Diverticulitis—an increasingly common digestive condition characterized by inflammation or infection of the small pouches (diverticula) that can form in your digestive tract—has a significant relationship with the food we consume. As such, understanding how your diet influences this condition is vital in managing it effectively and maintaining overall digestive health. This comprehensive article delves into the top ten foods you should consider avoiding when dealing with diverticulitis. It not only provides valuable insights into why these foods can potentially trigger diverticulitis symptoms but also suggests alternatives to help you achieve a balanced and gut-friendly diet.
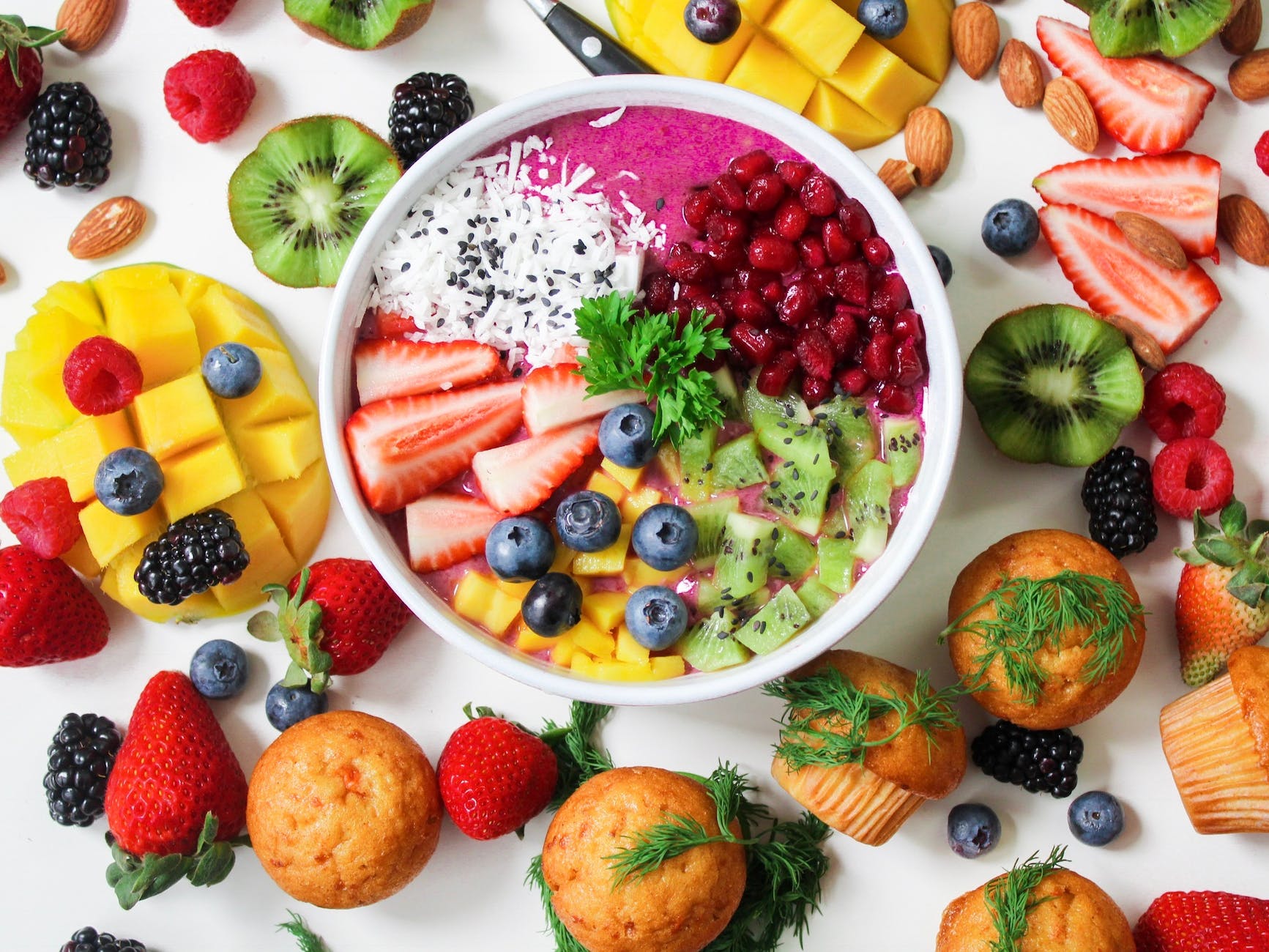
Fruits and Vegetables: The Hidden Perils Within🍅🥒
Fruits and vegetables, typically the cornerstones of a balanced and healthy diet, can be a bit more complicated when it comes to diverticulitis. While their nutrient-rich profiles are generally beneficial, certain types contain small, hard particles like seeds, skins, and hulls, which can irritate the diverticula, potentially causing a flare-up. Here are some examples:
- Tomatoes: While rich in vitamins and antioxidants, tomatoes contain small seeds that can irritate a diverticulitis-prone digestive tract.
- Cucumbers: As refreshing as they are, cucumbers can be problematic due to their seeds. Opting for seedless variants, or removing the seeds before consumption, could be a good workaround.
- Zucchini: This versatile vegetable also houses seeds that could potentially lead to diverticulitis discomfort.
- Strawberries: Delicious and antioxidant-rich, strawberries, unfortunately, contain numerous tiny seeds, which might not be friendly to your gut if you’re living with diverticulitis.
- Raspberries: Like strawberries, raspberries have numerous small seeds that can be challenging for diverticulitis sufferers.
Popcorn: A Snack That May Not Pop Well With Your Gut🍿
As innocuous and fun as popcorn may seem, it can be a disguised foe for those with diverticulitis. The popcorn hulls, the hard, shell-like remnants often left behind after the popcorn has been eaten, could potentially get trapped in the diverticula, leading to irritation and potentially a flare-up.
Nuts and Seeds: Size Doesn’t Reflect Impact🥜
Despite their nutritious profile, nuts and seeds—such as sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, and all types of nuts—can be tricky for individuals with diverticulitis. Their small size and hard texture may lead to them lodging within the diverticula, causing inflammation and discomfort.
Whole Grains: The Delicate Balancing Act🌾
Whole grains are typically celebrated for their high fiber content, essential for gut health. However, for those with diverticulitis, whole grains can sometimes contribute to symptoms during a flare-up. Here’s a breakdown of a few common whole-grain foods:
- Whole grain bread: While whole grain bread provides an excellent source of fiber, it can be tough on a sensitive gut during a diverticulitis episode due to the small grain pieces.
- Brown rice: As a complex carbohydrate, brown rice can support long-lasting energy, but its high fiber content can exacerbate symptoms during a flare-up.
- Oatmeal: Oatmeal, despite being a fantastic breakfast choice, can sometimes aggravate symptoms during a diverticulitis episode due to its fiber content.
- Whole grain pasta: Much like its bread and rice counterparts, the fiber content in whole grain pasta can pose problems during a flare-up.
The Red Meat Reduction: Embracing Leaner Proteins🍗
A diet high in red meat can lead to constipation, a condition that can exacerbate the discomfort of diverticulitis. By reducing your intake of red meat and leaning towards proteins such as poultry, fish, or plant-based options like lentils and tofu, you can help manage your symptoms more effectively.
Processed Foods: Navigating the Landmine of Low Fiber and High Fat Content🥓
Processed foods, often loaded with unhealthy fats and minimal dietary fiber, can be detrimental to those with diverticulitis. Foods like bacon, sausages, ham, and ready-made frozen meals may lack the fiber necessary to support a healthy gut, thereby potentially increasing the risk of a diverticulitis flare-up.
Fried Foods: Trading Unhealthy Fats for Healthier Cooking Methods🍟
Fried foods, laden with unhealthy fats and sparse in fiber, can contribute to diverticulitis discomfort. The high fat content in these foods can lead to constipation, a condition that can exacerbate the symptoms of diverticulitis. Instead, it would be beneficial to embrace cooking methods like grilling, baking, or steaming.
Dairy and Diverticulitis: The High-Fat Conundrum🧀
Not all dairy products are problematic for diverticulitis, but those high in fat might not be the most beneficial. High-fat cheese and full-fat milk could potentially trigger symptoms. Consider opting for low-fat or non-fat alternatives, which can be gentler on your gut.
Alcohol: The Dehydration Link and Diverticulitis🍷
Alcohol, especially in large amounts, can lead to dehydration, a condition that can cause constipation and subsequently exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms. Reducing your intake of alcohol, or avoiding it altogether, can be helpful in managing this condition.
Refined Carbohydrates: The Low-Fiber Culprit🍞
Refined carbohydrates, including white bread, pastries, and sugary drinks, often lack the dietary fiber necessary for a healthy gut. This lack of fiber can potentially increase your risk of a diverticulitis flare-up.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that everyone’s experience with diverticulitis is unique—what triggers a flare-up in one person might not in another. Therefore, maintaining a food diary to track your diet and its correlation with your symptoms can be a valuable tool in identifying your personal triggers. Furthermore, consulting with a healthcare professional or a dietitian can help create a customized dietary plan that considers your preferences, tolerances, and nutritional needs.
Top 10 Foods You Should Avoid If You Suffer From Diverticulitis
Here are the top ten foods you should avoid if you suffer from diverticulitis.
- Certain Fruits and Vegetables: If you have diverticulitis, it’s important to be cautious about your intake of certain types of fruits and vegetables. Foods with small, hard particles such as seeds, skins, and hulls can aggravate diverticulitis. Examples include tomatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, strawberries, and raspberries.
- Popcorn: The small, hard, and often sharp hulls of popcorn can potentially irritate diverticula and lead to a flare-up.
- Nuts and Seeds: Foods like sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, and all types of nuts are generally discouraged. These small, hard foods can lodge within the diverticula, causing irritation and inflammation.
- Whole Grains: While whole grains are typically beneficial for their high fiber content, during a diverticulitis flare-up, they can worsen symptoms. Foods like whole-grain bread, brown rice, oatmeal, and whole-grain pasta should be avoided.
- Red Meat: High intake of red meat can contribute to constipation, thereby aggravating diverticulitis. Opt for lean proteins such as poultry, fish, or plant-based proteins instead.
- Processed Foods: Processed foods are often high in unhealthy fats and lack dietary fiber, which is crucial for maintaining digestive health. Foods such as bacon, sausages, ham, and frozen meals can increase the risk of a diverticulitis flare-up.
- Fried Foods: Fried foods are high in unhealthy fats and low in fiber. The fat content in these foods can lead to constipation, which may worsen the symptoms of diverticulitis.
- Certain Dairy Products: While not all dairy products are off the table, those high in fat can increase the risk of a flare-up. This includes high-fat cheese and full-fat milk.
- Alcohol: Alcohol can cause dehydration, which may lead to constipation and exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms. It’s best to limit your intake of alcohol if you have diverticulitis.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Foods such as white bread, pastries, and sugary drinks lack the necessary fiber content for a healthy digestive system and may increase your risk of a diverticulitis flare-up.
When it comes to diverticulitis, everyone is different, and what triggers a flare-up in one person might not do the same in another. This is why it’s important to keep a food diary and track your symptoms to identify potential triggers. You should also work closely with your healthcare provider or a dietitian to develop a diet plan that works for you.
Ultimately, maintaining a healthy, balanced diet that’s high in fiber from a variety of sources, combined with regular physical activity, can go a long way in managing diverticulitis and promoting overall digestive health.
Frequently Asked Questions about Diverticulitis and Diet
1. Can I eat strawberries if I have diverticulitis? While strawberries are rich in antioxidants, their tiny seeds can potentially irritate the diverticula in your digestive tract. Monitor your symptoms when consuming strawberries. If you find they don’t aggravate your condition, you can enjoy them in moderation, possibly in smoothies where the seeds are well-blended.
2. Are tomatoes safe to eat with diverticulitis? Tomatoes are packed with vitamins, but their small seeds can potentially irritate a diverticulitis-prone digestive tract. Consider consuming seedless varieties or removing the seeds before eating. You could also try tomato-based sauces where the seeds have been strained out.
3. How does red meat affect diverticulitis? A diet high in red meat can lead to constipation, which can exacerbate the discomfort of diverticulitis. Balance your intake of red meat with other protein sources such as poultry, fish, or plant-based options like lentils and tofu. Also, ensure you’re drinking plenty of water and consuming enough fiber from other sources to promote regular bowel movements.
4. Can I eat oatmeal if I have diverticulitis? Oatmeal is a fantastic breakfast choice, but its fiber content can sometimes aggravate symptoms during a diverticulitis episode. Consume oatmeal in moderation and monitor your symptoms. You could also try eating oatmeal with a good amount of liquid, like milk or water, to help soften the fiber.
5. What vitamins should I avoid with diverticulitis? While vitamins are essential for overall health, some may not be suitable for those with diverticulitis. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new vitamin regimen. They can provide guidance on which vitamins to avoid and which ones may help support your digestive health.
6. How does dairy affect diverticulitis? Not all dairy products are problematic for diverticulitis, but those high in fat might not be the most beneficial. High-fat cheese and full-fat milk could potentially trigger symptoms. Consider opting for low-fat or non-fat alternatives, which can be gentler on your gut.
7. Can I eat pickles if I have diverticulitis? Pickles, due to their high sodium content, can potentially exacerbate symptoms of diverticulitis. Consume them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. If you enjoy the tangy taste of pickles, consider trying other fermented foods like sauerkraut or kimchi, which can be beneficial for gut health.
8. Is watermelon safe to eat with diverticulitis? Watermelon is a hydrating and nutritious fruit, but its seeds can potentially irritate the diverticula. Consider consuming seedless varieties or removing the seeds before eating. Watermelon can be a great addition to a diverticulitis-friendly diet when consumed properly due to its high water content.
9. What foods should I avoid if I have diverticulitis? Foods that can potentially irritate the diverticula and trigger diverticulitis symptoms include those with small, hard particles like seeds, skins, and hulls, as well as high-fat, low-fiber foods. These can include certain fruits and vegetables, popcorn, nuts and seeds, whole grains, red meat, processed foods, fried foods, high-fat dairy products, alcohol, and refined carbohydrates. Always listen to your body and monitor your symptoms after eating these foods.
10. Can I eat cucumbers with diverticulitis? Cucumbers can be problematic due to their seeds. Opting for seedless variants or removing the seeds before consumption could be a good workaround. Cucumbers are hydrating and can be a great addition to salads or as a crunchy snack with hummus.
11. Are zucchinis safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Zucchinis house seeds that could potentially lead to diverticulitis discomfort. Consider consuming them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. You could also try cooking zucchini thoroughly to soften the seeds or scoop them out before cooking.
12. How does popcorn affect diverticulitis? The popcorn hulls could potentially get trapped in the diverticula, leading to irritation and potentially a flare-up. If you miss the crunch of popcorn, consider trying other crunchy snacks like carrot sticks or bell pepper slices that are less likely to irritate your diverticula.
13. Can I consume nuts and seeds if I have diverticulitis? Nuts and seeds can lodge within the diverticula, causing inflammation and discomfort. Consume them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. If you find they don’t aggravate your condition, you can enjoy them as a healthy source of fats and proteins. Alternatively, try nut butters, which offer the same nutritional benefits without the hard, potentially irritating pieces.
14. How do whole grains affect diverticulitis? Whole grains can sometimes contribute to symptoms during a diverticulitis flare-up due to their high fiber content. If you find whole grains problematic, consider consuming them in moderation and balance your diet with other sources of fiber that are gentler on your gut.
15. Can I eat brown rice with diverticulitis? Brown rice’s high fiber content can exacerbate symptoms during a flare-up. Consume it in moderation and monitor your symptoms. You could also try pairing brown rice with plenty of liquids and softer foods to help ease digestion.
16. Is whole grain pasta safe for diverticulitis sufferers? The fiber content in whole grain pasta can pose problems during a flare-up. Consume it in moderation and monitor your symptoms. Consider pairing whole grain pasta with a smooth, seedless sauce to make it easier on your digestive tract.
17. How does processed food affect diverticulitis? Processed foods may lack the fiber necessary to support a healthy gut, thereby potentially increasing the risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. Try to limit your intake of processed foods and opt for fresh, whole foods whenever possible.
18. Can I eat bacon if I have diverticulitis? Bacon, being a processed food, may lack the fiber necessary to support a healthy gut, thereby potentially increasing the risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. If you enjoy the flavor of bacon, consider using it sparingly as a flavoring agent rather than a main component of your meals.
19. Are sausages safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Sausages, being processed foods, may lack the fiber necessary to support a healthy gut, thereby potentially increasing the risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. Consider choosing leaner meats or plant-based protein sources for your meals.
20. How does fried food affect diverticulitis? Fried foods, laden with unhealthy fats and sparse in fiber, can contribute to diverticulitis discomfort. Instead of frying, try healthier cooking methods like grilling, baking, or steaming.
21. Can I drink alcohol if I have diverticulitis? Alcohol, especially in large amounts, can lead to dehydration, a condition that can cause constipation and subsequently exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms. Consider limiting your alcohol intake and always drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
22. How do refined carbohydrates affect diverticulitis? Refined carbohydrates often lack the dietary fiber necessary for a healthy gut. This lack of fiber can potentially increase your risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. Try to choose whole grain options when possible, and balance your intake of refined carbohydrates with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
23. Can I eat white bread if I have diverticulitis? White bread, a refined carbohydrate, often lacks the dietary fiber necessary for a healthy gut. This lack of fiber can potentially increase your risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. Consider choosing whole grain breads instead, and always pair them with a good source of protein and healthy fats to balance your meal.
24. Are pastries safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Pastries, being refined carbohydrates, often lack the dietary fiber necessary for a healthy gut. This lack of fiber can potentially increase your risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. If you enjoy pastries, consider enjoying them as an occasional treat rather than a regular part of your diet, and balance them with other, more nutritious foods.
25. How do sugary drinks affect diverticulitis? Sugary drinks, being refined carbohydrates, often lack the dietary fiber necessary for a healthy gut. This lack of fiber can potentially increase your risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. Consider choosing water, herbal teas, or other low-sugar beverages to stay hydrated.
26. Can I eat raspberries if I have diverticulitis? Raspberries have numerous small seeds that can be challenging for diverticulitis sufferers. Consume them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. If you find they don’t aggravate your condition, you can enjoy them in moderation, possibly in smoothies where the seeds are well-blended.
27. Are sunflower seeds safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Sunflower seeds can lodge within the diverticula, causing inflammation and discomfort. Consume them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. If you find they don’t aggravate your condition, you can enjoy them as a healthy source of fats and proteins. Alternatively, try sunflower seed butter, which offers the same nutritional benefits without the hard, potentially irritating pieces.
28. How does pumpkin seeds affect diverticulitis? Pumpkin seeds can lodge within the diverticula, causing inflammation and discomfort. Consume them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. If you find they don’t aggravate your condition, you can enjoy them as a healthy source of fats and proteins. Alternatively, try pumpkin seed butter, which offers the same nutritional benefits without the hard, potentially irritating pieces.
29. Can I eat ham if I have diverticulitis? Ham, being a processed food, may lack the fiber necessary to support a healthy gut, thereby potentially increasing the risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. If you enjoy the flavor of ham, consider using it sparingly as a flavoring agent rather than a main component of your meals.
30. Are ready-made frozen meals safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Ready-made frozen meals often contain high levels of sodium and may lack the fiber necessary to support a healthy gut, thereby potentially increasing the risk of a diverticulitis flare-up. Consider preparing your meals from fresh, whole foods whenever possible, and choose frozen meals that are low in sodium and high in fiber when necessary.
31. How does high-fat cheese affect diverticulitis? High-fat cheese could potentially trigger diverticulitis symptoms. Consider opting for low-fat or non-fat alternatives, which can be gentler on your gut. If you enjoy the flavor of high-fat cheese, consider using it sparingly as a flavoring agent rather than a main component of your meals.
32. Can I drink full-fat milk if I have diverticulitis? Full-fat milk could potentially trigger diverticulitis symptoms. Consider opting for low-fat or non-fat alternatives, which can be gentler on your gut. If you enjoy the flavor of full-fat milk, consider using it sparingly and always pair it with a good source of fiber to balance your meal.
33. Are low-fat dairy products safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Low-fat dairy products can be a good source of protein and calcium for diverticulitis sufferers. They are typically gentler on the gut than their full-fat counterparts. Always monitor your symptoms when introducing new foods into your diet.
34. How does tofu affect diverticulitis? Tofu is a plant-based protein that is typically easy to digest and unlikely to irritate the diverticula. It can be a good protein option for those with diverticulitis, especially when cooked in a gentle method like steaming or baking.
35. Can I eat lentils if I have diverticulitis? Lentils are a high-fiber food that can potentially exacerbate symptoms during a diverticulitis flare-up. However, they are also a good source of protein and other nutrients. Consume them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. You could also try cooking lentils thoroughly to soften the fiber and make them easier to digest.
36. Is fish safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Fish is a lean protein that is typically easy to digest and unlikely to irritate the diverticula. It can be a good protein option for those with diverticulitis, especially when cooked in a gentle method like steaming or baking.
37. How does poultry affect diverticulitis? Poultry is a lean protein that is typically easy to digest and unlikely to irritate the diverticula. It can be a good protein option for those with diverticulitis, especially when cooked in a gentle method like steaming or baking.
38. Can I eat plant-based proteins if I have diverticulitis? Plant-based proteins like tofu, lentils, and beans can be a good option for those with diverticulitis. However, they are also high in fiber and can potentially exacerbate symptoms during a flare-up. Consume them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. You could also try cooking these foods thoroughly to soften the fiber and make them easier to digest.
39. Are grilled foods safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Grilled foods can be a good option for those with diverticulitis, as long as they are not high in fat or covered in spicy or irritating sauces. Choose lean proteins and vegetables for grilling, and always monitor your symptoms when introducing new foods into your diet.
40. How does baking affect diverticulitis? Baking is a gentle cooking method that can be a good option for those with diverticulitis. It allows for the preparation of a wide variety of foods without adding extra fat or irritating spices. Choose lean proteins and vegetables for baking, and always monitor your symptoms when introducing new foods into your diet.
41. Can I eat steamed foods if I have diverticulitis? Steamed foods are typically easy to digest and unlikely to irritate the diverticula. They can be a good option for those with diverticulitis, especially when choosing foods that are low in fiber and unlikely to get lodged in the diverticula.
42. Is non-fat dairy safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Non-fat dairy products can be a good source of protein and calcium for diverticulitis sufferers. They are typically gentler on the gut than their full-fat counterparts. Always monitor your symptoms when introducing new foods into your diet.
43. How does dehydration affect diverticulitis? Dehydration can lead to constipation, a condition that can exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms. Always drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, especially when consuming high-fiber foods.
44. Can I eat high-fiber foods if I have diverticulitis? High-fiber foods can potentially exacerbate symptoms during a diverticulitis flare-up. However, they are also important for overall gut health. Consume them in moderation and monitor your symptoms. You could also try cooking high-fiber foods thoroughly to soften the fiber and make them easier to digest.
45. Are seedless fruits safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Seedless fruits can be a good option for those with diverticulitis, as they are unlikely to irritate the diverticula. They can be enjoyed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Always monitor your symptoms when introducing new foods into your diet.
46. How does constipation affect diverticulitis? Constipation can exacerbate diverticulitis symptoms, as it can lead to increased pressure in the colon and potentially cause the diverticula to become inflamed. To prevent constipation, drink plenty of water, consume a balanced diet with adequate fiber, and engage in regular physical activity.
47. Can I eat high-fat foods if I have diverticulitis? High-fat foods can potentially trigger diverticulitis symptoms. Consider opting for foods that are low in fat and high in other nutrients, like lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
48. Are low-fiber foods safe for diverticulitis sufferers? Low-fiber foods can be easier to digest and less likely to irritate the diverticula, making them a good option during a diverticulitis flare-up. However, a long-term low-fiber diet is not recommended as it can lead to constipation and other digestive issues.
49. How does a balanced diet affect diverticulitis? A balanced diet can support overall gut health and potentially prevent diverticulitis flare-ups. This includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains, as well as plenty of water.
50. Can I maintain a food diary if I have diverticulitis? Maintaining a food diary can be a helpful tool for managing diverticulitis. It can help you identify any foods that trigger your symptoms, allowing you to make informed decisions about your diet.
Remember, everyone’s experience with diverticulitis is unique—what triggers a flare-up in one person might not in another. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet.













