Introduction
Eosinophilic Esophagitis, commonly known as EoE, is increasingly recognized as a significant cause of gastrointestinal discomfort and swallowing difficulties. This condition, where a type of white blood cell (eosinophil) builds up in the lining of the tube that connects your mouth to your stomach (esophagus), leads to a range of symptoms and potential complications. Our comprehensive guide delves into understanding EoE, highlighting its symptoms, diagnostic approaches, and effective management strategies, including diet and medical treatments.
Section 1: What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)?
Defining EoE
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune-mediated condition primarily characterized by the accumulation of eosinophils in the esophageal tissue. This accumulation is not typical for other more common esophageal conditions and is a response to certain allergens or irritants.
Eosinophils and Their Role in EoE
Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell part of our immune system. They typically combat parasites and contribute to allergic reactions. In EoE, these cells build up in the esophagus in response to an allergic trigger, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and the narrowing of the esophagus.
Contributing Factors
The exact cause of EoE is not fully understood but is thought to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a history of atopic diseases such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, eczema, or food allergies are at a higher risk of developing EoE. This correlation suggests a strong link to allergic sensitivities.
Section 2: Recognizing the Symptoms of EoE
Symptoms in Adults and Children
EoE can affect individuals of all ages, but the symptoms may vary:
- In Adults: The most prominent symptom is dysphagia, or difficulty swallowing, which can lead to food impaction (food getting stuck in the esophagus). Adults may also experience chest pain that is not related to heart disease.
- In Children: Symptoms can be more diverse and include vomiting, abdominal pain, failure to thrive (in severe cases), and food refusal.
Differentiating from Other Conditions
Symptoms of EoE can often mimic those of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), making accurate diagnosis challenging. Unlike GERD, EoE symptoms typically don’t respond well to acid-suppressing therapies like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs).
Section 3: Diagnosing EoE
Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing EoE involves several steps:
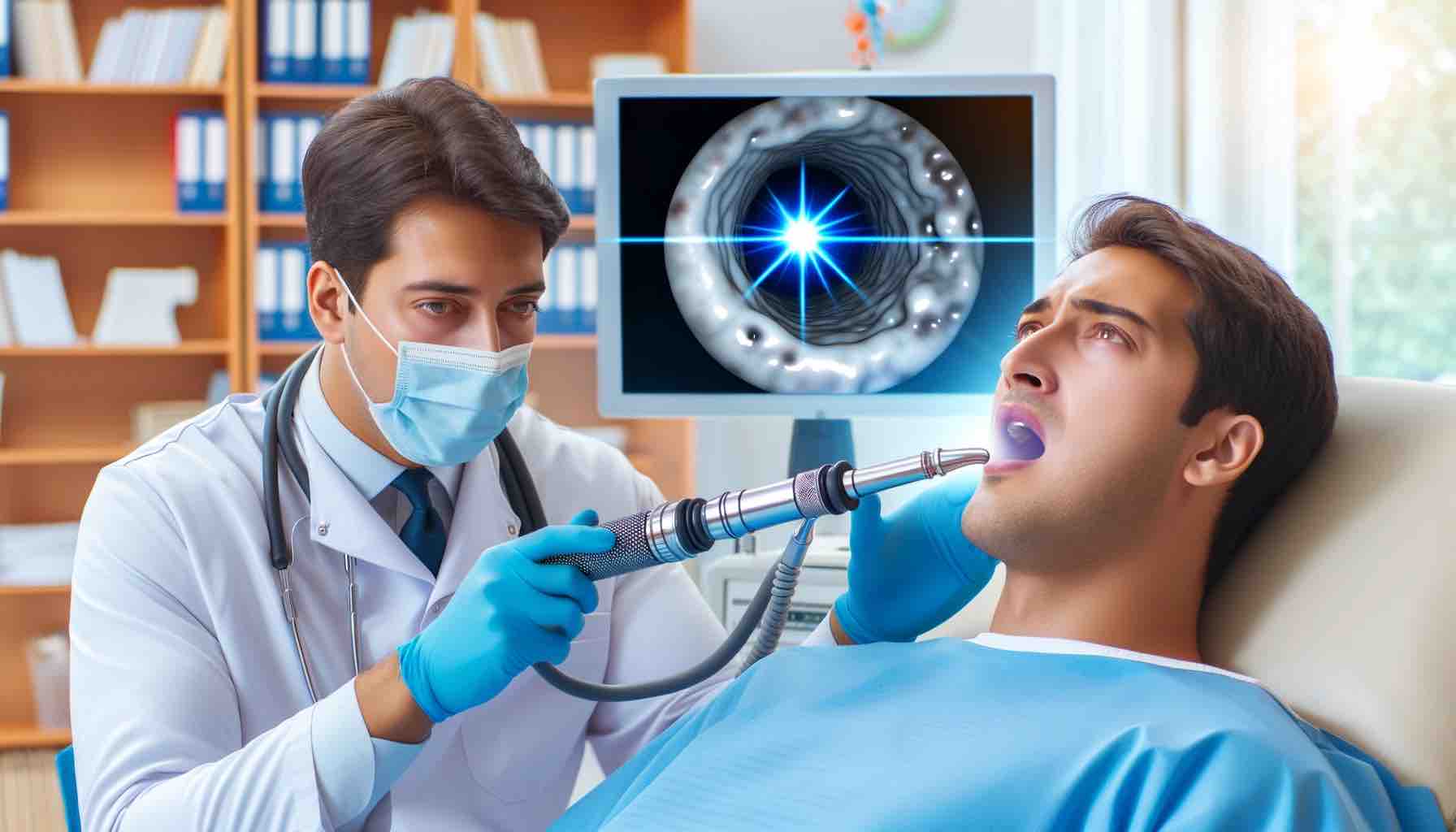
- Endoscopy: A key diagnostic tool where a flexible tube with a camera (endoscope) is used to examine the esophagus. This procedure can reveal characteristic signs of EoE such as rings, furrows, and white spots.
- Biopsies: Tissue samples are taken during endoscopy to be examined for the presence of eosinophils.
- Exclusion of Other Conditions: It’s crucial to rule out other causes of eosinophil accumulation, such as GERD or parasitic infections.
Challenges in Diagnosis
One of the challenges in diagnosing EoE is its overlap with other esophageal disorders. A detailed medical history, including any known food allergies or atopic diseases, aids in the diagnosis.
In the upcoming sections, we will explore the various treatment options for EoE, including the pivotal role of diet in managing this condition, as well as practical lifestyle tips for those affected.
Section 4: Treatment Options for EoE
Medical Treatments for EoE
Managing EoE often involves a combination of dietary changes and medical treatments to reduce eosinophil count in the esophagus and alleviate symptoms.
- Topical Steroids: Swallowed steroids, such as fluticasone or budesonide, are often the first line of treatment. They help reduce inflammation and eosinophil levels in the esophagus without significant systemic absorption.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): While EoE is not caused by acid reflux, PPIs can help control overlapping symptoms and may have anti-inflammatory effects beneficial for EoE.
- Biologic Therapies: Newer treatments, like monoclonal antibodies, are being explored for EoE, especially in cases unresponsive to other treatments.
- Dilation Therapy: In cases where EoE has led to significant narrowing (strictures) of the esophagus, endoscopic dilation can be used to widen the esophagus and relieve swallowing difficulties.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Regular monitoring is crucial to assess the effectiveness of treatments and make necessary adjustments. This typically involves repeat endoscopies and biopsies to evaluate the eosinophil count and esophageal health.
Section 5: Dietary Management in EoE
The Role of Diet in EoE
Diet plays a critical role in managing EoE. For many, specific foods act as triggers for eosinophil accumulation and inflammation.
Common Dietary Approaches
- Elimination Diets: These diets involve removing common allergens (dairy, wheat, eggs, soy, nuts, fish) and then gradually reintroducing them to identify triggers. The six-food elimination diet is a common approach.
- Elemental Diet: This involves consuming amino acid-based formulas that contain no allergenic proteins. It’s particularly effective but challenging to maintain due to taste preferences and social aspects of eating.
Implementing the Diet
- Working with a dietitian is essential to ensure nutritional needs are met, especially in children.
- Keeping a food diary can help identify potential triggers and track symptom improvements.
Section 6: Living with EoE
Lifestyle Modifications
Living with EoE may require adaptations to reduce symptom severity and improve quality of life:
- Avoiding Known Triggers: Once identified, avoid foods that trigger EoE.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so incorporating relaxation techniques can be helpful.
- Community Support: Joining EoE support groups can provide valuable tips and emotional support.
Conclusion
Eosinophilic Esophagitis is a complex condition requiring a multifaceted management approach. By combining medical treatments with dietary modifications and lifestyle changes, individuals with EoE can effectively manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare professionals, including gastroenterologists and dietitians, to tailor a treatment plan that meets individual needs.
Explore More About Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
For a comprehensive exploration of EoE, consider reading our series of articles, each offering unique insights and practical advice:
- EoE Elimination Diet – Free PDF: Discover the essentials of an elimination diet tailored for EoE management, complete with a downloadable PDF guide for easy reference.
- EoE Diet and Treatment Strategies: Learn about effective dietary strategies and treatment options that can help manage EoE symptoms.
- EoE Symptoms, Treatment, and Diet: Gain a thorough understanding of the symptoms of EoE and how diet plays a crucial role in treatment.
- Symptoms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE): Delve into a detailed analysis of the symptoms of EoE, helping you to identify and understand the condition better.
- EoE and Elimination Diets: Explore the connection between EoE and elimination diets, offering insights into how dietary adjustments can alleviate symptoms.
Each article in our series offers unique perspectives and practical tips, ensuring you have a well-rounded understanding of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Whether you’re looking for detailed dietary advice, symptom identification, or treatment strategies, our resources are here to guide you.
10 FAQs for the Blog Post
- What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) and how does it affect the body?
- EoE is a chronic immune/antigen-mediated esophageal disease characterized by eosinophil accumulation in the esophagus, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and symptoms like difficulty swallowing.
- Can EoE be cured, or is it a lifelong condition?
- EoE is generally considered a chronic condition. While there is no cure, symptoms can be effectively managed through dietary changes, medication, and lifestyle adjustments.
- What are the most common symptoms of EoE in adults?
- In adults, EoE often manifests as difficulty swallowing, food impaction, chest pain unrelated to heart disease, and sometimes symptoms similar to acid reflux.
- How is EoE diagnosed?
- EoE is diagnosed through endoscopy, where a camera is used to view the esophagus, and biopsies are taken to look for high levels of eosinophils in the tissue.
- Are there any specific foods that trigger EoE?
- Common triggers include dairy, wheat, eggs, soy, nuts, and seafood, but triggers can vary. Elimination diets are used to identify individual sensitivities.
- What is the role of an elimination diet in treating EoE?
- Elimination diets involve removing common allergenic foods and gradually reintroducing them to identify which ones trigger EoE symptoms, helping to manage the condition.
- Can medication be used to treat EoE?
- Yes, medications such as swallowed topical steroids and proton pump inhibitors are used to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms of EoE.
- Is EoE related to other allergic conditions?
- Yes, EoE is often associated with other atopic conditions like asthma, allergic rhinitis, and food allergies, indicating a common underlying allergic mechanism.
- What lifestyle changes can help manage EoE?
- Avoiding known food triggers, managing stress, and making dietary modifications are key lifestyle changes that can help manage EoE symptoms.
- How effective is the elemental diet in treating EoE?
- The elemental diet, consisting of amino acid-based formulas, is highly effective in treating EoE, especially in severe cases, as it eliminates potential allergenic proteins.
Blog Tags for the Post
eosinophilic esophagitis, EoE, esophagitis, eosinophilic gastroenteritis, esophagus inflammation, elimination diet, EoE symptoms, EoE treatment, dietary management of EoE, eosinophilic disorders, EoE in adults, EoE diagnosis, allergic esophagitis, eosinophil treatment, esophageal eosinophilia








