When it comes to diet and nutrition, fat is often at the center of controversy. For decades, fat was demonized, leading to the rise of low-fat products that flooded grocery store shelves. More recently, the pendulum has swung the other way, with high-fat diets like keto becoming mainstream. But what does science actually say about high-fat and low-fat diets? And how do we strike the right balance for long-term health?
In this post, we’ll explore the science-backed benefits and risks of both high-fat and low-fat diets and help you understand how to make fat work for your body—not against it.
🧠 What Is Fat and Why Does It Matter?
Fat is one of the three macronutrients essential to life, alongside carbohydrates and proteins. It provides energy, supports cell growth, protects organs, helps absorb nutrients (like vitamins A, D, E, and K), and produces important hormones.
But not all fats are created equal:
- Healthy fats: Unsaturated fats (monounsaturated and polyunsaturated) found in avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, and fish.
- Unhealthy fats: Saturated fats (in red meat, butter, cheese) and trans fats (in processed snacks and fried foods).
Understanding the type of fat you consume is more important than the amount.
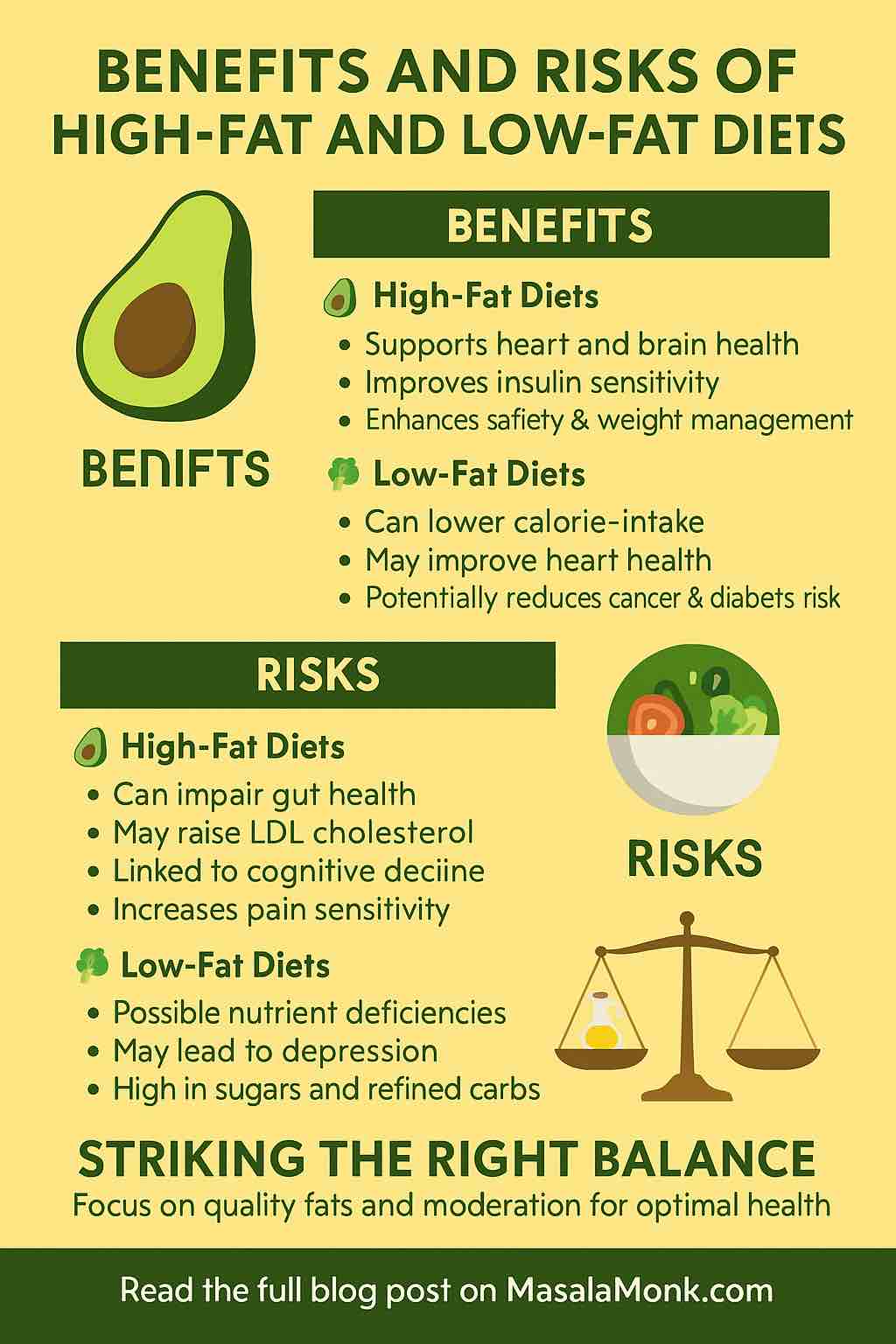
🥓 High-Fat Diets: Benefits & Risks
✅ Benefits of High-Fat Diets
- Supports Brain & Hormonal Health
- The brain is composed of nearly 60% fat.
- Diets rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids help improve cognition, mood, and memory.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity
- Studies from Harvard and Vanderbilt found that low-carb, high-fat diets improve insulin response and reduce visceral fat, especially in older adults.
- This can reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
- Enhanced Satiety & Weight Management
- Fats slow digestion, keeping you fuller for longer.
- This can help reduce overall calorie intake and make dieting more sustainable.
- Better Lipid Profiles (with the right fats)
- Replacing carbs with healthy fats can increase HDL (“good” cholesterol) and reduce triglycerides.
⚠️ Risks of High-Fat Diets
- Gut Health Disruption
- A 2025 study revealed that high saturated fat intake can impair gut immunity and increase inflammation within 48 hours.
- Increased LDL Cholesterol
- Diets high in saturated fats can raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, elevating cardiovascular risk.
- Cognitive & Physical Decline
- Research from Cambridge University noted that a high-fat diet may impair memory and physical endurance—even after just a few days.
- Pain Sensitivity & Poor Recovery
- Emerging studies indicate a link between high-fat intake and heightened pain perception or slower healing—even in the absence of weight gain.
🥗 Low-Fat Diets: Benefits & Risks
✅ Benefits of Low-Fat Diets
- Lower Caloric Intake
- Fat contains 9 calories per gram, compared to 4 calories per gram for carbs or protein.
- Reducing fat can help with weight loss through overall calorie control.
- Improved Heart Health (in some cases)
- Lower fat intake—especially reduced saturated fat—can decrease LDL cholesterol and blood pressure.
- Potential Cancer & Diabetes Risk Reduction
- Some studies have associated low-fat diets with lower risk of breast cancer, gallbladder disease, and type 2 diabetes.
⚠️ Risks of Low-Fat Diets
- Essential Nutrient Deficiencies
- Low-fat diets may deprive you of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) and essential fatty acids.
- Mental Health Effects
- New research links overly restrictive low-fat diets to increased risk of depression, particularly in men and those with higher BMI.
- Increased Sugar & Refined Carbohydrate Intake
- Many low-fat products compensate with added sugars or refined carbs—leading to blood sugar spikes and potential weight gain.
- Disrupted Hormone Production
- Fats are essential for hormone synthesis. Long-term fat deficiency can impair fertility, libido, and menstrual health.
🥦 Striking the Right Balance: Practical Tips for Optimal Fat Intake
Rather than labeling fat as “good” or “bad,” a more nuanced approach focuses on moderation and quality:
✔️ Tips for a Balanced Fat Strategy:
- Incorporate healthy fats daily: Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fatty fish.
- Limit saturated fats: Choose lean meats, avoid heavy cream and butter in excess.
- Eliminate trans fats: Check food labels for “partially hydrogenated oils.”
- Don’t fear full-fat dairy (in moderation): It may offer more satiety and metabolic benefits compared to low-fat versions.
- Mind your portions: Even healthy fats are calorie-dense.
- Combine with whole foods: Balance your fat intake with fiber-rich vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
🧬 The Best of Both Worlds: Diets That Blend Fat Intelligently
Several dietary patterns offer a healthy balance of fat intake without extremes:
🥙 Mediterranean Diet
- High in monounsaturated fats (olive oil, nuts)
- Emphasizes fish, whole grains, vegetables, and legumes
- Linked with reduced risk of heart disease, cognitive decline, and cancer
🧠 MIND Diet
- A hybrid of Mediterranean and DASH diets
- Focuses on brain-protective foods: leafy greens, berries, nuts, and healthy fats
🧾 Final Thoughts
The debate isn’t really about high-fat vs. low-fat—it’s about smart fat choices and personalized nutrition. Whether you lean toward a high-fat keto style or a low-fat plant-based diet, the quality of fat, your individual health status, and your sustainability of the diet matter more than labels.
Ultimately, the healthiest diet is the one you can enjoy, stick to, and that keeps your body thriving—not just surviving.
🙋♂️ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is fat bad for you?
No, fat is not inherently bad. Your body needs healthy fats to absorb vitamins, support brain function, and produce hormones. The key is to focus on unsaturated fats (like those in olive oil, avocados, and nuts) while limiting saturated fats and avoiding trans fats.
2. What are the best sources of healthy fats?
Top sources include:
- Monounsaturated fats: Olive oil, avocados, almonds
- Polyunsaturated fats: Walnuts, flaxseeds, fatty fish (like salmon)
These fats help reduce inflammation and improve heart and brain health.
3. Can a high-fat diet help with weight loss?
Yes, high-fat diets like keto or low-carb/high-fat (LCHF) have been shown to promote fat loss, reduce hunger, and improve metabolic markers. However, long-term success depends on the quality of fats and overall calorie balance.
4. Are low-fat diets still recommended?
Low-fat diets can be effective for weight loss and cardiovascular health—especially when they focus on whole foods and reduce processed sugars. But extremely low-fat diets may lead to nutrient deficiencies and reduced satiety.
5. What’s the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
- Saturated fats (found in red meat, butter, and cheese) can raise LDL cholesterol if consumed in excess.
- Unsaturated fats (found in plant-based oils, nuts, and fish) support heart health and reduce inflammation.
6. How much fat should I eat daily?
According to dietary guidelines:
- Fat should make up 20–35% of your total calories.
- Focus on keeping saturated fat below 10% of your daily intake.
- Avoid trans fats completely.
7. Can eating fat make me fat?
Not directly. Weight gain happens when you consume more calories than you burn, regardless of whether they come from fat, carbs, or protein. In fact, healthy fats can support weight management by making you feel full and reducing cravings.
8. Are all low-fat foods healthy?
No. Many low-fat packaged foods compensate by adding sugar, salt, or refined carbs, which can lead to blood sugar spikes, weight gain, and other health issues. Always check labels and prioritize whole, unprocessed foods.
9. Is it safe to follow a high-fat diet long-term?
Yes—if it’s balanced and based on healthy fat sources. Long-term high-fat diets like the Mediterranean or MIND diet have been linked to better heart and brain health. However, high saturated fat and animal fat intake may pose risks if not moderated.
10. How do I transition to a balanced fat intake?
Start by:
- Swapping butter for olive oil
- Snacking on nuts instead of chips
- Choosing fatty fish twice a week
- Reading labels to avoid trans fats
- Limiting deep-fried or heavily processed foods
Balance is key—incorporate fats wisely, not fearfully.