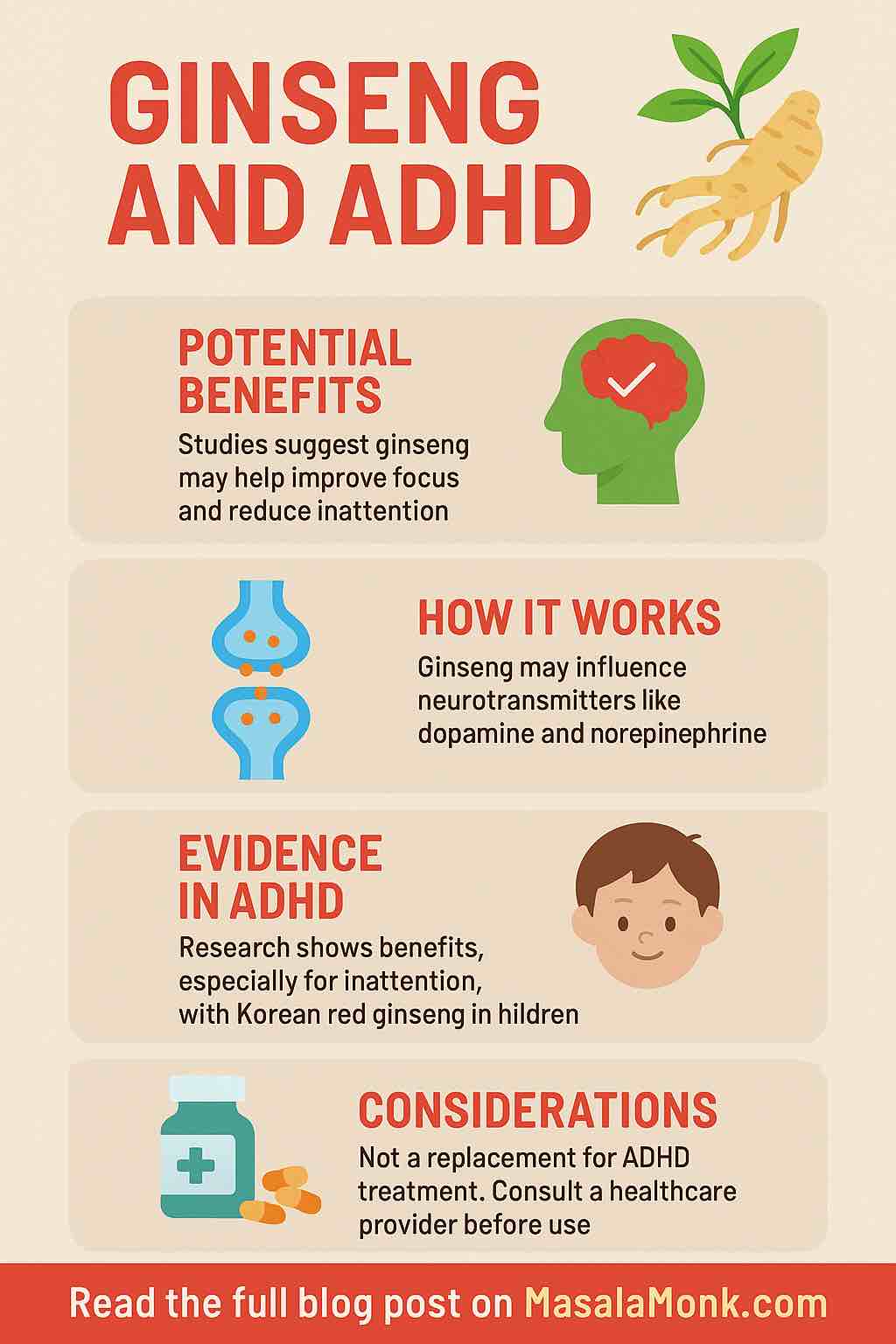
In the ever-evolving landscape of ADHD treatment, a growing number of people are turning to nature for complementary solutions. One such herbal remedy gaining traction is ginseng. Revered for centuries in traditional Asian medicine, ginseng is now under scientific scrutiny for its potential to support individuals with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). But does the science support the hype? Let’s explore the evidence, the mechanisms, and how this ancient root might fit into a modern ADHD management plan.
What Is Ginseng?
Ginseng refers to the roots of plants in the Panax genus, particularly Panax ginseng (Korean or Asian ginseng) and Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng). These roots contain active compounds called ginsenosides, which are believed to have neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and cognition-enhancing effects.
ADHD and the Brain: Where Ginseng Might Help
ADHD is linked to dysregulation in brain pathways involving dopamine and norepinephrine — neurotransmitters critical for attention, motivation, and impulse control. Emerging studies suggest that ginseng may help regulate these same neurotransmitters, offering a possible mechanism for symptom relief. Additionally, ginseng may enhance the activity of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which supports brain plasticity and learning.
What Does the Research Say?
1. Systematic Review (2024)
A comprehensive 2024 review analyzed six human and three animal studies and concluded that ginseng shows promise for improving inattention symptoms in children with ADHD. The review emphasized the need for more rigorous, larger-scale trials but found consistent positive effects on focus and cognitive function.
2. Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs)
- Korean Red Ginseng (KRG): An RCT involving children with ADHD found that 8 weeks of KRG led to improvements in omission errors and ADHD rating scores.
- KRG + Omega-3 Combo: A more recent study explored the combined use of Korean red ginseng and omega-3 fatty acids. The result? Marked improvement in attention, memory, and executive function in children with subthreshold ADHD.
3. Adult Populations and Healthy Individuals
Though most studies focus on children, some evidence suggests American ginseng may improve working memory and attention in healthy adults. However, dedicated ADHD studies in adult populations are lacking and urgently needed.
Practical Use: Dosage, Safety, and Integration
How Much?
Typical dosages used in studies:
- Korean Red Ginseng: 1000 mg/day (split into two doses)
- American Ginseng: 200-400 mg/day
- Combination with Omega-3: Often includes ~1g KRG + 500-1000 mg omega-3
Always start with a lower dose and titrate slowly under supervision.
Is It Safe?
Short-term use of ginseng is generally well-tolerated. Reported side effects include:
- Insomnia
- Headaches
- Gastrointestinal upset
However, caution is advised:
- Medication interactions: Especially with blood thinners, diabetes meds, and CNS stimulants
- Long-term safety: Still not fully known, especially in children
What to Look for in a Supplement
- Standardized extract (e.g., 10% ginsenosides)
- Third-party testing (e.g., NSF, USP, ConsumerLab)
- Transparent labeling and manufacturer reputation
How to Integrate Ginseng into an ADHD Support Plan
- Consult Your Healthcare Provider: Never self-prescribe. A knowledgeable practitioner can help monitor interactions and outcomes.
- Track Progress: Use rating scales like the ADHD-RS or Conners Scale to objectively assess changes.
- Combine with Lifestyle Strategies: Ginseng should complement, not replace, behavioral therapy, proper nutrition, sleep hygiene, and (if needed) prescription meds.
- Be Patient and Consistent: Herbal effects are subtle and cumulative. Give any trial at least 8-12 weeks.
Final Thoughts
Ginseng holds promise as a natural aid for managing ADHD, particularly for improving attention and cognitive function. While it’s no silver bullet, its mechanistic potential and clinical support make it a worthy candidate for further research and cautious integration into holistic ADHD care plans.
As with all natural supplements, the key is informed, personalized use. By partnering with qualified healthcare providers, individuals and families may find in ginseng a valuable tool in the ADHD toolbox.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting any new supplement or treatment.
📘 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can ginseng replace ADHD medication?
No. Ginseng may help support attention and focus, but it should not replace prescribed ADHD treatments like stimulant medications or behavioral therapy unless advised by a healthcare provider.
2. What type of ginseng is best for ADHD?
Studies most commonly use Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng) for children and American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) for adults or cognitive support. Korean red ginseng has the strongest ADHD-specific evidence.
3. How long does it take to see results from ginseng?
Most clinical trials show effects over 8 to 12 weeks. Herbal treatments like ginseng work gradually and require consistent use.
4. Is ginseng safe for children?
Short-term studies suggest it is generally well-tolerated in children, but medical supervision is essential, especially when combining with other medications.
5. Can adults with ADHD benefit from ginseng?
There’s promising evidence for ginseng improving attention and working memory in healthy adults, but more direct ADHD-focused studies in adults are needed.
6. Are there any side effects of taking ginseng?
Yes. Potential side effects include insomnia, headaches, digestive upset, and nervousness. It may also interact with medications like blood thinners or diabetes drugs.
7. Should I take ginseng with food?
Yes, it’s typically recommended to take ginseng with food to minimize stomach upset and enhance absorption.
8. What should I look for in a ginseng supplement?
Choose products with standardized ginsenoside content (around 10%), third-party testing (e.g., NSF, USP), and clear labeling of source and dosage.
9. Can I combine ginseng with omega-3 supplements?
Yes. Some studies show enhanced benefits when combining Korean red ginseng with omega-3 fatty acids, especially for cognitive performance and attention.
10. Is long-term use of ginseng safe?
Long-term safety data is limited. Most studies span 2–3 months. It’s best to use ginseng in cycles and consult a healthcare provider for extended use.










