
There’s a particular kind of craving that shows up the moment you’ve been eating low carb for a while: not hunger, exactly—more like a restless need for crunch. You can be completely satisfied after dinner, yet still want something salty, crisp, and snackable. That’s why keto chips are such a common sticking point. Chips aren’t just food; they’re texture, routine, and comfort.
The good news is that chips on keto can absolutely work. The even better news is that you don’t have to settle for a sad substitute that tastes like cardboard or crumbles the second it touches salsa. Once you understand how different low carb chips behave—thin and snappy, thick and scoopable, airy and crunchy—you can choose the right “chip” for the job: dipping, nachos, movie-night grazing, or a grab-and-go snack box.
The secret isn’t hunting for one magical chip. It’s building a small rotation based on how you actually eat chips:
- thin and snappy for salsa
- sturdy for thick dips
- something that survives nachos
- something that scratches “hot chips” cravings
- something that works when you’re busy and need a snack box situation
Once you stop forcing one chip to do every job, keto-friendly chips become much easier — and far more enjoyable.
This guide is built for real life. It covers keto chip snacks you can make at home, low-carb & keto friendly chips you can buy, and the chip replacements that quietly do the job better than most “keto chips” ever will. Along the way, you’ll also get dip pairings and a few easy snack setups that keep the crunch without turning into an accidental carb blowout.
What you’ll find in this keto chips guide
This post isn’t just a list—it’s a practical playbook, with easy recipes and real-life fixes you can actually use. Here’s what we cover below:
- What counts as keto chips (serving size, total carbs vs fiber, and how to compare options smartly)
- How to choose low carb chips by “dip-ability” (salsa vs thick dips vs nachos vs grab-and-go crunch)
- Keto cheese chips and parmesan crisps + a homemade cheese crisps recipe (the easiest win)
- Scoopable cheese “cracker chips” recipe (built for thick dips that destroy flimsy chips)
- Pork rinds and scratchings + a quick re-crisp trick and seasoning ideas (best for thick dips)
- Keto chicken skin chips and meat-chip crunch with oven + air fryer recipes (hard-crunch, “keto pringles” energy)
- Seed crackers and keto crackers + a simple DIY seed cracker recipe (reliable chip replacement)
- Almond flour crackers recipe that feels like real crackers (sturdy + dip-friendly)
- Keto tortilla chips and low carb tortilla chips + the homemade tortilla chips recipe (oven + air fryer) that actually gets crisp
- “Keto Doritos” seasoning dust recipe for hot-chip cravings and bland-chip rescues
- Dip recipes that make chips feel satisfying: thick queso + scoopable salsa + a quick guac-style idea
- Snack box setups, nacho layering, and crunch troubleshooting (so chips stay crisp and snacking doesn’t spiral)
What counts as keto chips?
At a practical level, keto chips are anything crunchy and chip-like that fits your carb target for the day. Sometimes that means a food that naturally has almost no carbs (like baked cheese crisps). Other times it means a low carb tortilla chip made from a wrap or a high-fiber dough. Either way, the “keto” part isn’t a vibe—it’s the numbers, plus how you actually eat them.
That’s why serving size matters more than the front-of-bag language. Even when a snack is marketed as low carb chips, the carb count is always tied to the listed portion. Double the portion, and you double the carbs. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s explanation of the Nutrition Facts label is a helpful baseline because it lays out how serving sizes and carbohydrate values are presented and how to compare products without fooling yourself: how to use the Nutrition Facts label.

Next, it helps to understand what “total carbohydrate” includes on labels. Fiber is listed under total carbohydrate, and some products use fiber-heavy formulations that look dramatically lower in net carbs than they do in total carbs. The FDA’s interactive explainer on total carbohydrate breaks down what’s inside that number and why it’s structured the way it is: FDA Interactive Nutrition Facts Label: Total Carbohydrate.
Finally, remember that keto approaches vary. Some people aim for very low carbs, while others are simply trying to keep things low carb and steady. If you want a neutral overview of how ketogenic patterns are typically described, this background from Mayo Clinic’s keto overview is a decent orientation point.
Once those basics are in place, choosing keto chips becomes much simpler: pick the texture you want, then pick the version that fits your numbers.
Also Read: Eggless Yorkshire Pudding (No Milk) Recipe
The simplest way to choose low carb chips: pick by “dip-ability”
Instead of chasing the perfect chip, start with a question that actually matches how you snack:
- Do you want something thin and crisp for salsa?
- Do you need sturdy chips for dipping into thick queso-style dips?
- Are you building nachos?
- Or are you just looking for a crunchy snack to eat by the handful?
From there, chip choices get easier fast. Thin and crisp chips don’t always scoop well. Thick chips don’t always feel “real” with salsa. Airy chips can be fun but may collapse in dips. So rather than forcing one option into every situation, it’s smarter to keep two or three types in rotation.
Below we cover the main “families” of keto chips and chip alternatives, plus how they behave in the real world.
Quick Cheat Sheet: Which Keto Chip Works for What?
Use this as the “pick-by-dip-ability” shortcut. Once you match chip style to the job, keto chips stop feeling like a compromise.

| What you’re craving | Best keto chip option | Why it works | Quick tip to make it better |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salsa (watery, acidic) | Tortilla-style low carb chips (baked extra-dry) | They feel most “real” with salsa and keep that tortilla snap | Bake 1–3 minutes longer than you think, then cool on a rack |
| Thick dips (queso, buffalo dip, creamy dips) | Cheese crisps / seed crackers / pork rinds | These scoop without dissolving or turning into mush | Choose the sturdier option when the dip is dense and warm |
| Nachos (melt + crunch) | Tortilla-style chips or cheese crisps | Tortilla chips give the classic vibe; cheese crisps stay sturdy | Put cheese first so it acts like a “seal,” keep wet toppings late |
| “Hot chips” cravings | Cheese crisps or tortilla chips with seasoning dust | Flavor carries the craving more than the base | Toss warm chips with spice + finish with lime for that “dusted” feel |
| Snack-by-the-handful | Seed crackers (portion-friendly) | They’re steadier, more filling, and less “accidental whole bag” | Pre-portion into a bowl or snack box so it stays intentional |
| Busy snack box situation | Seed crackers + cheese crisps | Easy to pack, less fragile, pairs with dips cleanly | Add something tangy (pickles/olives) so the snack feels “done” |
The 3 Rules That Make Keto Chips Work
- Pick the chip by dip. Salsa wants thin and dry; thick dips want sturdy and scoopable.
- Dry beats brown. Crispness is mostly moisture removal—especially for tortilla-style chips.
- Structure beats willpower. Portion into a bowl and pair with a dip so you stop snacking when you’re satisfied.
Also Read: Crock Pot Chicken Breast Recipes: 10 Easy Slow Cooker Dinners (Juicy Every Time)
Keto cheese chips and parmesan crisps: the classic crunch that rarely fails
If you want keto chips that feel instantly satisfying and require almost no negotiation with your carb budget, keto cheese chips are the easiest win. Cheese crisps and parmesan chips keto-style snacks deliver that loud snap and salty finish that most people miss first.
They also behave beautifully with dips. Because they’re sturdy and rich, they can scoop thicker dips without dissolving. Moreover, they’re easy to flavor without relying on anything complicated: smoked paprika, chili powder, garlic powder, black pepper, or a little dried oregano can shift the vibe from “plain cheese” to “nacho chip energy.”
Homemade cheese crisps you’ll actually repeat
What you need
- Finely shredded cheese (parmesan crisps the easiest; cheddar is bolder; a mix is great)
- Parchment paper
- A baking tray
- Optional seasoning (paprika, chili-lime, garlic powder)

How to do it
- Heat oven to 190°C / 375°F.
- Line a tray with parchment.
- Drop small mounds of cheese (about a tablespoon each). Keep space between them.
- Season lightly (if using).
- Bake until bubbling and browned at the edges, usually 5–8 minutes depending on cheese and thickness.
- Cool completely before lifting. Cooling is where they become crisp.
The cooling step is non-negotiable. They firm up as they cool. If you grab them warm, they’ll feel floppy and you’ll assume you messed up.
Make them taste like “hot chips” without pretending they’re the same
Sometimes you don’t want “cheese chips.” You want the aggressive spicy-dusted vibe — the low carb hot chips craving. If you’re chasing the keto doritos vibe—spicy, salty, dusted—season before baking with chili powder + smoked paprika. Then finish with lime right before eating. It lands surprisingly close to that “hot chips” craving without pretending it’s the same thing and gives the sharp, dusty, spicy feel people associate with nacho-style chips and “hot chip” snacks.
Make them sturdier for dipping
If your cheese chips snap too easily, two small tweaks help:
- Use a slightly thicker mound rather than a thin sprinkle.
- Mix parmesan with cheddar. Parmesan crisps hard and thin; cheddar adds body.
Turn cheese crisps into “cheese crackers” that scoop
Cheese crisps are amazing, yet sometimes you want a cracker-like bite that holds shape and dips without shattering. This version adds a tiny bit of structure.
Quick cheese crackers (keto cheese crackers)
- 1 cup shredded cheddar
- 1/3 cup finely grated parmesan
- 1 egg white
- 1–2 teaspoons psyllium husk powder (optional but helpful)
- Seasoning: garlic powder, paprika, black pepper

Method
- Heat oven to 175°C / 350°F.
- Mix everything until it forms a sticky mass.
- Roll between parchment to a thin sheet (about 2–3 mm).
- Score into squares.
- Bake 12–16 minutes until deeply golden.
- Cool on the tray, then snap along the score marks.
That gives you a sturdier “chip” that behaves like a scoopable cracker—perfect when you want keto crackers for cheese nights.
Want a lighter, tangier crunch? Keto cottage cheese chips are the “high-protein” version of cheese crisps — but the method is different: you’re dehydrating, not just melting cheese.

More dips that make cheese crisps feel like a full snack
Cheese crisps become dangerously snackable when they have the right dip next to them. A simple strategy is to keep a creamy base on hand and change the flavor each time. If you want a dependable base, homemade mayo with variations gives you a flexible starting point, especially for quick chip dips. If you prefer an egg-free option, eggless mayonnaise works as a smooth, neutral base too.
From there, spice it up with something bold. A spoon of hot sauce works, yet a layered sauce works even better. This pepper sauce guide is a great internal reference because it gives you multiple styles (bright vinegar heat, smoky heat, herb-forward heat) that can transform a basic dip in seconds.
If you want a party-ready option that’s hot, rich, and built for scooping, buffalo chicken dip is a classic pairing that feels like a proper snack table, not a compromise.
Pork rinds and scratchings: best keto chips for thick dips and “scoop” snacks
Pork rinds and similar crunchy scratchings are polarizing, yet they’re undeniably effective as keto chips for dipping—especially for thick dips. Their structure is airy but sturdy, and they hold up under creamy, dense dips in a way that thin tortilla-style chips often can’t.
That said, they’re not always the best match for watery salsa. If salsa is your main goal, you’ll often prefer a tortilla-style keto chip. However, if you love thick dips, these can be your best keto chips for dipping—especially for anything warm and cheesy or anything creamy and heavy.
Make store-bought pork rinds taste “fresh” again
Even good crunchy snacks can taste stale if they’ve been open for a day. A quick crisp-up makes them feel brand new:
- Spread on a tray and warm at 160°C / 325°F for 4–6 minutes
- cool completely

After that, toss with one of these seasoning blends:
- Chili-lime: chili powder + lime zest + salt
- Smoky: smoked paprika + garlic powder + pepper
- Ranch-ish without the packet: dried dill + garlic powder + onion powder + salt
Pair them with something cooling
A Greek yogurt dip changes everything here. A great fit is Greek Tzatziki Sauce. It’s bright, garlicky, and thick enough to cling. In addition, the cucumber freshness cuts through rich, salty snacks so you don’t feel like you’re eating pure intensity.
If you’re building a game-night platter, another strong option is Blue Cheese Dip for Wings—especially if you like spicy snacks.
Keto chicken skin chips and keto meat chips: the “keto pringles” level of crunch
Some cravings aren’t satisfied by airy crunch. Sometimes you want that hard, thick, aggressive crunch that feels like kettle chips or even the idea of keto pringles. That’s where keto chicken skin chips and keto meat chips come in.
These options tend to be high in fat and protein and very low in carbs, so the carb question is usually easy. The bigger issue is portioning, because they’re intensely snackable and easy to overeat. They’re also not always ideal for delicate dipping—some varieties scoop beautifully, while others shatter.
Chicken skin chips at home recipe (oven method)
If you have access to chicken skin, you can turn it into chicken chips keto-style with surprisingly little effort. Lay the skins flat on parchment, season with salt and pepper, and bake until deeply crisp. Flip once. Then drain and cool. The cooling step matters because it crisps further as it rests. To shift the flavor into “hot chips” territory, sprinkle chili powder or smoked paprika after baking, then add a squeeze of lime. The result is bold without becoming bitter.
Save this: oven vs air fryer timings + the 3 rules that make chicken skin chips snap instead of chew.

Ingredients
- Chicken skins (as flat as you can get them)
- Salt + pepper
- Optional: smoked paprika, chili powder, garlic powder
Method
- Heat oven to 200°C / 400°F.
- Lay skins flat on parchment. Single layer matters.
- Season lightly (they shrink, so seasoning concentrates).
- Bake until deeply crisp, flipping once, usually 12–20 minutes depending on thickness.
- Drain on paper and cool before eating.
For a hot chip vibe, sprinkle seasoning after baking and finish with lime.
Air fryer chicken skin chips (faster, crispier)
If you’ve got an air fryer, chicken skin chips can become dangerously easy.
Method
- Preheat air fryer (if yours benefits from it).
- Arrange skins in one layer (no overlap).
- Air fry around 190–200°C / 375–400°F, checking often.
- Flip once.
- Cool on a rack.
If you want to push the “hot chips” vibe, season after crisping and finish with lime.
Because air fryers vary wildly, watch the first batch carefully. Once you learn the timing, it becomes a repeatable “weekend snack” trick.
A “meat chip” idea that’s actually doable: jerky-style crisps
You’ll see phrases like keto turkey jerky, keto beef jerky, best jerky for keto, and beef sticks keto all grouped with chip terms because people use jerky as a crunchy-ish snack replacement. Jerky isn’t a chip, but you can make jerky crisp enough to feel chip-adjacent.

Crispy jerky-style strips (oven)
- Thinly slice very lean beef (freeze 30 minutes first to slice thin)
- Marinate with salt, pepper, garlic powder, smoked paprika, and vinegar or lemon juice
- Dry/bake at low heat (90–120°C / 195–250°F) until dry and crisp, flipping once
- Cool fully
The key is thinness and dryness. If it’s bendy, it’s jerky. If it snaps, it’s meat-chip territory.
For dipping, go thick rather than watery. Buffalo chicken dip works, and blue cheese dip works even better if you like tang.
Seed crackers and keto crackers: the most reliable low carb chip replacement
If you want something that feels like chips but behaves more like a stable, everyday snack, seed crackers are the quiet hero. They’re one of the best low carb chip replacement options because they’re easy to make, easy to portion, and generally less likely to trigger “I ate the whole bag” behavior.
They’re also a natural bridge into keto crackers and almond crackers keto-style snacks, since many cracker-style recipes are built around seeds, fiber, and low-carb flours.
Why seed crackers work so well
They usually deliver:
- a crisp, toasted crunch
- more “weight” than airy chips
- better dip performance than many thin keto chips
Plus, they pair beautifully with yogurt dips, mayo dips, and cheese-based dips.
If you want the dip that makes seed crackers feel restaurant-level, use Greek Tzatziki Sauce. It’s thick, bright, and makes the whole snack feel fresh.
Alternatively, if you’re going for a richer, more indulgent dip, use a mayo base:
- homemade mayonnaise for classic richness
- eggless mayo if you want no-egg convenience
Then add heat or tang with pepper sauce.
DIY seed cracker recipe (simple, not fussy)
Mix flaxseed meal with chia seeds, sesame, and water. Let it gel. Spread it very thin on parchment. Bake low and slow until dry and crisp, then break into shards.
You can turn these into “nacho chips” by adding cumin, paprika, and a pinch of garlic powder. You can also turn them into “cheese crackers” by baking with a light dusting of parmesan over the top.
Ingredients
- 1/2 cup flaxseed meal
- 2 tablespoons chia seeds
- 2 tablespoons sesame seeds (optional)
- 1/2 teaspoon salt
- 1 cup water
- Optional: garlic powder, paprika, dried herbs
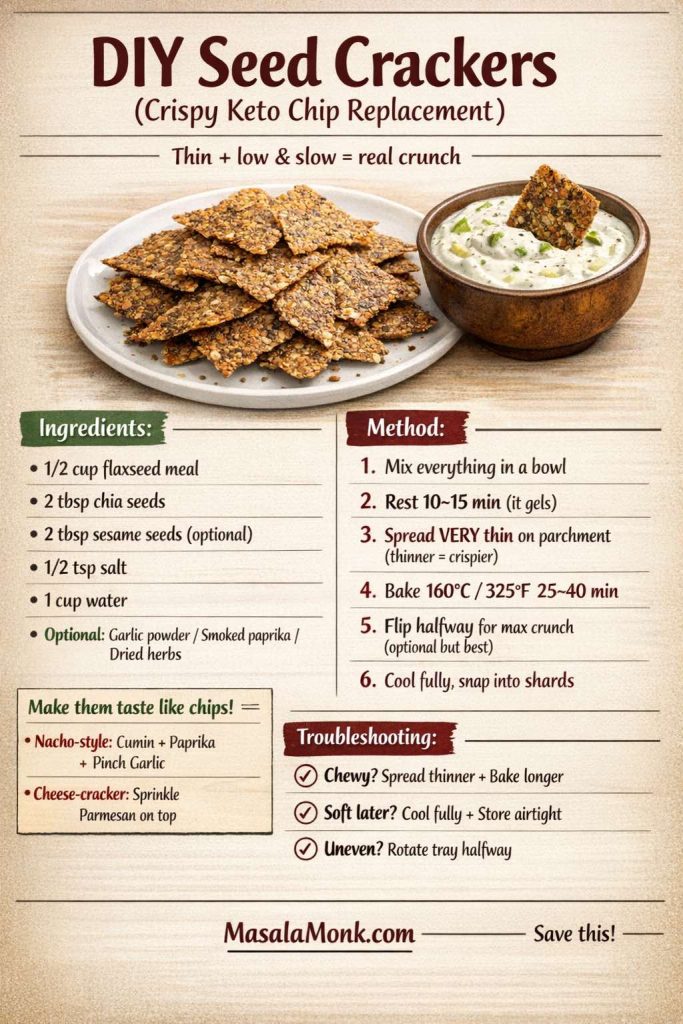
Method
- Mix everything in a bowl.
- Rest 10–15 minutes until gelled.
- Spread thin on parchment (thinner = crispier).
- Bake at 160°C / 325°F for 25–40 minutes, depending on thickness.
- Flip the sheet halfway through if you want extra crispness.
- Cool, then snap into shards.
This is a great base for chip-and-dip nights because it scoops well and holds up.
Almond flour crackers that feel like “real crackers”
If you want almond flour keto crackers, this version is simple and sturdy.
Ingredients
- 1 1/4 cups almond flour
- 1 tablespoon psyllium husk powder (helps structure)
- 1/2 teaspoon salt
- 1/2 teaspoon baking powder
- 1 egg
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- 2–4 tablespoons water as needed
- Optional: sesame seeds or everything-style seasoning

Method
- Heat oven to 175°C / 350°F.
- Mix dry ingredients, add egg + oil, then add water until a workable dough forms.
- Roll between parchment into a thin sheet.
- Score into squares.
- Bake 12–18 minutes until golden and crisp.
- Cool completely, then break.
If you want a deeper look at how keto-friendly flours behave across recipes, this keto flour guide is a great companion. If glucose stability is also on your mind, almond flour and diabetes supports why almond-based swaps often behave differently than wheat-based snacks.
Also Read: Sourdough Starter Recipe: Make, Feed, Store & Fix Your Starter (Beginner Guide)
Keto tortilla chips and low carb tortilla chips: for salsa nights and nachos
When people say “keto chips,” they often mean keto tortilla chips. They want triangles, they want that familiar tortilla snap and then they want the ability to do keto chips and salsa without feeling like they’re chewing on a substitute.
This is completely doable, but tortilla-style chips are the area where labels matter most. Two products can look similar and behave very differently. So start with the label basics from the FDA: understanding the Nutrition Facts label and the structure of total carbohydrate. That way, you’re comparing chips on the same foundation rather than trusting marketing language.
What’s actually inside many low carb tortillas (and why it matters)
A lot of low carb tortillas get their “net carb” profile from some combination of:
- added fibers (like inulin, oat fiber, or other plant fibers like cellulose)
- resistant starches or modified starches
- gluten or protein structure (in some versions)
- binding agents (like gums)
None of that is automatically “bad.” The point is simply this: a tortilla can look low carb on paper while still being very easy to overeat, and some people don’t feel great after huge fiber loads in one sitting. When that happens, it’s not a willpower issue—it’s how fiber-heavy products behave for some bodies.
If you ever want a neutral place to cross-check general nutrition numbers across foods and ingredients, USDA FoodData Central is useful.
Also Read: How to make No-Bake Banana Pudding: No Oven Required Recipe
Homemade keto tortilla chips that actually get crisp (oven + air fryer)
If you’ve tried making low carb tortilla chips and ended up with limp triangles, you’re not alone. Tortilla-style keto chips can be genuinely satisfying, but they need to be treated like a drying project, not a quick toast. You’re not just browning them — you’re removing moisture so they stay crisp long enough for salsa, dips, and nachos.
This is the master method: one approach that works with most low carb wraps and homemade tortillas, plus the fixes that matter when a batch goes wrong.

The oven method (most reliable for big batches)
What you’ll need
- Low carb tortillas or homemade tortillas
- Oil spray or a very light brush of oil
- Salt + optional seasonings
- 2 baking trays (or bake in batches)
- A cooling rack (highly recommended)
Step-by-step
- Heat the oven to 190°C / 375°F.
- Cut tortillas into triangles. Keep them similar in size so they crisp evenly.
- Arrange in a single layer. Overlap turns into steaming.
- Spritz or brush with oil lightly. Too much oil makes chips heavy and can keep them from drying properly.
- Season. Salt is non-negotiable. Add spices if you want a “nacho” vibe.
- Bake 8–12 minutes, then flip the chips.
- Bake another 6–10 minutes until the edges are clearly crisp and the center feels dry.
- Move to a cooling rack and let them cool 10 minutes. They finish crisping as they cool.
Pro move: after flipping, crack the oven door for the last 2–3 minutes to help moisture escape.
Why the rack matters: if you cool chips on a plate, steam softens the underside. A rack keeps air moving, which is the difference between “pretty good” and genuinely crisp.
The air fryer method (fastest for small batches)
The air fryer is perfect when you want keto chips and salsa right now and don’t need a giant batch. It also makes chips taste slightly “lighter” because airflow does more work than oil.
- Preheat the air fryer if yours benefits from it.
- Set it to 180–190°C / 350–375°F.
- Arrange triangles in a single layer (cook in batches if needed).
- Light oil spritz + salt + seasoning.
- Air fry 4–6 minutes, shake or flip, then another 2–5 minutes until crisp.
- Cool fully (this is where crisp happens).
Watch the first batch closely. Tortillas vary in thickness and fiber content, so the perfect time depends on your wrap. Once you find the sweet spot, it becomes repeatable.
Why your low carb tortilla chips aren’t crisp (quick fixes)
Most crunch problems come from a few predictable issues. The fixes are simple once you know what you’re looking at.
- They browned but stayed soft: they need more drying time. Lower the heat slightly and bake longer so the center dries without burning.
- They crisped, then softened later: they weren’t cooled properly. Always cool properly before storing.
- They taste bitter: the seasoning burned. Add delicate spices later or use slightly lower heat for longer.
- They’re crisp at the edges but chewy in the center: triangles are too big or the wrap is thick. Cut smaller, bake longer, and flip earlier.
- They feel greasy: too much oil. Use a mist, not a brush.
If you want salsa-style chips that don’t collapse fast, bake them a touch longer than you think you should. A slightly “over-dry” chip is exactly what survives salsa and nachos.
How to store homemade keto chips (so they don’t go stale)
Homemade chips go soft mainly because moisture sneaks back in. Once that happens, they’re not ruined — you just need to re-crisp them.
- Best storage: airtight container after chips are completely cool.
- If they soften: re-bake at 160°C / 325°F for 4–6 minutes, then cool again.
- If you live somewhere humid: add a small paper towel to the container (swap daily) to absorb moisture.
This makes tortilla-style keto chips far more practical. Instead of treating chips like a one-time project, you can bake once and refresh quickly when needed.
Also Read: Chicken Adobo — Step-by-Step Recipe — Classic Filipino Adobong Manok
“Keto Doritos” flavor dust: the fastest way to fix a bland batch
Even crisp chips can feel disappointing if they taste flat. Seasoning matters more than people expect — especially for low carb chips, where you’re not getting the same corn-based flavor you’d get from regular tortilla chips.
This simple seasoning blend takes plain tortilla chips, cheese crisps, seed crackers, or pork rinds and pushes them into that spicy, dusty “hot chips” zone.

Nacho-style seasoning (dry blend)
- 1 tsp smoked paprika
- 1/2 tsp chili powder
- 1/2 tsp garlic powder
- 1/2 tsp onion powder
- 1/4 tsp cumin (optional but excellent)
- Salt to taste
- Optional: pinch of citric acid, or a squeeze of lime after crisping
How to use it: toss warm chips with the seasoning (a light oil mist helps it stick), then finish with lime. Suddenly your “chip replacement” feels like a real snack, not a compromise.
If you like heat with depth instead of flat spice, a spoon of pepper sauce stirred into mayo makes an instant spicy dip that turns even simple chips into something you actually want to keep eating.
Also Read: Sweetened Condensed Milk Fudge: 10 Easy Recipes
Make low carb tortillas at home (then turn them into chips)
If you’ve found a store-bought wrap you like, turning it into chips is already a win. However, if you don’t love the ingredient list on some low carb tortillas—or you want chips that taste cleaner and crisp the way you like—making tortillas at home gives you full control.
The bonus is flexibility: make them slightly thicker for wraps, then roll them thinner when you want chips. Once you have a tortilla you like, the crisping method you already used becomes automatic.
Here are two reliable routes:
Almond flour tortillas (soft enough to wrap, crisp enough to chip)
If you’d rather make a dough-based chip, almond flour tortilla chips are the usual route. They take more effort, yet you control the thickness and the seasonings. This also naturally connects to a broader low-carb flour toolkit. If you want a deeper reference for how keto-friendly flours behave, MasalaMonk’s keto flour guide can help you understand why some doughs crisp while others stay soft.
Ingredients
- 1 1/2 cups almond flour
- 1 tablespoon psyllium husk powder (structure)
- 1/2 teaspoon salt
- 1 teaspoon baking powder (optional, for tenderness)
- 1 egg
- 2 tablespoons olive oil
- 3–6 tablespoons warm water (as needed)

Method
- Mix dry ingredients.
- Add egg and oil, then add water gradually until dough is pliable.
- Divide into balls.
- Press between parchment into thin circles.
- Cook on a hot dry skillet 60–90 seconds per side.
To make chips
- Let tortillas cool fully (they firm up).
- Cut into triangles.
- Bake at 190°C / 375°F until crisp, flipping once.
- Do not forget to cool properly.
If you’re building chips from almond flour and you care about glucose stability too, almond flour and diabetes is a relevant resource that reinforces why almond-based swaps often behave differently from wheat-based snacks.
Coconut flour tortillas (lighter, more delicate)
Coconut flour absorbs a ton of water, so these can be fragile. Still, they work when you want thin chips.
Ingredients
- 2 tablespoons coconut flour
- 2 eggs
- 2 tablespoons water
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- Salt
- Optional: pinch of baking powder

Method
- Whisk everything and let it sit 2 minutes.
- Pour thin circles into a lightly oiled skillet.
- Cook gently; flip carefully.
These are more fragile, but when they crisp successfully, they can be surprisingly satisfying as thin chips.
Also Read: Sourdough Recipe: 10 Easy Bread Bakes (Loaves, Rolls & Bagels)
Keto chips and salsa: how to make it actually satisfying
Keto chips and salsa can work beautifully if you stop treating salsa like the whole snack and start treating it as one part of a complete setup.
A strong chips-and-salsa plate usually has:
- a tortilla-style keto chip as the crunchy base
- something creamy to balance acidity
- something salty or cheesy to make it feel complete

That creamy element can be as simple as a quick mayo dip (mayo + pepper sauce), or a cooling yogurt dip like Greek Tzatziki. Meanwhile, if you want an avocado-based angle, this post on avocado for diabetes supports why avocado-based dips are often used in lower-carb eating patterns.
Watery salsa destroys weak chips. So the trick is pairing chip type to dip type:
- watery salsa → tortilla-style chips baked extra crisp
- thick dips → cheese crisps, seed crackers, pork rinds
- mixed plate → keep salsa in a small bowl and balance with something creamy so the snack feels complete
Also Read: Peanut Butter Fudge: Recipes & Guide (8 Methods + Easy Variations)
Keto nacho chips, keto taco chips, and the art of building low carb nachos
If you’re craving nachos, you’re not craving chips as much as you’re craving structure: crunchy base, melted toppings, and a little chaos on a tray.
The easiest way to do keto nacho chips without disappointment is to pick a base that stays crisp long enough to eat the plate.

Three keto nacho bases that work
1) Cheese crisps
They’re naturally sturdy and don’t become soggy as fast. Layer lightly, add toppings that aren’t too watery, and keep wet sauces on the side.
2) Tortilla-style low carb chips
Best when you want the most “normal” nacho vibe. Bake them extra crisp before topping, then layer cheese first so it acts like glue.
3) Pork rinds
They can work surprisingly well, especially if you assemble bite-by-bite instead of drowning the whole tray in sauce.
If you want a nacho topping that feels like party food, Buffalo Chicken Dip can double as a hot, creamy topping. For a cooler, tangier finish, Blue Cheese Dip works brilliantly on the side.
Keto veggie chips: when you want crunch that feels lighter
Keto veggie chips can work, but they’re the most likely to disappoint if you expect them to taste like potato chips. If you treat them as their own snack—thin, crisp, salty, and fresh—they can be genuinely good.
Keto kale chips that stay crisp
Keto kale chips are a classic for a reason. They crisp quickly and can be intensely snackable when seasoned well.
The biggest determinant is moisture. Dry the leaves thoroughly. Use a light touch of oil. Bake in a single layer. Then cool before storing.

If you want a dip that makes kale chips feel less “health snack” and more “snack snack,” serve them with Greek tzatziki sauce. It adds richness and tang, which makes veggie chips feel complete.
Zucchini chips, radish chips, and other veggie crisps
Zucchini, radish, and even thin-sliced eggplant can crisp if you slice them thin and bake them long enough to dry out. Salt them first to pull moisture, pat them dry, then bake.

If you’re looking for variety because cheese-based chips feel heavy every day, rotating in veggie chips is an easy way to keep snacks interesting while staying low carb.
Also Read: 10 Vegan Chocolate Cake Recipes (Easy, Moist, & Dairy-Free)
Protein chips keto-style: what they are and what to watch
High-protein low carb chips exist in many forms. Some are basically puffed protein snacks. Others are fiber-heavy crisps with added protein. Some are more like crackers.
They can fit into a low carb plan, yet they can also be the kind of snack that looks “too good to be true.” That doesn’t mean they’re bad; it simply means you want to read the label carefully and portion intentionally.

Start with the basics:
- serving size
- total carbs
- fiber
- any sugar alcohols
If you’re ever unsure how “net carb math” is being presented, the American Diabetes Association’s primer on carbohydrates and net carbs is a good neutral explanation: ADA: get to know carbs.
Quick note: “Net carbs” isn’t an official line on the label—it’s a calculation people use. Always compare products using the same serving size first.
For a purely neutral place to cross-check nutrition information across foods and ingredients, USDA FoodData Central is useful when you want a baseline reference.
Also Read: Kahlua Drinks: 10 Easy Cocktail Recipes (Milk, Vodka, Coffee)
No carb chips, zero carb chips, and “0 carb chips”: what that usually means in real life
It’s tempting to chase the idea of no carb chips. After all, if chips without carbs existed in a way that felt exactly like tortilla chips, everyone would eat them.
In reality, “0 carb” often happens because of one or more of the following:
- the serving size is small
- the carbs per serving are low enough to round down
- the snack is mostly fat/protein with tiny residual carbs

The important part isn’t to argue with the label; it’s to make sure the portion you actually eat still fits your day. This is exactly why the FDA’s breakdown of total carbohydrate and label structure is worth knowing: total carbohydrate explainer.
If you like the idea of near-zero carb chips, you’ll usually find the most reliable options in the “whole food turned crunchy” category: cheese crisps, chicken skin chips, pork rinds, and some seed crackers. Those aren’t perfect replicas of tortilla chips, yet they satisfy crunch in a way that makes you stop missing the original.
Also Read: Best Vermouth for a Negroni Cocktail Drink Recipe
Low carb hot chips without the gimmicks
Sometimes the craving isn’t simply chips. It’s low carb hot chips—the spicy, salty, dusted, can’t-stop kind.
You can get that feeling without chasing an exact imitation. A few ways that work:
- Season cheese crisps with chili powder, smoked paprika, garlic powder, and a pinch of salt, then finish with lime.
- Bake tortilla-style low carb chips, then toss them with a chili-lime blend while they’re still warm.
- Make a spicy dip that does the heavy lifting: mayo + pepper sauce is an instant “hot chips” companion.
For the dip base, use homemade mayo or eggless mayo. For the heat, use pepper sauce. That combination turns almost any chip substitute into a “this is what I wanted” snack.
Two dips that make keto chips feel like “real” chips: thick queso + scoopable salsa
Chips feel satisfying for two reasons: crunch and the dip. Most disappointment happens when thin chips meet watery salsa. Thicken the dip, and suddenly cheese crisps, tortilla-style chips, and seed crackers – which we cover in this post – all feel more like the “real” experience.
1) Thick queso-style cheese dip recipe (scoopable, not runny)
This is a simple, low carb queso-style dip you can make in minutes. It’s thick enough for sturdy chips, cheese crisps, and pork rinds — and it doesn’t turn watery the moment it hits the table.
Ingredients
- 1 tbsp butter
- 1/2 cup heavy cream (or full-fat milk if you tolerate it)
- 1 cup shredded cheddar (or a cheddar-parmesan mix)
- 1/2 tsp garlic powder
- 1/2 tsp smoked paprika
- Salt to taste
- Optional: chopped jalapeños, green chilies, or a spoon of pepper sauce

Method
- Melt butter on low heat.
- Add cream and warm gently (don’t boil).
- Reduce heat and add cheese in handfuls, stirring until smooth.
- Season, then taste and adjust.
Keep it thick: low heat and patience. High heat makes cheese seize, and overheated dips often separate.
If you prefer cold dips, a mayo base works beautifully too — especially when you want a quick spicy dip without cooking.
2) Salsa that’s thick enough for dipping (not watery)
Watery salsa is the fastest way to ruin keto chips. The fix is simple: remove excess moisture so salsa stays scoopable.

Quick scoopable salsa method
- Chop tomatoes and salt them lightly.
- Let them sit 10 minutes.
- Drain off the excess liquid.
- Add onion, cilantro, chili, lime, and salt to taste.
That draining step changes everything. Your chips stay crisp longer, and your salsa feels like a dip instead of a soup.

Bonus: quick guac-style dip that plays well with chips
If you want a creamy dip that makes tortilla-style keto chips feel more like the real experience, avocado is the shortcut. Mash avocado with salt and lime, add a little onion, then finish with chili or pepper sauce for heat. It takes two minutes and makes chips feel like an actual snack.

Also Read: Manhattan Cocktail Recipe (Classic + 6 Variations)
Keto snack box and low carb snack box ideas that keep chips from taking over
Chips are easy to overeat because they don’t feel like a meal. A keto snack box fixes that by turning snacking into a small plate with structure. Instead of eating keto chips until you’ve accidentally eaten your carb budget, you pair crunch with protein and something fresh or tangy.

This also helps if you need shelf stable keto snacks, or if you’re building a simple approach for work, travel, or busy days.
1) Savory keto snack box (chips + dip + something bright)
- cheese crisps or seed crackers
- a dip: Greek Tzatziki Sauce
- olives or pickles
- a few nuts
It feels complete, and the freshness keeps you from wanting endless handfuls of chips.
2) “Game day” keto chip snacks box
- chicken skin chips or pork rinds
- a thick dip: Buffalo Chicken Dip
- optional cool dip: Blue Cheese Dip
- raw veggies (even cucumber slices help)
The contrast between spicy and cool makes it more satisfying than chips alone.
3) Keto hiking food and road-trip crunch (less messy, more stable)
For travel, you want snacks that don’t crumble into dust instantly and don’t melt.
- seed crackers or sturdy low carb tortilla chips
- nuts
- jerky (watch sweet marinades)
- a small jar of mayo-based dip if you can keep it cold, or a dry seasoning blend if you can’t
If you’re choosing snacks for blood sugar steadiness rather than strict keto, having a reference list can help you build better snack patterns. This internal resource is useful as a broad companion: Low Glycemic Index foods list PDF.
Also Read: Baked Ziti Recipe Collection: 15 Easy Variations
Drinks that pair well with keto chips (and don’t make snack time feel like a compromise)
A snack moment feels more complete when there’s a drink alongside it. That doesn’t have to mean something sugary. Even coffee can be a satisfying pairing, especially with salty snacks.
A few internal pairings that work across moods:
- For a cold, refreshing pairing: Iced coffee recipes
- For a warm café-style moment: Cappuccino recipe
- For a savory, spicy party drink (including non-alcoholic variations): Bloody Mary recipes
- For cocktail night: Cold brew espresso martini
The point isn’t to turn chips into a production. It’s to make the snack feel finished so you don’t keep circling back to the bowl.
Also Read: Keto Flour: Guide to Low-Carb Flours That Bakes Like the Real Thing
How to build a snack board that works for keto and non-keto guests
If you’re hosting, you don’t want a separate “diet plate.” You want one table that works for everyone. This is where chip alternatives shine, because nobody complains about cheese crisps, dips, and snack boards.
A simple approach is to use a structure like the one described in the 3-3-3-3 charcuterie board rule, then swap the starch section into “a few crunchy options,” including at least one low carb chip option.
For the dips, keep it simple and crowd-pleasing:
- buffalo chicken dip for hot, creamy, scoopable
- Greek tzatziki for fresh, cool, bright
- a quick spicy mayo using homemade mayo plus pepper sauce
Then set out two or three “chip” options:
- cheese crisps
- tortilla-style low carb chips
- pork rinds or seed crackers
People will build their own bites. Meanwhile, you get the crunch you want without needing a separate plan.
Also Read: Keto pancakes that actually taste like pancakes
Why your keto chips aren’t crunchy (and how to fix it without overthinking)
Crunch problems are usually one of three things: moisture, thickness, or cooling.

Moisture problems
Veggie chips and tortilla-style chips often soften because they’re holding water. Slice thinner, salt and pat dry, bake longer, and cool properly. If you stack chips while they’re still warm, steam gets trapped, and crispness disappears.
Thickness problems
Thin chips snap and feel “real,” yet they often fail in thick dips. Thick chips scoop better, but can feel dense. Choose based on the moment: salsa wants thin, queso wants thick.
Cooling problems
Cheese crisps need to cool to become crisp. If they feel bendy out of the oven, that’s normal. Let them rest, and the texture changes dramatically.
Also Read: Macaroni & Cheese Recipe: Creamy Stovetop, Baked & Southern
Low carb nachos that don’t turn soggy (layering that works)
Nachos fail for one boring reason: moisture. Once you accept that, it becomes easy to build keto nachos that stay crisp long enough to enjoy the tray.
The rule is simple: cheese first, wet toppings last — often on the side.

How to build them
- Start with your base (tortilla-style low carb chips, cheese crisps, or pork rinds).
- Add shredded cheese first so it melts into a “seal.”
- Add cooked toppings next (meat, mushrooms, peppers).
- Bake until melted.
- Add wet toppings at the end (salsa, sour cream, guac) or serve them on the side for dipping.
If you want a party-ready topping that works as both dip and nacho layer, buffalo chicken dip is perfect. For a tangy companion dip that makes spicy nachos feel complete, blue cheese dip belongs on the side.
This is also the easiest way to make keto taco chips feel right: keep wet elements off the chips until the last second, then build bite-by-bite.
How to pick store-bought keto chips without relying on hype
If you buy low carb chips, you’ll notice something quickly: two bags can look similar, yet one stays crisp in salsa while the other collapses. One tastes clean and savory, another tastes oddly sweet. So instead of trusting marketing language, choose based on use—and read the label like you’re comparing tools, not snacks.

For salsa: choose chips that are “dry + rigid,” not bendy
Salsa is the toughest test because it’s watery and acidic. For salsa nights, you want chips that feel dry, stiff, and snappy straight from the bag. If a chip bends before it snaps, it will soften fast once it hits salsa. Likewise, thin chips can be great—but only when they’re truly dry. If your goal is keto chips and salsa that feels satisfying, rigidity matters more than thickness.
Quick check: break one chip. You want a clean snap, not a bend.
For sensitive stomachs: watch fiber stacking and portion size
Many low carb tortilla chips and high-fiber “keto chips” get their numbers by leaning hard on added fibers. That can be totally fine—until you eat a big portion and suddenly your stomach feels like it’s negotiating terms. When that happens, it’s not a discipline issue; it’s simply how heavy fiber loads can feel for some people.
So, start small. In addition, avoid stacking fiber-heavy chips with other fiber-heavy snacks in the same sitting if you already know you’re sensitive. If you want chips to be a repeatable habit, comfort matters as much as macros.
Simple strategy: treat the first serving like a “test portion,” then decide if it works for you.
Avoid the “sweet chip” problem (yes, it happens)
Some store-bought keto friendly chips taste faintly sweet—even if they’re labeled as savory. That usually comes from certain sweeteners or flavor systems meant to balance bitterness. If that sweet note bugs you, don’t assume you “don’t like keto chips.” Instead, shift toward options that taste naturally savory: cheese crisps, seed crackers, or chips that rely on spices rather than sweetness to create flavor.
Meanwhile, if you’re chasing a nacho-style vibe, you can also fix a bland or slightly sweet chip by adding your own seasoning dust and a little acidity (like lime). That moves the flavor back into the “salty, dusty, snacky” zone.
Quick fix: warm chips briefly, then toss with a dry seasoning blend so it sticks better and tastes bolder.
One more thing that makes the whole “low carb chips” routine easier: keep a dip base ready
If you want keto chips to feel effortless, the real trick is having a dip base that’s always in the fridge. When dips are ready, you snack once and feel done; when dips aren’t ready, you keep hunting.
Three easy “always works” bases:
- Homemade Mayonnaise as a creamy canvas
- Eggless Mayo for egg-free convenience
- Greek Tzatziki for a fresh, cooling option
Then, whenever you want to upgrade the flavor fast, Pepper Sauce gives you multiple directions—bright, smoky, herb-forward—without needing a long ingredient list.
Also Read: Peanut Butter Bars: A No-Bake Treat That’s Impossible to Resist
A quick health note that keeps this honest
A lot of keto snacks lean high in saturated fat and sodium. That doesn’t mean you can’t enjoy them; it simply means variety helps. If you want a balanced, evidence-based view of potential pros and cons, Harvard’s overview is a useful reference: Harvard Nutrition Source on the ketogenic diet and Harvard Health on whether to try keto.
Rotating your chip styles—cheese one day, seed crackers another, tortilla chips for salsa nights, veggie chips for lighter crunch—keeps the routine enjoyable and easier to stick to.
Make-ahead rhythm: a simple rotation that keeps cravings calm
Most people don’t drift off low carb because they can’t cook. They drift because snack cravings hit when nothing is ready. A small rotation fixes that without turning your week into a project.

A practical rotation looks like this:
- One sturdy option for thick dips: cheese crisps or cheese crackers
- One salsa-friendly option: tortilla-style low carb chips baked extra crisp
- One everyday option: seed crackers for quick snack plates
Then keep one dip base in the fridge — either tzatziki for fresh and cooling, or a mayo base you can change instantly with pepper sauce.
That’s the difference between constantly battling cravings and simply handling them. You’re not trying to remove cravings. You’re meeting them with something that works.
Also Read: Classic Rum Punch + 9 Recipes (Pitcher & Party-Friendly)
A calmer way to think about keto chips
At the end of the day, the easiest way to stay consistent isn’t finding one perfect keto chips brand or one magical “zero carb” option. It’s building a small rotation that matches real cravings—salsa nights, thick dips, nachos, and quick snack plates—so you always have a crunch option that actually works.
- For maximum crunch and minimal carbs: cheese crisps, chicken skin chips, pork rinds
- For salsa and nachos: low carb tortilla chips
- For steady everyday snacking: seed crackers and keto crackers
- For variety: keto kale chips and other veggie chips
Then, instead of relying on willpower, rely on structure: a bowl portion instead of a bag, a dip that makes it feel satisfying, and a snack box approach when you need something grab-and-go.
Also Read: 19 Essential Kitchen Tools That Make Cooking Easier
Keto Chips FAQ
1) What chips can I eat on keto?
You can eat chips on keto if the portion fits your daily carb target. In practice, that usually means choosing chips that are naturally low in carbs (like cheese crisps and pork rinds) or making low carb tortilla chips from wraps that are designed to be lower in net carbs. Either way, the simplest test is this: pick the crunch you want, then portion it so the numbers still work for your day.
2) Are chips allowed on keto or do they ruin ketosis?
Chips don’t “ruin keto” by default—overdoing carbs does. So, if you keep your serving controlled and choose keto friendly chips that stay within your carb budget, chips can fit. That said, mindless bag-snacking is where people get tripped up, because chips are easy to overeat even when the label looks friendly.
3) What are the best keto chips for salsa?
For salsa, tortilla-style keto chips usually feel the most “normal.” However, salsa is tough on weak chips because the moisture softens them fast. Therefore, you’ll get better results with chips that are extra dry and rigid—either baked low carb tortilla chips cooled on a rack, or seed crackers that hold their structure longer than thin chips.
4) What are the best keto chips for dipping in thick dips?
If the dip is thick—think queso-style dips, buffalo dips, or creamy ranch-style dips—sturdier options win. For example, cheese crisps and parmesan chips are naturally strong, pork rinds scoop surprisingly well, and seed crackers behave like reliable chip replacements. Meanwhile, thin tortilla chips often snap before you even get a proper scoop.
5) What’s the best low carb substitute for tortilla chips?
If you mainly want a scoopable crunch, seed crackers are one of the most reliable tortilla chip alternatives. On the other hand, if you want that salty “snack chip” hit with minimal carbs, cheese crisps and pork rinds are strong stand-ins. In contrast, veggie chips can work, yet they’re usually better as their own snack rather than a direct tortilla-chip replacement.
6) Do keto tortilla chips actually exist?
Yes—keto tortilla chips exist in two common forms: store-bought low carb chips, and homemade chips made from low carb tortillas or wraps. Even so, the experience varies a lot. Some tortilla-style chips are snappy and great for salsa, whereas others are more cracker-like and better for thicker dips. That’s why choosing by “dip-ability” is more useful than chasing a single perfect chip.
7) How do you make homemade keto tortilla chips crispy?
To get crispy homemade keto tortilla chips, treat it like a drying job, not just browning. First, cut evenly. Next, keep a single layer with no overlap. Then bake long enough to remove moisture, flip midway, and cool on a rack so steam doesn’t soften the underside. Finally, store only after fully cooled—warm chips sealed in a container turn soft fast.
8) Why are my low carb tortilla chips not crisp?
Usually it’s one of three things: moisture, thickness, or cooling. If chips brown but stay bendy, they need more drying time at a slightly lower heat. If they crisp and then soften later, they likely cooled on a plate instead of a rack, or they were stored before fully cooled. And if the edges crisp but the centers stay chewy, the triangles are too large or the wrap is too thick—cut smaller and bake longer.
9) How do I keep keto chips crispy after baking?
Let chips cool completely, then store them airtight. Still, humidity can soften them over time. In that case, re-crisp them in the oven for a few minutes, then cool again. Also, avoid stacking warm chips, because trapped steam is basically a crispness killer.
10) Are cheese chips low carb and keto-friendly?
Yes—cheese chips are one of the classic low carb keto chips because cheese has very few carbs. Plus, they’re naturally salty, crunchy, and satisfying. Even so, they’re calorie-dense, so portioning matters. Additionally, if you need extra scoop strength, make them slightly thicker or blend parmesan with cheddar for more body.
11) What are “keto cottage cheese chips,” and are they worth it?
Cottage cheese chips are a baked crisp made by drying small portions of cottage cheese until they turn crunchy. They can be a solid option when you want a lighter, tangier crunch than cheddar crisps. However, results depend on how wet the cottage cheese is, so drying time and spacing matter a lot. If your batch turns chewy, it usually needs more time to fully dehydrate. Results vary a lot by brand and moisture level, so they’re more finicky than cheese crisps or seed crackers. If you want a dependable crunch, start with cheese crisps or seed crackers first.
12) What are keto chicken skin chips and keto meat chips?
Keto chicken skin chips are crispy baked or air-fried chicken skins that turn into a hard, snackable crunch. Keto meat chips are similar in spirit—thin, dried, and crisped strips of meat that land in “chip-adjacent” territory. They tend to be very low carb, though they can be high in sodium and easy to overeat because the crunch is intense.
13) Are pork rinds keto, and do they work like chips?
Pork rinds are typically keto-friendly and often used as a no carb chip substitute. They work best with thick dips because they scoop well. Still, they’re not always ideal with watery salsa, since salsa can make them soften quickly. For that reason, they shine more in queso, creamy dips, and layered snack plates.
14) Are there any truly “0 carb chips”?
Sometimes “0 carb” is real in practice, but often it’s a label outcome tied to serving size and rounding. In other words, the carbs may be low enough per serving to show as zero, yet a larger portion could add up. So instead of chasing the label, focus on what you’ll actually eat and whether it still fits your carb target.
15) What are the best low carb chips for nachos?
For nachos, you need a base that stays crisp long enough to finish the tray. Tortilla-style low carb chips work when they’re baked extra dry, while cheese crisps are naturally sturdy if you keep wet toppings under control. Likewise, pork rinds can work if you assemble bite-by-bite or keep sauces on the side, because moisture is what makes nachos collapse.
16) How do I stop keto nachos from turning soggy?
Use a simple layering rule: cheese first, wet toppings last. Start with the chips, add shredded cheese to create a “seal,” then add cooked toppings. After baking, add salsa, sour cream, and guac at the end—or serve them on the side. That way, you keep the crunch instead of turning everything into a soft pile.
17) What’s a good low carb hot chips alternative?
If you’re craving “hot chips,” focus on the flavor dust rather than chasing an identical chip. Cheese crisps, tortilla-style keto chips, and pork rinds all work when tossed warm with a chili-forward seasoning and finished with a little acidity. As a result, you get that spicy, salty, dusted feel that scratches the craving without gimmicks.
18) Are veggie chips keto?
Some veggie chips can fit keto, yet they’re the easiest to misunderstand. Many store-bought veggie chips can still be starchy, while homemade versions are often more about “light crunch” than “chip replacement.” If you want the best experience, treat veggie chips as their own category and pair them with a creamy dip so they feel satisfying rather than flimsy.
19) What should I look for when buying store-bought keto chips?
Start with the serving size, then check total carbs, fiber, and any sugar alcohols. After that, think about how you’ll use them: thin, dry chips for salsa; thicker, sturdier options for dips; and chips that don’t crumble for nachos. Finally, buy the portion size that matches your habits—because even the best keto chips won’t help if the bag disappears in one sitting.
20) What are easy keto snack box ideas using chips?
A simple keto snack box works best when crunch is paired with protein and something bright. For instance, use seed crackers or cheese crisps as the base, add a thick dip, include olives or pickles for tang, and finish with a small portion of nuts or a protein bite. That structure makes snacking feel complete, so you’re less likely to keep grazing.






















