Living with psoriasis is rarely just about skin. It’s about waking up to itchiness that disrupts your sleep, feeling self-conscious about flakes on your shirt, and sometimes explaining — yet again — that psoriasis is not contagious. Many people turn to natural remedies when flare-ups hit, and one option that keeps coming up is coconut oil for psoriasis, a gentle yet time-tested approach that offers relief beyond prescription creams or harsh shampoos.
Coconut oil has been used for centuries in tropical regions to soothe dry skin, condition hair, and even heal minor wounds. Today, these traditions are being revisited with scientific curiosity. Could something as simple and affordable as coconut oil really help people manage psoriasis more comfortably?
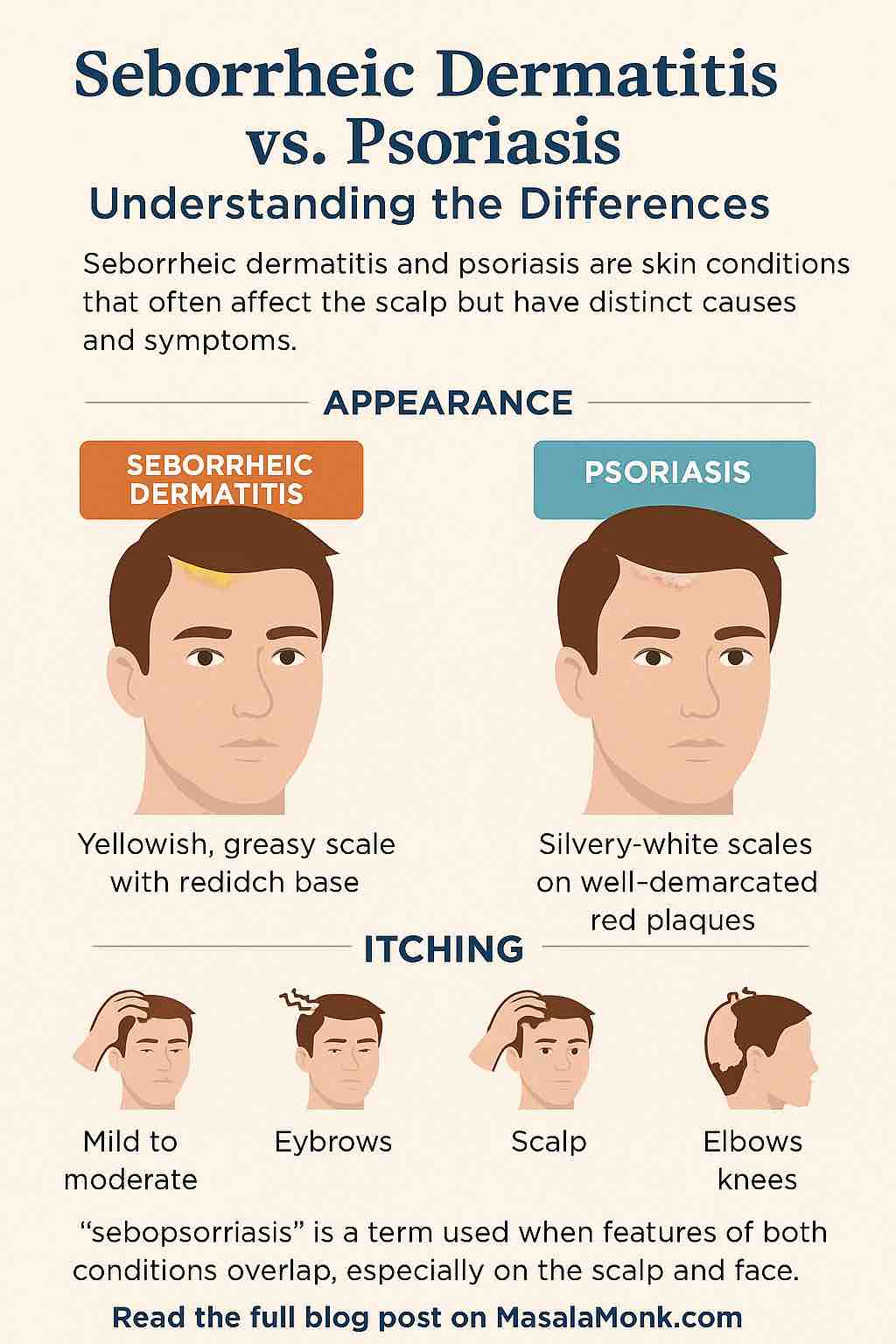
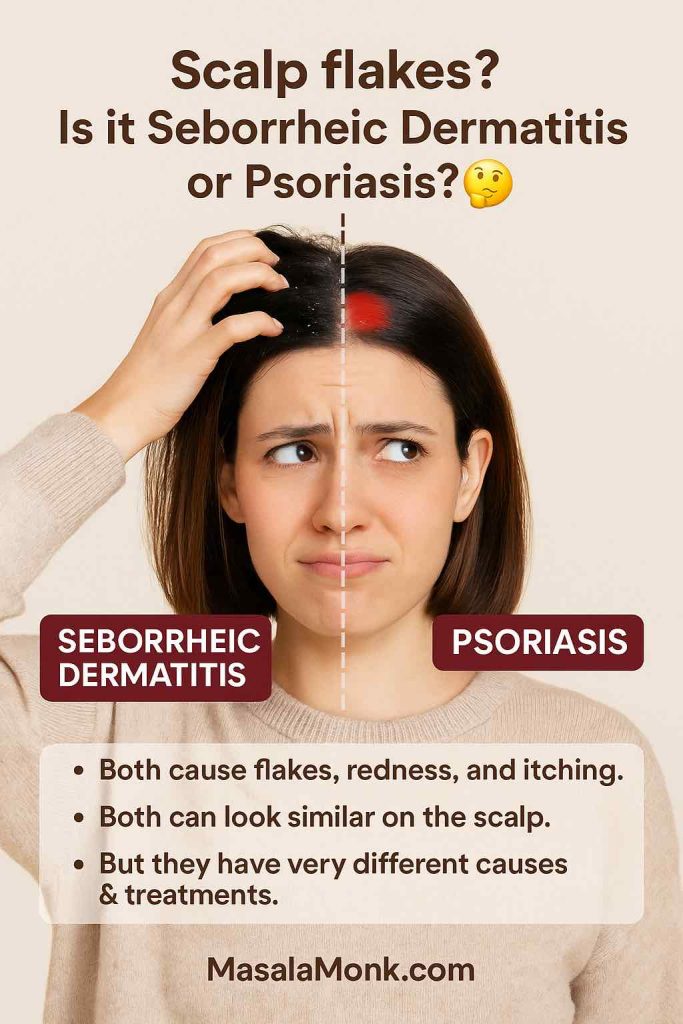
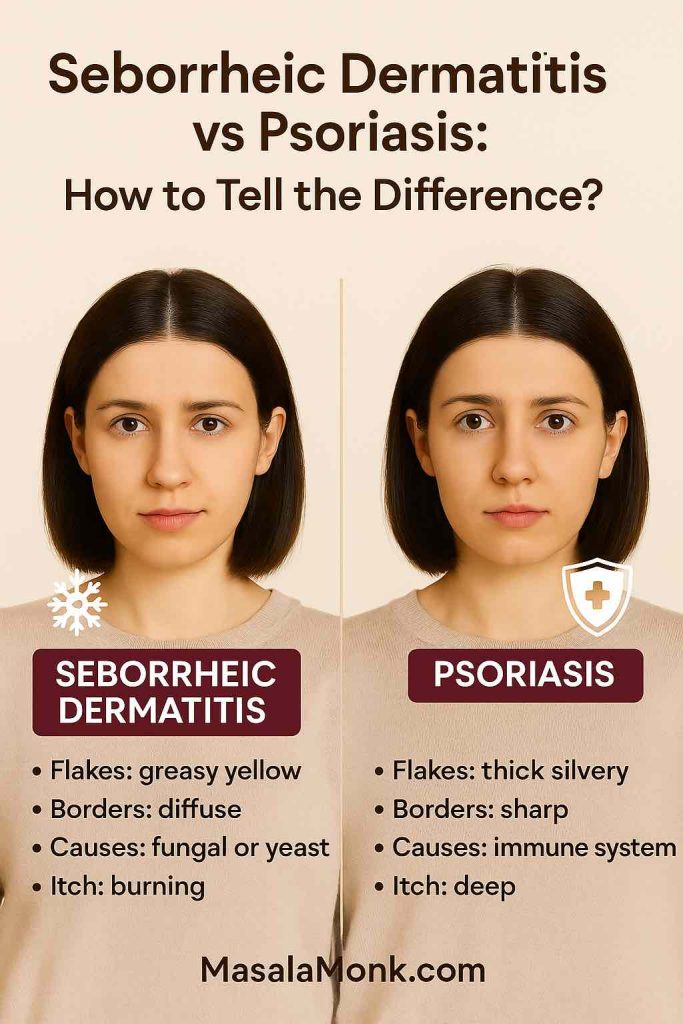
Many people confuse psoriasis with other skin issues. If you’re not sure what you’re dealing with, our guide on Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis helps you understand the difference.
In this article, we’ll go deep — really deep — into the science, history, and everyday practicality of using coconut oil for psoriasis. We’ll explore what researchers have discovered, what dermatologists advise, and how real people can thoughtfully weave it into their daily routines.
⚠️ Note: This post is for general educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Please consult a dermatologist for personalized care.
Do read our detailed guide where we discuss on using various aspects of Coconut Oil on skin here: Coconut Oil for Skin: Frequently Asked Questions.
1. Understanding Psoriasis: The Starting Point
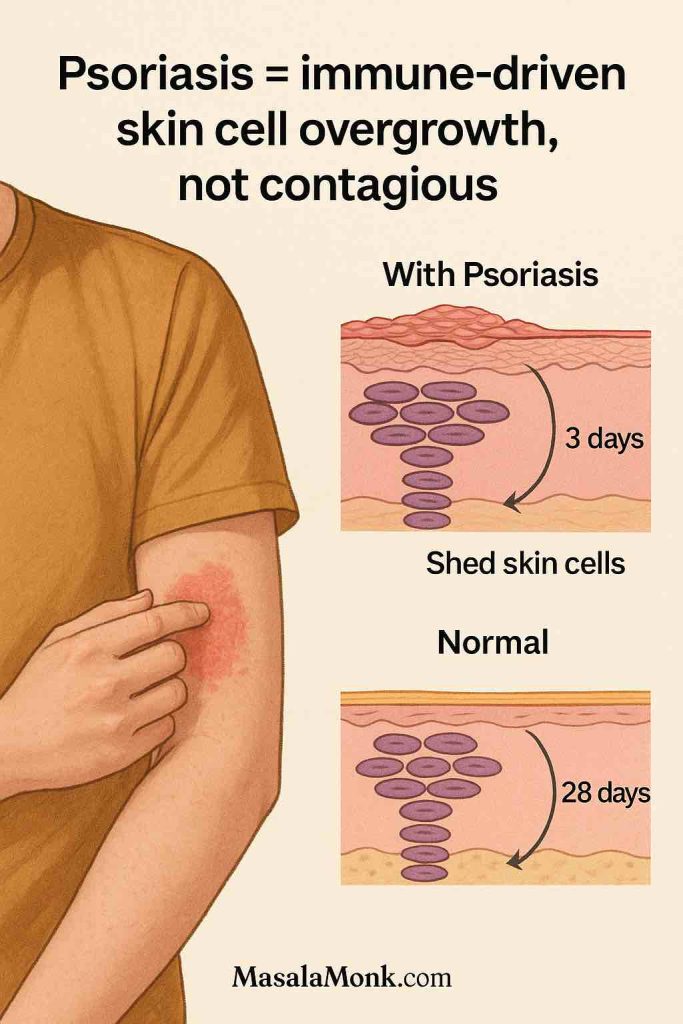
To appreciate why coconut oil might help, we need to understand what psoriasis is — and what it is not.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease, not just a skin problem. In this condition, the immune system speeds up the skin cell turnover cycle dramatically. Instead of the normal 28–30 days it takes for a skin cell to mature and shed, it happens in about 3–4 days. This rapid cycle causes skin cells to pile up before the old ones can be shed, creating raised, scaly plaques that are red, itchy, and sometimes painful.
Common areas include:
- Elbows and knees, where plaques can crack and bleed.
- Scalp, where scales can flake onto clothes and resemble stubborn dandruff.
- Lower back and other friction points.
- Nails, which may show pitting, ridges, or discoloration.
Psoriasis isn’t contagious, but it often carries social stigma. According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, up to 30% of people with psoriasis also develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint stiffness and pain.
Current treatments vary:
- Topical creams and ointments (like corticosteroids or vitamin D analogues) can reduce inflammation.
- Phototherapy, where skin is exposed to UV light under medical supervision.
- Systemic treatments (like methotrexate, cyclosporine, or biologics) target the immune system itself.
Yet even with advanced therapies, dermatologists emphasize one simple daily habit: keep skin moisturized. Moisturized skin flakes less, itches less, and responds better to medicated treatments (Medical News Today). That’s where coconut oil may shine.
Read More: Eczema vs Psoriasis vs Dermatitis
2. Coconut Oil 101: More Than a Kitchen Ingredient
We often think of coconut oil as something for frying or smoothies, but the oil extracted from coconuts has a long history in both medicine and self-care. In Ayurveda, the traditional medicine system of India, coconut oil is described as a “cooling” oil, used to calm heat, irritation, and inflammation.

Types of Coconut Oil
Not all coconut oils are created equal:
- Virgin coconut oil (VCO): Cold-pressed from fresh coconut meat. This is the most beneficial for skin because it retains antioxidants and bioactive compounds.
- Refined coconut oil: Made from dried copra, then bleached and deodorized. It loses many natural properties during processing.
- Fractionated coconut oil (MCT oil): A liquid form that contains mostly medium-chain triglycerides like caprylic and capric acid, but not the full nutrient profile.
When it comes to psoriasis care, virgin coconut oil is the gold standard.
What’s Inside the Jar?
- Lauric acid (about 50%): Known for antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity (Verywell Health).
- Caprylic and capric acid: Support the skin’s natural defenses.
- Vitamin E: An antioxidant that helps protect skin from oxidative stress.
- Polyphenols: Plant-based compounds that calm inflammation.
This unique composition explains why coconut oil is not just a moisturizer — it may also have therapeutic effects on irritated or inflamed skin.
3. What Research Really Says About Coconut Oil and Psoriasis
Many natural remedies are promoted without evidence, so it’s worth asking: what do studies actually say?
Clinical Trials
- A 1993 PubMed study found that coconut oil, when applied before phototherapy, reduced UV penetration. In simple terms: don’t use it right before light treatment.
- In an Indian Journal of Dermatology trial, patients using coconut oil — with or without medicated tar — saw 57–64% improvement in scalp psoriasis. This suggests coconut oil has standalone benefits.
- An observational study showed that scaling improved within 4–6 weeks of using virgin coconut oil daily. By weeks 6–8, redness also decreased.
Mechanisms at Play
Laboratory research explains why:
- Coconut oil reduces inflammatory markers like TNF-α and IL-6 (NCBI).
- It helps the skin produce proteins that strengthen the skin barrier.
- Compared to mineral oil, coconut oil is more effective in improving hydration in dry skin conditions (ResearchGate trial).
Beyond Psoriasis
- In children with eczema, virgin coconut oil reduced severity better than mineral oil (Healthline). While eczema and psoriasis are different, both involve skin barrier disruption and inflammation, making the findings relevant.
- A scalp microbiome study showed coconut oil improved the balance of healthy bacteria and reduced fungal overgrowth — a potential game-changer for scalp psoriasis.
Bottom line? Coconut oil won’t cure psoriasis, but it can ease symptoms, reduce flaking, and make medicated treatments more effective.
⚠️ Note: This post is for general educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Please consult a dermatologist for personalized care.
Coconut oil works best as part of a broader natural toolkit. Beyond oils, spices and herbs can reduce inflammation. See our Top 10 Natural Anti-Inflammatory Remedies for ideas backed by research.
For DIY lovers, there are simple blends — like turmeric masks combined with coconut oil. Try recipes from our DIY Turmeric Skincare Guide.

4. Coconut Oil for Scalp Psoriasis: Practical How-To
Scalp psoriasis is often the hardest to manage. The plaques can feel tight, itchy, and hard to remove. Shampoo alone rarely helps because thick scales block active ingredients from penetrating.
Here’s a practical way to use coconut oil:
- Warm 1–2 teaspoons of virgin coconut oil in your hands.
- Massage gently into affected areas of the scalp.
- Cover with a shower cap or towel, and leave it overnight.
- In the morning, comb out softened scales.
- Wash with a medicated shampoo (salicylic acid, coal tar, or vitamin D analogues).
Tips:
- Repeat 2–3 times a week.
- Don’t overdo it — too much oil can clog pores or make hair greasy.
- Avoid using it just before phototherapy.
Many people find this not only softens plaques but also creates a calming, self-care ritual that reduces the stress of dealing with scalp psoriasis.
Scalp psoriasis can be particularly challenging. Coconut oil helps loosen plaques and reduce itching, but it isn’t the only natural moisturizer. You might also explore Shea Butter for Scalp Psoriasis, which many find equally soothing.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical advice and should not replace consultation with a qualified healthcare provider. Psoriasis can vary greatly from person to person, so always talk to your dermatologist or healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or home remedy, including the use of coconut oil
5. Coconut Oil for Other Psoriasis Types
While scalp psoriasis gets the most attention, coconut oil can support other types:
- Plaque psoriasis (elbows, knees): Helps soften thick patches.
- Inverse psoriasis (skin folds): May reduce friction but be careful, as excess moisture in folds can cause irritation.
- Nail psoriasis: Massaging into cuticles may reduce brittleness, though research is limited.
- Genital psoriasis: Can ease dryness, but note that coconut oil weakens latex condoms.
- Facial psoriasis: Use sparingly, especially if acne-prone — coconut oil can clog pores.
Psoriasis on hands can be painful and disruptive. Coconut oil softens rough patches and restores moisture, but if you’re unsure whether your symptoms are psoriasis or eczema, check out Palmar Psoriasis vs Hand Eczema for clarity.
6. DIY Blends and Everyday Uses
Many people mix coconut oil with other soothing agents:
- Coconut oil + aloe vera: Cools and hydrates.
- Coconut oil + turmeric: Anti-inflammatory boost from Ayurveda.
- Coconut oil + apple cider vinegar: ACV reduces itch, coconut oil restores moisture (WebMD).
- Coconut oil + neem-based creams: Traditional blends like Sorion are studied for psoriasis (Research Registry).
While not all combinations are clinically proven, they often make self-care more pleasant and personalized.
7. Dermatologists’ Perspective
When living with psoriasis, it’s natural to wonder what the experts recommend. While many people experiment with home remedies like coconut oil, dermatologists stress the importance of keeping expectations realistic—while also recognizing that coconut oil can play a gentle, supportive role in managing symptoms.

Coconut Oil as an Emollient, Not a Cure
Dermatologists often highlight that coconut oil works as an emollient, which means it helps lock in moisture and create a protective barrier over the skin. According to Medical News Today, there is no conclusive scientific evidence that coconut oil can cure psoriasis. However, its natural moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties can make skin feel less dry and irritated—providing comfort alongside prescribed treatments.
Dr. Kurt Ashack, a dermatologist at Michigan State University, explains that coconut oil forms an occlusive seal, much like petroleum jelly, while also offering antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory benefits. This makes it especially helpful for dry, peeling plaques, though it should always be seen as a complementary step—not a replacement for medical care (HealthCentral).
Best Way to Apply Coconut Oil
Experts recommend applying coconut oil immediately after a warm shower, when the skin is still slightly damp. This helps the oil trap hydration more effectively. A thin layer, massaged in circular motions, is usually enough to make skin feel softer and calmer. This simple daily ritual can be both soothing and practical (HealthCentral).
Scalp Psoriasis: Preparing the Ground
Scalp psoriasis is notoriously difficult to manage, but coconut oil can help soften stubborn scales. Dermatologists quoted by Byrdie note that using coconut oil overnight can loosen plaques, making medicated shampoos or treatments more effective. Similarly, Healthline points out that coconut oil may provide temporary relief from itching and flaking, though it shouldn’t be relied on as the only treatment.
Dermatologists with Psoriasis Trust Oils Too
Interestingly, even dermatologists who live with psoriasis themselves often turn to natural oils. One expert quoted by the Global Healthy Living Foundation shared that she applies jojoba oil or coconut oil at night to help soften scales—because skin’s natural repair processes are most active during sleep. This practical advice blends medical science with lived experience.
Evidence from Clinical Guidelines
On a broader level, clinical evidence does support the use of coconut oil as a supportive therapy. A rapid evidence summary published by the Joanna Briggs Institute concluded that virgin coconut oil shows Level B evidence for psoriasis care, especially when access to corticosteroid creams is limited. While not a cure, it can be a cost-effective, natural addition to skincare routines.
⚠️ Note: This post is for general educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Please consult a dermatologist for personalized care.
Hope with Balance
In the end, dermatologists advise approaching coconut oil with hope but caution. It can ease dryness, reduce itchiness, and make plaques more manageable. But for moderate to severe psoriasis, coconut oil is best used alongside prescribed treatments such as topical steroids or systemic medications (Verywell Health).
✅ Key Takeaway: Dermatologists recognize coconut oil as a safe, soothing companion to medical treatments—not a standalone cure. By using it strategically (after showers, overnight on the scalp, or layered under other therapies), you can bring more comfort into your daily routine while still following your doctor’s guidance.
8. Pros and Cons: A Balanced View
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Natural, affordable, widely available | Not a cure |
| Hydrates and softens plaques | May clog pores |
| Reduces scaling and itch | Can block UV in phototherapy |
| Supports scalp microbiome | Limited psoriasis-specific trials |
Choosing the right oil can feel overwhelming. While coconut oil is a great start, some prefer Castor Oil for Psoriasis due to its thicker texture and different fatty acid profile.
Similarly, turmeric has long been used in Ayurvedic practices. Pairing the two may enhance results — see our deep dive into Turmeric for Psoriasis.
9. Choosing and Using Coconut Oil Wisely
Not all coconut oils are created equal. If you’re considering adding it to your psoriasis care routine, choosing the right type—and knowing how to use it properly—can make a big difference. Dermatologists and nutrition experts alike stress that the quality of coconut oil matters, as does the way you apply it.
Virgin vs. Refined Coconut Oil
When it comes to skincare, dermatologists generally recommend virgin coconut oil over refined varieties. Virgin coconut oil is extracted without high heat or chemicals, which helps it retain more antioxidants and beneficial fatty acids. These compounds are thought to contribute to its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, which can be soothing for irritated skin.
Refined coconut oil, on the other hand, often undergoes bleaching and deodorizing, which can strip away some of these natural benefits. While it’s still moisturizing, it may not offer the same skin-friendly extras that virgin oil provides.
Look for Cold-Pressed and Organic Options
If possible, reach for cold-pressed, organic virgin coconut oil. Cold-pressing helps preserve delicate nutrients, while organic certification ensures fewer pesticide residues. This can be especially important if you’re applying oil to sensitive areas such as the scalp or face.
Patch-Test Before You Commit
Even natural remedies can sometimes trigger reactions. Experts recommend doing a patch test—apply a small amount of coconut oil to a discreet area of skin and wait 24 hours. If there’s no redness, itching, or rash, it’s likely safe to use more broadly.
Best Times to Apply Coconut Oil
Timing makes coconut oil more effective. For psoriasis-prone skin, dermatologists suggest:
- After a warm shower – Apply a thin layer while your skin is still slightly damp to lock in hydration.
- Before bed – Letting coconut oil sit overnight allows it to soften plaques and relieve tightness.
- Before medicated treatments – For scalp psoriasis, gently massaging coconut oil into plaques can help loosen scales, making medicated shampoos work better (Healthline).
When Coconut Oil May Not Be Enough
While coconut oil is generally safe and soothing, dermatologists caution that it may not be sufficient for moderate to severe psoriasis. In those cases, it’s best used as a supportive step alongside prescribed treatments. If you notice worsening symptoms, persistent itching, or pain, consult your dermatologist before continuing use (Verywell Health).
Storage and Shelf Life
Finally, remember that coconut oil has a shelf life of about two years when stored in a cool, dark place. Keep it in a clean, dry container and always use clean hands or a spoon to scoop it out. This prevents contamination and keeps your oil fresh for longer.
✅ Key Takeaway: To get the most benefit, choose organic, cold-pressed virgin coconut oil, patch-test before regular use, and apply at the right times—especially after bathing or before bed. Used wisely, coconut oil can be a simple yet comforting tool in your broader psoriasis care plan.
Conclusion: A Gentle Ally in a Lifelong Journey
Psoriasis is a marathon, not a sprint. While medical treatments target the immune system, daily self-care makes a huge difference in comfort and quality of life. Coconut oil may not erase psoriasis, but it can:
- Moisturize dry skin.
- Soften stubborn scales.
- Improve scalp health.
- Create a calming ritual in an otherwise stressful routine.
For many, that’s not just “alternative medicine” — it’s practical, everyday support that makes life with psoriasis a little more manageable.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as medical advice and should not replace consultation with a qualified healthcare provider. Psoriasis can vary greatly from person to person, so always talk to your dermatologist or healthcare professional before starting any new treatment or home remedy, including the use of coconut oil.
Frequently Asked Questions About Coconut Oil for Psoriasis
1. Can coconut oil really help with psoriasis?
Yes, coconut oil may help relieve dryness, itching, and flaking associated with psoriasis. Thanks to its moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties, it can soften plaques and calm irritation. However, it works best as a supportive care option rather than a standalone treatment.
2. Is coconut oil good for scalp psoriasis?
Absolutely. Many people find that applying coconut oil on scalp psoriasis helps loosen scales and reduce itchiness. For best results, massage it into the scalp, leave it on overnight, and wash gently the next morning with a mild shampoo.
3. Which is the best coconut oil for psoriasis?
Dermatologists usually recommend organic, virgin, cold-pressed coconut oil. This type retains the highest levels of antioxidants and beneficial fatty acids, making it more soothing for sensitive, psoriasis-prone skin.
4. How do you use coconut oil for psoriasis on the scalp?
A practical routine is to warm a small amount of oil in your hands, massage it gently into affected areas, and cover your head with a shower cap overnight. This softens plaques and makes medicated shampoos more effective the next day.
5. Can coconut oil treat psoriasis naturally?
Coconut oil is often considered part of natural psoriasis treatment. While it can’t cure the condition, it may reduce flare-up discomfort, hydrate dry skin, and support overall skin barrier health when used regularly.
6. Does coconut oil help with plaque psoriasis?
Yes, applying coconut oil for plaque psoriasis may soften the thickened, scaly patches and make them less painful. Pairing it with dermatologist-recommended treatments usually yields the best results.
7. Are there side effects of using coconut oil for psoriasis?
For most people, coconut oil is safe. However, some may experience clogged pores or mild irritation. To avoid this, always patch-test on a small area before applying it widely, especially on the face or sensitive areas.
8. Can I mix coconut oil with other remedies like apple cider vinegar?
Yes, some people combine coconut oil and apple cider vinegar for scalp psoriasis to boost effectiveness. Vinegar may help reduce itch and balance scalp pH, while coconut oil provides moisture. Always consult a dermatologist before trying combinations.
9. Is coconut oil helpful for psoriatic arthritis?
While coconut oil may soothe dry skin linked with psoriasis, there is no scientific evidence that it helps psoriatic arthritis directly. Still, as part of a holistic self-care routine, it can improve comfort and skin health.
10. How long does it take to see results from coconut oil for psoriasis?
Consistency is key. Some people notice softer skin and reduced flaking within a week of regular use, especially on the scalp. However, improvements in psoriasis symptoms vary, and long-term management usually requires medical treatments too.
Further Reading & References
If you’re interested in exploring more about coconut oil for psoriasis and natural skin health, here are some trusted resources and additional reads:
Scientific Studies & Expert Resources
- Topical Coconut Oil and Skin Health – A review in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences shows that virgin coconut oil supports the skin barrier and reduces inflammatory markers like TNF-α and IL-6. Read the study here.
- Moisturizer Effectiveness on Dry Skin – Research found coconut oil works as well as mineral oil in hydrating and smoothing dry skin. See the findings.
- Coconut Oil Before Phototherapy – A controlled trial revealed that applying coconut oil before PUVA or UVB light therapy does not improve outcomes. View the study.
- Dermatologists’ Tips for Scalp Psoriasis – The American Academy of Dermatology explains how scale softeners, gentle care, and avoiding scratching can make treatments more effective. Read more here.
- Natural Oils and Skin Barrier Repair – A scientific review emphasizes how fatty acid profiles (like lauric acid in coconut oil) influence skin repair. Learn more.
Additional Context & Resources
- Managing Psoriasis Symptoms – Mayo Clinic outlines simple routines like lukewarm baths, moisturizing, and avoiding harsh triggers. Check the guide.
- Botanical Treatments for Psoriasis – A 2023 review looks at how essential oils and plant extracts can complement traditional treatments. Explore the review.