If you identify with the endomorph body type, you probably gain weight quickly, hold fat readily around the hips and waist, and feel hungrier than friends when calories get tight. However, none of that is a drawback—it’s simply a starting point. With clear macro targets, repeatable meals, and a realistic blend of strength and cardio, you can create steady fat loss while protecting muscle. For a broader backdrop on somatotypes—and why labels are just heuristics—skim our concise primer on ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph. If you end up realizing your traits skew leaner and hard-gainer, pivot to our ectomorph body type guide. And then we also have Mesomorph Body Type: Diet, Workouts & Weight Loss (Female & Male).
What the Endomorph Body Type Implies in Practice
Typically, an endomorph frame features a wider pelvis, shorter average limb length, and a natural tendency to store energy rather than burn it off. Nevertheless, your outcomes are governed by habits: consistent calorie control, protein-forward meals, progressive resistance training, and enough movement outside the gym. Moreover, because appetite, mood, and sleep can swing during a diet, your plan should be resilient on bad days, not just perfect ones.
At a glance, the pillars are simple. First, create a modest daily deficit, avoiding crash diets that multiply cravings. Next, hit protein high enough to spare lean tissue. Then, lift 3 full-body sessions per week and layer 2 cardio days you actually enjoy. Finally, track what matters—weekly average weight, daily steps, and a handful of “north-star” lifts—so adjustments become objective rather than impulsive.
For training frequency and progression, the consensus echoed by ACSM’s resistance training models is clear: expose each muscle group at least twice weekly, progress loads or reps gradually, and manage fatigue so you can keep showing up. Simultaneously, modern hypertrophy research indicates muscle grows across a spectrum of loads if sets are taken sufficiently close to failure; strength, by contrast, tends to favor heavier work (Schoenfeld 2017). In short, your best plan is deliberately simple and ruthlessly repeatable.
Also Read: 5 Top Battle Rope Workout for Fat Loss
Macros for an Endomorph Body Type (Women & Men)
Calorie targets that don’t wreck adherence
Start around bodyweight (lb) × 10–12 kcal/day (≈ 20–25 kcal/kg). After 14 days, review your weekly average weight. If you’re not losing roughly 0.25–0.75% per week, trim 100–150 kcal/day and reassess. Conversely, if performance or mood crashes, nudge calories up 50–100/day and stabilize for a week before changing again. Importantly, consistency beats aggressiveness: a “good enough” deficit you can sustain outperforms a harsh one you abandon.
Protein, fat, and carbs configured for fat loss
- Protein: Aim for 1.6–2.2 g/kg/day to preserve muscle, curb hunger, and support recovery. This practical range aligns with the open-access ISSN protein position stand and is reinforced by meta-analyses in resistance-trained populations (Morton et al., 2018).
- Fat: Allocate 0.7–1.0 g/kg/day for hormones and satiety; generally keep fat at ≥20–25% of total calories so meals feel satisfying (see distribution discussion in JISSN protein dosing review).
- Carbs: Fill the remainder; bias higher-fiber, minimally processed choices and cluster a bigger chunk of carbs around training to support performance.
Furthermore, consider a light, behavior-driven carb cycle: add 30–50 g carbs on lifting days and subtract the same amount on rest days. If it enhances adherence and energy, keep it. If it complicates life, drop it and return to a steady intake.
Gender-specific nuances without stereotyping
Women: during higher-symptom cycle phases, hold calories steady (or upshift 50–100 kcal/day), maintain protein, and prioritize sleep; once symptoms ease, resume the earlier deficit. For training, keep intensity but reduce a set if soreness lingers (ACSM recovery guidance).
Men: weekends are the silent saboteur; one uncontrolled evening can erase five compliant days. Plan social meals with a protein-first plate, share desserts, and limit liquid calories.
Also Read: The Science of Protein: Maximizing Muscle Growth and Recovery
Endomorph Meal Plan Templates You Can Actually Repeat
To begin, here are two one-day frameworks—adjust portions to your target calories. Swap proteins freely (fish, chicken, eggs, tofu/tempeh, dal/rajma), pile vegetables high, and choose carbs you enjoy but can measure.
~1,400 kcal day (often suits smaller or sedentary women)
Breakfast: Greek yogurt (200 g) + berries + 20 g mixed nuts
Lunch: Chickpea & veggie bowl, olive-oil drizzle; side salad
Snack: Whey or soy shake + apple
Dinner: Grilled fish or paneer, roasted potatoes, steamed greens
Macro ballpark: ~110 g protein / 120 g carbs / 45 g fat
~1,900–2,100 kcal day (often suits active women or average men)
Breakfast: Two eggs + 100 g tofu scramble, whole-grain toast
Lunch: Chicken (120–150 g) or chana masala, brown rice, sautéed veg
Snack: Skyr/curd + fruit; 15 g almonds
Dinner: Lean mince or rajma bowl, quinoa, big salad
Macro ballpark: ~130–150 g protein / 170–210 g carbs / 55–65 g fat
Beyond that, think in templates: a protein, a high-fiber carb, a colorful veg, and a measured fat. Similarly, keep a short rotation of batch-cooked staples—rice or quinoa, boiled potatoes, roasted mixed vegetables, and a couple of ready proteins—so “busy day” eating is still aligned with the plan. If you’re uncertain about where you sit on the body-type spectrum—or you’re guiding family members with different builds—this somatotypes explained article helps you choose the right emphasis per person.
Also Read: How to Eat 100 Grams of Protein a Day
Best Workout Plan for an Endomorph Body Type
Although trendy programs promise shortcuts, endomorphs typically thrive on full-body strength three days weekly, paired with two cardio sessions. Crucially, you’ll progress slowly and manage fatigue so appetite doesn’t spike uncontrollably. Accordingly, here’s a template that balances stimulus and recovery.
Weekly layout (5 days; 3 strength + 2 cardio)
Mon — Full-Body A (strength)
Back Squat 3×6–10 • DB Bench 3×8–12 • One-arm Row 3×8–12 • RDL 3×8–12 • Plank 3×45s
Tue — Conditioning (intervals)
8–12 × (40 s easy / 20 s brisk) on bike/rower • 10-min cool-down walk
Wed — Full-Body B (strength)
Trap-bar Deadlift 3×4–6 • Split Squat 3×8–12/leg • Lat Pulldown 3×8–12 • Incline DB Press 3×8–12 • Pallof Press 3×10/side
Thu — Steps & restore
7–10k steps • light mobility 15 min • early bedtime
Fri — Full-Body C (strength; glute/upper bias)
Hip Thrust 4×8–12 • Leg Curl 3×10–15 • Overhead Press 3×6–10 • Seated Row 3×8–12 • Lateral Raise 2×15–20 • Curl/Triceps 2×12–15
Sat — Cardio choice
30–40 min brisk zone-2 or a compact 20-min HIIT block if time-crunched
Sun — Off
Notably, this layout hits each major muscle about twice weekly, which aligns with ACSM progression models. Meanwhile, the rep ranges exploit the hypertrophy-across-loads principle; strength trends heavier, but moderate loads performed near technical failure still add muscle (Schoenfeld 2017).
Also Read: Beginner’s Guide to the Gym
Progression rules that encourage momentum
- Add one rep per set each week until you reach the top of the prescribed range, then add the smallest plate and reset the reps lower.
- Keep 1–3 reps in reserve on most sets to manage fatigue.
- If a lift stalls for 2–3 weeks, add a back-off set at 60–70% (12–15 reps) or swap to a close variation and rebuild confidence.
HIIT versus steady cardio—what to choose?
Time-efficient HIIT complements busy schedules, while steady zone-2 tends to be gentler on recovery. Consequently, the “best” option is the one you’ll execute consistently alongside lifting and steps. Rotate as life demands; consistency trumps dogma.
Intermittent Fasting with an Endomorph Body Type
Intermittent fasting (IF) can match traditional daily restriction for weight loss; it’s a tool for adherence, not a metabolic cheat code. Begin conservatively with 14:10; if you’re training well and sleeping soundly, explore 16:8. Place 2–3 protein feedings inside the eating window, keep fiber high, and avoid the classic trap—“I fasted, so I earned a feast.” If performance drops or evening overeats bloom, shorten the window or return to regular meal spacing. Ultimately, choose the schedule that keeps you honest over the long run. Big picture, randomized data and reviews show IF is broadly comparable to continuous restriction when calories and protein are equated (JAMA 2020 TRE RCT).
Also Read: Intermittent Fasting: Daily Discipline or Overdoing It?
A 12-Week Endomorph Body Type Fat Loss Plan
Phase 1 (Weeks 1–4): Lay the foundation
- Calories ≈ BW×12 (or your calculator’s equivalent).
- Protein 1.8 g/kg; vegetables at 2+ meals/day.
- Three full-body sessions, one short interval day, one zone-2 day.
- 7–10k steps daily; bedtime routine to secure 7–9 h sleep.
- Track weekly average weight, steps, and loads on 3–4 key lifts.
Phase 2 (Weeks 5–8): Drive the process
- Trim 100 kcal/day if weight loss has slowed below ~0.25%/week.
- Progress presses, squats, rows, and hinges by tiny increments; small jumps compound.
- Add one HIIT block post-strength once weekly if energy permits; otherwise keep cardio steady.
Phase 3 (Weeks 9–12): Plateaus, solved simply
Choose one lever at a time, then hold for 10–14 days:
- another −100 kcal/day, or
- a single light-day (e.g., 5:2-style) once weekly, or
- +15 min zone-2 after two strength sessions.
Meanwhile, maintain protein, keep fiber high, and guard sleep like a lifter’s secret supplement.
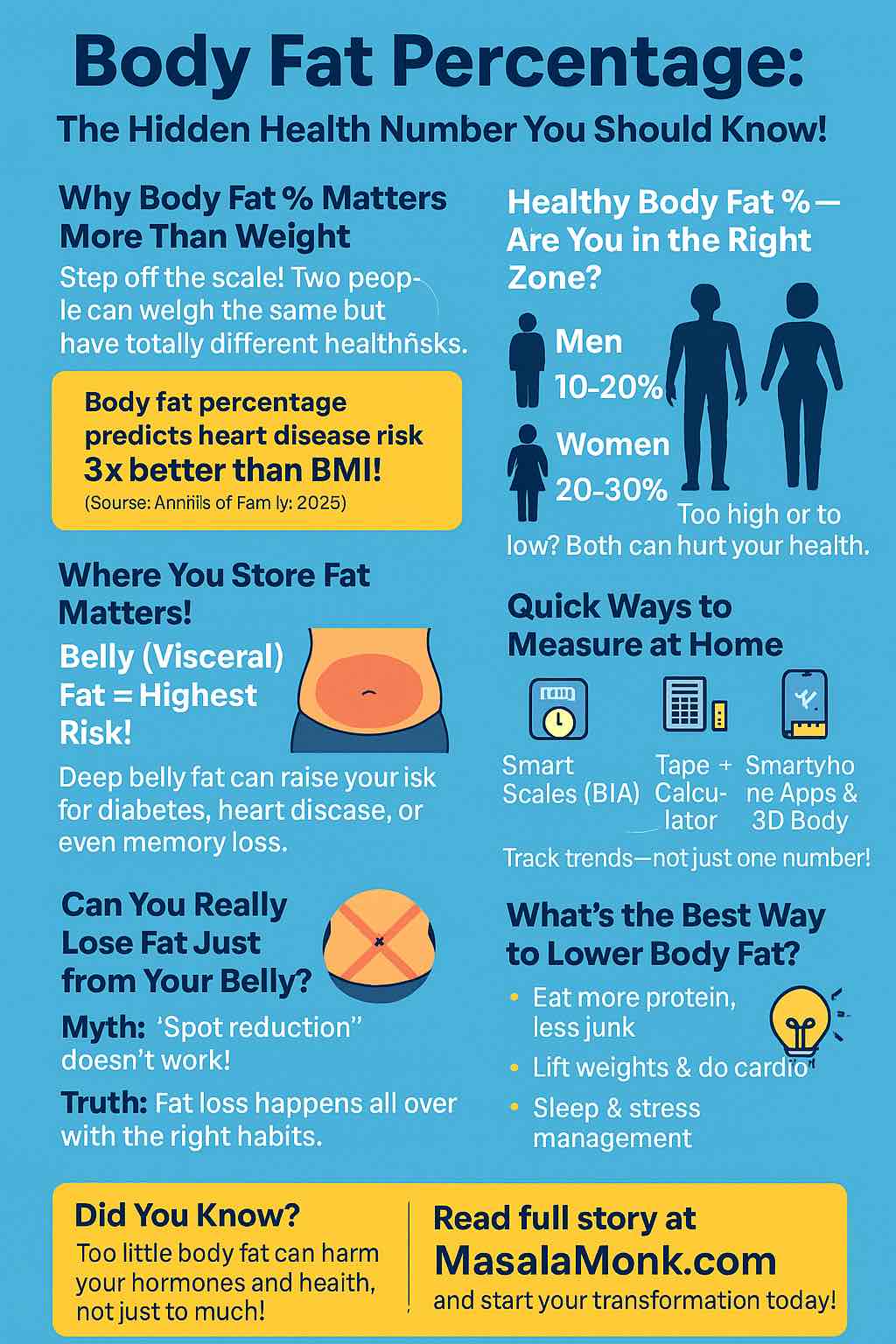
Also Read: Guide to Body Fat Percentage
Troubleshooting an Endomorph Body Type Without Panic
Scale stuck despite “perfect” weeks? Verify adherence first: calories, steps, training sessions, and weekend totals. If everything checks out, reduce 100 kcal/day or add 1,000–2,000 weekly steps; reassess after another fortnight.
Evening cravings destroying momentum? Front-load 30–40 g protein at breakfast, include a high-fiber carb at lunch, and reserve 20–30 g of your daily carbs for dinner to blunt nighttime hunger. Additionally, swap ultra-palatable snacks for fruit + yogurt or air-popped popcorn sprinkled with spice.
Energy low, lifts slipping? Shift 50–100 kcal from fats toward carbs—especially pre- and post-workout—while holding protein steady. Furthermore, confirm hydration and add a short walk after meals to improve digestion.
Weekends wiping out progress? Pre-commit: choose the restaurant, scan menus, and plan a protein-anchored main. Share starters and desserts, sip water between alcoholic drinks, and log roughly—accuracy beats avoidance.
Soreness snowballing? Drop one accessory set per muscle for a week, keep steps, and focus on sleep. Once soreness normalizes, restore the set or leave volume lower if progress resumes.
Also Read: 10 Examples of Egg Dishes, with 2 Eggs
How This Fits Women and Men Without Overcomplicating It
Although goals and preferences differ, the physiology of fat loss is shared. Women often benefit from keeping fiber high at lunch and a protein anchor at breakfast to tame evening cravings. Men, by contrast, may need stricter boundaries around weekends and liquid calories. Nevertheless, programming is nearly identical: full-body strength, modest cardio, generous protein, and a measured calorie deficit. As you refine, check that your identity as “endomorph” isn’t boxing you in; if training reveals you tolerate volume easily or gain muscle briskly, keep the structure but increase performance ambitions accordingly.
Also Read: How Does a High Protein, High Fiber Diet Support Weight Loss?
Why This Works Even When Life Gets Messy
To be blunt, the endomorph body type isn’t a verdict—it’s a reminder to bias your plan toward satiety, structure, and sustainability. Progress arises from stacking small, consistent wins: turning up to three strength sessions, walking daily, eating the next planned meal, and nudging loads up over time. Importantly, the research base supports the core tactics you’re using:
- Muscle can grow across a spectrum of loads when effort is high (Schoenfeld 2017), so you don’t have to chase one “magic” rep range.
- Frequency and progressive overload, delivered in recoverable doses, are reliable drivers of improvement (ACSM progression).
- Protein targets around 1.6–2.2 g/kg are both practical and protective of lean mass during a deficit (ISSN position stand).
Meanwhile, internal links help readers explore adjacent paths without leaving your ecosystem. If someone realizes they’re actually a leaner hard-gainer, direct them to the ectomorph body type guide. If another reader wants a quick refresher on the spectrum and mixed types, route them to somatotypes explained. Either way, your post remains the practical blueprint they return to when it’s time to act.
Final Word
Ultimately, an endomorph body type signals how you might respond—not how your story ends. Set a modest deficit you can maintain, anchor protein, train full-body with intent, and walk more than you think you need. Add small amounts of cardio you’ll actually do, sleep like an athlete, and adjust patiently every couple of weeks. Consequently, your waistline will trend down, your lifts will creep up, and your relationship with food will get calmer. Keep showing up, keep the plan boringly effective, and let the compounding do its work.
FAQs
1) What is the endomorph body type?
An endomorph body type generally carries fat more easily, with a wider hip/waist structure and strong legs. Nevertheless, results still come from habits—calorie control, protein-forward meals, strength training, and consistent movement.
2) How do I know if I’m truly an endomorph?
Look for patterns: easier fat gain, softer midsection, better performance on lower-body lifts, and noticeable appetite when dieting. Conversely, if you gain muscle quickly while staying lean, you may lean mesomorphic instead.
3) What are the best macros for endomorph weight loss?
Aim for protein 1.6–2.2 g/kg/day, fat 0.7–1.0 g/kg/day, and fill the rest with carbs. Importantly, keep fats above ~20–25% of calories for satiety while timing more carbs around workouts.
4) How many calories should an endomorph eat to lose weight?
Begin near bodyweight (lb) × 10–12 kcal (≈ 20–25 kcal/kg). Thereafter, adjust every 14 days so weight trends down ~0.25–0.75% per week.
5) What’s the best workout for an endomorph body type?
Prioritize full-body strength 3 days per week plus 2 cardio sessions. Notably, use big lifts (squat, hinge, push, pull) with moderate reps and leave 1–3 reps in reserve.
6) Do endomorphs need HIIT or steady cardio?
Both work; choose the one you’ll repeat. HIIT is time-efficient; meanwhile, steady zone-2 is easier to recover from. Ultimately, consistency beats style.
7) Should women train differently than men with an endomorph body type?
Principles match—protein, progression, and a modest deficit. However, women can emphasize glutes, hamstrings, lats, and delts for shape, while men may guard against weekend calorie spikes.
8) What’s an endomorph meal plan structure that works?
Organize 4–5 meals with one “anchor” protein serving (≈40–50 g) and high-fiber carbs at daytime meals. Consequently, cravings at night diminish and adherence improves.
9) Which foods are best for endomorph fat loss?
Lean proteins (fish, poultry, eggs, tofu/tempeh, dals), high-fiber carbs (oats, potatoes, rice, quinoa), colorful vegetables, and measured fats (olive oil, ghee, nuts, seeds). Conversely, limit ultra-processed snacks and sugary drinks.
10) Should endomorphs try intermittent fasting?
Yes—if it helps adherence. Start with 14:10, then consider 16:8 only if energy, sleep, and training remain solid. Place 2–3 protein feedings inside the window. Do read Foods to Eat During 16:8 Intermittent Fasting.
11) What is the best way to carb cycle for endomorphs?
Lightly: +30–50 g carbs on lifting days and −30–50 g on rest days. Furthermore, keep protein steady every day to protect lean mass.
12) How fast should weight loss happen for an endomorph body type?
Target 0.25–0.75% of bodyweight per week. Faster drops risk muscle loss and rebound hunger; slower changes may signal the deficit is too small.
13) What if progress stalls?
First, confirm adherence (meals, steps, training, weekends). If solid, reduce calories 100–150/day or add 1,000–2,000 steps/week. Reassess after 10–14 days.
14) What’s the best endomorph weight-loss workout split for beginners?
Three full-body days:
- Day A: Squat, Press, Row, Core
- Day B: Deadlift or Trap-bar, Split Squat, Pull-down, Core
- Day C: Hip Thrust, Leg Curl, Overhead Press, Seated Row, Accessories
Additionally, add two short cardio sessions on non-lifting days.
15) Which supplements actually help endomorphs?
Keep it simple: creatine monohydrate (3–5 g/day) for strength and lean mass support, protein powder for convenience, and basics like vitamin D or omega-3s if intake is low. Everything else is optional.
16) Are there special tips for endomorph men?
Yes: plan social meals in advance, cap liquid calories, and track weekend totals. Likewise, keep a few “north-star” lifts (e.g., squat, bench, row) to measure progress objectively.
17) Are there special tips for endomorph women?
Absolutely: during higher-symptom cycle phases, hold calories steady (or up 50–100 kcal), keep protein high, and reduce one accessory set if soreness lingers. Thereafter, resume the original deficit.
18) What are the best exercises for endomorph fat loss?
Compound moves that recruit lots of muscle: squats, deadlifts or trap-bar pulls, hip thrusts, lunges, presses, rows, and pull-ups or pulldowns. Moreover, sprinkle in accessories (leg curls, lateral raises, curls, triceps) for balance.
19) Do endomorphs need more cardio than other body types?
Not necessarily. Instead, match cardio to recovery and step count. Hence, aim for 7–10k steps/day and 2 cardio sessions; increase only if fat loss stalls and energy remains good.
20) How should an endomorph track progress?
Use a weekly average weight, waist/hip measurements, progress photos every 2 weeks, and top-set logs on key lifts. Thus, tweaks are driven by data rather than emotion.
21) What’s the best way for an endomorph to handle cravings?
Front-load protein at breakfast, include fiber at lunch, and save 20–30 g carbs for dinner. Additionally, keep low-calorie “volume” foods ready (berries, yogurt, soups, air-popped popcorn).
22) Can an endomorph build muscle while losing fat?
Yes—especially if new to lifting or returning from a layoff. Nevertheless, prioritize protein, train hard with progressive overload, and avoid overly aggressive deficits.
23) Is a “free” day OK for an endomorph body type?
Occasionally, yes; but plan it. Alternatively, use a single free meal and keep the rest of the day on plan. Importantly, resume your routine at the very next meal.
24) When should an endomorph change the plan?
After 10–14 days without progress despite adherence. Then, adjust one lever—calories, steps, cardio minutes, or training volume—and hold steady before judging again.