If you have an ectomorph body type, you probably gain weight slowly, carry less muscle by default, and feel “full” fast. The upside? With the right training focus and a reliable calorie surplus, your frame can add size and strength—often faster than you expect—once you standardize the basics and track progress weekly. For broader context on how somatotypes are used (and misused), see this plain-English primer on ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph.
The two other body types you might want to read more about are:
- Endomorph Body Type: Diet & Workout Plan for Women & Men
- Mesomorph Body Type: Diet, Workouts & Weight Loss (Female & Male)
What the Ectomorph Body Type Actually Means
At a glance, ectomorphs tend to have narrower shoulders and hips, longer limbs, smaller joints, and a leaner look at the same bodyweight as peers. Crucially, somatotypes are not destiny; treat them as a quick heuristic that suggests where to start your plan, not how it must end. That’s why we’ll combine practical experience with established guidelines from the American College of Sports Medicine and current hypertrophy research to steer your programming choices.
Key takeaways up front
- You’ll build best with compound lifts first, modest accessories second, and steady progression week to week. Evidence shows hypertrophy occurs across a range of loads when sets are taken sufficiently hard; nevertheless, heavier loading still favors strength (see Schoenfeld et al., 2017).
- Gaining requires a daily calorie surplus, not occasional feasts. You’ll anchor protein at evidence-based targets and then push carbs to fuel training (supported by Morton et al., 2018 and the ISSN protein position stand).
Also Read: Mesomorph Body Type: Diet, Workouts & Weight Loss (Female & Male)
Best Workout Plan for the Ectomorph Body Type
Although many ectomorphs assume they need super-high reps or marathon sessions, the research indicates you can build muscle with both lighter and heavier loads—as long as you train close enough to failure and accumulate sufficient weekly volume. Schoenfeld et al. (2017) reported similar hypertrophy outcomes across a low-to-high loading spectrum; strength, however, favored heavier work. Practically, that means mixing heavy compounds with moderate-rep accessories is ideal.
Weekly frequency and progression (why it works)
Begin with 3–4 lifting days each week so you can hit major muscle groups about 2× weekly. This lines up with ACSM progression models for novices and intermediates and matches what most busy lifters can recover from while still eating enough. Just as importantly, cap most sessions at 60–75 minutes so you leave fresh enough to eat well.
Also Read: Beginner’s Guide to the Gym
A. 4-Day Hypertrophy Split (Ectomorph-Friendly)
Day 1 — Upper (push-bias)
Bench Press 4×6–8 • Incline DB Press 3×8–10 • Overhead Press 3×6–8 • Cable Fly 2×12–15 • Triceps Pressdown 3×10–12 • Lateral Raise 2×15–20
Day 2 — Lower (squat-bias)
Back Squat 4×6–8 • Romanian Deadlift 3×8–10 • Walking Lunge 3×10/leg • Leg Press 2×12–15 • Calf Raise 4×10–15
Day 3 — Rest / easy walk / mobility
Day 4 — Upper (pull-bias)
Weighted Pull-ups 4×6–8 (or Lat Pulldown) • Barbell Row 3×6–8 • Chest-Supported Row 3×8–10 • Face Pull 2×15–20 • EZ-Bar Curl 3×10–12 • Hammer Curl 2×12–15
Day 5 — Lower (hinge/glute-bias)
Conventional Deadlift 3×3–5 • Front Squat 3×6–8 • Hip Thrust 3×8–10 • Lying Leg Curl 3×10–12 • Ab Wheel 3×8–12
Days 6–7 — Rest
B. Progression that builds muscle on an ectomorph body type
- Add load or reps weekly within the stated ranges while keeping top sets 1–3 reps shy of failure most of the time.
- If a lift stalls for three weeks, add one set to that movement or swap to a close variation (e.g., high-bar to low-bar squat) and rebuild.
- Keep long steady-state cardio minimal during gain phases; short walks (10–20 minutes) help appetite and recovery without draining you.
Why this works: moderate volume across two exposures per muscle keeps stimulus frequent without wrecking recovery. It also encourages skill with the big lifts while leaving time and energy to eat.
Also Read: Guide to Essential Equipment for Home & Office Workout
Ectomorph Diet Plan for Muscle & Weight Gain
Let’s keep it simple: most ectomorphs undereat. You don’t need “dirty bulks,” but you do need consistent surplus. Start by estimating maintenance with the RMR calculator, then set macros using Macro Master and adjust from the scale each week.
- Start with maintenance +250–500 kcal/day (choose the higher end if you’re very lean and training 4×/week).
- Set protein at ~1.6–2.2 g/kg/day, a range supported by Morton et al., 2018 and the ISSN protein position stand.
- Allocate fat at 0.6–1.0 g/kg/day, then fill the rest with carbs to fuel training and recovery.
- Weigh yourself 2–3 mornings/week (post-restroom, pre-breakfast) and average the data. If your 14-day average hasn’t moved up, add +150–250 kcal/day.
High-calorie, easy-to-eat foods (when appetite is low)
Liquid calories and carb-dense staples are your friends:
- Use this nut-infused smoothie framework to blend milk, oats, mixed nuts, honey, and a scoop of protein.
- Build meals from rice, oats, pasta, potatoes; then add a spoon of oil or ghee. For ideas, scan healthy weight-gain foods.
- Prefer local, seasonal fruit; for eg. enjoy mangoes in moderation—myth-busting here: mangoes & weight gain.
Hitting protein targets without drama
Vegetarian or simply busy? No problem. Anchor your day with one “linchpin” meal that delivers ~40–50 g protein, then distribute the rest. For plant-forward batch cooks, these quinoa meal-prep ideas and high-protein chia prep posts provide simple, repeatable templates you can scale.
Why we care about protein: a large meta-analysis suggests benefits accrue up to ~1.6 g/kg/day for trained individuals, with possible advantages a bit above that depending on context (Morton et al., 2018). The International Society of Sports Nutrition aligns with daily and per-meal recommendations that are practical and sustainable. For extra context on supplementation, see reviews like Nunes et al., 2022 and Cintineo et al., 2018.
Also Read: The Science of Protein: Maximizing Muscle Growth and Recovery
Sample day (≈3,000–3,200 kcal) you can scale up or down
- Breakfast — Oats cooked in milk + whey mixed in after; banana; spoon of peanut butter.
- Mid-morning smoothie — Use the nut-infused smoothie template; blend milk, oats, nuts, honey, protein.
- Lunch — Rice or roti with chicken thighs or paneer; olive-oil tossed veg; yogurt.
- Pre-workout — Toast with jam + a handful of raisins; sip water.
- Post-workout — Whey or a plant blend shaken with milk; a ripe mango (in season) or two dates.
- Dinner — Pasta with beef/turkey or chickpeas; parmesan; side salad with olive oil.
- Before bed — Cottage cheese or casein; a few almonds or peanuts.
Also Read: Classic Deviled Eggs (Easy) + 8 Flavorful Variations
Protein & Creatine for the Ectomorph Body Type
Protein powders are not magic—only convenient. Use whey, casein, or a good plant blend to reach the day’s total. If nighttime appetite exists, casein can help you tick the box without feeling stuffed. For whole-food variety (and minerals), rotate dairy, eggs, dals/legumes, tofu/tempeh, poultry, and fish.
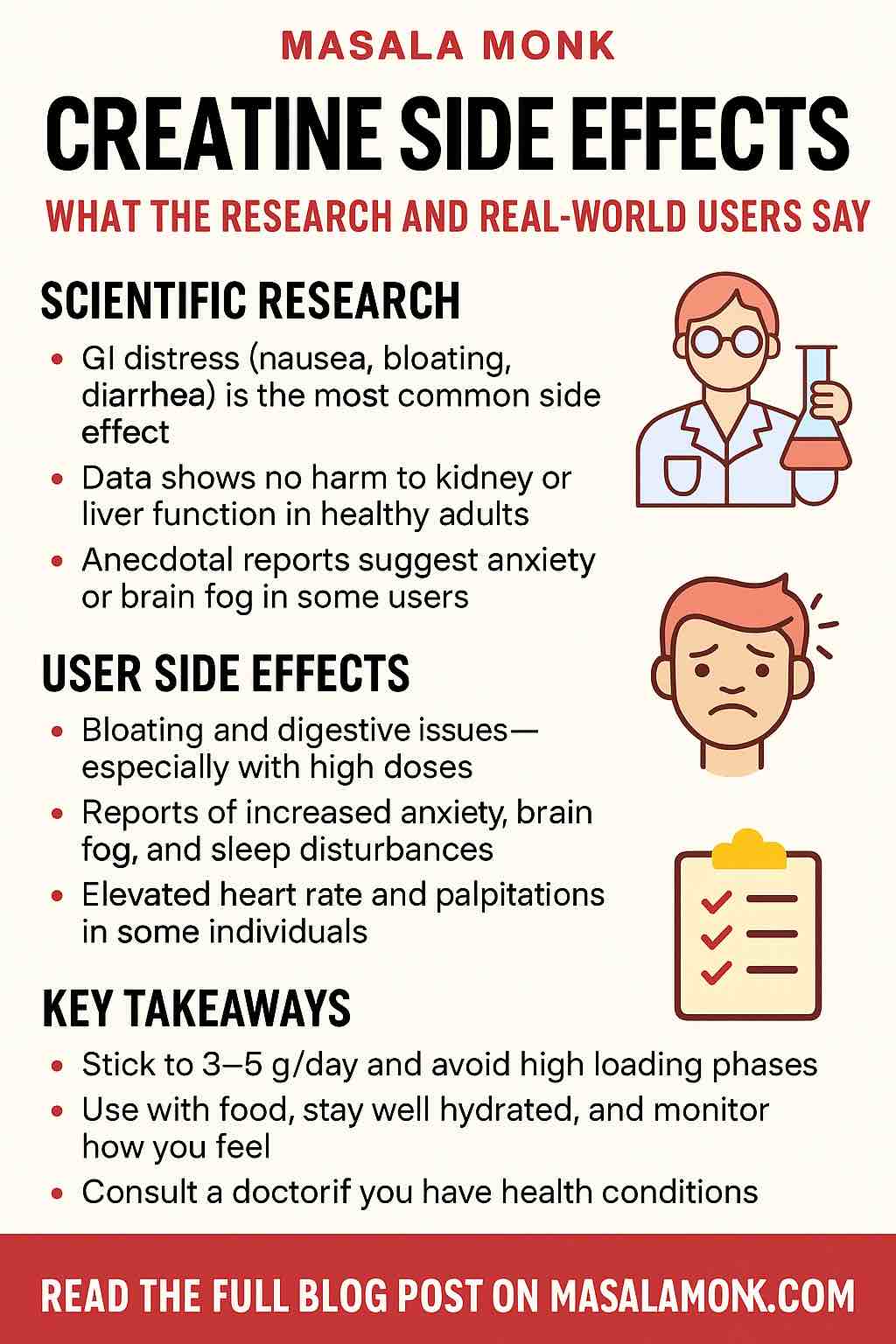
As for supplements, creatine monohydrate (3–5 g/day) remains the best-supported single add-on for strength and lean mass. For safety and efficacy, rely on the ISSN creatine position stand (2025 update) and the earlier accessible open-access review. You don’t need a loading phase, and timing is flexible—take it whenever you remember. If you want a consumer-friendly explanation first, here’s a plain-English creatine side-effects guide.
Also Read: How to Eat 100 Grams of Protein a Day
Male vs Female: Applying the Plan to Your Ectomorph Body Type
Despite different goals, men and women succeed with the same principles—volume, progression, calories, and patience—while fine-tuning emphasis.
Men:
- Push compounds that expand the silhouette: bench and overhead presses for chest/delts, rows and pull-ups for back width, squats and deadlifts for legs.
- Eat more on lower-body days, when systemic fatigue (and thus fuel need) is higher.
- Track a few “north star” lifts (e.g., 5-rep max on squat/bench/row) and chase slow increases monthly.
Women:
- Prioritize glutes, hamstrings, lats, and delts for shape. Hip thrusts, RDLs, Bulgarian split squats, pull-downs/pull-ups, and lateral raises do heavy lifting here.
- Keep protein every day, not just on training days, to support recovery and appetite control.
- Consider slight carb cycling: +20–30 g carbs on hard days, –20–30 g on rest days—only if it helps adherence.
Either way, movements, sets, and reps differ less than you think; the ectomorph body type benefits most from consistency, not perfect exercise selection.
Also Read: Best Tea to Lower Cortisol: Green, Black, Matcha & Herbal
A Simple Weekly Checklist for Ectomorph Weight Gain
- Train 3–4×/week, mostly compounds first, accessories second; take most sets within 1–3 reps of failure, keep 60–75 minutes per session. See the load-range evidence in Schoenfeld 2017.
- Eat in surplus daily, not “whenever.” If your 14-day average weight doesn’t rise, add +150–250 kcal/day and reassess a week later.
- Hit protein (~1.6–2.2 g/kg/day). That range is supported by Morton 2018 and the ISSN position stand; split across 3–5 meals you actually like.
- Use shakes strategically when appetite is low: milk, oats, nuts, honey, protein. Templates: nut-infused smoothies and high-iron shakes.
- Supplement simply: creatine 3–5 g/day (see ISSN 2025); optional whey/plant protein to fill gaps.
- Walk most days (10–20 minutes) to improve appetite and recovery; keep long cardio minimal while gaining.
- Sleep 7–9 hours; if life spikes stress, scale volume down for a week—progress requires recovery.
Also Read: Benefits of Nuts and Seeds – Protein-Packed Superfoods
Troubleshooting for the Ectomorph Body Type (quick fixes)
- “I feel stuffed and can’t eat more.”
Shift calories to liquids and semi-solids: milk-based shakes with oats and nut butters; yogurt bowls with granola and honey; fruit plus dates between meals. If needed, add 1–2 tsp of olive oil or MCT to smoothies for 80–160 easy calories. Borrow blueprint ideas from nut-infused smoothies or macadamia & sunflower protein shakes, but swap in regular milk and oats to boost calories. - “My lifts aren’t moving.”
First, eat. Then add a back-off set at 60–70% for higher reps (12–15) after your top sets, or add a small 2.5 kg increment to your main lift every other week. Finally, rotate variations to keep momentum. - “I’m getting softer.”
Ease the surplus down 100–150 kcal/day and maintain for two weeks. Keep protein steady; optionally increase steps slightly (no need for long cardio blocks). - “I miss sessions.”
Use a 3-day full-body rotation instead (A/B/C), repeating weekly and sliding days as life allows. Each session: a squat/hinge, a press, a pull, plus 1–2 accessories.
Final Word
The ectomorph body type isn’t a limitation; it’s a programming clue. Build around heavy compounds, feed your training with a dependable surplus, standardize protein, and repeat—week after week. Use shakes when appetite fades, walk to recover, and choose a small handful of lifts to improve relentlessly. Then, let time do what time does best: compound your effort into visible muscle.
FAQs
1) What is the ectomorph body type?
An ectomorph body type is typically lean with a narrower frame, long limbs, and lower baseline muscle and fat. Consequently, ectomorphs often find it harder to gain weight or size without a structured plan.
2) What does “ectomorph meaning/definition” imply for training?
Practically, it signals you’ll respond best to progressive strength work, compound lifts first, and consistent recovery. Moreover, keep sessions focused (60–75 minutes) and push effort close to failure.
3) Ectomorph vs mesomorph vs endomorph—what’s the difference?
Briefly: ectomorphs gain slowly, mesomorphs are naturally more muscular, and endomorphs store fat more easily. Nevertheless, most people are a blend; use the category that best matches your current traits.
4) Can an ectomorph become “mesomorphic” in appearance?
Yes. With years of progressive overload, appropriate calories, and patience, an ectomorph can build a visibly more muscular, “meso-like” physique. Ultimately, habits drive results more than labels.
5) What’s the best ectomorph workout plan?
Prioritize a 3–4 day split that hits each muscle twice weekly. Notably, use heavy compounds (squat, deadlift, bench, row, pull-ups, overhead press) plus moderate-rep accessories for volume.
6) Best exercise for ectomorphs—what should top the list?
Start with multi-joint moves: back squat, Romanian deadlift, bench press, barbell row, overhead press, and weighted pull-ups. Additionally, add hip thrusts, lunges, leg curls, laterals, and curls to round out weak points.
7) How many sets and reps suit an ectomorph body type?
Aim for ~10–16 hard sets per muscle per week. Likewise, work mostly in 6–12 reps on compounds, 8–15 on accessories, keeping 1–3 reps in reserve most sets.
8) Should ectomorphs do cardio while gaining?
Yes—lightly. Meanwhile, prefer short walks or 10–20 minutes of easy cardio to aid appetite and recovery; avoid long, frequent endurance sessions during surplus phases.
9) What is the best ectomorph diet plan?
Build a daily calorie surplus of +250–500 kcal above maintenance. Furthermore, anchor protein at ~1.6–2.2 g/kg/day, set fats at 0.6–1.0 g/kg/day, and let carbs fill the remainder to fuel training.
10) How fast should ectomorph weight gain happen?
Target roughly 0.25–0.5 kg per week. Consequently, if your two-week average weight stalls, increase intake by +150–250 kcal/day and reassess after seven days.
11) What foods help an ectomorph gain weight without feeling stuffed?
Choose energy-dense staples: milk, oats, rice, pasta, potatoes, breads, dried fruit, nuts, nut butters, olive oil, and ghee. Beyond that, use smoothies and shakes to sneak in liquid calories.
12) Best protein for ectomorphs—what should I pick?
Whey concentrate/isolate, casein (especially at night), or a quality plant blend (pea/rice/soy) are all effective. Importantly, the “best” is the one you’ll take consistently to hit your daily total.
13) Which supplements are worth it for an ectomorph body type?
Keep it simple: creatine monohydrate (3–5 g/day), basic protein powder for convenience, omega-3s if intake is low, and vitamin D as needed. Otherwise, focus primarily on food and training.
14) Do ectomorph women need a different plan than men?
Principles are identical—volume, progression, surplus, and sleep. However, exercise selection can emphasize glutes, hamstrings, lats, and delts for shape while still progressing the big lifts.
15) What does an “ectomorph meal plan for muscle gain” look like?
Organize 4–6 feedings with at least one 40–50 g protein “anchor” meal; surround workouts with carbs; and include a calorie-dense shake daily. Additionally, pre-prep staples (rice, oats, potatoes, proteins) every 2–3 days.
16) Is a mass gainer necessary for ectomorph weight gain?
Not at all. Instead, blend your own: milk, oats, banana, nut butter, and a scoop of protein. This homemade option is flexible, cheaper, and easier to tailor to your targets.
17) What’s an ectomorph compound workout day example?
Try: Back Squat 4×6–8, Romanian Deadlift 3×8–10, Bench Press 4×6–8, Barbell Row 3×6–8, Hip Thrust 3×8–10, Lateral Raise 2×15–20. Furthermore, rest 90–150 seconds between hard sets.
18) How should an ectomorph track progress?
Use a simple trio: weekly average bodyweight, key lift logs (e.g., 5-rep bests), and biweekly front/side photos. Consequently, make small adjustments—load, reps, or calories—based on those trends.
19) Are “ecto endo meso” types fixed for life?
No. Genetics set starting points, yet training, nutrition, and recovery shift your look substantially. Nevertheless, accept your structure while maximizing what you can control.
20) What’s the fastest way for an ectomorph to add muscle safely?
Lift 3–4×/week with progressive overload, maintain a daily surplus, hit protein every day, sleep 7–9 hours, and repeat. Ultimately, disciplined consistency—more than novelty—drives visible change.