Castor oil has lived in home cabinets for decades. Yet modern wellness trends stretched the uses for castor oil far beyond a simple massage oil—from warm packs for cramps to glossy hair routines and even bold claims about “liver detox.” This guide stays practical and evidence-aware: what castor oil is, where it genuinely helps, how to do a safe pack, what to expect for hair and skin, when ingestion makes sense, how to choose a quality bottle, and when to see a clinician.
⚠️ Medical information only: This article shares general information and practical tips. It is not a diagnosis or a treatment plan and does not replace a consultation with a licensed clinician. Always follow your doctor’s advice for your health, skin, and eyes.
Uses for Castor Oil: Start with What It Is
Castor oil is pressed from the seeds of Ricinus communis (often labeled ricinus oil, ricino oil, eranda oil, or castor seed oil). Its dense slip comes from ricinoleic acid, which also explains its laxative activity. For skin and hair, cold-pressed, hexane-free oils are a sensible default. If a clinician recommends ingestion, USP-grade labeling signals pharmacopoeia-level quality; for a concise medical overview, see the monograph in StatPearls: Castor Oil. For a plain-English safety snapshot, the clinical explainer from Cleveland Clinic is equally useful.
Not every adjective on the label is meaningful. For example, “extra virgin” isn’t regulated for castor oil. Consequently, prioritize extraction method, solvent-free claims, and dark-glass packaging over buzzwords. For style, Jamaican black castor oil is simply a roasted variant; functionally it’s still castor oil—choose by scent and viscosity.
Uses for Castor Oil That Actually Help (and Where Hype Creeps In)
Comfort care and moisturization. As a highly occlusive oil, castor helps seal in moisture on dry skin and along the hair shaft. Therefore, it excels as a pre-wash scalp mask, a cuticle rub, or part of a warm-pack routine.
Occasional constipation (with caution). Ingested castor oil is a stimulant laxative appropriate for occasional use; however, it is not first-line because cramping and diarrhea are common. For clinical context, rely on Cleveland Clinic’s explainer and the medical overview in StatPearls.
Clinic-only wound-care adjunct (not DIY). Ointments that combine Balsam Peru + castor oil (e.g., Venelex) help maintain a moist wound environment and protect delicate edges; these are regulated indications, not home substitutes. If you’re curious about the exact wording, read the label on DailyMed: VENELEX Ointment.
What it does not do: detox. Despite viral claims, there’s no good evidence that castor-oil packs “detox” the liver or purge toxins. For a science-based perspective on detoxes and cleanses in general, see MD Anderson’s detox explainer and the research summary from NCCIH on detoxes and cleanses.
Castor-Oil Packs: How to Use Them Safely
Many readers begin their uses for castor oil with warm packs, so here is a stain-smart, step-by-step method.
You’ll need: cold-pressed castor oil; a cotton/flannel cloth; a wrap (old T-shirt or reusable cover to prevent stains); gentle dry heat (heating pad or hot-water bottle); and a towel.
- Patch-test first (inner elbow, 24 hours).
- Fold the cloth; saturate it—wet but not dripping.
- Place over the target area (lower abdomen for cramps, lower back, or upper chest/neck for comfort).
- Cover with the wrap; add low, steady heat.
- Relax 45–60 minutes.
- Wipe away excess oil. Store the cloth sealed in the fridge; replace when discolored or odorous.
- Begin with 1–3 sessions per week and adjust to skin tolerance.
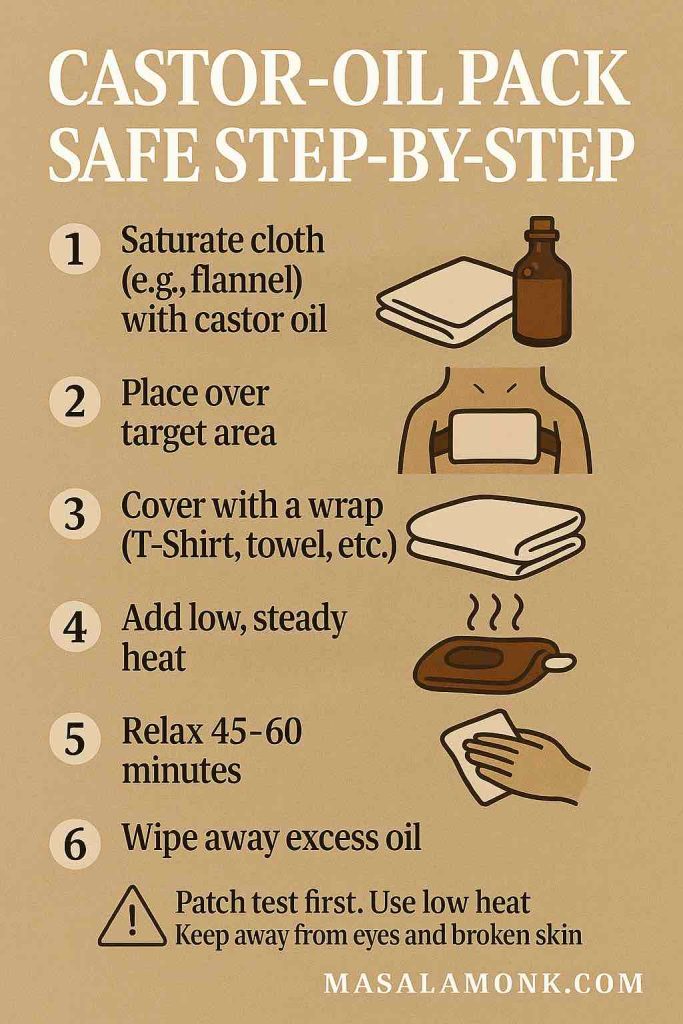
Safety notes. Keep packs away from eyes and broken skin. Moreover, discuss abdominal heat during pregnancy with your clinician; ingestion can stimulate the gut and may affect uterine activity—another reason medical guidance matters (see Cleveland Clinic, as noted earlier). People often describe post-pack comfort due to warmth, gentle pressure, and stillness; nevertheless, comfort is not “detox,” as MD Anderson and NCCIH explain.
Related reads on MasalaMonk: for pack-style comfort on musculoskeletal issues, see Castor Oil for Back Pain. For myth-busting on belly-button oiling—and how to try it safely if you choose—see Castor Oil in the Belly Button.
⚠️ Education, not prescription: Use the ideas here for learning. For symptoms, medications, or procedures, speak with your clinician first.
Uses for Castor Oil in Hair, Brows, Lashes & Scalp (Realistic and Mess-Smart)
In beauty routines, uses for castor oil center on conditioning—not medically proven regrowth. Dermatology-informed guidance aligns on this: sealing the shaft reduces breakage and boosts shine; robust regrowth evidence is lacking. For a clinician-reviewed stance, Cleveland Clinic (linked earlier) is a good starting point. For consumer safety—including rare tangling incidents—see Verywell Health’s castor oil guide.
How to use it well
- Pre-wash scalp mask: mix 1 part castor oil with 2–3 parts a lighter carrier (jojoba/almond) for spreadability and easier wash-out. Massage the scalp and mid-lengths; leave 30–60 minutes; then double-cleanse if needed.
- Dry ends only: on damp hair, smooth a pea-sized amount through the last few centimeters to reduce friction.
- Brows & lashes (cosmetic): with a clean spoolie, apply a micro-amount to hairs—not the waterline—and wipe excess.
- Frequency: start once weekly to avoid buildup.

When to escalate care. If you’re shedding rapidly or noticing widening parts/patches, consult a professional. The American Academy of Dermatology’s hair-loss hub explains diagnosis and evidence-based options; as noted earlier, rely on medical treatments for true regrowth.
Related reads on MasalaMonk: for wrinkle-focused skincare, browse Castor Oil for Face Wrinkles. For scalp-skin questions that overlap with flaking and plaques, compare approaches in Castor Oil for Psoriasis.
Uses for Castor Oil on Skin & Body (Simple, Satisfying, Non-Hype)
Because castor oil is thick and occlusive, it seals in hydration on very dry areas—heels, elbows, cuticles—and can calm that tight, post-shave feel on intact skin. In clinical settings, regulated formulations that include castor oil (such as Venelex) help maintain a moist healing environment for specific wounds; again, that is a professional indication, not a DIY swap. For exact labeling, see DailyMed (linked earlier).
At-home wins
- Cuticles & nails: one drop nightly for flexibility and shine.
- Massage blends: cut with lighter oils for better glide; patch-test if adding essentials.
- Laundry sanity: designate an “oil towel” and pre-treat stains with dish soap.
Related read on MasalaMonk: if eye comfort is on your mind, review do’s and don’ts in Castor Oil for Eyes, then follow your eye-care professional’s guidance.
Uses for Castor Oil During Colds & Sore Throats (Comfort-Only)
Castor oil does not treat infections, thin mucus, or shorten illness. Nevertheless, a warm neck or chest pack can feel soothing while you rest, hydrate, and use proven measures. For side-effect and safety basics—including why ingestion isn’t for colds—see Cleveland Clinic as noted earlier. For detox myths that often get bundled into cold-care tips, recall MD Anderson and NCCIH from earlier.
Comfort protocol (non-curative): 45–60 minutes of low, steady heat over an oil-saturated cloth, up to 3×/week. Stop if skin reacts. Seek care for high fever, breathing issues, suspected strep, or symptoms that persist beyond a few days.
⚠️ Heads up: This guide is educational. It isn’t medical advice, a diagnosis, or a treatment plan.
Uses for Castor Oil by Mouth: Constipation Basics & When to Avoid
Here is the straight talk: ingested castor oil works because ricinoleic acid stimulates intestinal smooth muscle; however, side effects are common. Consequently, reserve it for occasional constipation and only as labeled or advised. For dosing cautions, interactions, and who should avoid it, rely on Cleveland Clinic and StatPearls cited earlier. If you prefer a patient-friendly walk-through of timing and cramping, the Verywell Health guide mentioned previously is practical.
Pregnancy & labor (medical territory only)
Evidence on labor induction is mixed and nausea is frequent. A classic synthesis—see the Cochrane review on castor oil for labor induction—judged much of the data low quality; small studies since then suggest it may help initiate labor in select contexts. Even so, this is obstetric care, not a home experiment—discuss it with your own team. I’ll refer back to Cochrane by name where needed.
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing Quality for All Castor-Oil Uses
To support all the uses for castor oil above—especially packs—buy wisely.
On the label, prioritize:
- Cold-pressed, hexane-free extraction.
- USP-grade if there’s any chance of clinician-directed ingestion.
- Dark-glass bottles with batch/lot info.
- Sizes: 250–500 ml suits most homes; go bulk only if you truly do frequent packs.
- Roll-on bottles for brows/lashes to minimize mess.

Pack accessories:
- Washable cotton/flannel pack or a reusable wrap that prevents stains.
- Heating pad or hot-water bottle with adjustable warmth.
- A dedicated towel—because oil always finds a way.
Finally, apply a sanity filter to marketing. No kit or bottle turns castor oil into a detoxifier or a hair-growth drug. Anchor expectations to the Cleveland Clinic overview and the detox summaries from MD Anderson or NCCIH referenced earlier.
Storage, Patch-Testing & Cleanup (Everyday Practicalities)
- Store tightly capped in a cool, dark cabinet; wipe the bottle neck to prevent off smells.
- Patch-test any new bottle/blend on the inner elbow for 24 hours.
- Clean up stains by pre-treating with dish soap, then wash warm. Keep one “sacrifice” towel for pack nights.
Myths vs Facts (Quick Reality Checks)
- “Castor-oil packs detox the liver.” → No evidence. Comfort ≠ detox. (MD Anderson and NCCIH, as noted earlier.)
- “It regrows hair.” → Not proven. It conditions and reduces breakage; new growth requires evidence-based treatments (Cleveland Clinic and AAD, as noted earlier).
- “It’s fine to drink regularly.” → No. Occasional use only, if advised; side effects are common (again, Cleveland Clinic and StatPearls).
- “Kitchen oil works as eye drops.” → Never. Only sterile, formulated eye products belong in eyes.
Bottom Line: Sensible Uses for Castor Oil
In summary, the most sensible uses for castor oil are cozy, soothing packs; simple conditioning for hair and skin; and occasional, clinician-guided help for constipation. Skip detox hype, keep heat gentle, patch-test patiently, and choose quality oil in dark glass. Most importantly, if you notice persistent pain, signs of infection, eye issues, or significant hair loss, step away from DIY and see a clinician—sooner rather than later.
⚠️ Medical information only: This article shares general information and practical tips. It is not a diagnosis or a treatment plan and does not replace a consultation with a licensed clinician. Always follow your doctor’s advice for your health, skin, and eyes.
FAQs
1) What are the most sensible uses for castor oil—quick overview?
Short answer: the most reliable uses for castor oil are (1) comfort packs with gentle heat, (2) conditioning hair/skin (occlusive moisture lock), and (3) occasional clinician-guided help for constipation. For clinical safety basics and side effects, start with this plain-English explainer from Cleveland Clinic.
2) Does castor oil really “detox” the liver?
No. There’s no solid evidence that castor-oil packs “detox” the liver or purge toxins. Therefore, think of packs as comfort care, not cleansing. For a science-based view of “detox” claims, see MD Anderson’s detox explainer and the research summary from NCCIH on detoxes and cleanses.
3) How do I make a castor-oil pack—step by step?
You’ll need: cold-pressed castor oil, cotton/flannel, a wrap (old T-shirt or reusable cover), gentle dry heat (heating pad/hot-water bottle), and a towel.
Steps: patch-test → saturate cloth (not dripping) → place on target area → cover → add low, steady heat → relax 45–60 minutes → wipe excess → store cloth sealed in the fridge and replace when discolored.
Safety: keep away from eyes/broken skin; discuss abdominal heat if pregnant; and never microwave oily cloths. For more pack context on pain comfort, see MasalaMonk: Castor Oil for Back Pain.
4) Can I drink castor oil for constipation?
Sometimes—but sparingly. Castor oil is a stimulant laxative suitable for occasional use only; cramping and diarrhea are common. Therefore, try gentler options first and follow labeled doses if your clinician advises castor oil. For pharmacology and cautions, the medical monograph in StatPearls: Castor Oil is useful.
5) What are the uses for castor oil in hair care—does it regrow hair?
It conditions; it doesn’t reliably regrow. Castor oil can reduce breakage by sealing moisture, making hair look smoother and fuller; however, evidence for new growth is weak. For a clinician-reviewed stance, check Cleveland Clinic (as noted earlier). If you suspect medical hair loss, see the American Academy of Dermatology’s hair-loss hub once.
6) What’s the best way to apply castor oil for hair, brows, and lashes?
Less is more.
- Pre-wash mask: 1 part castor : 2–3 parts lighter oil (jojoba/almond), massage scalp/lengths 30–60 minutes, then double-cleanse.
- Dry ends: pea-sized amount on damp tips.
- Brows/lashes: micro-amount with a clean spoolie; avoid the waterline.
Tip: start once weekly to prevent buildup. For wrinkle-oriented routines, see MasalaMonk: Castor Oil for Face Wrinkles.
7) Is Jamaican black castor oil different?
Mostly in aroma and color. It’s roasted during processing, so it’s darker and has a toasted scent. Functionally, it’s still castor oil; therefore, choose by texture and smell—not promises. For scalp/skin use, the same uses for castor oil apply.
8) Can castor oil help psoriasis or eczema?
Sometimes for comfort, not cure. Because it’s occlusive, castor oil can reduce transepidermal water loss, which may ease dryness and tightness on intact skin. However, it doesn’t treat immune-driven inflammation. For practical comparisons and routines, see MasalaMonk: Castor Oil for Psoriasis; for general safety and triggers, lean on Cleveland Clinic as noted earlier.
9) Can castor oil help sore throat, cold, cough, or chest congestion?
Only for comfort. A warm neck/chest pack can feel soothing; however, castor oil does not thin mucus, treat infection, or shorten illness. Therefore, rest, fluids, humidified air, and medical care for red-flag symptoms still matter. For risks and side effects, see Cleveland Clinic as noted earlier. If you’re curious about navel-oiling myths that appear in cold season, read MasalaMonk: Castor Oil in the Belly Button.
10) Are there any medical-grade castor oil products?
Yes—clinic-only indications. For example, Balsam Peru + castor oil ointments (e.g., Venelex) maintain a moist wound environment and protect delicate edges; they are not DIY substitutes. If you want the exact labeling, check DailyMed: VENELEX Ointment.
11) Is castor oil safe during pregnancy or for inducing labor?
Only with your obstetric team. Evidence is mixed and nausea is common. A classic synthesis—see the Cochrane review on castor oil for labor induction—judged much of the data low quality. Consequently, this is medical territory, not a home experiment;.
12) Can castor oil help thyroid issues or “support the liver” with packs?
No clinical proof. Although a warm pack can feel relaxing, there’s no evidence it changes thyroid function or detoxifies the liver. Therefore, treat these as comfort rituals and keep taking prescribed meds. For the detox angle, recall MD Anderson or NCCIH as noted earlier.
13) Will castor oil fix ovarian cysts, fibroids, or fertility problems?
No evidence of cure. Some people use packs for pelvic comfort; nevertheless, cysts, fibroids, and fertility concerns require gynecologic evaluation. In short, use packs for relaxation only, and keep your medical plan front and center.
14) Does castor oil help with warts, lipomas, boils, bruises, or cellulite?
Not really. Warts and lipomas need clinical treatments; boils may require antibiotics or drainage; bruises fade with time; and cellulite responds better to lifestyle + targeted procedures. Castor oil may soften surrounding skin, but it doesn’t remove lesions.
15) Can castor oil lighten dark spots or tighten skin?
Expect moisture, not miracles. Occlusion can make skin look smoother and more luminous short-term; however, pigment and laxity respond to evidence-based actives (retinoids, vitamin C, niacinamide) and procedures. Therefore, think of castor oil as a supporting moisturizer, not the main treatment.
16) Is it safe to put castor oil in the eyes for dry eyes or cataracts?
No kitchen oils in eyes. Use only sterile, formulated eye products. Kitchen-bottle oils can irritate or contaminate the ocular surface. For do’s/don’ts and alternatives, review eye safety on Cleveland Clinic as noted earlier, then consult your eye-care professional. Meanwhile, for broader context, see MasalaMonk: Castor Oil for Eyes.
17) What grade, bottle, and size should I buy?
Choose quality to support all the uses for castor oil:
- Cold-pressed, hexane-free extraction;
- USP-grade if ingestion is clinician-directed;
- Dark-glass bottle with batch/lot;
- 250–500 ml for most homes; and
- Roll-on bottles for brows/lashes to reduce mess.
As a reminder, “extra virgin” isn’t regulated for castor oil—thus, focus on extraction, solvents, and packaging.
18) How should I store castor oil, and how do I handle stains?
Storage: cool, dark place; cap tightly; wipe the bottle neck to prevent off odors.
Stains: pre-treat with dish soap; then wash warm. Pro tip: keep a dedicated “oil towel” for pack nights.
19) Are there side effects I should watch for?
Yes. Topically, watch for contact dermatitis or pore clogging (use less or dilute). Rarely, heavy oiling + friction can cause severe tangling (aka acute hair felting); if it happens, saturate with conditioner and gently detangle—then pause oils. Orally, expect cramping/diarrhea; do not rely on castor oil chronically (Cleveland Clinic, as noted earlier). If anything feels off—especially eye irritation, severe abdominal pain, fever, or persistent symptoms—see a clinician.
20) Where can I read more specifics on common home myths and routines?
For pragmatic deep dives, try these internal guides on MasalaMonk:
- Comfort and packs: Castor Oil for Back Pain
- Navel myths & safety: Castor Oil in the Belly Button
- Skin concerns: Castor Oil for Face Wrinkles, Castor Oil for Psoriasis
For medical context referenced earlier : Cleveland Clinic, StatPearls, DailyMed, MD Anderson, NCCIH, AAD, and Cochrane.
⚠️ Medical information only: This article shares general information and practical tips. It is not a diagnosis or a treatment plan and does not replace a consultation with a licensed clinician. Always follow your doctor’s advice for your health, skin, and eyes.