If you’ve ever searched for collagen rich foods or wondered what foods contain collagen, you’re not alone. Collagen is everywhere in the body—it makes up nearly 75% of your skin and is responsible for about 30% of your body’s total protein, giving strength to bones, joints, and connective tissues (Cleveland Clinic). Because of this, it’s often called the “glue” that holds everything together. It’s also the secret behind smooth skin, strong hair, resilient nails, and flexible joints.
As we grow older, collagen production begins to slow. That’s why fine lines, wrinkles, sagging skin, brittle nails, and stiff joints start to appear, often sooner than we’d like. While creams and treatments can help on the surface, they can’t truly rebuild what’s fading beneath. Instead, the most effective way to support collagen is from the inside out.
This is where food makes the difference. Some foods contain collagen directly, giving your body an immediate supply. Others act as collagen protectors, supplying the nutrients that stimulate production and keep existing collagen from breaking down. When you combine both types, you create the perfect recipe for glowing skin, strong hair, and lasting joint health.
In this guide, we’ll explore the top 10 collagen rich foods backed by science—and you’ll discover not just what to eat, but how these foods actually work in harmony to help you glow from within.
🧬 How Collagen Rich Foods Work in Your Body
Collagen isn’t just a wellness trend—it’s the structural protein that accounts for 60–90% of the dry weight in your skin, tendons, and bones, which explains why it’s so critical to your body’s strength and resilience (Nature). It forms the framework that supports your skin, cushions your joints, and even strengthens your hair and nails. Yet, as time passes, your natural collagen supply steadily declines, leaving behind visible signs of aging.
The good news is that food can change the story. Collagen rich foods fall into two categories:
- Collagen Sources – Animal-based foods such as bone broth, chicken, fish, beef, and shellfish contain collagen itself. When you eat them, your body absorbs collagen peptides and amino acids that it can immediately use to rebuild and repair.
- Collagen Protectors – Foods like eggs, garlic, avocado, and tomatoes don’t contain collagen directly. Instead, they provide the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants your body needs to produce collagen more efficiently and to protect the collagen you already have from breaking down.
When these two groups are eaten together, they work synergistically. Direct collagen replenishes what’s been lost, while protectors ensure it lasts longer and functions better. In other words, diet isn’t just fuel—it’s a toolkit your body uses to build strength and radiance from within.
👉 By understanding how collagen foods work, you can start combining them in daily meals to support your skin, hair, nails, and joints naturally—without relying only on quick fixes.
🦴 Collagen Foods & Joint Health
Since collagen is a key component of cartilage, foods high in collagen like bone broth, chicken cartilage, and beef tendon can support joint cushioning and flexibility. In fact, studies suggest that collagen intake can help reduce joint pain and improve mobility, especially in people with osteoarthritis (UC Davis Health).
10 Collagen Rich Foods for Glowing Skin & Strong Joints
When it comes to collagen rich foods, some deliver collagen directly, while others help your body protect and rebuild it. By mixing both types, you give your body everything it needs for firmer skin, stronger hair, and healthier joints.
🥇 1. Bone Broth – The Gold Standard of Collagen Foods
Bone broth is often called liquid gold. When bones and connective tissues simmer for hours, collagen, gelatin, glycine, and proline are released into the broth —something researchers have confirmed as its main nutritional value (Harvard Nutrition Source). This makes it one of the richest natural sources of collagen peptides.

Why it’s great:
- Supplies collagen in its most absorbable form.
- Strengthens skin elasticity and joint mobility.
- Supports gut lining and digestion.
How to enjoy it:
Sip it warm as a drink, use as a soup base, or cook grains in it for extra nutrition.
👉 If you’re searching for the ultimate collagen food source, bone broth is unbeatable. Although the exact collagen content can vary, dietitians agree it still provides amino acids and protein that support gut, joint, and skin health (Food & Wine)
🍗 2. Chicken – Natural Type II Collagen Rich Food
Chicken skin, cartilage, and connective tissue are rich in Type II collagen. That’s why many collagen supplements are actually derived from chicken. If you want to know more about how poultry collagen supports skin and joints, see our post on the Health Benefits of Chicken Collagen.

Why it’s great:
- Delivers natural Type II collagen.
- Provides amino acids that support connective tissue.
How to enjoy it:
Roast with the skin on, simmer into chicken soup, or add shredded chicken to salads.
👉 Chicken is an everyday collagen rich food hiding in plain sight.
🥚 3. Eggs – Collagen Allies for Skin & Hair
Eggs don’t contain collagen directly, but they provide proline, a key amino acid needed for collagen synthesis. The yolks also supply biotin, which promotes shiny hair and strong nails.
Why it’s great:
- Proline fuels collagen production.
- Biotin strengthens hair and nails.
How to enjoy it:
Scrambled, boiled, or folded into veggie omelets.
👉 Eggs are an affordable collagen-friendly food you can eat every day.
🐟 4. Fish & Fish Skin – Marine Collagen Richness
Fish, especially with the skin, is one of the best natural collagen sources. Marine collagen is known for being highly bioavailable, meaning your body absorbs it quickly.

Why it’s great:
- Provides collagen peptides that support skin firmness.
- Rich in omega-3s, which reduce inflammation.
How to enjoy it:
Grill salmon with the skin, make fish soups, or enjoy crispy skin snacks.
👉 Fish skin is a delicious and underrated collagen rich food for beauty and joint health.
🥩 5. Beef Cuts – Collagen-Dense Comfort Foods
Beef shank, oxtail, brisket, and tendon are loaded with connective tissue, which makes them naturally rich in collagen. Slow cooking draws out the collagen into a tender, nutrient-dense meal.
Why it’s great:
- Packed with collagen from connective tissue.
- Boosts joint strength and resilience.
How to enjoy it:
Make slow-cooked stews, braised beef dishes, or traditional soups.
👉 For meat lovers, beef is one of the most accessible collagen rich foods.
🐖 6. Pork Skin & Pork Rinds – Crispy Collagen Source
Pork skin is another direct collagen source. In fact, porcine collagen is commonly used in supplements. Pork rinds and slow-cooked pork skin are not only tasty but also collagen-packed.

Why it’s great:
- Direct source of collagen peptides.
- Supports skin elasticity and repair.
How to enjoy it:
Snack on crispy pork rinds, or add pork skin to soups and braises.
👉 Pork skin is both indulgent and a natural collagen food source.
🦐 7. Shellfish – Shrimp, Crab & Lobster for Collagen
Shellfish are rich in collagen found in their shells and connective tissue. Even eating shrimp with the shell-on boosts your intake of natural collagen.

Why it’s great:
- Provides marine-based collagen.
- High in trace minerals that aid collagen production.
How to enjoy it:
Grill shrimp with shells, simmer crab into broths, or enjoy lobster with lemon.
👉 Shellfish are flavorful collagen rich foods with extra beauty benefits.
🧄 8. Garlic – Small but Mighty Collagen Protector
Garlic doesn’t contain collagen, but it helps preserve it. Rich in sulfur, taurine, and lipoic acid, garlic supports collagen cross-linking and prevents breakdown.

Why it’s great:
- Sulfur strengthens collagen structures.
- Helps rebuild damaged collagen fibers.
How to enjoy it:
Add to pasta sauces, roast with vegetables, or stir into soups.
👉 Garlic is proof that small foods can play a big role in collagen protection.
🥑 9. Avocados – The Skin-Softening Collagen Ally
Avocados are packed with vitamin E and glutathione, both of which shield collagen from free radical damage. Their healthy fats also keep skin plump and hydrated.

Why it’s great:
- Protects collagen from oxidative stress.
- Hydrates skin and reduces visible wrinkles.
How to enjoy it:
Smash on toast, toss into salads, or blend into creamy dips.
👉 Avocados are beauty-boosting collagen allies in every sense.
🍅 10. Tomatoes – Lycopene-Rich Collagen Guardian
Tomatoes deliver lycopene, a powerful antioxidant that protects collagen from UV-induced damage. Their vitamin C content also ensures collagen synthesis stays strong.

Why it’s great:
- Lycopene shields collagen from sun exposure.
- Vitamin C supports collagen creation.
How to enjoy it:
Roast with olive oil, stir into sauces, or enjoy fresh in salads.
👉 Tomatoes are everyday collagen protecting foods that deserve more credit.
✨ Why This Top 10 Works
This list balances direct collagen sources (bone broth, chicken, fish, beef, pork, shellfish) with powerful protectors (garlic, avocado, tomato). Nutrition experts highlight these very same foods—like chicken cartilage, fish skin, and pork rinds—as some of the best natural collagen boosters you can add to your diet (NY Post). Together, they create the ideal combination for building, repairing, and protecting collagen in your skin, hair, nails, and joints.

🌱 Collagen Rich Vegetarian Foods – Building Collagen Without Meat
If you’re vegetarian or vegan, you might feel left out when people talk about collagen. After all, collagen itself only comes from animal sources. However, that doesn’t mean you can’t support your body’s natural collagen production. Plant-based foods provide the vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that act as the “construction crew” for building and protecting collagen.
For a deeper dive, check out our guide to the Top 10 Plant-Based Foods to Boost Collagen for Skin. Here are some of the best options:
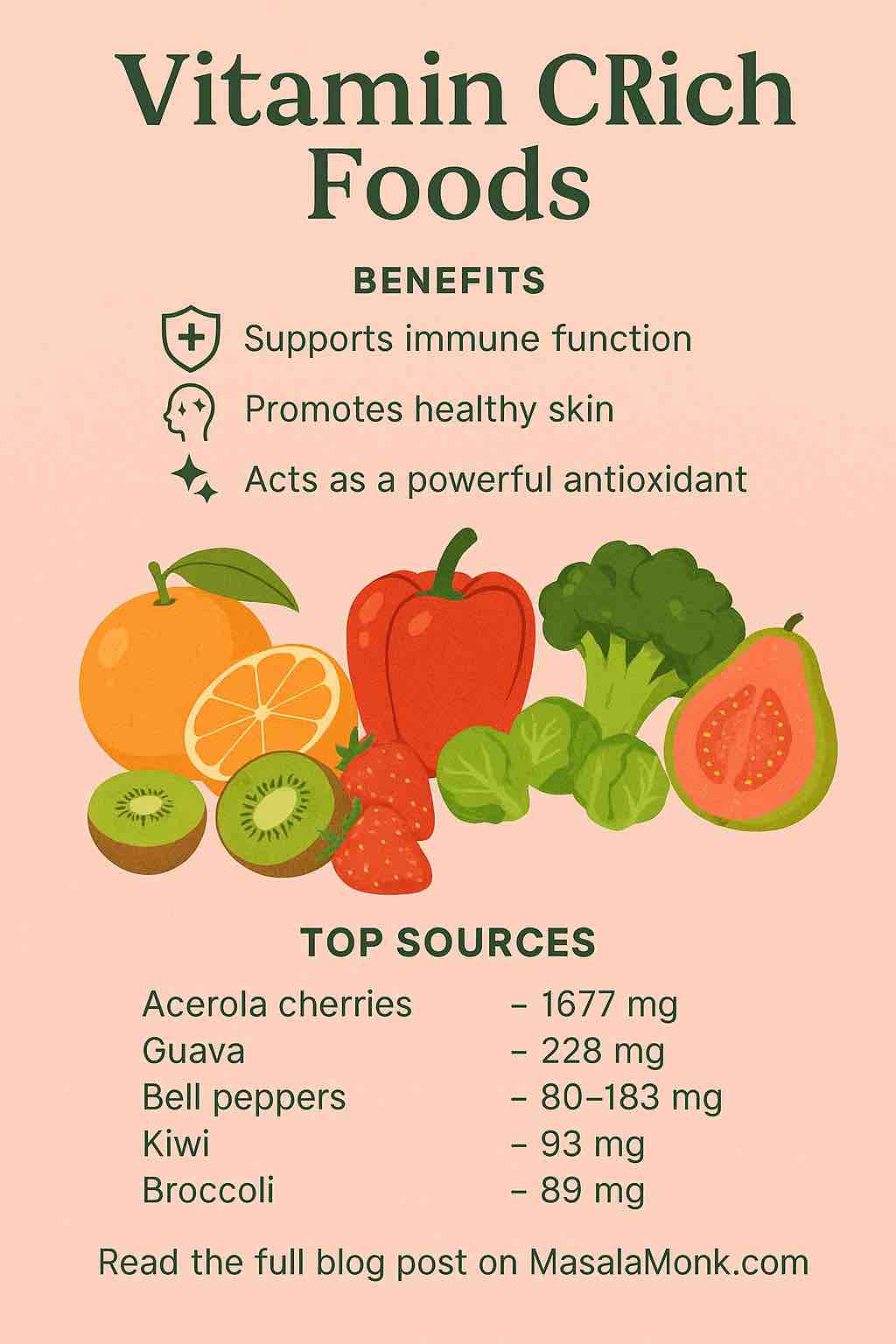
🍊 Citrus Fruits – Essential for Collagen Synthesis
Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are loaded with vitamin C. This vitamin is absolutely vital because, without it, your body simply cannot produce collagen. In addition, the antioxidants in citrus help protect the collagen you already have from breaking down.
🥬 Leafy Greens – Protecting Collagen Naturally
Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard don’t just provide vitamins A and C; they also contain chlorophyll, which gives them their vibrant green color. Interestingly, chlorophyll has been linked to stimulating collagen precursors in the skin, making leafy greens an easy way to give your body extra support.
🥜 Nuts & Seeds – Plant-Based Collagen Allies
Almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds may not provide collagen directly, but they deliver zinc, vitamin E, and omega-3s. Together, these nutrients help repair collagen fibers, reduce inflammation, and keep your skin hydrated from the inside out.
🧄 Garlic – Small but Mighty for Collagen
Garlic might seem like an unlikely beauty food, yet it plays a surprisingly important role. Its sulfur content strengthens collagen and prevents it from breaking down too quickly. Moreover, garlic contains compounds that help rebuild damaged fibers, making it a quiet hero in the collagen story.
🍓 Berries – Sweet Protection for Your Skin
Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are rich in vitamin C and packed with antioxidants. As a result, they both encourage new collagen production and protect existing collagen from free radical damage. Plus, they make a naturally sweet snack that feels more like a treat than a supplement. For example, strawberries are packed with vitamin C and antioxidants—learn more in Strawberries: Nature’s Berries of Beauty.
Also Read: Vitamin D Deficiency and Skin Health
📊 Quick Comparison of Collagen Rich Foods
| Food | Collagen Role | Extra Benefits | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🥇 Bone Broth | Direct collagen peptides | Gut healing, joint mobility | Skin + Joints |
| 🍗 Chicken (with skin & cartilage) | Natural Type II collagen | Protein + connective tissue support | Joints + Skin Firmness |
| 🥚 Eggs | Proline + biotin for collagen synthesis | Stronger nails & shinier hair | Hair + Nails + Skin Glow |
| 🐟 Fish & Fish Skin | Marine collagen peptides | Omega-3s reduce inflammation | Skin Elasticity + Joints |
| 🥩 Beef Cuts (Shank, Oxtail, Tendon) | Collagen from connective tissue | Iron + complete protein | Joint Health + Strength |
| 🐖 Pork Skin & Rinds | Direct collagen source | Supports elasticity, anti-aging | Skin Repair + Firmness |
| 🦐 Shellfish (Shrimp, Crab, Lobster) | Collagen in shells/connective tissue | Minerals support collagen | Skin Firmness + Mobility |
| 🧄 Garlic | Collagen protector (sulfur, taurine) | Rebuilds damaged collagen | Skin Structure + Protection |
| 🥑 Avocado | Shields collagen with vitamin E & glutathione | Hydrates + plumps skin | Anti-Wrinkle + Glow |
| 🍅 Tomatoes | Lycopene protects collagen | Vitamin C supports synthesis | UV Protection + Elasticity |
🧠 Lifestyle Tips to Protect Collagen Levels
Eating collagen rich foods is a powerful first step, but food alone can’t do all the heavy lifting. In fact, your daily habits play just as important a role in protecting and preserving the collagen you already have. The good news is a few small changes can make a big difference.
💧 Stay Hydrated
Collagen fibers rely on water to stay elastic and flexible. Without enough hydration, your skin can appear dull and your joints may feel stiff. Keeping a water bottle nearby is a simple way to give your collagen what it needs to function.
🍭 Reduce Sugar
Too much sugar in the diet leads to glycation, a process that weakens and stiffens collagen fibers. As a result, skin loses its bounce more quickly. Choosing whole, unprocessed foods instead of sugary snacks helps protect your collagen long-term.
☀️ Wear Sunscreen
UV rays are one of the fastest destroyers of collagen. Even on cloudy days, sun exposure accelerates collagen breakdown. A broad-spectrum sunscreen works like an invisible shield, keeping your skin firmer for longer.
🏃 Exercise Regularly
Movement improves circulation, which means more oxygen and nutrients get delivered to your skin and connective tissues. Moreover, regular exercise helps reduce inflammation, which otherwise breaks down collagen faster.
😴 Sleep Deeply
Your body does its most effective repair work at night. Therefore, deep, restful sleep is essential for collagen renewal. Aim for seven to nine hours each night to allow your body to restore itself fully.
👉 In short, glowing skin and healthy joints come from more than just your plate. By pairing collagen rich foods with smart daily habits, you give your body the best chance to protect its natural scaffolding and age gracefully from the inside out.
✨ Conclusion: Glow From Within With Collagen Rich Foods
Collagen is more than just a beauty buzzword—it’s the foundation of smooth skin, strong hair, resilient nails, and flexible joints. In fact, researchers estimate collagen makes up 70–80% of your skin’s structure, which is why maintaining it through diet is so important as you age (UCLA Health). As production naturally slows with age, the signs show up on the outside and are felt on the inside. However, the story doesn’t end there. With the right choices, you can give your body the fuel it needs to keep collagen levels strong.
By adding more collagen rich foods to your meals, you’re taking a simple but powerful step toward protecting your body from within. Direct sources like bone broth, chicken, fish, beef, pork, and shellfish supply collagen in its natural form. At the same time, protectors such as eggs, garlic, avocado, and tomatoes ensure that this collagen doesn’t break down too quickly and continues to support you over time.
Together, these foods work in harmony. One group rebuilds what you lose, while the other defends what you already have. And when you combine them consistently, the results go far beyond skincare—they touch every part of your health, from the way your joints move to how radiant your skin feels.
Ultimately, glowing skin and youthful energy aren’t about chasing quick fixes. They come from a lifestyle that pairs nourishing food with smart habits like hydration, movement, sun protection, and rest. When you eat and live this way, collagen isn’t just something you supplement—it becomes a natural part of your everyday strength and vitality.
👉 In short: collagen rich foods are more than ingredients—they’re daily investments in your skin, hair, and overall well-being.
🙋♀️ Frequently Asked Questions About Collagen Rich Foods
1. What are collagen rich foods, and why are they important?
Collagen rich foods are foods that either supply collagen directly—such as bone broth, chicken, fish, beef, pork, and shellfish—or provide nutrients that help your body produce and protect collagen, like eggs, garlic, avocado, and tomatoes. Since collagen makes up most of your skin, hair, nails, and connective tissues, eating these foods helps you maintain youthful skin, strong hair, and flexible joints.
2. Which foods actually contain collagen?
Only animal-based foods contain collagen itself. These include bone broth, chicken skin, fish (especially fish skin), beef cuts with connective tissue, pork skin, and shellfish. Plant foods don’t contain collagen directly, but they offer vitamins and antioxidants that help your body make and preserve collagen.
3. Can vegetarians or vegans boost collagen naturally?
Yes, absolutely. While collagen itself is only found in animal foods, vegetarians and vegans can still boost collagen production through plant-based protectors. Foods like citrus fruits, leafy greens, garlic, nuts, seeds, avocados, and berries provide vitamin C, zinc, and antioxidants that stimulate collagen building and defend against collagen breakdown.
4. How long does it take to see results from collagen rich foods?
Consistency matters. Many people notice improvements in skin hydration and texture within 6–8 weeks of regularly eating collagen rich foods. However, since collagen also supports joints, hair, and nails, you may start feeling benefits—like smoother movement or stronger nails—even sooner.
5. Are collagen supplements better than food sources?
Collagen supplements can be convenient, but food sources offer more than just collagen. For example, bone broth delivers collagen along with minerals, while fish provides both collagen and omega-3s. Moreover, whole foods give you co-factors like vitamin C and zinc that supplements often lack. Ideally, a mix of nutrient-rich foods and, if needed, supplements works best. Before trying supplements, it’s wise to check out possible side effects. We’ve covered them in detail here: Potential Side Effects of Collagen Supplements.
6. Do collagen rich foods really help with aging skin?
Yes, they do. As collagen levels naturally decline with age, eating foods that replenish and protect collagen can slow the visible signs of aging. Bone broth, fish skin, and chicken supply collagen directly, while foods like tomatoes, garlic, and avocados protect your existing collagen from damage caused by sun, stress, and free radicals.
7. Can collagen foods help with joint pain?
Definitely. Since collagen is a key component of cartilage, foods high in collagen like bone broth, chicken cartilage, and beef tendon can support joint cushioning and flexibility. Over time, this may reduce stiffness and discomfort, especially when paired with an anti-inflammatory diet.
8. What lifestyle habits support collagen alongside food?
Diet is only half the story. To truly protect collagen, it’s important to stay hydrated, get enough sleep, exercise regularly, limit sugar intake, and protect your skin from the sun. When these habits are combined with collagen rich foods, your results are stronger and longer-lasting.
9. How can I easily add collagen foods to my diet?
It’s simpler than you think. Start your day with eggs, enjoy a hearty chicken soup, sip on bone broth in the evening, or add avocado and tomatoes to your salads. Even small daily choices create a long-term impact when it comes to collagen support.
10. Do collagen rich foods also improve hair and nails?
Yes, collagen plays an essential role in the structure of hair and nails. Regularly eating collagen sources like bone broth and fish, along with protectors such as eggs and nuts, can lead to stronger nails and shinier, healthier hair over time.