Cinnamon For Diabetes Is A Preventative Wand Against Sugar Spikes!
Introduction:
Cinnamon, a fragrant spice derived from the bark of cinnamon trees, has been a staple in traditional medicine for centuries. Beyond its culinary uses, cinnamon has garnered attention for its potential benefits in managing diabetes. In this guide, we’ll explore the relationship between cinnamon and diabetes, addressing common queries and diving deep into the science behind this sweet remedy.
Table of Contents:
- The Cinnamon-Diabetes Connection
- Types of Cinnamon: Which is Best for Diabetes?
- How to Incorporate Cinnamon into Your Diet
- Scientific Studies on Cinnamon and Diabetes
- Precautions and Recommendations
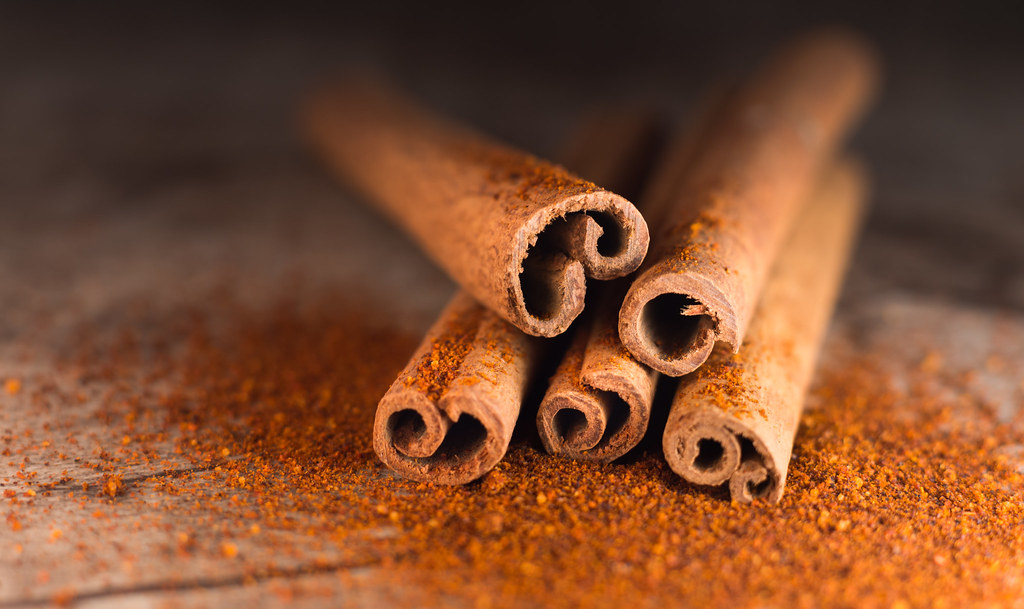

1. The Cinnamon-Diabetes Connection
Is Cinnamon Beneficial for Diabetes?
Cinnamon is believed to have properties that can improve insulin sensitivity, thereby aiding in blood sugar regulation. It contains bioactive compounds that may mimic the action of insulin and enhance glucose uptake by cells.
Dalchini and Diabetes:
‘Dalchini’ is the Hindi term for cinnamon. Just like its English counterpart, dalchini has been recommended in Ayurvedic medicine for its potential in controlling blood sugar levels.
2. Types of Cinnamon: Which is Best for Diabetes?
There are several types of cinnamon, but the two most common are:
- Ceylon Cinnamon (True Cinnamon): This type is native to Sri Lanka and is considered to be of higher quality.
- Cassia Cinnamon: More commonly available and is what people typically refer to as “regular” cinnamon.
For diabetes management, Ceylon cinnamon is often recommended due to its lower coumarin content, which can be harmful in large doses.
3. How to Incorporate Cinnamon into Your Diet
Cinnamon Tea:
Steeping cinnamon sticks in hot water creates a soothing tea that not only tastes great but can also help in blood sugar regulation.
Cinnamon Supplements:
For those who prefer a more measured approach, cinnamon supplements are available. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
Cooking with Cinnamon:
From sprinkling on oatmeal to adding it to curries, there are countless ways to incorporate cinnamon into your meals.
4. Scientific Studies on Cinnamon and Diabetes
Several studies have explored the effects of cinnamon on blood sugar levels. While some indicate positive results, others are inconclusive. It’s essential to approach the topic with a balanced view, understanding that while cinnamon can be a helpful adjunctive therapy, it shouldn’t replace prescribed diabetes medications.
5. Precautions and Recommendations
Dosage:
The recommended dosage can vary, but generally, 1-2 teaspoons of cinnamon daily can be beneficial. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Potential Side Effects:
While cinnamon is safe for most people, excessive consumption can lead to issues like liver damage due to the coumarin content in Cassia cinnamon.
Who Should Avoid Cinnamon?
Pregnant women and those with liver conditions should exercise caution. Additionally, if you’re on medication for diabetes, monitor your blood sugar levels closely as cinnamon can potentiate the effects of these drugs.
Conclusion:
Cinnamon, with its aromatic allure, offers more than just flavor. Its potential benefits in diabetes management make it a topic of interest for both researchers and those living with the condition. As with any natural remedy, it’s essential to use it judiciously, in conjunction with a balanced diet, regular monitoring, and prescribed medications.
Blog Tags:
Cinnamon for Diabetes, Blood Sugar Regulation, Natural Remedies for Diabetes, Ceylon vs. Cassia Cinnamon, Cinnamon Supplements, Dalchini Benefits, Ayurvedic Solutions for Diabetes, Cinnamon Dosage, Cinnamon Side Effects, Dietary Solutions for Diabetes.
Cinnamon and Diabetes: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can cinnamon help manage diabetes?
Yes, cinnamon has properties that can improve insulin sensitivity, potentially aiding in blood sugar regulation. Some studies suggest that it can enhance glucose uptake by cells.
2. How does cinnamon affect blood sugar levels?
Cinnamon contains bioactive compounds that may mimic the action of insulin, helping to lower blood sugar levels by enhancing the uptake of glucose by cells.
3. What is ‘dalchini’ and how is it related to diabetes?
‘Dalchini’ is the Hindi term for cinnamon. Like cinnamon, dalchini has been recommended in traditional medicine for its potential benefits in controlling blood sugar levels.
4. Which type of cinnamon is best for diabetes?
Ceylon cinnamon, often referred to as “True Cinnamon,” is considered better for diabetes management due to its lower coumarin content, which can be harmful in large doses.
5. How can I incorporate cinnamon into my diabetic diet?
You can drink cinnamon tea, take cinnamon supplements (after consulting a healthcare professional), or simply sprinkle it on your meals, like oatmeal or smoothies.
6. Are there scientific studies supporting the use of cinnamon for diabetes?
Yes, several studies have explored the effects of cinnamon on blood sugar levels. While some indicate positive results, others are inconclusive. It’s essential to approach the topic with a balanced view.
7. How much cinnamon should a diabetic take daily?
The general recommendation is 1-2 teaspoons of cinnamon daily. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
8. Are there any side effects of consuming cinnamon for diabetes?
While cinnamon is safe for most people, excessive consumption, especially of Cassia cinnamon, can lead to potential liver damage due to its coumarin content.
9. Can pregnant women consume cinnamon for diabetes management?
Pregnant women should exercise caution and consult with their healthcare provider before consuming large amounts of cinnamon.
10. I’m on medication for diabetes. Can I still take cinnamon?
Yes, but monitor your blood sugar levels closely. Cinnamon can potentiate the effects of some diabetes drugs. Always consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your regimen.
11. Can cinnamon tea help with diabetes?
Cinnamon tea can be a soothing way to incorporate cinnamon into your diet, potentially offering blood sugar-regulating benefits. However, it should be consumed as part of a balanced diet and not as a sole treatment.
12. Does cinnamon offer benefits for both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes?
Most studies focus on the effects of cinnamon on Type 2 diabetes. While it may offer some benefits for Type 1 diabetes, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for specific advice.
13. How does cinnamon compare to other natural remedies for diabetes?
Cinnamon is among several natural remedies believed to help manage diabetes. While it has unique properties, it’s essential to understand that natural remedies should complement prescribed treatments and not replace them.
14. Can I take cinnamon supplements instead of the spice?
Yes, cinnamon supplements are available and can offer a more measured approach. However, always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
15. Is cinnamon beneficial for prediabetes?
Some studies suggest that cinnamon can help improve insulin sensitivity, potentially benefiting those with prediabetes. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for guidance.