Oily fish have long been celebrated as a nutritional powerhouse, but their true benefits go far beyond just being a rich source of protein. Bursting with essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, oily fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies are a crucial part of a healthy diet. At the heart of their health-promoting properties lies omega-3 fatty acids — particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) — which are vital fats our bodies cannot produce on their own.
In this post, we’ll take a deep dive into the remarkable health benefits of oily fish, exploring how these nutrients support cardiovascular health, brain function, eye health, joint strength, skin vitality, sleep quality, and even prenatal development. By the end, you’ll understand why regular consumption of oily fish is one of the simplest and most effective ways to enhance your overall well-being.
What Makes Oily Fish So Special?
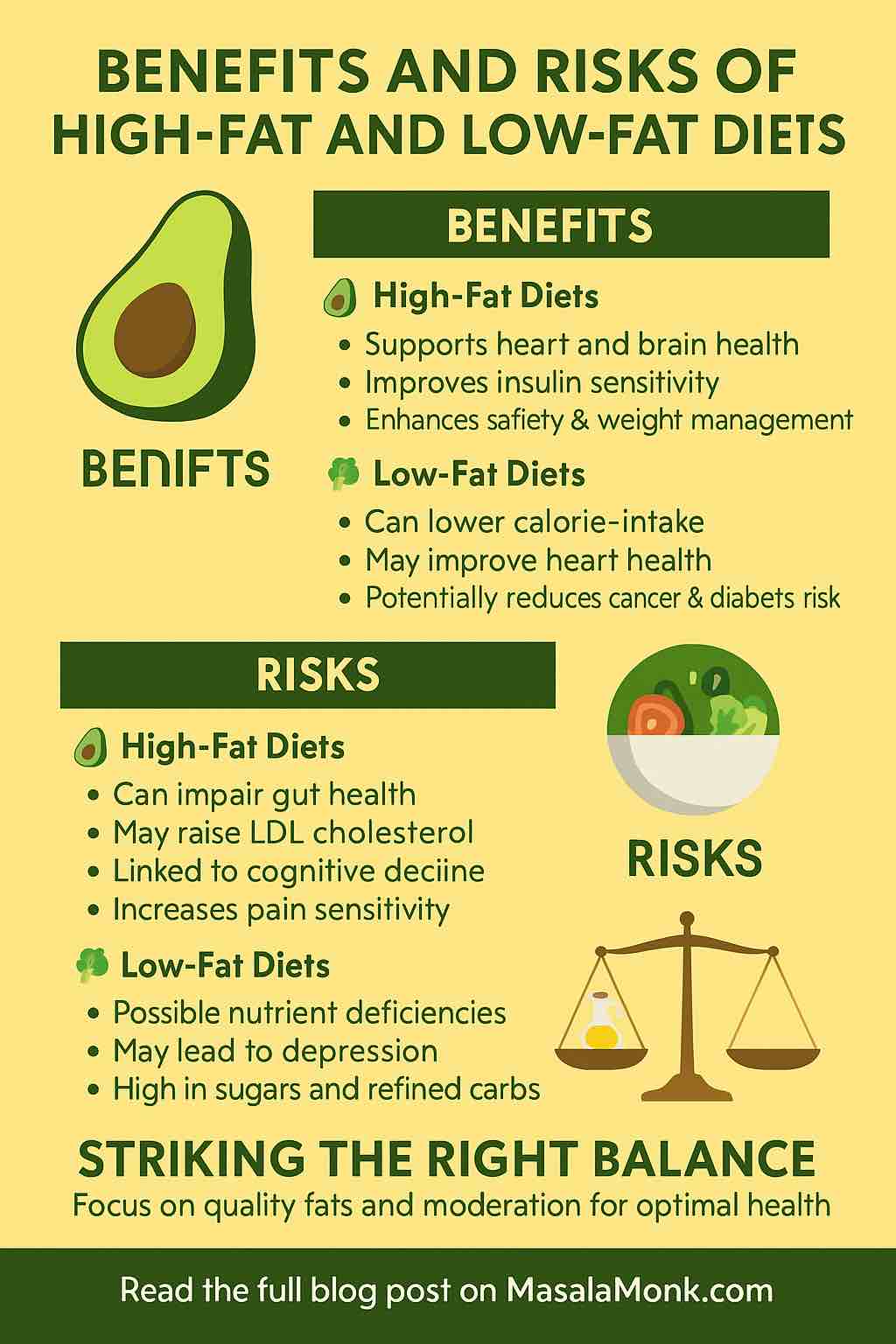
Unlike lean fish, oily fish have higher fat content distributed throughout their tissues. This fat is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been extensively studied for their anti-inflammatory, heart-protective, and neuroprotective effects. These essential fats are critical for many physiological processes and have been linked to reduced risk of chronic diseases that are among the leading causes of death globally.
Beyond omega-3s, oily fish also provide:
- Vitamin D — important for bone health and immune function.
- High-quality protein — for muscle repair and enzyme production.
- Minerals such as calcium, selenium, and iodine.
- Antioxidants like astaxanthin (especially in salmon), which protect cells from oxidative damage.
1. Cardiovascular Health: The Heart of the Matter
Heart disease remains the number one killer worldwide. Luckily, consuming omega-3-rich oily fish can significantly reduce your risk by:
Lowering Triglycerides and Cholesterol
Omega-3 fatty acids help lower triglyceride levels — fats in the blood that, when elevated, increase heart disease risk. They also raise HDL (good cholesterol) while lowering LDL (bad cholesterol), promoting a healthier lipid profile.
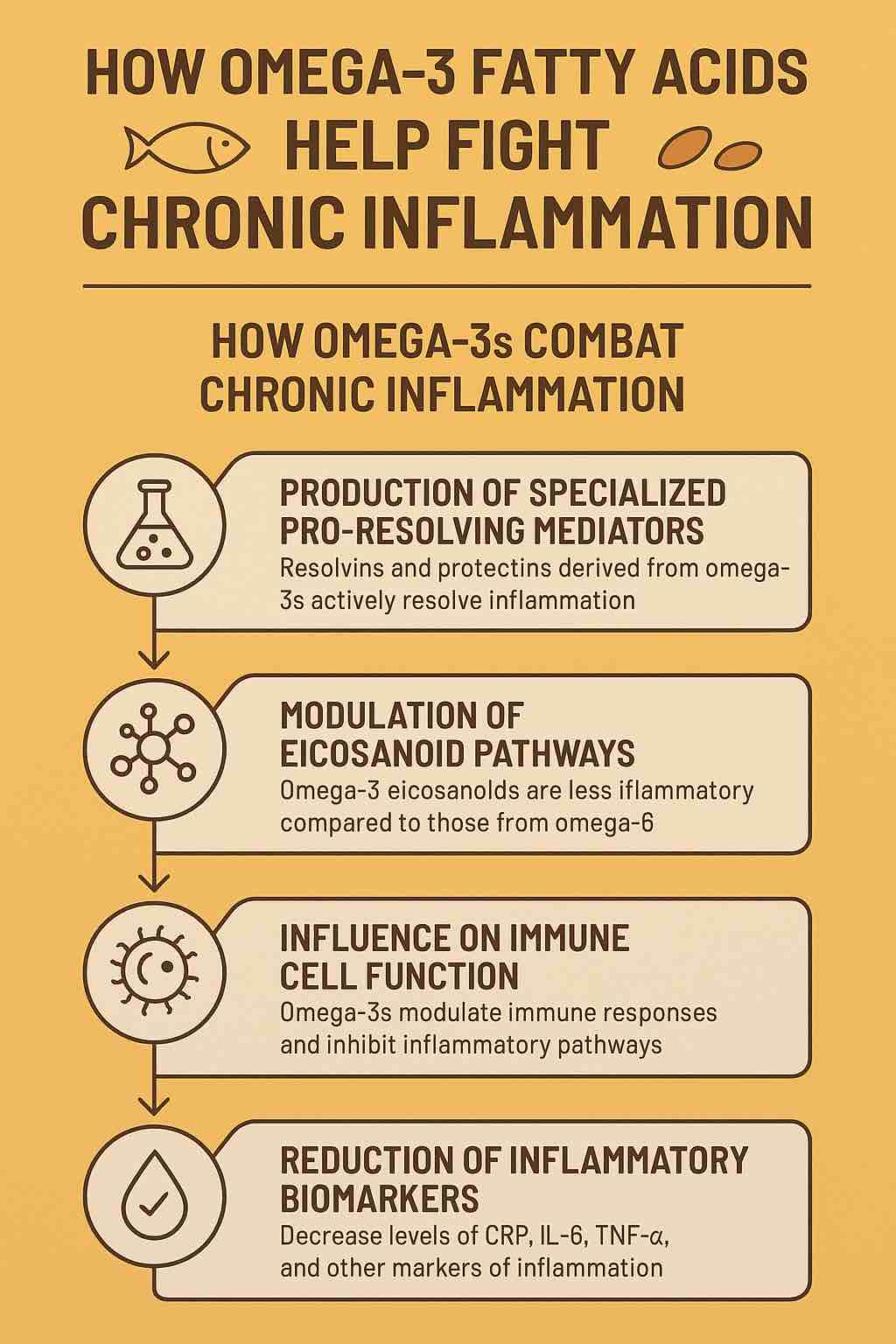
Reducing Inflammation
Chronic inflammation contributes to plaque buildup in arteries. Omega-3s suppress inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP), reducing artery damage and improving overall cardiovascular function.
Supporting Heart Rhythm
Omega-3s help stabilize heart rhythms, reducing the risk of arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats) and sudden cardiac death.
2. Brain Function and Mental Health: Fuel for the Mind
The brain is nearly 60% fat, with DHA constituting a large portion of this fat. Omega-3s are essential for maintaining brain structure and function throughout life.
Cognitive Function and Development
Adequate DHA intake is crucial during fetal development and early childhood to support neuron growth and synapse formation. In adults, omega-3s help maintain memory, learning ability, and cognitive flexibility.
Mental Health Benefits
Numerous studies link omega-3 supplementation with reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety. The anti-inflammatory effects may help mitigate neuroinflammation implicated in mood disorders.
Neuroprotection and Aging
Omega-3s may slow age-related cognitive decline and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s by protecting neurons from oxidative stress and inflammation.
3. Eye Health: Visionary Benefits of Omega-3s
DHA is a primary structural component of the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
- Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD): Research shows omega-3 intake may reduce the risk or slow progression of AMD, a leading cause of vision loss.
- Dry Eye Syndrome: Omega-3s improve tear production and eye surface health, alleviating dryness and irritation.
4. Bone and Joint Health: Strength from Within
Inflammation is a significant driver of joint pain and bone loss.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Omega-3 supplementation can reduce joint tenderness and stiffness by decreasing inflammatory cytokines.
- Bone Density: Omega-3s improve calcium absorption and may stimulate bone formation, lowering osteoporosis risk.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Combating Chronic Disease
Chronic inflammation underpins many health conditions including heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and some cancers. Omega-3 fatty acids regulate inflammatory pathways, balancing the immune response to prevent excessive tissue damage.
6. Skin Health: Glow from the Inside Out
Omega-3s help maintain the skin’s natural barrier by regulating oil production and retaining moisture.
- Hydration: Improved skin hydration can reduce dryness and scaling.
- Acne and Eczema: The anti-inflammatory properties may reduce redness and flare-ups.
- Anti-Aging: Omega-3s protect against UV-induced damage, reducing wrinkles and improving elasticity.
7. Sleep Quality: Restoring Natural Rhythms
Emerging research suggests omega-3s, especially DHA, influence melatonin production—the hormone responsible for regulating sleep-wake cycles.
- Better Sleep: Supplementing with omega-3s has been shown to improve sleep quality, duration, and reduce disturbances, which is vital for overall health and recovery.
8. Prenatal and Postnatal Health: Essential for New Life
Omega-3 fatty acids are indispensable during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Fetal Brain and Eye Development: Maternal intake of DHA supports optimal neural and visual development.
- Reduced Risk of Prematurity: Omega-3s may lower the chances of preterm birth.
- Enhanced Cognitive Outcomes: Children born to mothers with sufficient omega-3 levels tend to perform better on cognitive tests.
9. Top Oily Fish to Incorporate Into Your Diet
To maximize these benefits, aim to consume oily fish at least two to three times per week. Here are the best options:
- Salmon: Richest in DHA and EPA, widely available.
- Mackerel: High in omega-3s and vitamin D, great grilled or smoked.
- Sardines: Small but mighty, also packed with calcium and vitamin D.
- Anchovies: Lower mercury levels, ideal for salads and sauces.
- Herring and Trout: Other excellent sources.
Tips for Choosing and Preparing Oily Fish
- Choose Wild-Caught When Possible: Often richer in omega-3s and less contaminated.
- Avoid Overcooking: Grill, bake, or lightly pan-fry to preserve nutrients.
- Beware of Mercury: Larger predatory fish like tuna and swordfish can have higher mercury — moderate consumption.
- Consider Supplements: Fish oil or algal oil supplements are alternatives if you can’t eat fish regularly.
Final Thoughts
Oily fish are a nutritional gem packed with omega-3 fatty acids and a host of other essential nutrients that support heart, brain, joint, skin, and eye health — not to mention improving sleep and prenatal development. Regular consumption is an easy and delicious way to boost your health naturally.
If you’re looking to optimize your diet for longevity and vitality, adding oily fish to your meals a few times per week should be at the top of your list.
FAQs: Unpacking the Health Benefits of Oily Fish
1. Why are omega-3 fatty acids important for health?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that support heart, brain, and eye health. They help reduce inflammation, improve cholesterol levels, support cognitive function, and protect against chronic diseases.
2. Which oily fish have the highest omega-3 content?
Salmon, mackerel, sardines, anchovies, herring, and trout are among the richest sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA.
3. How often should I eat oily fish to get health benefits?
Health experts generally recommend eating oily fish at least two to three times per week to obtain sufficient omega-3s and related nutrients.
4. Can omega-3 supplements replace eating oily fish?
Supplements like fish oil or algal oil can help if you don’t consume enough fish, but whole fish provide additional nutrients like protein, vitamins, and minerals that supplements alone don’t offer.
5. Are there any risks associated with eating oily fish?
While oily fish are very healthy, some species can accumulate mercury or other contaminants. It’s best to choose smaller fish like sardines or anchovies and limit consumption of large predatory fish.
6. Can oily fish consumption improve mental health conditions?
Studies show omega-3s can help reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, thanks to their anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects, though they are not a substitute for medical treatment.
7. How do omega-3s benefit prenatal and postnatal development?
Omega-3s, especially DHA, are vital for fetal brain and eye development. Pregnant and breastfeeding women are encouraged to consume enough omega-3s to support their child’s cognitive and visual growth.
8. Does eating oily fish help with joint pain and arthritis?
Yes, omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
9. What are some good ways to prepare oily fish to retain its nutrients?
Grilling, baking, steaming, or lightly pan-frying oily fish helps preserve omega-3 content. Avoid deep frying or overcooking to maintain nutritional benefits.
10. Are there vegetarian sources of omega-3 similar to those in oily fish?
While plant sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts contain ALA (a form of omega-3), the body converts it inefficiently to EPA and DHA. Algal oil supplements provide a direct vegetarian source of EPA and DHA.