Zone training isn’t just a buzzword. Over the last few years, it’s become the go-to method for athletes, weekend warriors, and anyone aiming to get more out of their workouts—without burning out. And with the latest Apple Watch updates, you can turn your wrist into a personal coach, guiding every workout to maximize results.
But how do you make the most of these features? This guide breaks down the science, the setup, and the daily hacks—no matter if you’re a runner, cyclist, walker, or someone who just wants to boost health and burn fat smarter, not harder.
The Basics: What Are Heart Rate Zones, and Why Do They Matter?
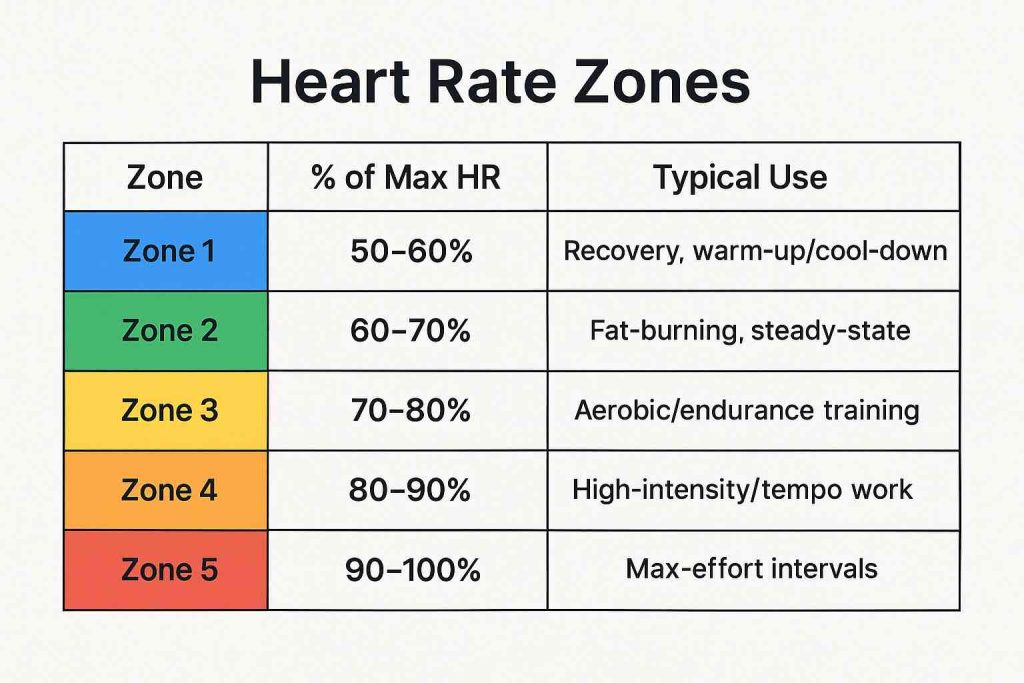
Let’s start simple. Heart rate zones are intensity levels based on your heart’s beats per minute (BPM), each corresponding to a percentage of your maximum heart rate (HRmax). Each zone taps into a different energy system, delivering unique benefits:
- Zone 1 (50–60% HRmax): Easy warm-ups, cool-downs, and active recovery
- Zone 2 (60–70% HRmax): Fat burning, aerobic base building, long-term health
- Zone 3 (70–80% HRmax): Endurance, tempo workouts, sustainable effort
- Zone 4 (80–90% HRmax): Threshold, speed, high-intensity bursts
- Zone 5 (90–100% HRmax): Sprints, max effort, peak athleticism
Think of each zone as a “training dial”—tune it to your goal, and you get results faster and safer than just going all-out, all the time.
How the Apple Watch Calculates Your Zones (And Why That Matters)
Here’s the cool part:
The Apple Watch uses the Heart Rate Reserve (HRR) or Karvonen formula by default, which is more accurate than just “220 minus your age.” It considers your resting heart rate (a powerful health marker!) and your age. The formula:
Target Zone = ((HRmax – HRrest) x %Intensity) + HRrest
- HRmax: Estimated as
208 – (0.7 × age)(Mayo Clinic standard) - HRrest: Taken from your Health app data (ideally, measure when you wake up)
Result? Your zones are more personalized—and much more useful—than the old-school gym charts.

Setting Up Zone Training on Your Apple Watch (2025 Edition)
1. Enter Your Real Resting Heart Rate
- Open the Health app on your iPhone.
- Tap Browse > Heart > Resting Heart Rate.
- Check that it matches your morning, just-awake measurement for a week.
- If not, wear your watch to sleep and adjust your habits to get a true resting value.
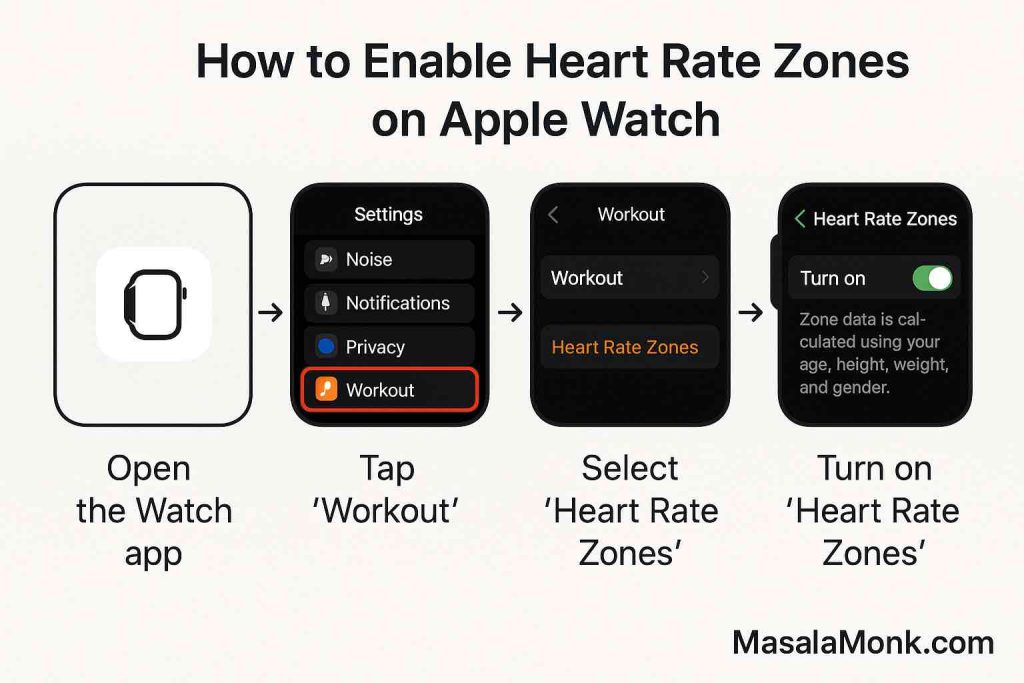
2. Enable Heart Rate Zones in Workouts
- On Apple Watch: Open Workout → tap “…” by your preferred workout → Preferences → Workout Views → turn on Heart Rate Zones.
- Or, in iPhone’s Watch app: My Watch → Workout → Heart Rate Zones → toggle Include.
3. (Optional) Customize Zones
If you know your actual max HR (from a lab test or hard intervals), set it:
- Watch: Settings → Workout → Heart Rate Zones → Manual
- Adjust zone boundaries as needed.
4. Start a Workout—See Your Zone in Real Time
- Begin an Outdoor Run, Walk, Cycle, or HIIT session.
- Rotate the Digital Crown until you see the Heart Rate Zone screen.
- You’ll get gentle taps as you move between zones—no need to constantly check your wrist!
Science-Backed Benefits: Why Train by Zones?
The Zone 2 Revolution
Zone 2 is having a moment—and for good reason. Decades of studies show training here is:
- Sustainable (you can do it for a long time)
- Great for fat loss (up to 65% of energy comes from fat oxidation)
- Powerful for metabolic health (improves insulin sensitivity)
- Low on injury risk (less pounding, more consistency)
- Perfect for beginners and advanced athletes alike
Want a real-world tip?
If you can hold a conversation—but not sing—during your workout, you’re probably in Zone 2. If you’re gasping for air, you’re above it!
Higher Zones: Use Sparingly, But Don’t Ignore
Zones 3–5 aren’t “bad.” In fact, you need them for speed, power, and breaking through plateaus. But for most people, the magic happens when you spend 80% of your time in Zones 1–2 and the rest pushing harder.
Advanced: Maximizing Accuracy & Avoiding Common Mistakes
1. Get a Good Fit
Wear your watch snugly, about 1–2 fingers above your wrist bone. Loose = wobbly readings!
2. Clean the Sensors
Wipe sweat and dirt away before workouts. Optical sensors need a clear view.
3. Tattoos & Skin Tone
Very dark tattoos under the sensor? Consider a compatible Bluetooth chest strap (like Polar H10) for absolute accuracy.
4. Choose the Right Workout Type
Selecting Outdoor Walk vs. HIIT affects how Apple Watch logs your data and zones. Always match the workout type to your real activity.
Practical Example: A Week of Zone-Based Training
Here’s what a balanced, research-backed week could look like for someone aiming for fat loss, better endurance, or general health (adjust as needed):
| Day | Session Type | Zone Target | Duration | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mon | Brisk Walk or Jog | 2 | 45 min | Can talk, not sing |
| Tue | HIIT Intervals | 4–5 (bursts) | 30 min | 1 min hard, 2 min easy |
| Wed | Active Recovery | 1 | 30 min | Gentle walk/stretch/yoga |
| Thu | Bike or Swim | 2–3 | 40 min | Slightly breathless |
| Fri | Rest or Mobility | — | — | Stretch or foam roll |
| Sat | Long Zone 2 Workout | 2 | 60–90 min | Endurance walk, hike, ride |
| Sun | Fun Activity | Any | Flexible | Play, dance, casual sports |
Tracking Progress: How to Read & Use Your Apple Watch Data
- During workout: Watch the zone screen to adjust pace in real-time.
- After workout: On your iPhone’s Fitness app, tap the workout → Show More under Heart Rate to see zone breakdowns.
- Weekly review: Look for trends: Are you spending enough time in your target zones? Are your resting heart rates dropping? Is your VO₂ max trending up?
- Third-party apps: Apps like Cardio Rings, Aerobic Pro, or Zones offer even more breakdowns, helping you spot gaps and celebrate milestones.
Common Pitfalls—and How to Avoid Them
- Chasing “higher is better”: More intensity isn’t always better. Overtraining in high zones can stall progress and increase injury risk.
- Ignoring rest days: Recovery in Zone 1 (or complete rest) is as important as the workouts themselves.
- Relying only on calories burned: Apple Watch calorie estimates are helpful, but less accurate than heart rate zones. Don’t let them drive every decision.
The Future: What’s Next for Apple Watch and Zone Training?
Recent research points to AI-powered metabolic tracking—soon, your Watch may estimate not just heart rate, but real-time fat and carb burn using advanced modeling (arxiv.org). Until then, Apple Watch remains the best mainstream device for zone training—reliable, easy to use, and always on your wrist.
Final Thoughts: Your Next Steps
Zone training isn’t a trend. It’s science-backed, practical, and—thanks to Apple Watch—more accessible than ever. Here’s what to do next:
- Set up your Apple Watch zones today.
- Plan your week with a mix of Zone 2, recovery, and high-intensity.
- Review your progress, adjust, and celebrate the small wins.
Whether you’re running your first 5K, walking for health, or chasing a marathon PR, your wrist just became your smartest workout partner yet.
Questions, tips, or success stories? Drop them in the comments below—let’s zone in together!
References & Further Reading
- How to Use Heart Rate Zones on Apple Watch – TechRadar
- What Is Zone 2 Training? Expert Viewpoints
- University of Mississippi Apple Watch Validation Study (2025)
- Kalman-ODE Hybrid Models for Wearable VO₂ (arXiv 2025)
Ready to take your training to the next level?
Put on your watch, pick a zone, and let’s go!
FAQs
1. How does Apple Watch calculate my heart rate zones?
Apple Watch uses your age and resting heart rate (from your Health app data) with the Karvonen formula to estimate personalized zones. You can also adjust them manually if you know your actual max heart rate.
2. How do I turn on heart rate zone tracking for my workouts?
On your Apple Watch, start a workout, tap the “…” next to your workout type, go to Preferences, select Workout Views, and enable Heart Rate Zones. Or, use the Watch app on your iPhone under “Workout” settings.
3. Can I manually set my heart rate zones?
Yes. Go to Settings > Workout > Heart Rate Zones on your Watch, choose Manual, and set your custom limits for each zone based on your lab-tested or field-tested values.
4. How accurate is Apple Watch for heart rate and zone tracking?
Recent studies show Apple Watch is highly accurate for heart rate (about 4–5% margin of error), especially during steady workouts. Accuracy may drop for calorie counts or intense, erratic motion.
5. What if my Watch gives odd readings during exercise?
Ensure a snug fit (1–2 finger-widths above your wrist bone), keep the sensor clean, and consider using a Bluetooth chest strap for activities with lots of wrist movement or if you have tattoos under the sensor.
6. Which workout types support heart rate zones on Apple Watch?
Most cardio workouts (Outdoor/Indoor Run, Walk, Cycling, HIIT, Rowing, Swimming) support zone tracking. Always choose the workout that best matches your activity.
7. How can I track how much time I spend in each heart rate zone?
After your workout, open the Fitness app on your iPhone, tap your workout, and view the heart rate breakdown by zone. Third-party apps can offer more detailed summaries over days or weeks.
8. How do I know if I’m really in Zone 2?
Use both the Apple Watch zone screen and the “talk test”—if you can speak in sentences but not sing, you’re likely in Zone 2. The watch’s alerts will also notify you as you move between zones.
9. Can I set alerts to stay in a certain heart rate zone?
Yes. When starting a workout, tap “…” > Alerts > Heart Rate, then set an alert for your preferred zone. You’ll get haptic (vibration) and/or audio feedback if you leave that zone.
10. Is it safe to train in higher heart rate zones (4–5)?
For most healthy adults, brief efforts in Zones 4–5 are safe and beneficial, but should be limited to a few sessions per week. Always consult a physician before starting any new high-intensity training, especially if you have health concerns.










