A hemorrhoids high fiber diet is the most dependable way to soften stools, reduce straining, and calm flare-ups. When you shape everyday meals around fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds—and when you steadily sip fluids—bowel movements typically become easier and less painful. Moreover, small bathroom-habit tweaks make a surprisingly big difference: keep toilet time brief, avoid straining, and respond to the urge promptly. For the medical basics behind this approach, see the NIDDK’s guidance on eating, diet, and nutrition for hemorrhoids and the ASCRS patient page.
In short, diet and simple habits are your foundation. Everything else—creams, cushions, even procedures—usually works better once your food, fiber, and fluids are dialed in.
Why fiber (and water) matter in a hemorrhoids high fiber diet
To put it plainly, fiber pulls water into stool and adds bulk; as a result, stool moves with less scraping and fewer long pushes. Additionally, water helps that fiber function smoothly; without enough fluid, even a “high-fiber” plate can feel sluggish. Therefore, keep a water bottle within reach, sip regularly, and lean on foods with natural water—citrus, cucumbers, leafy greens, soups, and stews. Finally, increase fiber gradually over a week or two so your gut adapts without gas and bloating. If you’d like an authoritative refresher, review NIDDK’s diet guidance and the Mayo Clinics’ Food Sources of Fiber list.

Bottom line: fiber makes stool softer and easier to pass; fluids make fiber work
Also Read: Significance of Fiber in Diet: Understanding Its Health Benefits
How much fiber is “enough,” and how fast should you increase it?
Typically, the sweet spot is 25–35 grams of fiber per day, which aligns with common surgical-society guidance (see ASCRS). However, your gut comfort matters as much as the number. Consequently, start where you are and move up in small steps—say, an extra 5 grams every few days—while drinking enough fluid. Furthermore, consider splitting fiber evenly across meals and snacks; distributing intake helps your gut adapt and keeps stools consistently soft.

If you want to “top up” intake, a teaspoon of psyllium mixed in water (once daily to start) is a gentle way to close the gap. Notably, randomized trials and a Cochrane review show that adding fiber reduces persistent symptoms and improves bleeding over several weeks; a meta-analysis indexed on PubMed reports similar benefits.
High-fiber foods for hemorrhoids (piles)
To build a hemorrhoids high fiber diet, stack your plate with three dependable pillars, then season and swap to taste.
1) Whole grains and legumes
Oats, barley, brown rice, whole-wheat roti/wraps, lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans, split peas, and black beans are your “anchors.” As a guide, ½ cup cooked lentils/beans adds ~7–8 g of fiber; 1 cup cooked barley ~6 g; 1 cup cooked oats ~4 g. Mix and match: oats at breakfast, beans at lunch, barley or brown rice at dinner. For an easy bake to keep around, try Oatmeal Bread (great with soups and salads).
2) Vegetables and fruits
Aim to fill half your plate with plants. Notably, broccoli, green beans, carrots, squash, sweet potato, and leafy greens bring both fiber and water. Meanwhile, pears, apples (skin on), berries, oranges, kiwis, and prunes add gentle sweetness and regularity. For soothing sides, see Spinach (Palak) Raita; for heat-free options, skim these no-cook cucumber raita ideas.
3) Nuts and seeds
Small portions, big payoff. Two tablespoons of chia deliver ~8–10 g of fiber; one tablespoon of ground flaxseed adds ~2 g; a small handful of peanuts or roasted chana contributes ~2–3 g. Sprinkle seeds into curd or oats, or stir them into smoothies and batters. For breakfast inspiration, rotate Chia Pudding (almond milk) and this round-up of 10 creative chia puddings. For a flavorful snack bowl, try Vegan Som Tam Salad Recipe | Raw Papaya Salad.
If you like precise numbers for labels and meal planning, double-check portions in USDA FoodData Central.
In practice: aim for one fiber “anchor” each meal (for example, oats → beans → barley), then add two to three produce servings across the day. Gradually, you’ll settle into that comfortable 25–35 g/day range.
Also Read: Fiber in Food
Foods to avoid (and smart swaps)—including “bleeding hemorrhoids foods to avoid”
There isn’t a single villain food. However, low-fiber patterns and dehydration make stools firmer—and that’s the real problem. Consequently, it helps to dial down:
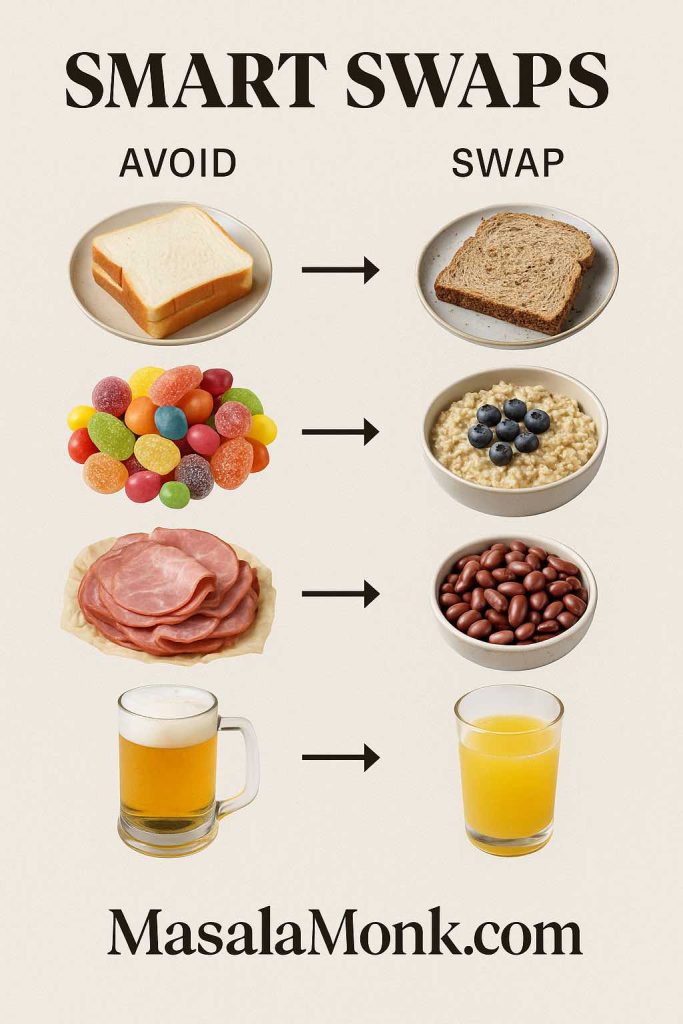
- Ultra-processed, low-fiber meals (white breads, refined snacks, fast food).
Swap: whole-grain breads/wraps, oats, barley, or brown rice—then double the veg side. - Excess alcohol or heavy caffeine (can dehydrate some people).
Swap: water, diluted juices, clear soups, herbal teas, and fruit with pulp. - Very spicy foods (if they irritate you).
Swap: milder spice blends and cooling sides like curd/raita while you recover.
Therefore, aim for pattern over perfection. Nudge lunches and dinners toward whole grains and plants, and relief usually follows. For fundamentals, revisit NIDDK’s eating & hydration tips.
“Fiber 5” foods to avoid with hemorrhoids (quick hit):
- White breads and crackers;
- Low-fiber desserts and candies;
- Processed meats-heavy meals without veg;
- Large portions of cheese or cream-heavy dishes (if they constipate you);
- Alcohol binges.
These don’t “cause” hemorrhoids, but they can stall a hemorrhoids high fiber diet and firm up stools when you least want it.
Common food questions (bananas, curd/yogurt, chicken, cucumber, milk, juices)
Because searchers ask these constantly, here are fast, practical answers:
- Banana and hemorrhoids/piles: generally gentle and helpful; include it within the daily fiber target.
- Curd/yogurt and piles: soothing for many; add ground flaxseed or chopped fruit to keep fiber front and center.
- Chicken and hemorrhoids: lean protein is fine—just balance the plate with vegetables and whole grains so fiber still leads.
- Cucumber and piles: hydrating and cooling, especially useful as a raita or salad component.
- Milk is good for piles? It depends. If dairy constipates you, limit it or switch to smaller servings and add fiber-rich sides. If it suits you, pair milk/curd with oats, chia, or fruit to keep the overall meal fiber-forward.
- Best fruit/juice for hemorrhoids: pears, apples (skin on), berries, oranges with pulp, kiwis, and small prune portions. Prefer pulp-rich juices or smoothies; pair any juice with whole foods so total fiber stays high.

Liquid diet for hemorrhoids—when (and when not) to use it
Occasionally, during severe pain or immediately after a procedure, clinicians suggest briefly using liquids and very soft foods. Nevertheless, this is a short-term comfort strategy, not a cure. As symptoms ease, transition back to a hemorrhoids high fiber diet—soft high-fiber meals (khichdi-style rice + lentils, vegetable soups with barley, oats with fruit, raitas) plus fluids. For step-by-step self-care that often accompanies these phases, see Mayo Clinic’s hemorrhoids page.
Fiber supplements for hemorrhoids: what actually helps
Food first, supplements second. If you still fall short, psyllium is a reliable first choice; methylcellulose or wheat dextrin can also help. Start low, go slow, and always pair with water. Notably, randomized trials and a Cochrane review show that adding fiber reduces persistent symptoms and improves bleeding over several weeks; a meta-analysis on PubMed reaches similar conclusions. Practically, many people do well with 1 tsp psyllium daily to “top up” what they’re eating.

Also Read: Psyllium Husk (Isabgol/Ispaghula) Side Effects: Risks, Benefits & How to Take It Safely
Relief add-ons: icing, petroleum jelly, seating, and “hemorrhoid donuts”
Diet does the heavy lifting, but a few comfort measures can make each day easier:
- Warm sitz baths for 10–15 minutes, two or three times daily, often reduce pain and itching. See the routine on Mayo Clinic’s hemorrhoids page.
- Brief icing or cool packs can ease swelling—use a thin cloth barrier and keep sessions short.
- A thin layer of petroleum jelly can protect irritated skin during bowel movements; it’s an adjunct, not a cure. You’ll see this suggestion across many clinician handouts.
- Seating choices: soft seats help. However, limit long sessions on donut cushions because they can redistribute pressure in unhelpful ways. Instead, take frequent standing and walking breaks. (This balanced stance reflects many colorectal clinics’ practical advice.)


Hemorrhoids Diet Plan: 7-Day Menu (≈28–35 g/day)
To begin, treat this as a flexible scaffold for a hemorrhoids high fiber diet. Additionally, sip fluids consistently, avoid straining, and limit toilet time to 1–2 minutes. Finally, adjust portions to your appetite and add a fiber “plug” (beans, fruit, or chia) to any meal that needs a boost.
Day 1
- Breakfast: Masala oats with mixed vegetables; add a kiwi for extra fiber.
- Lunch: Brown rice with kidney beans and a crisp salad; squeeze lemon for brightness.
- Snack: Chia pudding (2 tablespoons chia); keep sipping water.
- Dinner: Grilled chicken or paneer, sautéed broccoli and carrots, plus a whole-grain wrap.
Day 2
- Breakfast: Curd parfait with chia and an apple; stir in ground flaxseed.
- Lunch: Whole-grain flatbread with lentil stew and salad; keep fluids up.
- Snack: Roasted chickpeas with lemon; add a small orange.
- Dinner: Rice-and-lentil “khichdi-style” bowl with a cooling spinach raita.
Day 3
- Breakfast: Vegetable upma and orange segments; sip warm water.
- Lunch: Whole-wheat roti with chickpea curry and mixed vegetables; add cucumber for hydration.
- Snack: Five prunes plus a few nuts.
- Dinner: Barley “risotto” or quinoa pilaf with sautéed green beans.
Day 4
- Breakfast: Two slices of Oatmeal Bread with cucumber raita; add a small fruit.
- Lunch: Brown rice and vegetable sambar with a side salad.
- Snack: Curd with 1 tablespoon ground flaxseed.
- Dinner: Tofu or paneer stir-fry, leafy greens, and whole-grain roti.
Day 5
- Breakfast: Poha with peas and papaya; keep portions moderate yet fiber-rich.
- Lunch: Millet or whole-grain roti, mixed dal, and salad; sprinkle seeds on top.
- Snack: A handful of roasted peanuts or roasted chana.
- Dinner: Grain-legume-veg bowl (Mediterranean or Thai style) with plenty of vegetables.
Day 6
- Breakfast: Overnight oats with berries; add chia if you need a boost.
- Lunch: Lemon brown rice with a yogurt-based side; keep the meal soft and soothing.
- Snack: Higher-fiber oat cookies (no refined flour) (occasional treat).
- Dinner: Lean chicken or tofu, sautéed greens, and a whole-grain flatbread.
Day 7
- Breakfast: Dalia (broken wheat) porridge with a banana; start gently.
- Lunch: Jeera brown rice with lentils and salad; cover both protein and fiber.
- Snack: Buttermilk plus a small nut-and-roasted-chana mix.
- Dinner: Vegetable barley soup with whole-grain toast; finish the week light.
Helpful “fiber plugs”: ½ cup lentils or beans ≈ 7–8 g; 2 tablespoons chia ≈ 8–10 g; one apple or pear ≈ 4–6 g. Therefore, add one plug to any meal that looks light on fiber.
Hemorrhoids dietary supplement: how to choose (and what to avoid)
Because supplement aisles can be confusing, here’s a quick filter:
- Best-supported: psyllium husk. It’s a soluble fiber that’s well-studied for stool softening and symptom relief (see Cochrane review).
- Reasonable alternatives: methylcellulose or wheat dextrin, especially if psyllium feels too “gel-like” for you.
- What to avoid: “Detox” laxatives, harsh stimulant teas, or anything promising overnight miracles. These often worsen cramping or lead to rebound constipation.
Start with ½–1 tsp once daily for a few days; if you feel good, increase slowly. Always drink a full glass of water with each dose.
Post-procedure and post-flare diet (gently back to fiber)
If you’ve just had a procedure or you’re in a bad flare, your team’s advice comes first. That said, most leaflets echo the same basics—soft, high-fiber foods, steady fluids, sitz baths, brief icing, and gentle activity. For a representative example of post-op tips, see this UHCW NHS hemorrhoidectomy leaflet. Gradually, you’ll move from liquids and smooth foods back to your regular hemorrhoids high fiber diet. In other words: keep meals soft, hydrating, and fiber-forward; layer on comfort measures; and avoid long bathroom sessions.
Daily habits that reinforce a hemorrhoids high fiber diet
Small changes compound:
- Respond to the urge—don’t delay.
- Avoid straining; if stools feel firm, add a fiber plug and a glass of water.
- Limit toilet time to 1–2 minutes; take the phone/book outside the bathroom.
- Move your body: gentle walks stimulate gut motility.
- Avoid heavy lifting during flares; rebuild gradually with core-friendly routines.

Collectively, these habits amplify what your hemorrhoids high fiber diet is already doing for you.
Recipes and Resources
- Oatmeal Bread – whole-grain swap for low-fiber breads
- Spinach (Palak) Raita – cooling, soothing side
- No-Cook Cucumber Raita Ideas – soft and fresh
- Chia Pudding (almond milk) – breakfast that actually fills you up
- 10 Creative Chia Puddings – rotate flavors for consistency
- Oat Cookies—No Refined Flour – smarter occasional treat
External medical references
- NIDDK – Eating, Diet & Nutrition for Hemorrhoids – fundamentals on diet and fluids
- ASCRS – Hemorrhoids (Patient Page) – fiber targets, bathroom habits, and conservative care
- Mayo Clinic – Hemorrhoids: Diagnosis & Treatment – sitz baths, icing, and home measures
- Cochrane Review – Fiber for Hemorrhoids – evidence that fiber reduces symptoms/bleeding
- Meta-analysis (PubMed) – corroborates fiber benefits
- USDA FoodData Central – fast look-ups for per-food fiber
- Mayo Clinic – Food Sources of Fiber – planning list for shoppers
- UHCW NHS – Haemorrhoidectomy Leaflet – practical post-op advice
FAQs
1) What is a “hemorrhoids high fiber diet,” and why does it help?
A hemorrhoids high fiber diet simply means eating enough fiber (generally 25–35 g/day) alongside steady fluids. Consequently, stools stay softer and bulkier, which reduces straining and irritation. Moreover, when you increase fiber gradually and hydrate consistently, bowel movements tend to feel easier, gentler, and more regular.
2) Which high-fiber foods for hemorrhoids should I prioritize daily?
Start with dependable anchors: oats, barley, brown rice, whole-wheat rotis/wraps, and legumes (lentils, chickpeas, kidney beans). Additionally, pile on vegetables (leafy greens, green beans, broccoli, carrots, gourds, sweet potato) and fruits (pears, apples with skin, berries, oranges, kiwis, prunes). Finally, add small boosters like chia or ground flaxseed.
3) What are fiber-rich foods for hemorrhoids that are easy to add?
Convenient choices include overnight oats, bean bowls, dal-rice combos, vegetable soups with barley, fruit + chia puddings, roasted chana, and whole-grain toast with soft veggie sides. Furthermore, sprinkling a tablespoon of ground flaxseed into curd or oatmeal is a painless upgrade.
4) Is there a difference between a high fiber diet and hemorrhoids relief?
Yes. A high-fiber diet is the eating pattern; hemorrhoids relief is the outcome you’re aiming for. In practice, both rely on the same levers: more fiber, more fluids, less straining, and shorter toilet time. Therefore, the diet is the method; relief is the measurable result.
5) What foods are good for hemorrhoids right now if I’m in a flare?
Choose gentle, fiber-forward meals: soft dal-rice, vegetable soups, oats with fruit, and curd with ground flaxseed. Additionally, emphasize ripe fruit, cooked vegetables, and whole grains that you tolerate well. Ultimately, keep meals simple, moist, and easy to chew.
6) Which foods should I avoid with bleeding hemorrhoids?
Avoid patterns that firm stools: ultra-processed, low-fiber meals; large amounts of cheese or cream-heavy dishes (if constipating for you); and heavy alcohol sessions. Instead, pivot toward whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruit with pulp. As a result, stool softness improves and aggravation usually decreases.
7) What’s the “best diet for hemorrhoids” or “best diet for piles”?
Practically, it’s the plan you can follow: one fiber anchor each meal (oats → beans → barley), two to three produce servings per day, steady hydration, and brief bathroom sessions. Moreover, add small “fiber plugs” (½ cup beans, one apple/pear, or 2 Tbsp chia) whenever a meal looks light.
8) What should a hemorrhoids diet plan include day-to-day?
Aim for variety and rhythm: whole-grain breakfasts, legume-based lunches, veggie-heavy dinners, and fruit-plus-seed snacks. Additionally, schedule water sips between meals, not only at meals. Consequently, your gut sees a steady flow of fiber and fluid rather than sporadic spikes.
9) Are fiber supplements for piles worth it?
Often, yes—especially when food alone falls short. Psyllium is a strong first choice; methylcellulose or wheat dextrin are reasonable alternatives. Nevertheless, start low, increase slowly, and always take with water. Ultimately, supplements “top up” your fiber; they don’t replace fiber-rich meals.
10) What is the best “hemorrhoids dietary supplement” to start with?
Begin with a small daily dose of psyllium (for example, ~1 teaspoon) and assess comfort for a few days. Then, if needed, titrate upward. Additionally, watch your hydration; without water, even the best supplement can feel heavy.
11) Do “hemorrhoid donuts” help or hurt?
They can feel comfortable temporarily; however, prolonged sitting on donut-shaped cushions may shift pressure in unhelpful ways. Therefore, if you use one, do so briefly, stand up regularly, walk around, and vary your seating. Ultimately, diet, hydration, and bathroom habits still drive long-term relief.
12) Is petroleum jelly on hemorrhoids safe or useful?
Yes—as a thin barrier it can reduce friction and help stools pass more comfortably. Even so, it’s an adjunct, not a cure. Consequently, keep the spotlight on fiber, fluids, and habits, and use petroleum jelly sparingly as needed.
13) Should I try icing hemorrhoids?
Brief icing can ease swelling and pain, particularly during flares or after procedures. Meanwhile, place a cloth between skin and ice and keep sessions short. Additionally, combine this with warm sitz baths at other times of day for balanced comfort.
14) When would a liquid diet for hemorrhoids be appropriate?
Occasionally, during severe pain or immediately after a procedure, a short phase of liquids and very soft foods is suggested. Nevertheless, transition back to a fiber-rich diet as symptoms settle. In short, liquids are a bridge; high fiber is the destination.
15) Does manuka honey help hemorrhoids?
Evidence is limited and mixed. Although honey can feel soothing topically for some skin conditions, it is not a substitute for a hemorrhoids high fiber diet, hydration, and smart bathroom habits. Accordingly, prioritize proven basics first.
16) What is a good breakfast for a piles patient?
Think “soft and fiber-forward”: oats with fruit, chia-curd parfaits, dalia (broken wheat) porridge with banana, or whole-grain toast with a cooling veggie side. Additionally, sip water or buttermilk to keep the meal moist and balanced.
17) What are the best fruits for piles?
Pears, apples (with skin), berries, oranges (with pulp), kiwis, and small portions of prunes. Crucially, rotate options through the week; variety helps you hit fiber targets without boredom.
18) What are the best vegetables for piles?
Leafy greens, cruciferous vegetables (like broccoli and cabbage), gourds/squash, carrots, green beans, and sweet potato. Furthermore, lightly cooking vegetables can make them easier to tolerate during flares while preserving fiber.
19) What is the best juice for hemorrhoids?
Prefer pulp-rich juices or veggie-fruit smoothies. However, do not rely on juice alone; pair it with whole foods so total fiber remains high. Ultimately, it’s the combination—liquid plus solids—that keeps stools soft.
20) Are bananas good for hemorrhoids?
Generally, yes. Bananas are gentle, portable, and easy to digest. Even so, they’re more effective when paired with other fiber sources across the day (for instance, oats at breakfast and beans at lunch).
21) Is chicken okay in a hemorrhoids high fiber diet?
Yes—lean chicken is fine. Nevertheless, balance the plate with vegetables and whole grains so the overall meal remains fiber-forward. Conversely, a meat-heavy, low-fiber plate can work against your goals.
22) Is curd/yogurt good for piles?
Often yes, particularly as a cooling side. Additionally, you can stir in ground flaxseed or add chopped fruit to keep the meal fiber-balanced. During flares, many people appreciate curd’s soothing texture.
23) Is cucumber good for piles?
Yes. Cucumber is hydrating and refreshing; therefore, it’s a helpful addition in salads or raitas. Moreover, its high water content complements a fiber-rich plate by supporting stool softness.
24) Is milk good for piles?
It depends. If milk tends to constipate you, keep portions modest and pair it with fiber-rich foods. Alternatively, consider fermented dairy (like curd) or non-dairy options you tolerate better. As always, notice how your own body responds.
25) What is a proper diet for hemorrhoids during recovery after a procedure?
Begin with liquids and very soft foods as advised, then progressively reintroduce whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruit. Meanwhile, maintain hydration, continue sitz baths, and limit toilet time. Ultimately, returning to a fiber-rich routine supports healing and comfort.
26) What are the best foods to eat in hemorrhoids for quick relief?
Start with gentle staples: oats with fruit, dal-rice bowls, vegetable soups with barley, and curd with ground flaxseed. Additionally, use small “fiber plugs” (½ cup beans, 2 tablespoons chia, or one apple/pear) to bring any light meal up to target.
27) Which foods to stay away from with hemorrhoids long-term?
As a pattern: low-fiber refined carbs, heavy processed meals, and frequent alcohol binges. Nevertheless, occasional treats are fine—just counterbalance them with produce-dense meals and plenty of water. In the end, consistency matters more than perfection.
28) How do I prevent piles with diet?
Consistently hit your fiber target, drink water throughout the day, move your body, and avoid straining. Additionally, keep toilet sessions brief (about one to two minutes) and respond to the urge promptly. Consequently, flare frequency and intensity typically decline.
29) What if I need a “diet change for hemorrhoids” but don’t know where to start?
Begin with one swap per meal: oats instead of refined cereal at breakfast; beans + salad with your usual lunch; and a whole-grain side plus cooked vegetables at dinner. Furthermore, add one fruit and one seed serving daily. Gradually, your totals will reach the fiber zone with very little friction.
30) Is there a “best food to cure hemorrhoids”?
No single food cures hemorrhoids. However, the combination of fiber-rich meals, steady fluids, smart bathroom habits, and—when needed—gentle fiber supplements is what reliably improves comfort. Therefore, think “routine,” not “magic bullet.”
31) What’s a good “diet plan for piles” if I travel a lot?
Plan simple anchors you can find almost anywhere: oats or whole-grain toast at breakfast; bean-based salads or bowls at lunch; whole-grain sides plus cooked vegetables at dinner. Meanwhile, carry easy snacks like roasted chana, nuts, or a banana. Hence, travel stops become manageable rather than disruptive.
32) Do chia seeds help with hemorrhoids?
Yes—indirectly. Chia adds soluble fiber and holds water, which supports stool softness. Nevertheless, chia works best as part of a broader routine with grains, legumes, vegetables, fruits, and fluids.
33) What about “diet to avoid piles” if I’ve never had symptoms?
Proactively aim for fiber in the 25–35 g/day range, hydrate well, move daily, and keep toilet time short. In addition, avoid habitual low-fiber patterns (refined snacks, ultra-processed meals). By and large, prevention mirrors treatment.
34) Is “anus pie” related to hemorrhoids or diet?
No. That term pops up as a stray or mistaken search phrase; it isn’t a recognized diet, food, or therapy for hemorrhoids. Instead, focus on the proven fundamentals above.