n the ongoing quest to cut down on sugar while still satisfying our sweet tooth, two major contenders continue to divide opinions: stevia and aspartame. Both offer sugar-free sweetness, yet each carries a unique profile of health effects, user experiences, and controversies. In this practical, research-backed blog post, we’ll break down the differences, sift through the latest science and user reviews, and help you decide which is best for your needs.
The Basics: What Are Stevia and Aspartame?
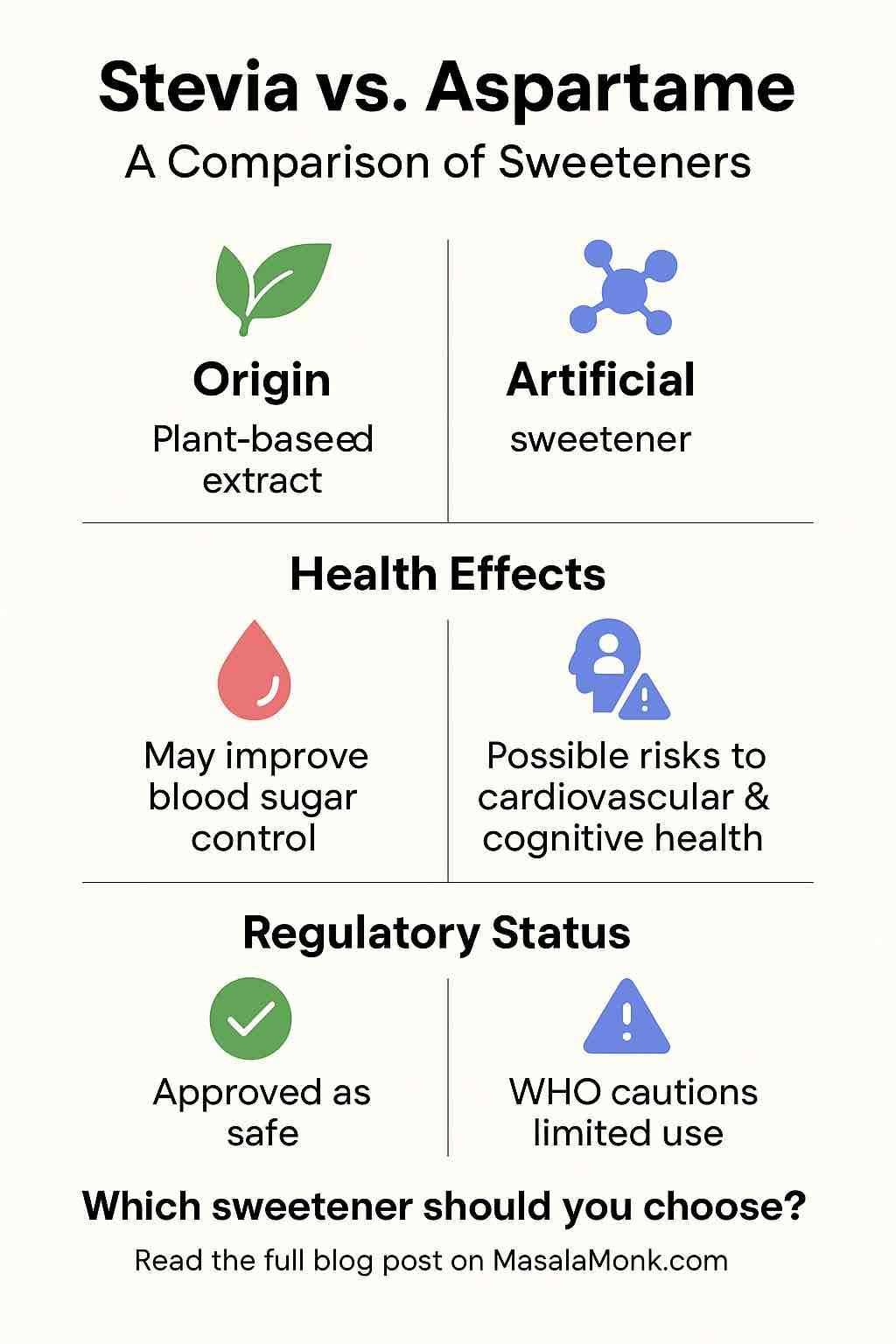
- Stevia is derived from the Stevia rebaudiana plant. Its active compounds, steviol glycosides, are 200–300 times sweeter than sugar. It’s natural, calorie-free, and heat-stable, making it great for baking and cooking.
- Aspartame is a synthetic sweetener made from two amino acids: phenylalanine and aspartic acid. It’s about 200 times sweeter than sugar but breaks down at high temperatures, limiting its use in baked goods.
Taste Test: A Matter of Preference
- Stevia: Many users describe its taste as slightly bitter or herbal, especially in pure form. However, newer stevia blends are milder and often mixed with erythritol or monk fruit to reduce aftertaste.
- Aspartame: Often praised for its clean, sugar-like sweetness, particularly in soft drinks. However, some find it has a mild chemical aftertaste.
User Tip: If you’re baking or cooking, opt for stevia. If you want a sweetener for cold drinks, aspartame may blend better.
Health Impacts: Science Meets Real Life
Stevia
- May help reduce blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, especially in people with diabetes.
- Limited evidence shows it may offer antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Short-term use shows minimal impact on gut flora, although blends with sugar alcohols may cause bloating or gas in some people.
- Some users report headaches or dizziness, especially when consuming stevia in processed beverages.
Aspartame
- Extensively studied and generally considered safe within limits (40 mg/kg/day EFSA; 50 mg/kg/day FDA).
- Animal studies in 2024 and 2025 show concerns: elevated insulin, arterial plaque formation, and heritable cognitive effects.
- Classified as “possibly carcinogenic” by WHO’s IARC in 2023, but WHO and FDA have not changed their intake guidelines.
- May cause issues in people with phenylketonuria (PKU) and occasionally headaches or mood effects in sensitive individuals.
Bottom Line: Stevia may be better for those with diabetes or blood sugar concerns. Aspartame remains acceptable for general use but may raise long-term health questions in frequent consumers.
The Gut Factor: What Your Microbiome Thinks
- Stevia: Appears to have little short-term impact on gut flora when used in moderation. However, stevia blends (especially those with erythritol) may disrupt digestion for some people.
- Aspartame: Some preclinical data suggest aspartame may disrupt gut-brain communication via inflammation, but human studies are limited.
Real User Insight: Reddit users often report gas, bloating, and discomfort from stevia blends, but pure stevia is usually better tolerated. Aspartame users report fewer GI issues but sometimes mention headaches.
Diet, Weight Loss & WHO’s Warning
In 2023, the WHO advised against using non-sugar sweeteners like stevia and aspartame for weight control, citing insufficient evidence for long-term effectiveness and possible metabolic risks.
- Stevia may reduce hunger by stabilizing blood sugar but could also lead to compensatory eating.
- Aspartame doesn’t raise blood sugar but may increase appetite or cravings in some individuals.
Tip: Consider sweeteners as a short-term aid, not a long-term weight loss solution.
So Which One Should You Choose?
| Goal | Best Choice | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Baking or high heat use | Stevia | Heat-stable, natural, no breakdown products |
| Cold drinks or sodas | Aspartame | Smooth taste, blends well in beverages |
| Blood sugar management | Stevia | May lower glucose and improve insulin response |
| Fewer digestive issues | Aspartame (moderate) | Often easier on gut, though watch for headaches |
| Natural product preference | Stevia | Plant-derived, less processed |
| Cognitive or cardiovascular concerns | Stevia | Lacks the red flags seen in new aspartame studies |
🔬 1. Origin & Composition
| Feature | Stevia | Aspartame |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural – from Stevia rebaudiana plant | Synthetic – made from aspartic acid & phenylalanine |
| Main Compounds | Steviol glycosides (e.g., Rebaudioside A) | Aspartame (L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine methyl ester) |
| Sweetness | 200–300x sweeter than sugar | ~200x sweeter than sugar |
✅ 2. Regulatory & Safety
| Aspect | Stevia | Aspartame |
|---|---|---|
| FDA Status (USA) | Purified forms (e.g., Rebaudioside A) = GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) | Approved by FDA since 1981 |
| EFSA Status (EU) | Approved as a sweetener (E960) | Approved as a sweetener (E951) |
| Safety Limits | ADI: 4 mg/kg body weight/day | ADI: 40 mg/kg body weight/day |
| Warnings | Whole-leaf & crude extracts not FDA-approved | Unsafe for people with PKU (phenylketonuria) |
⚕️ 3. Health Effects
| Area | Stevia | Aspartame |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Sugar | May reduce blood glucose and improve insulin sensitivity | Generally no effect, but some early studies raised concerns (largely unsupported) |
| Weight Management | May aid weight loss due to non-caloric nature | Also non-caloric, but debated whether it helps or hinders weight loss |
| Gut Health | May alter gut flora – research is ongoing | Some early data suggest possible microbiome impact, still inconclusive |
| Cancer Risk | No strong evidence of carcinogenicity (EFSA & WHO affirm safety) | Extensively studied; no conclusive link to cancer at approved intakes |
| Other Concerns | Some report bitter aftertaste or minor GI upset | Can cause headaches, dizziness, or mood effects in sensitive individuals |
👅 4. Taste & Use
| Feature | Stevia | Aspartame |
|---|---|---|
| Taste Profile | Sweet, slightly bitter or licorice-like aftertaste | Clean, sugar-like – can taste metallic to some |
| Stability | Heat-stable → good for cooking & baking | Not heat-stable – breaks down during baking |
| Common Uses | Beverages, baking, tabletop sweeteners | Diet sodas, yogurts, gum, sugar-free desserts |
🧪 5. Recent Scientific Insights (2020s)
- Stevia:
- Shown to potentially improve glucose metabolism and reduce oxidative stress.
- Being studied for anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects.
- May support oral health by reducing plaque-forming bacteria.
- Aspartame:
- WHO’s IARC (2023) classified aspartame as “possibly carcinogenic” (Group 2B) – based on limited evidence.
- JECFA (also WHO) reaffirmed the ADI of 40 mg/kg and found no need to change it.
- Some studies suggest frequent use may impact learning/memory in high doses in animal models, but human evidence is weak.
🧾 Summary Table
| Category | Stevia | Aspartame |
|---|---|---|
| Natural/Synthetic | Natural extract | Artificial/synthetic |
| Sweetness | 200–300x sweeter than sugar | 200x sweeter than sugar |
| Safety Status | GRAS (approved) | Approved, but controversial (Group 2B by IARC) |
| Health Impact | May lower blood sugar, possible gut effects | Generally safe, but PKU risk & some sensitivities |
| Use in Cooking | Heat-stable | Not heat-stable |
| Taste | Slight bitterness for some | Generally sugar-like, may have chemical notes |
🧠 Verdict (Contextual Recommendation)
| Goal / Concern | Preferred Option | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Natural product | ✅ Stevia | Plant-derived |
| Baking/cooking | ✅ Stevia | Heat-stable |
| Smooth taste in drinks | ✅ Aspartame | More sugar-like in liquids |
| Blood sugar control | ✅ Stevia | May improve glycemic response |
| PKU or phenylalanine issues | ❌ Avoid Aspartame | Stevia is safe |
| General daily use | Depends on tolerance | Both are safe in moderation |
Final Thoughts: Moderation is Key
In the stevia vs. aspartame debate, there’s no one-size-fits-all winner. Your best choice depends on your taste, goals, health status, and how your body reacts. Whichever sweetener you choose, keep your intake within recommended limits and listen to your body.
Pro Tip: For some, the best approach may be rotating or minimizing sweeteners altogether—rediscovering a taste for natural foods without added sweetness.
Have you experimented with both sweeteners? What was your experience? Share your thoughts below!
Here’s a comprehensive comparison of Stevia vs. Aspartame, analyzing their origins, safety, health impacts, regulatory status, taste profiles, and applications:
🔍 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is stevia better than aspartame for diabetics?
Yes. Stevia may improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar, making it a preferred option for people managing diabetes. Aspartame does not affect blood glucose but offers no glycemic benefit. - Can I use stevia or aspartame while pregnant?
In moderation, yes. Both are approved for use during pregnancy by regulatory authorities like the FDA, but it’s best to consult your doctor to account for personal health conditions. - Does stevia cause bloating or gas?
Possibly. Pure stevia is usually well tolerated, but blends with sugar alcohols like erythritol may cause digestive discomfort in some individuals. - Why is aspartame controversial if it’s FDA-approved?
While approved and considered safe within daily intake limits, recent studies in animals suggest possible cardiovascular and cognitive risks. The WHO classified it as “possibly carcinogenic” in 2023, but this does not reflect a confirmed human cancer risk. - Can I cook or bake with aspartame?
No. Aspartame is not heat-stable and breaks down at high temperatures, potentially altering flavor and safety. Use stevia or another heat-stable sweetener instead. - Does stevia have a bitter aftertaste?
Sometimes. Especially in pure forms. However, newer formulations with added flavor-balancing agents significantly reduce bitterness. - Which sweetener is more natural?
Stevia. It’s derived from a plant and considered a natural sweetener, while aspartame is synthetically manufactured from amino acids. - Are these sweeteners safe for children?
Generally, yes in moderation. Regulatory bodies have not issued restrictions, but limiting non-nutritive sweeteners in children is advised due to unknown long-term developmental effects. - How do these sweeteners affect weight loss?
Neither guarantees weight loss. While they reduce calorie intake, studies show they may alter hunger hormones or promote compensatory eating. WHO advises against relying on them for weight management. - What’s the safest strategy if I want to reduce sugar?
Use stevia or aspartame sparingly, focus on whole foods, and gradually retrain your taste buds to enjoy less sweetness overall.