We’ve all heard them — the home remedies passed down like sacred secrets. “Rub lemon on your scalp, it will make your hair grow faster.” Or, “Rinse with lemon water after oiling, and your hair will shine like silk.”
For many of us, these aren’t just tips; they’re memories. Of sitting on a charpai on hot afternoons while a grandmother massaged warm coconut oil mixed with a few drops of lemon into our scalp. Of rinsing hair after henna with lemon water, hoping the strands would catch that extra glint of copper under the sun.
Lemon has always had a place in traditional beauty care — across Ayurveda, Unani medicine, and even Western DIY culture. In Ayurveda, lemon (Nimbuka) is described as a cooling, cleansing fruit, balancing excess oil and refreshing the body. In folk rituals, it wasn’t just used for cooking — it was rubbed on oily scalps, applied to lighten mehndi stains, and even added to oils as a “purifier.”
Fast forward to today, and Google is filled with questions like:
- Is lemon good for hair growth?
- Can lemon stop dandruff?
- How do I use lemon juice safely on my scalp?
The good news: lemon really does have benefits for hair. But the truth is also more nuanced than the old wives’ tales. Lemon won’t magically regrow bald spots. It can, however, support scalp health, reduce mild dandruff, add shine, and make your hair feel fresher — if used correctly.
So, let’s explore what science and tradition agree on, what’s hype, and how you can safely use lemon for your hair today.
Is Lemon Good for Hair? What Science and Ayurveda Say
🍋 The Ayurvedic view
In Ayurveda, lemon is known as Nimbuka and is considered “kapha-shamaka” — meaning it balances Kapha, the dosha associated with excess oil, heaviness, and sluggishness. When Kapha is high, you often see greasy scalps, buildup, or dandruff-like flakes. That’s why traditional remedies often involved squeezing lemon juice into hair oils or using lemon rinses after washing — to purify and lighten the scalp.
Ayurvedic texts also describe lemon as shita virya (cooling in potency), which makes it soothing for scalp irritation and itchiness.
🔬 The scientific explanation on Lemon for Hair
From a modern perspective, lemon’s biggest gift to hair is its acidity. Here’s why that matters:
- Hair and scalp are naturally slightly acidic (pH 4.5–5.5).
- Many shampoos are alkaline, which raises the hair cuticle (the outer layer), making strands rough, frizzy, and prone to breakage.
- Acidic rinses — like lemon water — flatten the cuticle, lock in moisture, and make hair shinier (Dias, 2014).
Think of it this way: your hair cuticle is like roof tiles. When alkaline products lift them, the roof leaks — your hair loses moisture, feels rough, and looks dull. When you restore acidity with lemon, those tiles flatten and seal again, keeping everything smooth and reflective.

✅ The bottom line
So, is lemon good for hair? Yes — but mainly as a clarifier, shine booster, and scalp balancer.
It won’t give you Rapunzel-like growth overnight, but it will help your hair look and feel healthier when used wisely.
Lemon for Hair Growth: What’s True & What’s Hype
If you search online for “lemon for hair growth”, you’ll find endless blogs, YouTube videos, and Instagram reels promising that a squeeze of lemon will make your hair sprout like grass after rain. The truth? It’s not that simple.
🌱 Why people believe lemon makes hair grow
There are reasons this belief became so popular:
- The tingling effect: When you apply lemon juice directly to the scalp, it stings a little. That sensation gets mistaken for “stimulation” — people assume if it tingles, it must be working to grow new hair.
- Mixed remedies: Traditional recipes often combined lemon with coconut oil, onion juice, or castor oil — all of which do support growth or thickness. Over time, lemon became associated with those effects, even though it was more of a supporting player.
- The “clean scalp = growth” link: A clean, fresh scalp does create a better environment for follicles. So when people used lemon and saw less buildup, they assumed it was directly making hair grow.
🔬 What science actually says about Lemon for Hair
Modern research gives us a more nuanced picture:
- Citrus compounds like limonin: Lab studies suggest limonin (found in citrus seeds and peels) can activate pathways linked to follicle activity and hair regeneration (Kang, 2022).
- Citric acid and fiber strength: A 2025 study showed citric acid helps reinforce chemically treated hair fibers, making them stronger and less prone to breakage (Zhang, 2025). Stronger strands can give the appearance of fuller hair, even if no new hair is growing.
- The cautionary side: Other research has found that disruptions in citric acid metabolism may actually suppress follicle growth and increase inflammation (Shi, 2022). This means using lemon carelessly could backfire — especially if applied too often or too harshly.
✅ So, does lemon regrow hair?
Here’s the straight answer: No, lemon cannot regrow hair on bald patches or reverse genetic hair loss.
What it can do is:
- Cleanse the scalp and reduce buildup → better follicle environment
- Strengthen existing strands → less breakage, more thickness retention
- Support overall scalp health → which indirectly supports natural growth
Think of lemon as a gardener: it cleans and prepares the soil, but it doesn’t plant new seeds. For true regrowth, you’d need proven treatments like minoxidil, microneedling, or rosemary oil. Lemon’s role is supportive, not transformative.
🙋 Common reader questions
- “Does lemon juice stop hair fall?” → It may reduce breakage and improve scalp condition, but it doesn’t stop hormonal or genetic hair loss.
- “Can I apply lemon daily to grow hair?” → No. Daily use will irritate and dry out your scalp. Stick to once a week.
- “Can lemon grow new hair?” → No. It helps maintain the hair you have, not regrow what’s lost.
Lemon and Dandruff: Does It Really Work?
For many people, dandruff is the real reason they reach for lemon. Those embarrassing white flakes on your shoulders, the constant urge to scratch your scalp — it’s frustrating, and the kitchen often feels like the first place to look for a fix. But does lemon really help?
🌿 The traditional wisdom
In South Asian homes, lemon has long been rubbed directly on flaky scalps or squeezed into oils as a quick antidote. Ayurveda describes lemon as cleansing and light, which makes it a natural choice for conditions linked with excess oiliness (Kapha imbalance). Folk wisdom believed that because lemon “cuts through grease,” it could also cut through flakes.
And culturally, it became a go-to “first aid” before weddings, festivals, or social events — whenever you needed your scalp to feel instantly fresher.
🔬 The science behind it
Modern dermatology tells us dandruff is mainly caused by:
- An overgrowth of a yeast-like fungus called Malassezia.
- Excess scalp oil (sebum), which feeds the fungus.
- A sensitive scalp that reacts with irritation and flaking.
Here’s where lemon can help:
- Citrus oils vs. fungi → Citrus fruits (lime, kaffir lime, lemon) have shown antifungal activity against Malassezia in lab studies (Tadtong, 2025).
- Human trial evidence → A small clinical study found that a citrus-extract shampoo reduced dandruff and scalp greasiness within four weeks (Lee, 2019).
- Clarifying action → The acidity of lemon helps strip excess oil and buildup, making the scalp feel lighter and less itchy.
So yes — lemon can help with mild dandruff, especially if your scalp is very oily.
⚠️ But here’s the catch
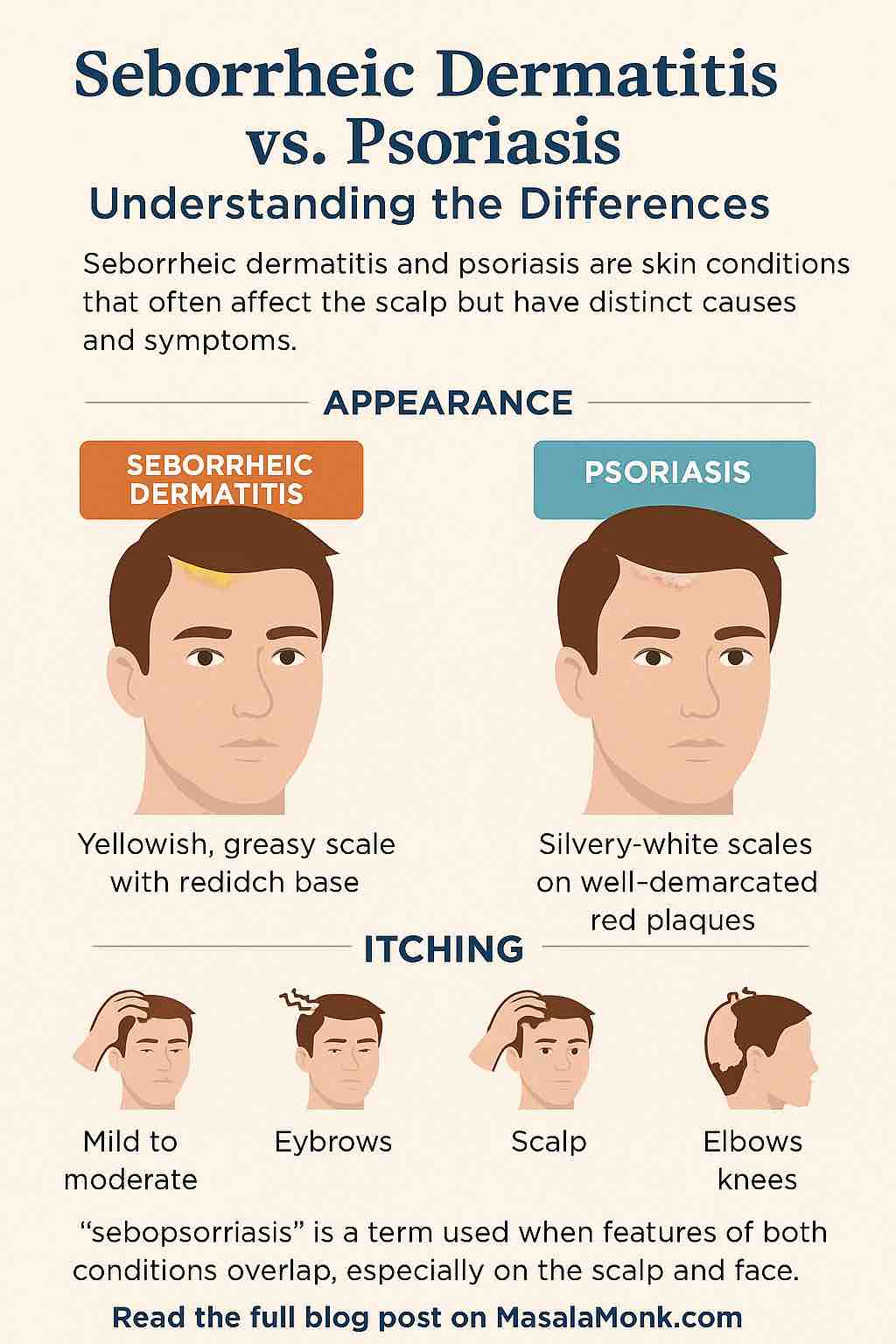
- It’s not as strong as medicated shampoos. Ingredients like ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione are proven to fight dandruff more effectively. Lemon is more of a supporting remedy than a standalone cure. If flakes are thick or itchy, and don’t respond to mild remedies, see What’s the Difference Between Dandruff and Psoriasis? to know when it might be something more serious.
- It can irritate sensitive skin. Overusing lemon — or applying it undiluted — may sting, redden, or even worsen flakes if your scalp barrier is already weak.
- Results vary. Some people find relief, while others feel more itchy after.
✅ Best way to use lemon for dandruff
- Always dilute lemon juice with water or mix with oil/yogurt before applying.
- Use it once a week, not daily.
- Combine with your regular dandruff shampoo if you have moderate-to-severe flakes.
👉 Think of lemon as a “quick refresher” or mild helper for oily, flaky scalps — not a replacement for proven medical treatments.
Other Benefits of Lemon for Hair (Shine, Strength, Antioxidants)
Even if lemon won’t magically regrow hair, it still brings plenty to the table. Think of it as a natural multi-tasker: part clarifier, part shine-booster, part protector. Here’s how it helps beyond growth and dandruff.
✨ For shine and smoothness
One of the first things you’ll notice after a lemon rinse is how much lighter and shinier your hair feels. That’s not an illusion — it’s chemistry.
Hair is covered in overlapping scales called cuticles. When they lie flat, light reflects smoothly, making hair look glossy. When they lift (as happens with alkaline shampoos or hard water), hair feels rough, looks dull, and tangles easily.
Lemon juice, being acidic, helps flatten those cuticles back down. It’s like sealing tiles on a roof — suddenly the “surface” is smoother, and the shine returns. That’s why women across India and the Middle East traditionally rinsed their hair with lemon water after oiling or henna: it left strands sleeker, softer, and more manageable.
A similar method is using apple cider vinegar and lemon rinses, which are popular for removing buildup and restoring shine.
🛡️ For antioxidant protection
Modern life is tough on hair. Pollution, dust, harsh styling, and UV rays all create oxidative stress, which weakens follicles and makes strands brittle.
Lemon is naturally rich in flavonoids and vitamin C — compounds that act like tiny shields against free radicals. Recent studies confirm citrus extracts help buffer oxidative damage and support healthier tissue (Du, 2024; Klimek-Szczykutowicz, 2020).
While rubbing lemon on your scalp won’t erase years of sun damage, using it occasionally can give your hair an antioxidant “boost” — and consuming lemons in your diet supports both skin and hair health from within.
🧴 For oil control
If your scalp turns greasy within a day of washing, lemon can be a lifesaver. The citric acid cuts through excess sebum, giving you that just-washed freshness without needing another round of shampoo.
That’s why many DIY recipes recommend lemon water rinses for people with oily scalp types. Used sparingly, it can help extend the time between washes, keeping your hair feeling cleaner and lighter.
☀️ For natural lightening
This one is both a benefit and a warning. Lemon juice + sunlight can lighten hair, which is why it became a popular hack among teens in the West. On lighter brown or blonde shades, it creates sun-kissed highlights.
But on darker hair, it often leads to uneven tones, dryness, and even scalp burns if applied carelessly in the sun. So yes, lemon can lighten — but it’s a risky trick best avoided unless you know what you’re doing (and are willing to accept some damage).
🍊 From the inside out
Interestingly, lemon’s benefits aren’t limited to topical use. A 2019 study on mice showed that lemon polyphenols in drinking water helped delay age-related hair thinning and coarseness (Shimizu, 2019).
We can’t directly translate mouse studies to humans, but it does hint at a bigger truth: your diet impacts your hair. Eating a citrus-rich diet supports collagen, immunity, and overall scalp health — all of which reflect in stronger, shinier hair.
For example, Amla, another vitamin-C-rich natural, also supports scalp health and antioxidant protection.
How to Use Lemon for Hair (DIY Recipes That Actually Work)
One of the reasons lemon is so popular is its versatility. You don’t need expensive products — just a fruit you probably already have in your kitchen. But the secret is how you use it. Apply lemon the wrong way (too strong, too often), and you risk dryness and irritation. Use it wisely, and it can become a refreshing, effective part of your routine.
Here are some tried-and-tested ways to use lemon for hair:
1. The Classic Lemon Rinse (for Shine & Oil Control)
Best for: Oily scalps, dull or frizzy hair.
- How to make it: Mix 1 tablespoon of fresh lemon juice with 1 cup of cool water. After shampooing, pour it slowly over your scalp and hair, massage gently for a minute, then rinse off with plain water.
- Why it works: The acidity balances scalp pH, flattens cuticles, and cuts through excess oil. You’ll instantly notice softer, shinier strands.
- Pro tip: Don’t leave lemon water sitting in your hair for long — rinse it off after a minute or two to avoid over-drying.
- Mistake to avoid: Using concentrated juice directly — it can sting, especially if you have scratches or sensitive skin.
2. Coconut Oil + Lemon Scalp Massage (for Mild Dandruff Relief)
Best for: Oily, flaky scalps with mild dandruff.

- How to make it: Warm 2 tablespoons of coconut oil, add 1 teaspoon of lemon juice, and mix well. Massage gently into the scalp for 10–15 minutes, then wash with a mild shampoo.
- Why it works: Coconut oil nourishes and moisturizes, while lemon adds antifungal power and clarifies buildup.
- Pro tip: Wrap your head in a warm towel after applying — it helps the oil penetrate better.
- Mistake to avoid: Leaving it overnight. Lemon sitting too long on the scalp can irritate.
3. Lemon + Honey + Yogurt Mask (for Softness & Shine)
Best for: Dull, rough, or frizzy hair.

- How to make it: Mix 1 tablespoon lemon juice, 1 tablespoon honey, and 2–3 tablespoons plain yogurt. Apply evenly to scalp and hair. Leave on for 15 minutes, then rinse and shampoo.
- Why it works: Honey adds moisture, yogurt soothes and nourishes, and lemon clarifies. It’s like a natural spa treatment for your scalp.
- Pro tip: Apply on damp hair for better spread and absorption.
- Mistake to avoid: Sitting out in the sun with this mask on — lemon + sunlight can burn skin.
You could also experiment with traditional pairings, like lemon + garlic or fenugreek. See Garlic for Hair and Fenugreek Seeds for Hair for detailed guides on how these work.
4. Aloe Vera + Lemon Soother (for Itchy, Sensitive Scalps)
Best for: Itchy, irritated scalps or people with mild dermatitis.

- How to make it: Blend 2 tablespoons of aloe vera gel with 1 teaspoon of lemon juice. Massage gently into scalp, leave for 10 minutes, then rinse.
- Why it works: Aloe calms and hydrates, while lemon balances oiliness and adds a cooling effect.
- Pro tip: Use fresh aloe gel (from the plant) if possible — it works better than store-bought.
- Mistake to avoid: Don’t rub harshly; a gentle massage is enough.
5. Lemon Highlight Hack (Use with Caution)
Best for: Light brown or blonde hair only.
- How to do it: Dilute lemon juice with water (1:1 ratio), apply with a spray bottle to strands you want to lighten, and sit in the sun for 15–20 minutes. Rinse thoroughly and condition afterward.
- Why it works: Citric acid reacts with UV light, breaking down melanin and making hair appear lighter.
- Pro tip: Apply only on sections (like face-framing strands), not your whole head, for a sun-kissed look.
- Mistake to avoid: Doing this often. It can severely dry out and damage hair. Always deep-condition after.
Side Effects of Applying Lemon on Hair (Read Before You Try)
While lemon has real benefits for hair and scalp, it also comes with risks. The same compounds that make it refreshing and clarifying can be harsh if you overuse them or apply them the wrong way. Here’s what you need to know before squeezing that lemon onto your head.
🍋 1. Dryness & Brittleness
Lemon juice is highly acidic and astringent. While this helps cut grease and balance pH, it can also strip away natural oils if used too often. The result? Dry, brittle strands that snap more easily.
What to do instead: Always dilute lemon juice with water, oil, or yogurt. And never use it more than once a week. If you already have dry or curly hair, pair it with moisturizing ingredients like honey or aloe.
To balance lemon’s drying effect, combine with hydrating ingredients like yogurt or coconut water, or nourishing oils such as almond oil.
🍋 2. Scalp Irritation & Stinging
Have you ever squeezed lemon on a tiny cut and winced at the sting? The same thing happens on your scalp if you have scratches, eczema, or sensitivity. Undiluted lemon juice can cause redness, burning, and even small chemical-like burns.
What to do instead: Always do a patch test first. Apply a little diluted lemon juice behind your ear or on your inner arm — if it stings or causes redness after 10 minutes, don’t use it on your scalp.
🍋 3. Phototoxicity (The “Lime Burn” Problem)
One of the biggest hidden dangers of lemon is phototoxicity — a skin reaction when citrus juice meets sunlight.
Dermatologists even have a name for it: phytophotodermatitis. It happens because compounds in lemon (furanocoumarins) react with UV light, causing redness, dark patches, or even blister-like burns.
It’s so common among bartenders who mix drinks with lime that it’s nicknamed “Margarita Burn.” Case reports have shown severe burns on skin exposed to citrus juice followed by sun (Abugroun et al., 2019).
What to do instead:
- Never sit in the sun with lemon juice on your scalp or skin.
- Always rinse your hair thoroughly after a lemon treatment.
- If you want natural highlights, do it carefully and condition deeply afterward.
🍋 4. Uneven Hair Lightening
While lemon can lighten hair, it does so unpredictably. On darker hair, it often creates brassy, patchy tones instead of golden highlights. And combined with dryness, this can leave hair looking worse than before.
What to do instead: If you want highlights, consider safer options like chamomile tea rinses or professional coloring.

✅ Golden Rules for Safe Use
- Always dilute lemon juice before applying.
- Use lemon no more than once a week.
- Patch test before first use.
- Rinse thoroughly before going out in sunlight.
- Pair with hydrating ingredients (coconut oil, honey, aloe) to balance dryness.
Final Thoughts on Lemon for Hair
For centuries, lemon has been part of our hair care traditions — whether squeezed into oil, poured as a rinse, or simply rubbed onto the scalp before a big occasion. Our grandmothers didn’t have lab studies, but they noticed the effects: a fresher scalp, shinier strands, and a cleaner feel.
Modern science now helps us understand why those remedies worked:
- Lemon’s acidity balances scalp pH and smooths the cuticle.
- Its antioxidants help protect against everyday damage.
- Its citrus compounds show mild antifungal effects that can ease dandruff.
At the same time, research also shows us where lemon falls short. It doesn’t regrow lost hair, it’s not as effective as medicated dandruff treatments, and careless use can irritate or damage hair.
The sweet spot? Using lemon as a supportive ally — not as a miracle cure. A weekly rinse, a drop in warm oil, or a soothing mask can refresh your scalp and add shine without harm. Pair it with good nutrition, gentle hair care, and proven treatments when needed, and lemon becomes a safe, natural addition to your toolkit.

So next time you slice a lemon for your salad or chai, remember: that humble fruit carries generations of wisdom, a touch of science, and just enough magic to keep your hair feeling fresh and alive. ✨🍋
FAQs About Lemon for Hair
1. Is lemon good for hair?
Yes — lemon can be good for your hair when used correctly. Its acidity balances scalp pH, reduces excess oil, and adds shine. However, it should always be diluted and not applied daily, otherwise it may dry out or irritate your scalp.
2. Does lemon juice help hair growth?
Not directly. Lemon juice doesn’t regrow new hair, but it can improve scalp health and strengthen strands, which helps reduce breakage. A clean, balanced scalp creates a better environment for natural growth.
3. How do I use lemon for hair growth?
The safest way is to dilute 1 tablespoon of lemon juice in 1 cup of water and use it as a post-shampoo rinse once a week. You can also mix a few drops with coconut oil or aloe vera gel for scalp massages.
4. Can lemon stop hair fall?
Lemon may reduce breakage-related hair fall by strengthening strands and clarifying the scalp. But it does not stop genetic or hormonal hair loss. For persistent hair fall, it’s best to consult a dermatologist.
5. Is lemon good for dandruff?
Yes — lemon has mild antifungal properties that can help with oily, flaky dandruff. Studies show citrus extracts can reduce Malassezia fungus, which is linked to dandruff. Still, it’s less effective than medicated shampoos and works best for mild cases.
6. How do I apply lemon on my scalp safely?
Always dilute lemon juice before applying. Mix it with water, oil, or yogurt, and leave it on for no longer than 10–15 minutes. Then rinse thoroughly. Never apply lemon directly before going out in the sun — it can cause burns.
7. Can drinking lemon water help with hair growth?
Indirectly, yes. Lemon water provides vitamin C and antioxidants that support collagen production and overall scalp health. While it won’t regrow hair by itself, it helps strengthen your body’s foundation for healthy hair.
8. Does lemon lighten hair naturally?
Yes, lemon juice combined with sunlight can lighten hair — especially lighter shades like brown or blonde. But it often leads to uneven tones and dryness. If you want highlights, use this trick carefully and follow with deep conditioning.
9. Can lemon cause side effects on hair?
Yes. Overuse can cause dryness, brittleness, scalp irritation, and even phototoxic burns if exposed to sunlight. That’s why moderation is key — use lemon no more than once a week.
10. Is lemon good for all hair types?
Not really. Lemon works best for oily scalps and straight or wavy hair types. If your hair is already dry, curly, or chemically treated, use lemon with extra caution and always combine it with moisturizing ingredients like honey or aloe vera.
11. Can lemon regrow hair on bald spots?
No — lemon cannot regrow hair on bald patches caused by genetics or conditions like alopecia. It only supports existing hair and scalp health. For baldness, proven treatments like minoxidil or medical therapies are required.
12. How often can I use lemon on hair?
Once a week is enough for most people. Using it daily or even every other day increases the risk of dryness and scalp irritation. Think of lemon as a scalp refresher, not an everyday tonic.