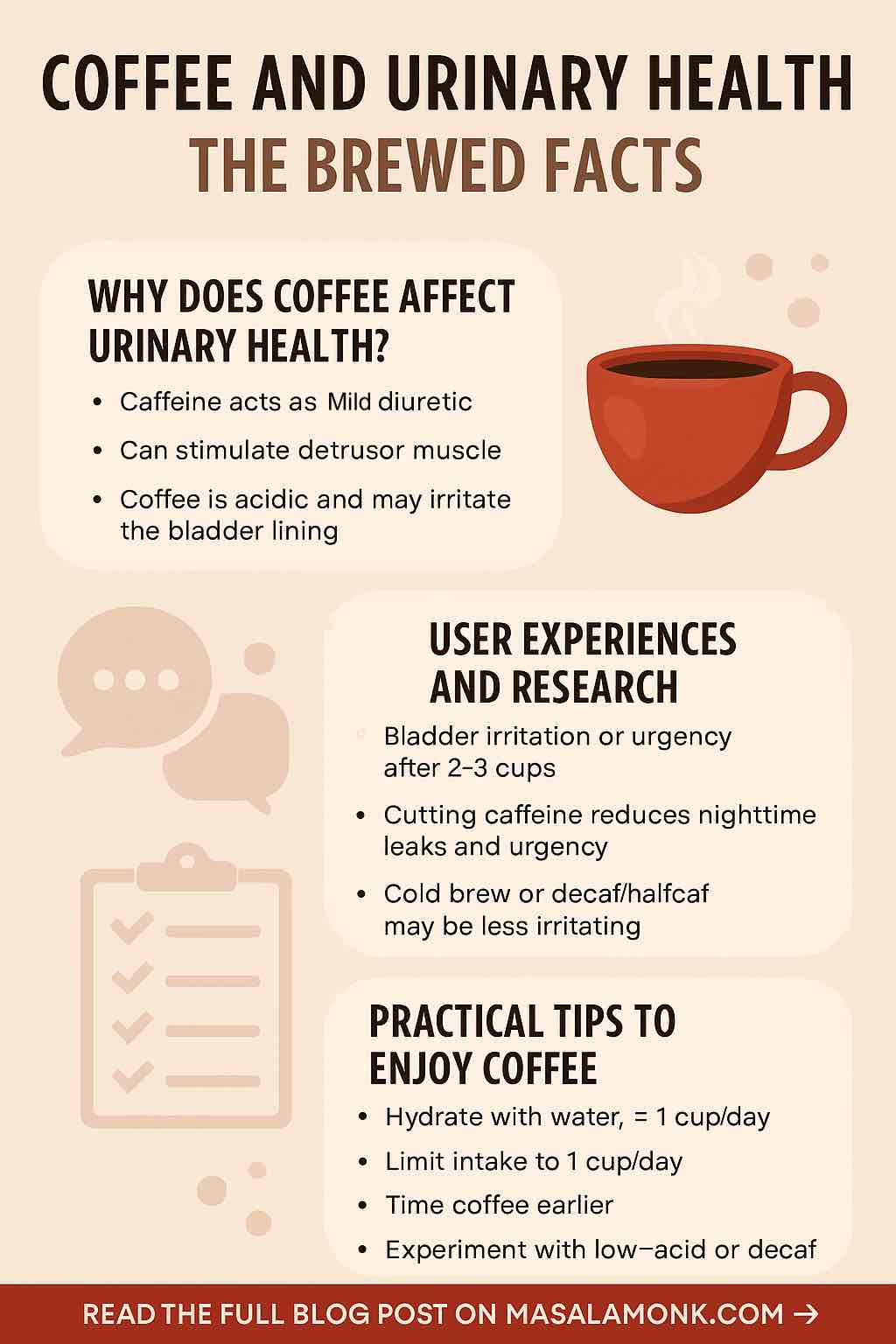
☕ Why Does Coffee Affect Urinary Health?
Coffee contains caffeine—a natural stimulant that perks up your brain and can make your bladder a bit hyperactive, too. But it’s not just caffeine; coffee is also acidic and contains other compounds that can potentially irritate the bladder lining.
The Science in Simple Terms
- Caffeine acts as a mild diuretic, meaning it can make your kidneys produce more urine, especially in people who don’t consume it regularly.
- It can stimulate the detrusor muscle (the muscle in your bladder wall), leading to increased urgency and frequency for some.
- Coffee’s acidity may irritate the bladder lining, especially for those with sensitive systems, such as people with interstitial cystitis (IC) or during a urinary tract infection (UTI).
🚽 Real User Experiences: Not Just “In Your Head”
It’s one thing to read about coffee’s effects in a medical journal. It’s another to hear from people who live it every day:
- On Reddit’s r/Interstitialcystitis, users describe how even a single cup of coffee can trigger burning, pelvic pain, or a constant urge to pee—sometimes mimicking the feeling of a mild UTI.
- Some find relief by switching to cold brew or decaf, or by using supplements like Prelief that reduce acidity.
- Others share that symptoms seem to vary: a person might tolerate coffee for years, then suddenly develop bladder sensitivity out of nowhere.
It’s not just those with medical diagnoses, either. Many people—especially those new to coffee or who ramp up their intake—notice an increase in bathroom visits or nighttime trips (nocturia) after a few cups.
🔬 What Does the Latest Research Say?
Recent scientific reviews back up these lived experiences:
- Caffeine can aggravate symptoms of overactive bladder (OAB) and increase urgency/frequency in some people. Cutting down on caffeine often leads to fewer nighttime leaks and fewer frantic bathroom runs.
- For urinary incontinence, research shows that moderate coffee intake isn’t a major risk factor for most people—but heavy intake (three or more cups a day) can worsen symptoms in those already prone.
- In men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), higher caffeine intake has been linked to increased urinary symptoms (such as frequency and urgency).
- Kidney stones? Interestingly, moderate coffee drinking may actually lower your risk for some kinds (such as calcium oxalate stones), thanks to increased urine flow.
- UTIs: Coffee doesn’t cause infections but may increase discomfort if you’re already experiencing one, due to its acidity and stimulation of the bladder.
🧪 Why the Variability? It’s All About You
Why can your friend drink coffee all day without issue while you’re running for the bathroom? Here’s what matters:
- Tolerance: Habitual coffee drinkers build up a tolerance to caffeine’s diuretic effects.
- Individual Sensitivity: Some people are more prone to bladder irritation or muscle stimulation.
- Health Conditions: IC, OAB, BPH, and UTIs all make you more sensitive to the effects of coffee.
- Dose & Timing: Two cups in the morning may have a different effect than sipping all day, or drinking a strong cup at night.
🔎 How to Tell if Coffee is Affecting You
- Track Your Symptoms: Keep a “bladder diary” for a week. Note your coffee intake (amount and time), other fluids, bathroom trips, and any symptoms (urgency, discomfort, frequency).
- Experiment with Elimination: Try cutting out coffee (and other caffeine sources) for a week or two. Reintroduce gradually and note any changes.
- Consider the Type of Coffee: Cold brew and some decaf options are lower in acidity and may be less irritating. Some people do better with lighter roasts.
🛠️ Practical Tips: Enjoy Coffee Without Losing Control
- Hydrate Wisely: Drink water alongside coffee to dilute its effects on your bladder.
- Limit Intake: If you notice symptoms, try cutting back to 1 cup per day, or switching to half-caf/decaf.
- Time It Right: Avoid coffee late in the day if you struggle with nighttime urination.
- Try Supplements: Acid-reducing supplements like Prelief may help some people (but check with your doctor first).
- Explore Alternatives: Herbal teas, low-acid coffee blends, or caffeine-free “grain coffees” may be less irritating.
🗣️ Voices from the Community
- “I switched to cold brew, and it made a huge difference! No more running to the bathroom after every cup.”
- “Even decaf triggers urgency for me. I miss my morning ritual, but my bladder thanks me.”
- “I found that drinking a big glass of water before my coffee helps. It’s not perfect, but it’s better.”
- “Symptoms totally disappeared when I cut coffee out for a month. Came right back when I started again. Guess I need to stick with tea!”
🩺 When to See a Doctor
If you experience:
- New or worsening urinary symptoms
- Pain, burning, or blood in your urine
- Difficulty emptying your bladder
…see a healthcare provider. Sometimes, what seems like “coffee bladder” may be a sign of infection or another condition that needs attention.
✅ Bottom Line: Can You Keep Your Cup?
For most healthy adults, moderate coffee intake is safe and unlikely to cause major urinary issues. But if you have a sensitive bladder, overactive bladder, BPH, or you’re prone to UTIs, even one or two cups can make a big difference.
The key is paying attention to your own body, tracking your symptoms, and adjusting your habits. Coffee is meant to be enjoyed, not endured—so brew wisely and listen to what your bladder is telling you!
Have you noticed a connection between coffee and your urinary health? Share your story in the comments, or try a one-week coffee break and tell us what happens!
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Coffee and Urinary Health
1. Does coffee always make you pee more?
Not always, but caffeine in coffee is a mild diuretic and can increase urine output, especially in people who aren’t regular coffee drinkers. Over time, your body builds a tolerance, so frequent coffee drinkers may notice less of an effect.
2. Can coffee cause urinary incontinence?
High caffeine intake can worsen symptoms of urgency and incontinence, particularly for people already prone to overactive bladder or urinary issues. However, moderate intake (1–2 cups daily) is not a proven cause of incontinence in healthy adults.
3. Is decaf coffee safer for the bladder?
Decaf coffee has less caffeine but is still acidic, so it can still irritate the bladder in sensitive individuals. Some find decaf less bothersome, while others still notice symptoms.
4. What is the best coffee for sensitive bladders?
Cold brew coffee and low-acid coffee blends are generally gentler on the bladder. Experiment with different roasts and brewing methods to find what works for you.
5. Should I avoid coffee if I have a UTI?
It’s best to avoid coffee during a UTI, as both caffeine and acidity can worsen irritation and discomfort.
6. How much coffee is too much for urinary health?
For those with urinary symptoms, staying below 100 mg of caffeine per day (about 1 small cup) is often recommended. Listen to your body—if symptoms flare up, consider lowering your intake further.
7. Can coffee cause permanent bladder damage?
No evidence shows that coffee causes permanent bladder damage. Its effects are typically reversible once intake is reduced or stopped.
8. Can I still drink coffee with interstitial cystitis (IC)?
Many people with IC are sensitive to coffee and may need to avoid it altogether. Some tolerate small amounts of low-acid or decaf coffee, but triggers vary individually.
9. Does coffee contribute to dehydration?
Not in regular drinkers. The water in coffee counts toward your daily hydration needs. Any mild diuretic effect in regular coffee users is minimal.
10. Are there supplements to reduce coffee’s impact on the bladder?
Some use acid-reducing supplements (like Prelief) to make coffee less irritating. These may help, but effectiveness is personal and not a substitute for professional medical advice.